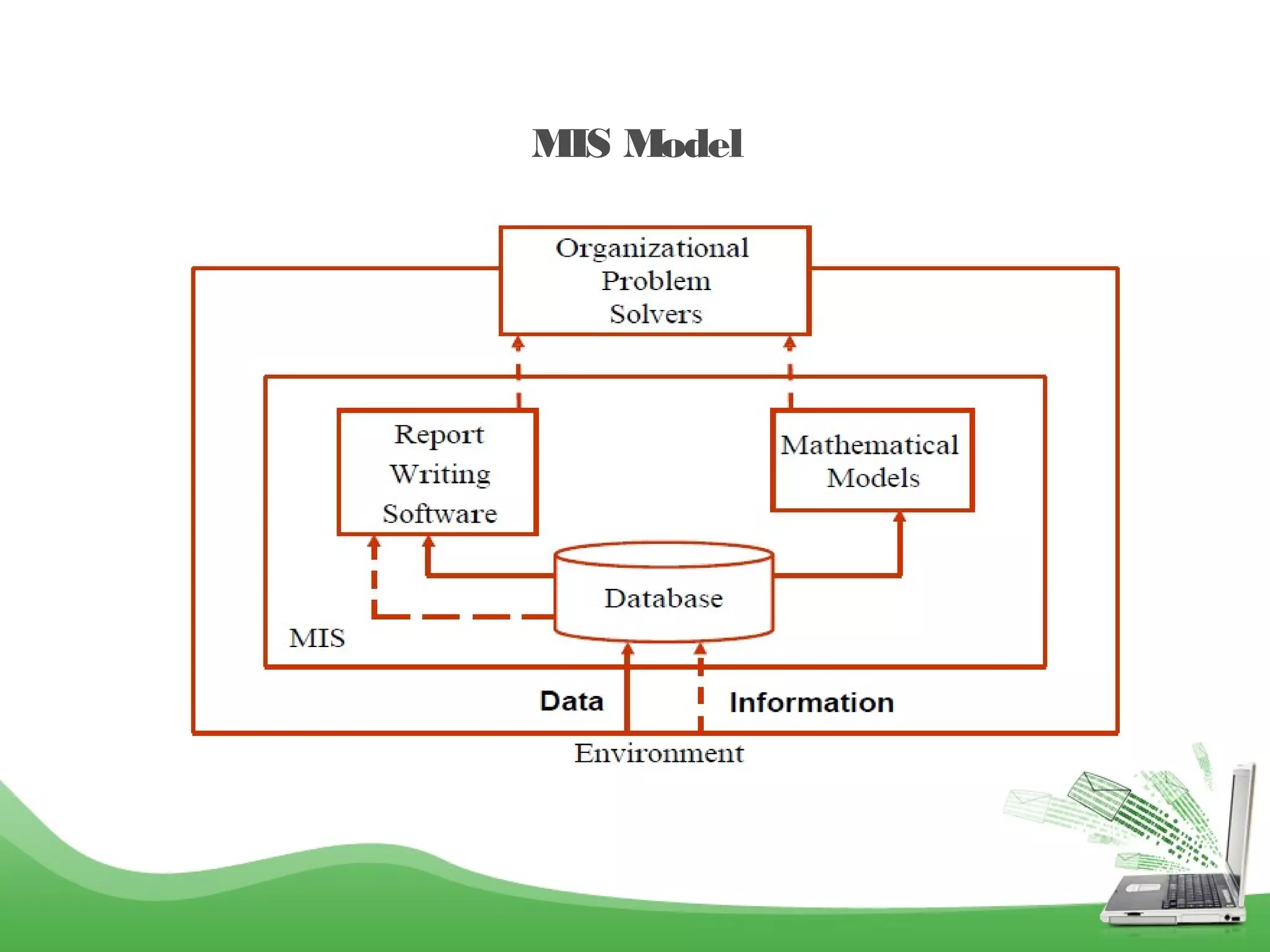
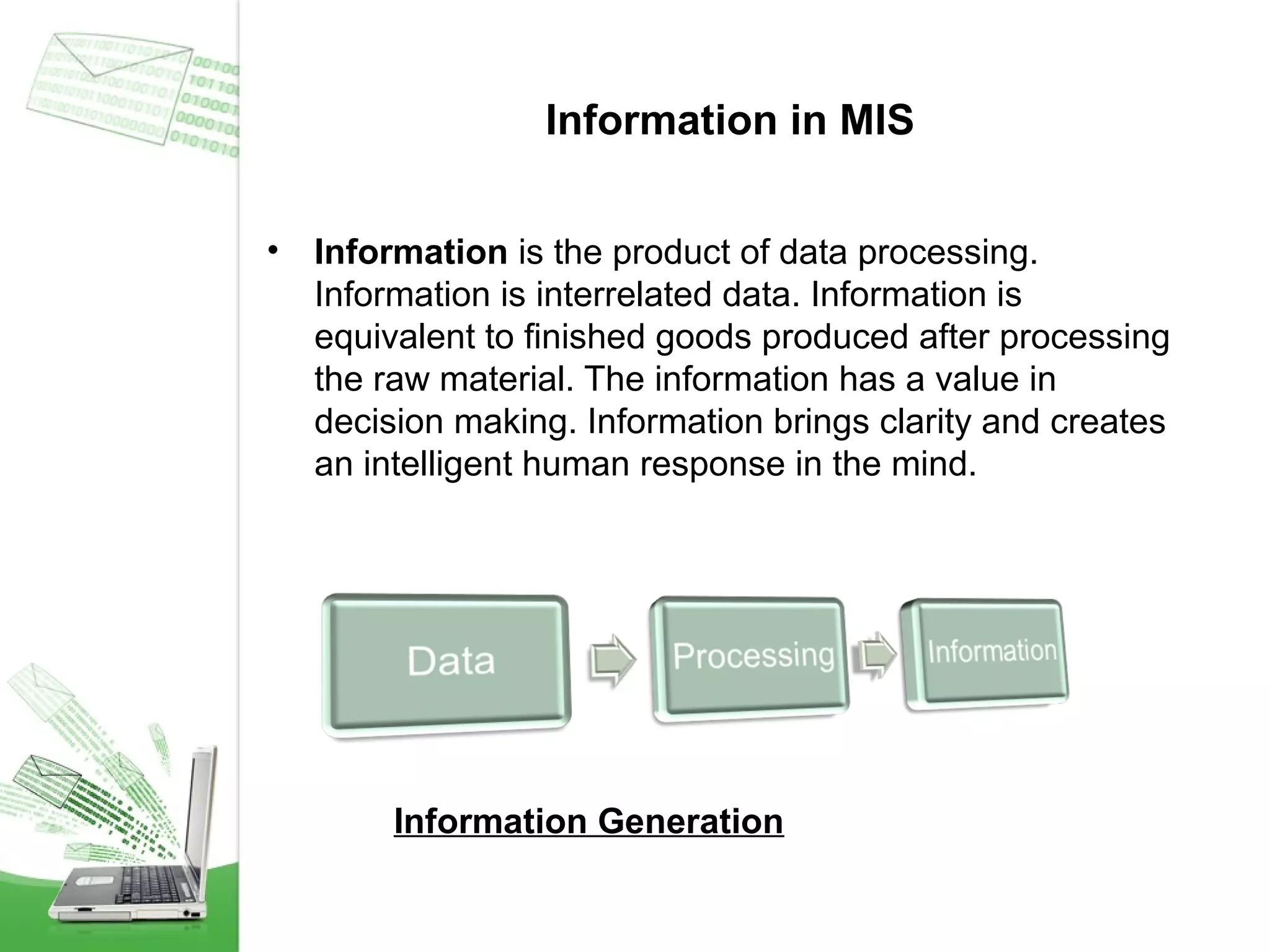
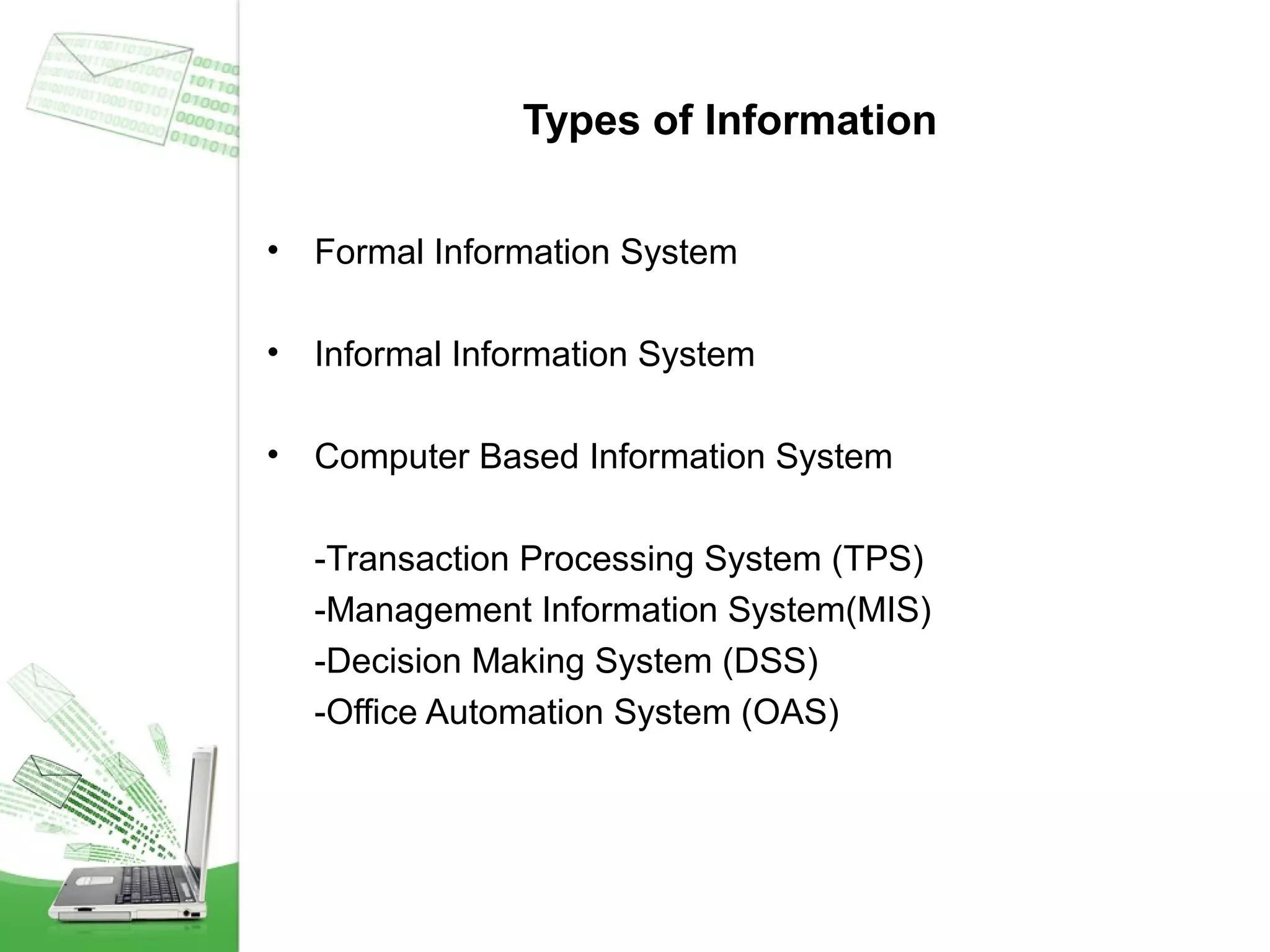
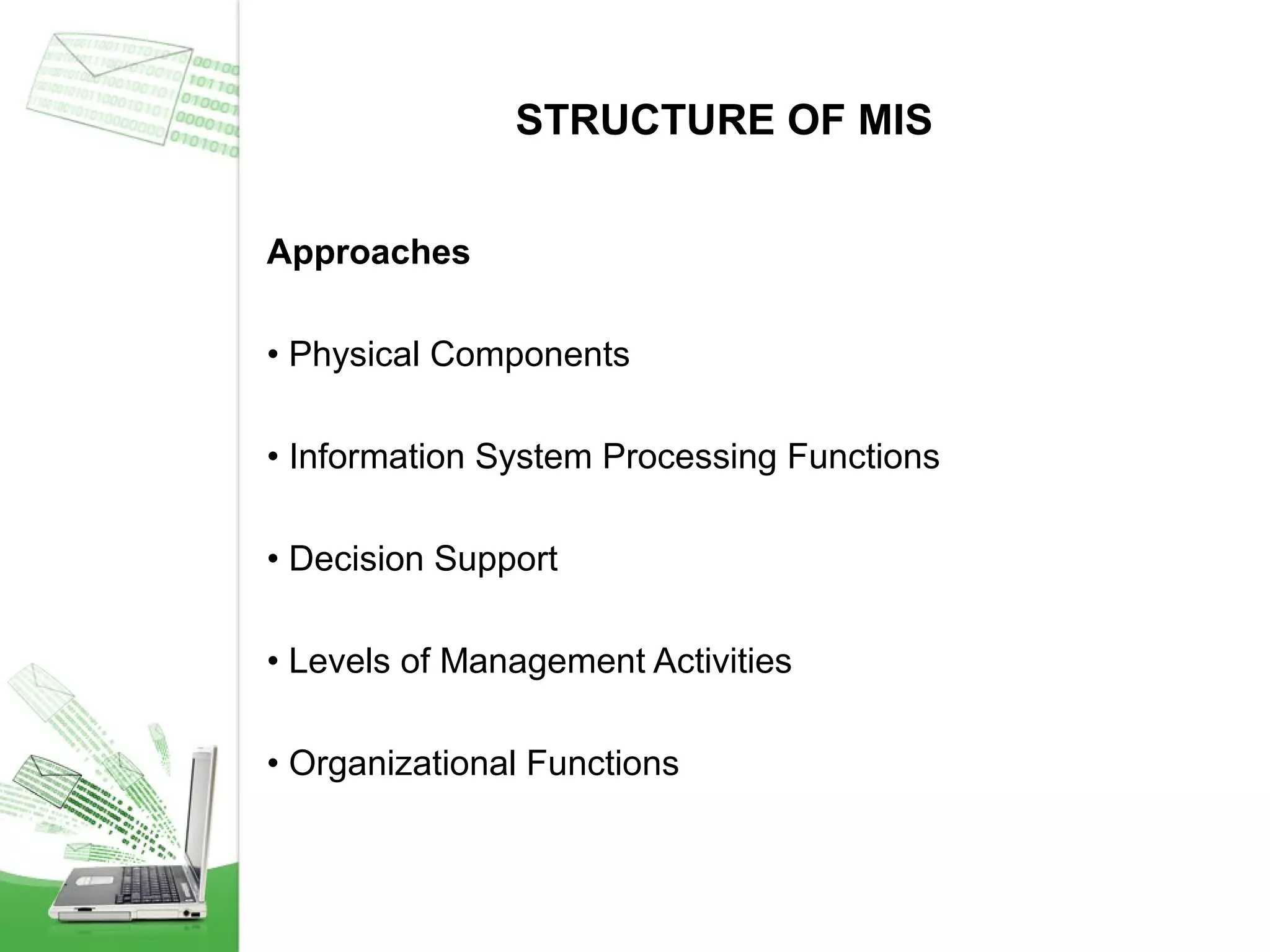
