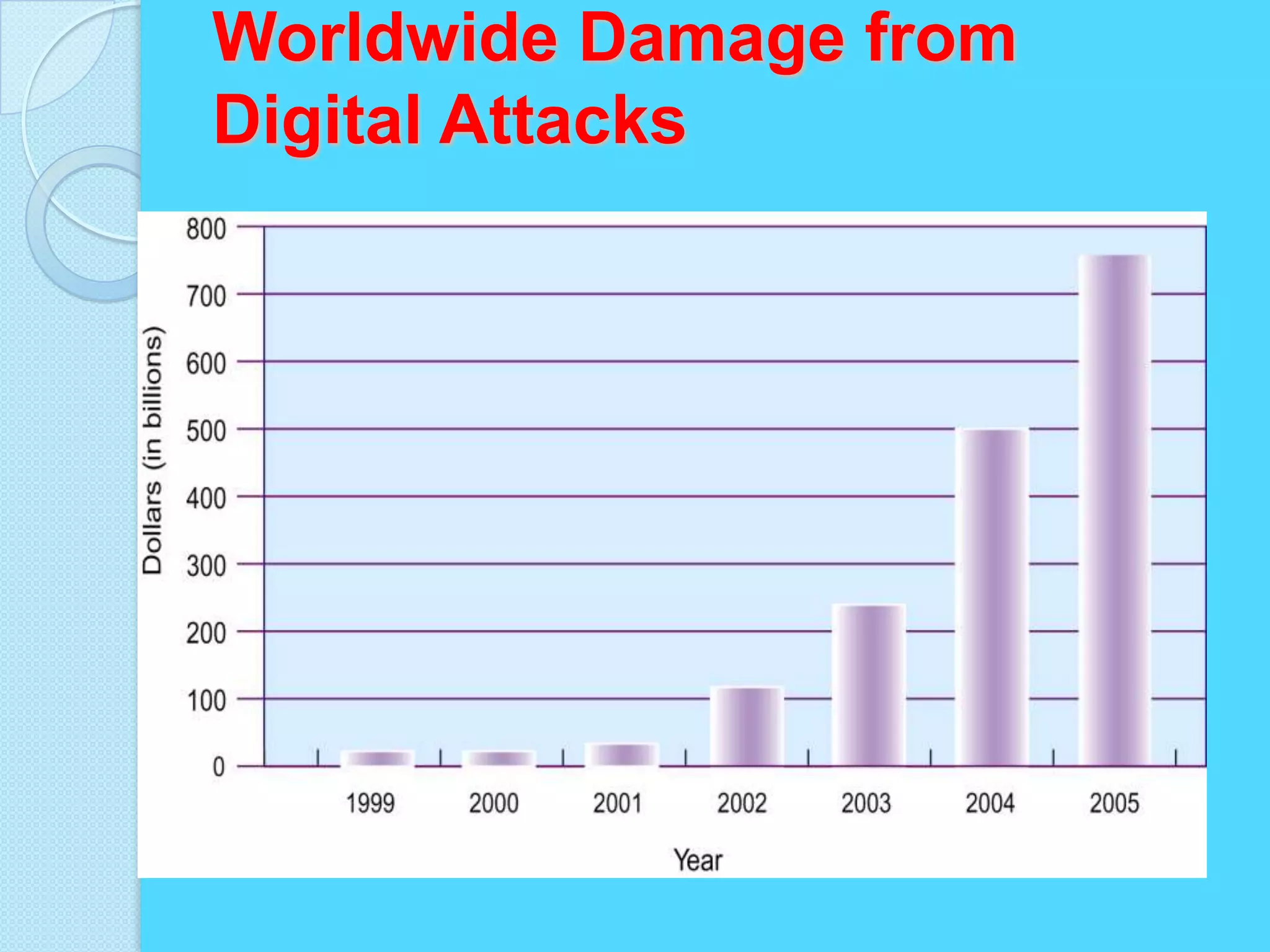