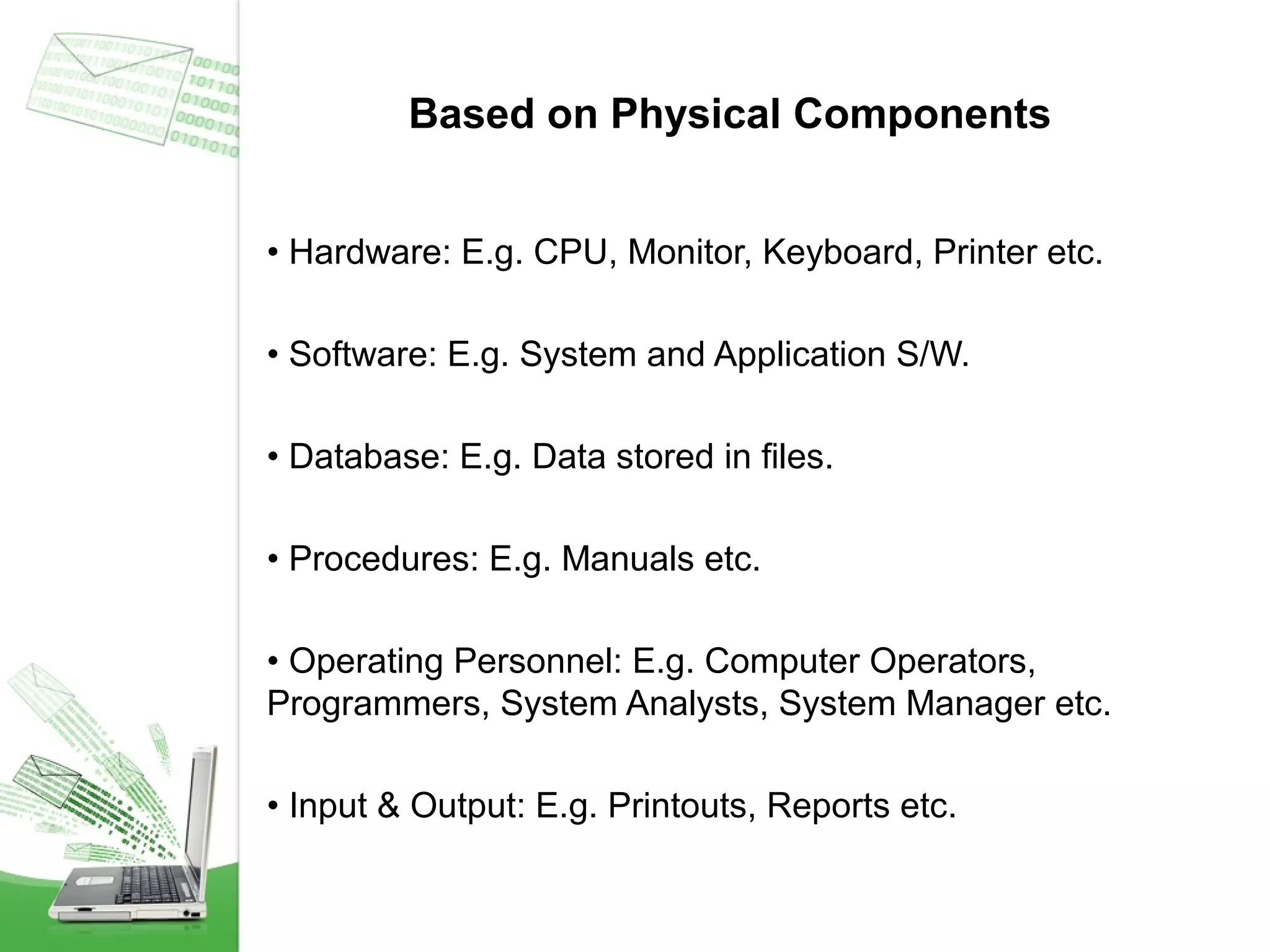
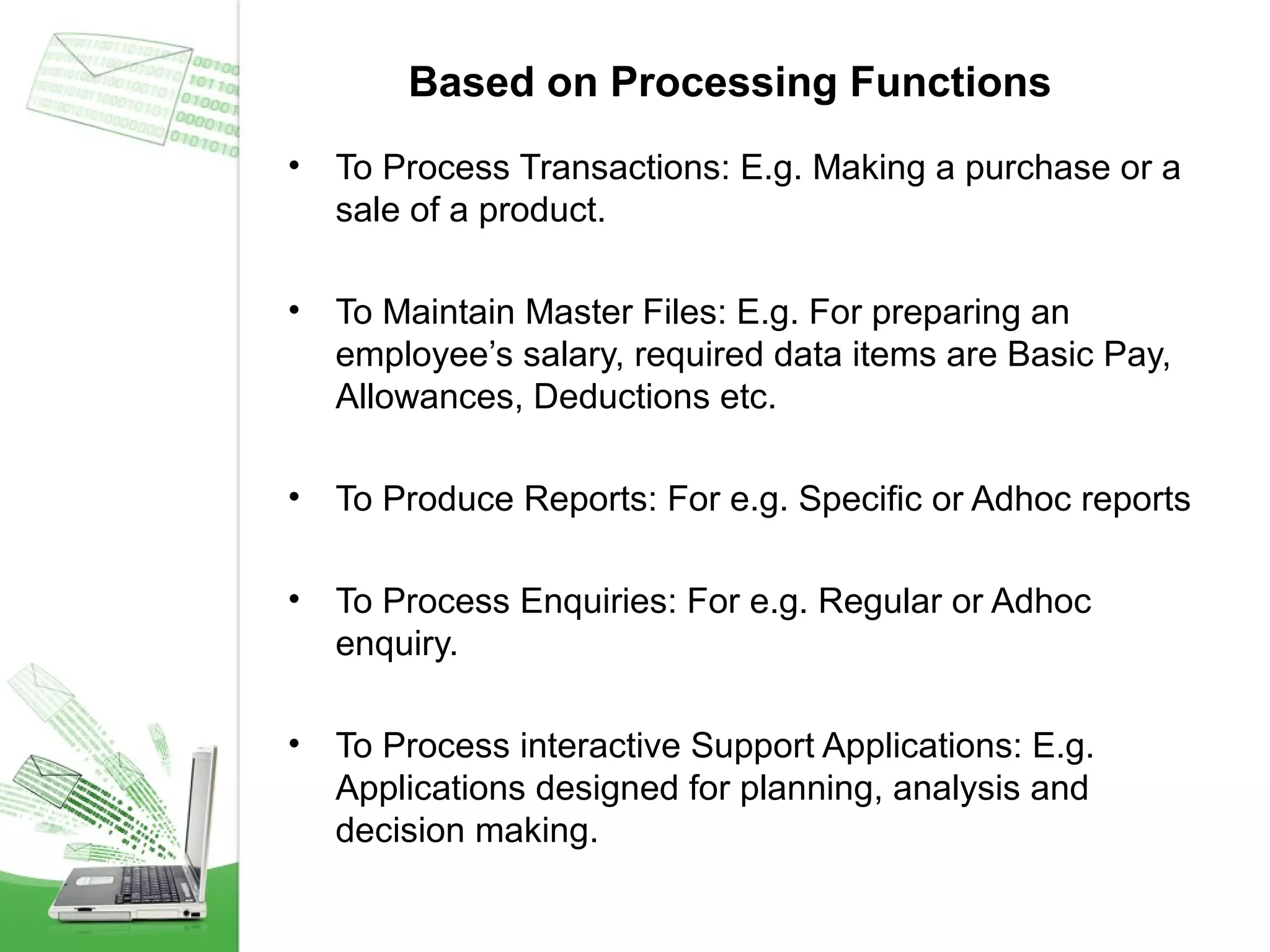
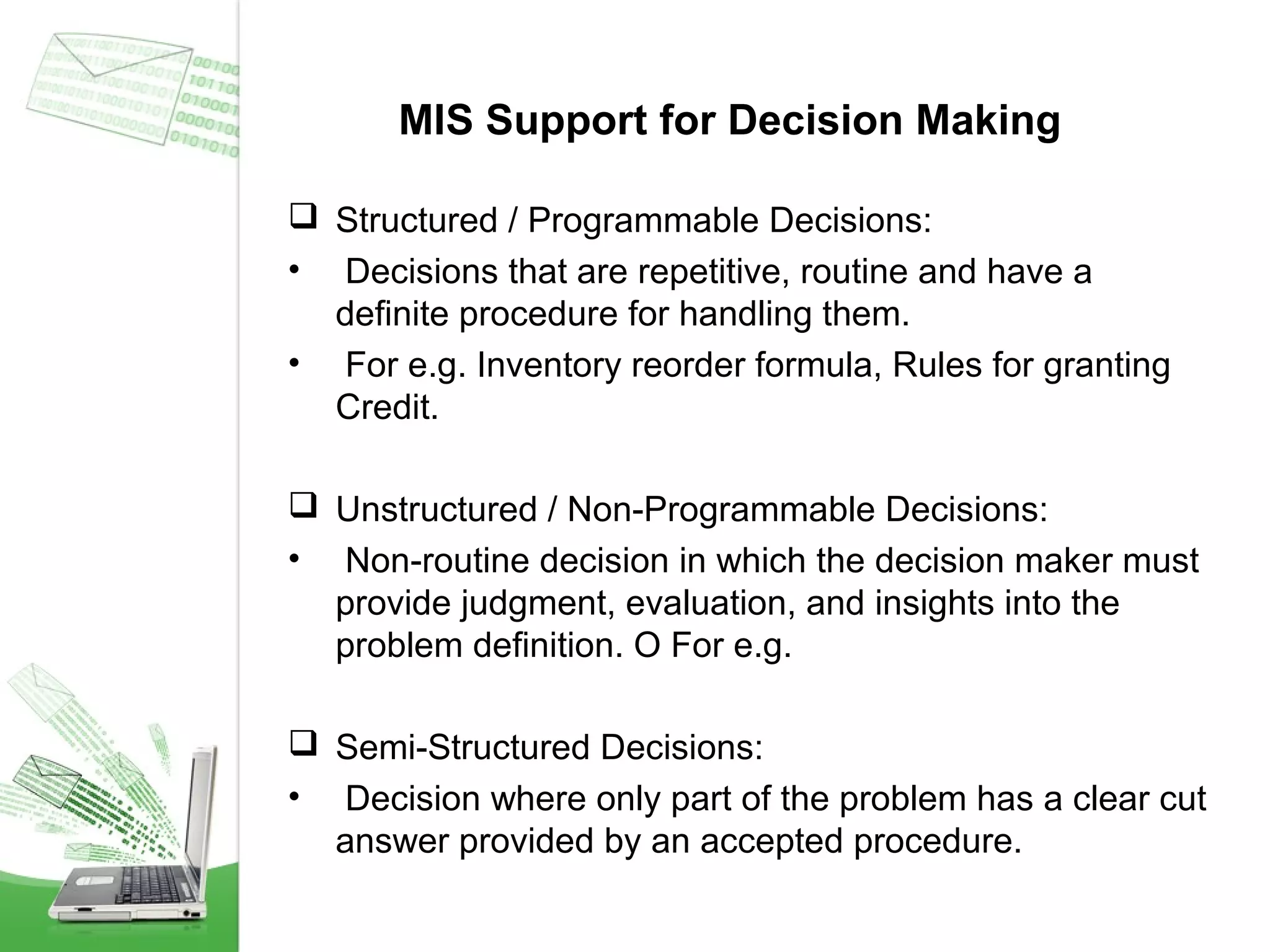
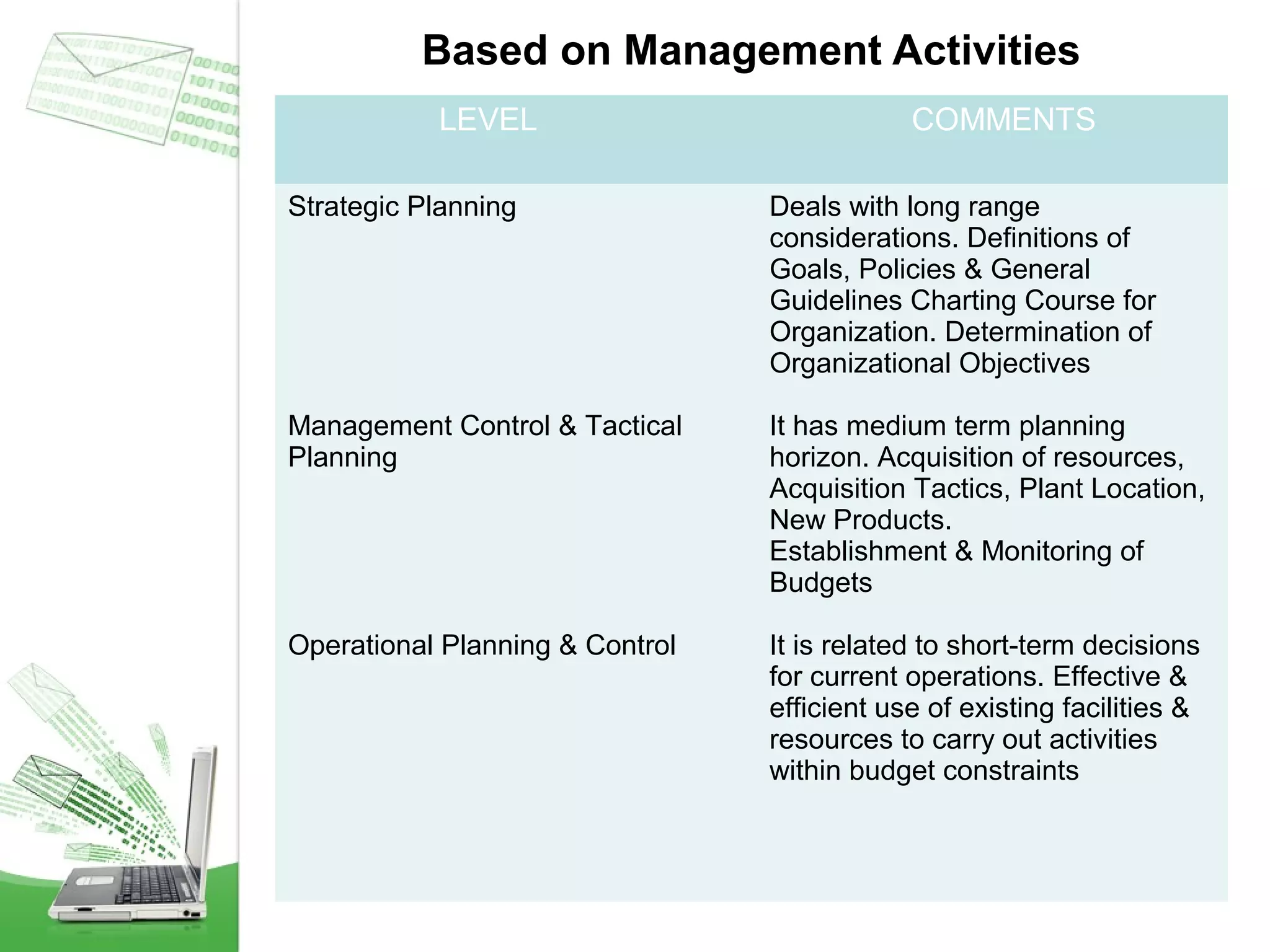
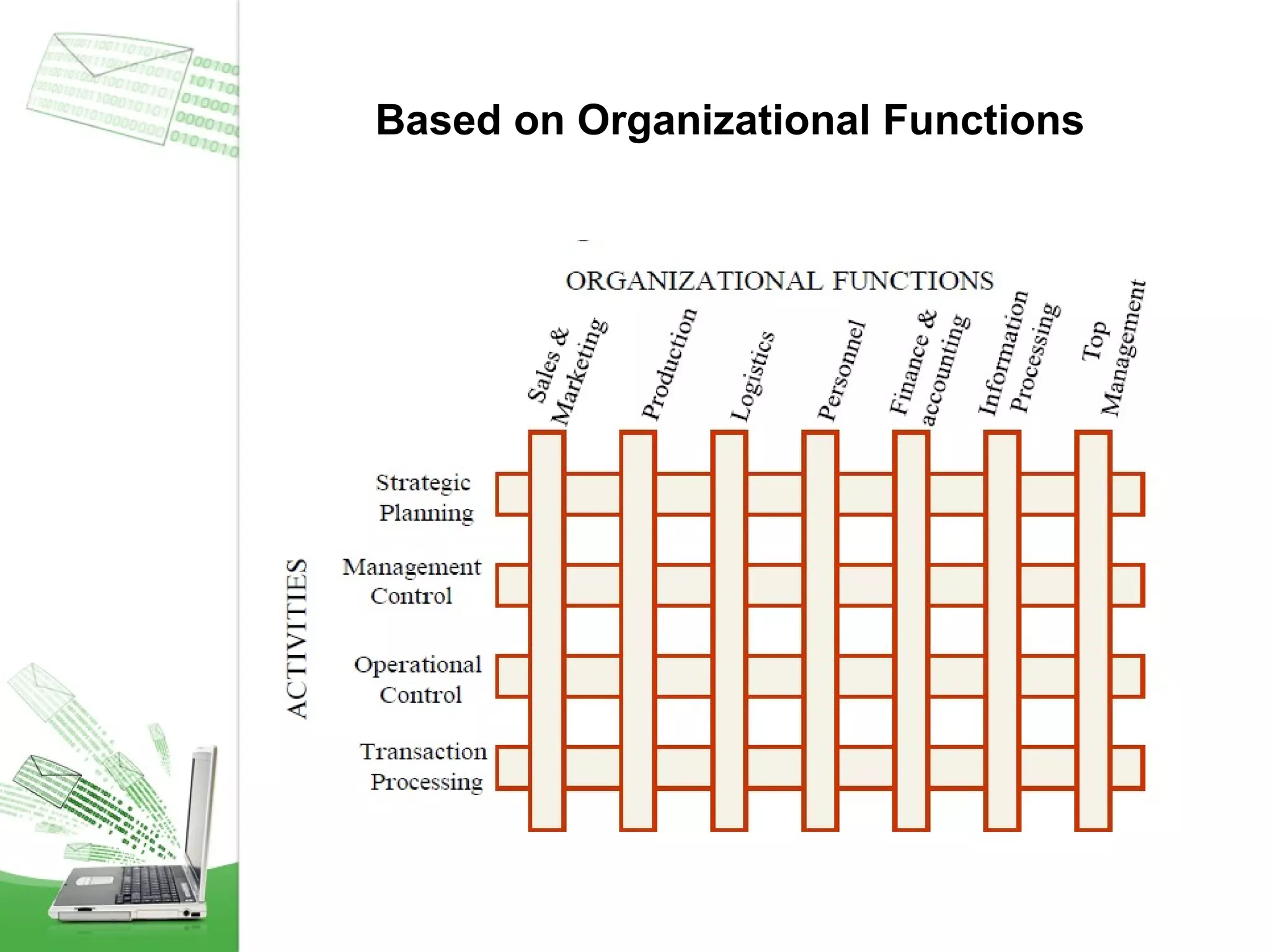
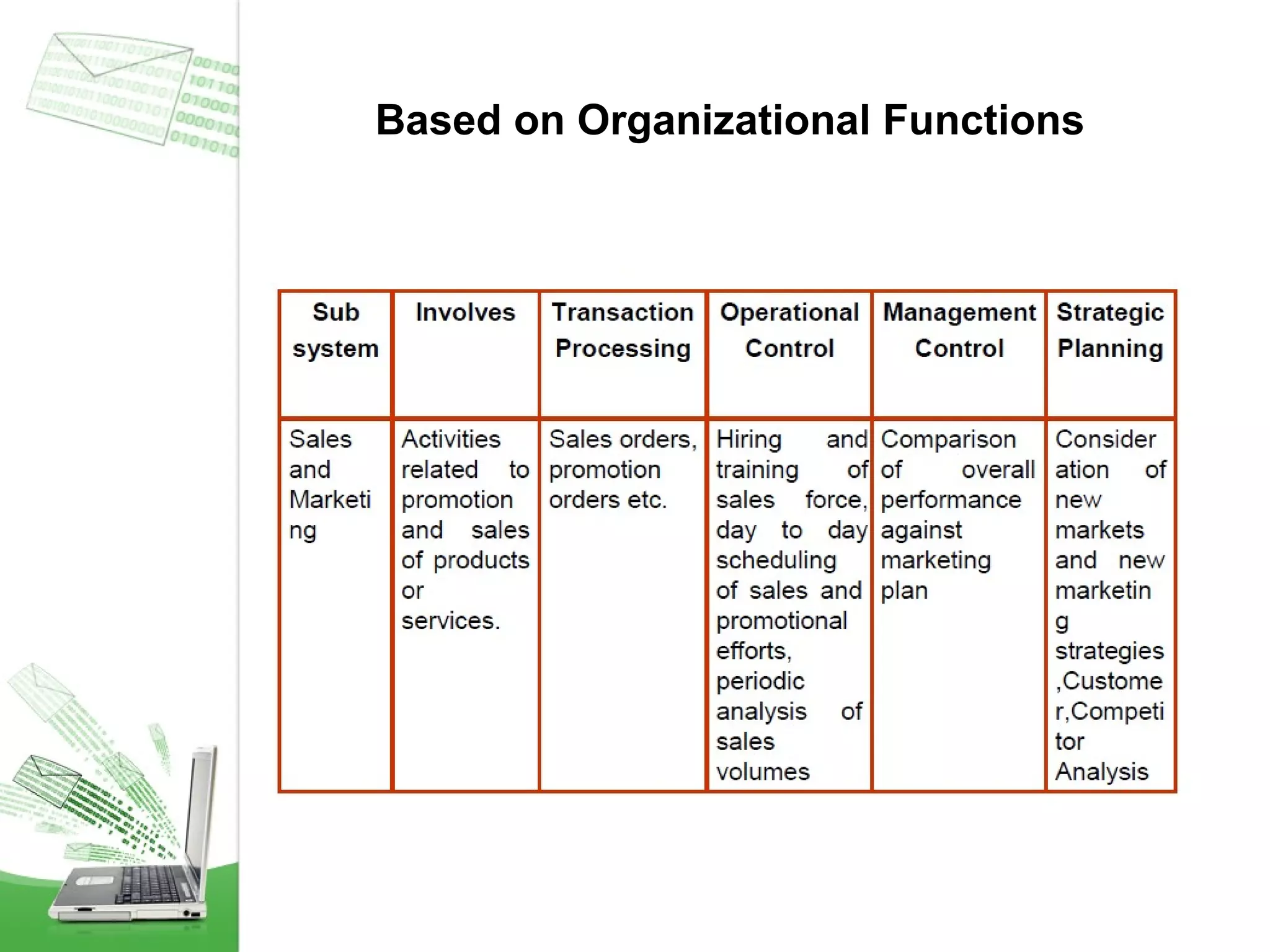
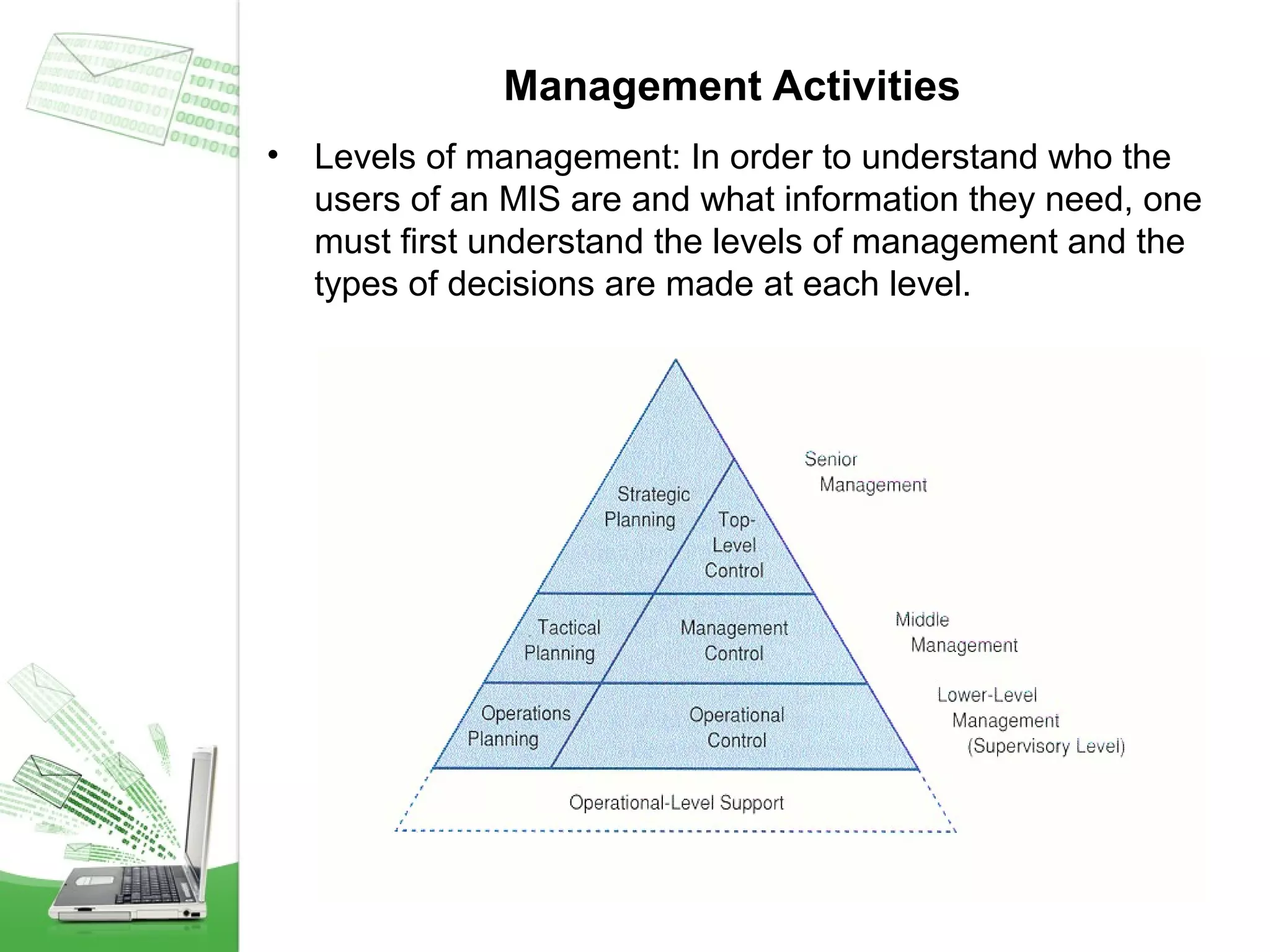
This document provides an overview of management information systems (MIS). It defines MIS as using people, technologies, and procedures to solve business problems by collecting, storing, and disseminating data needed for management functions. Some key advantages of MIS are that it allows companies to identify strengths and weaknesses, gives an overall picture of the company to aid communication and planning, and helps companies align with customer needs. MIS is characterized by a systems approach, management orientation, being need-based, exception-based, and future-oriented with integrated common data flow and long-term planning. Information generated by MIS is interrelated data that has value for decision making.