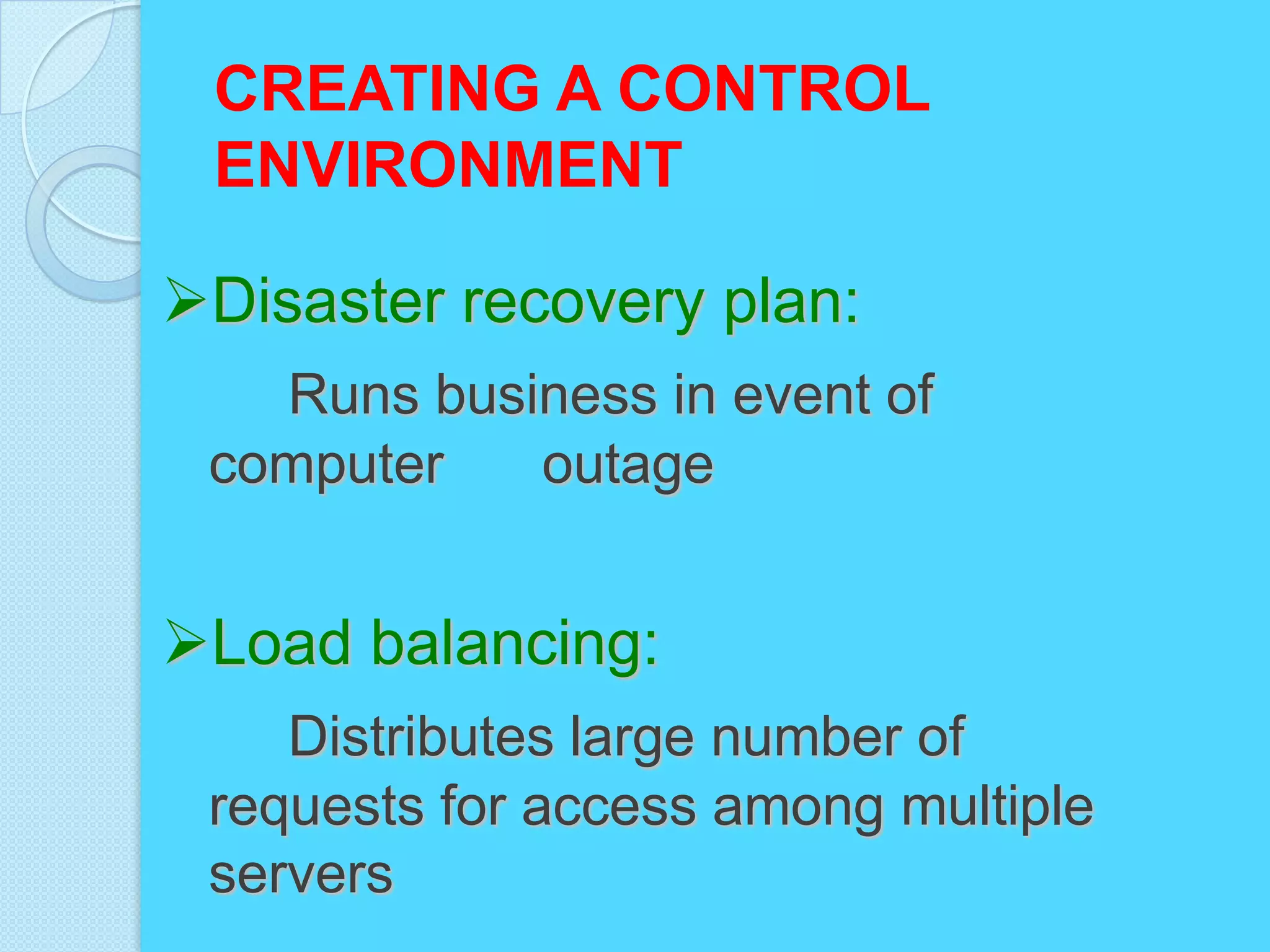
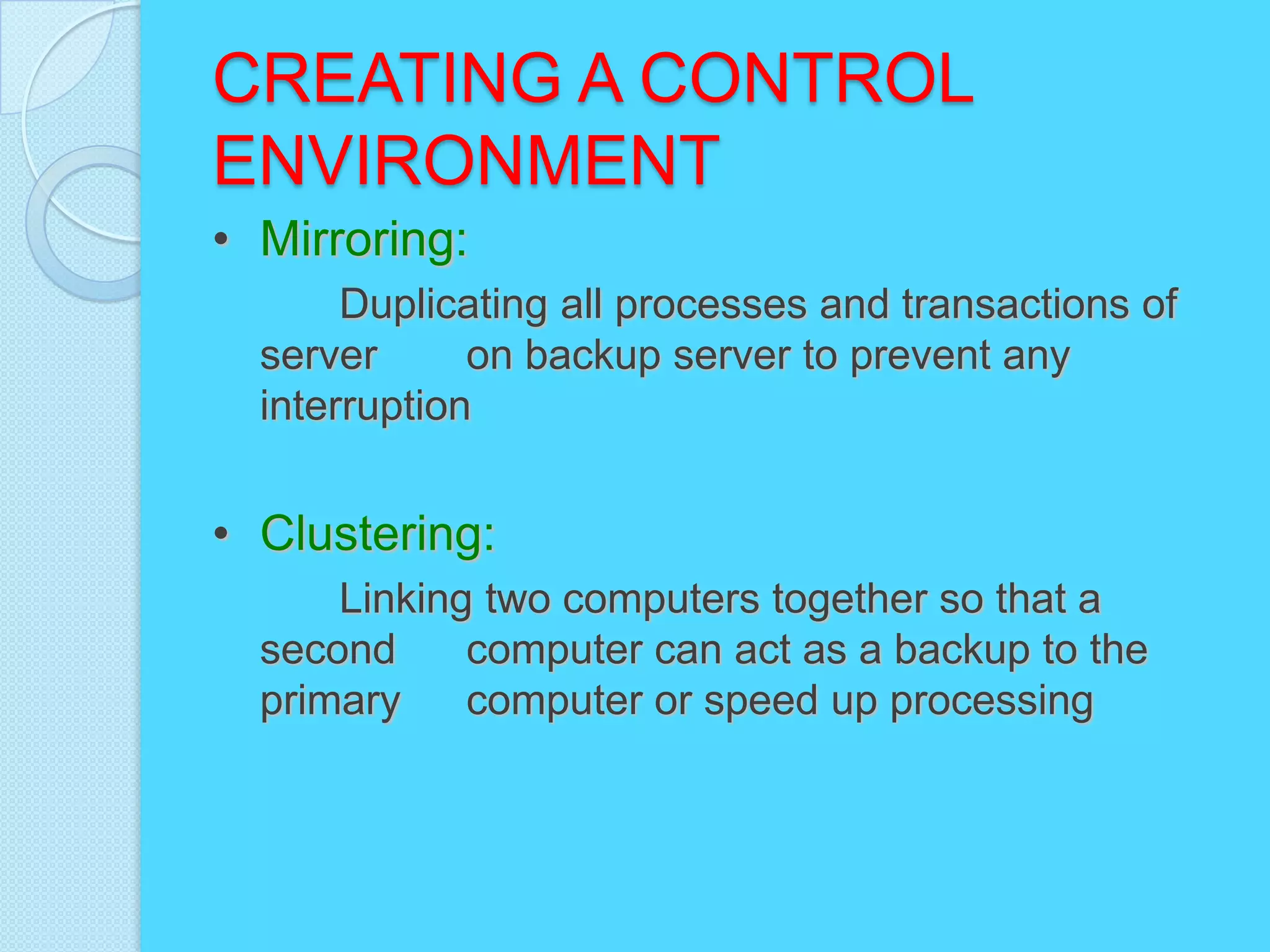
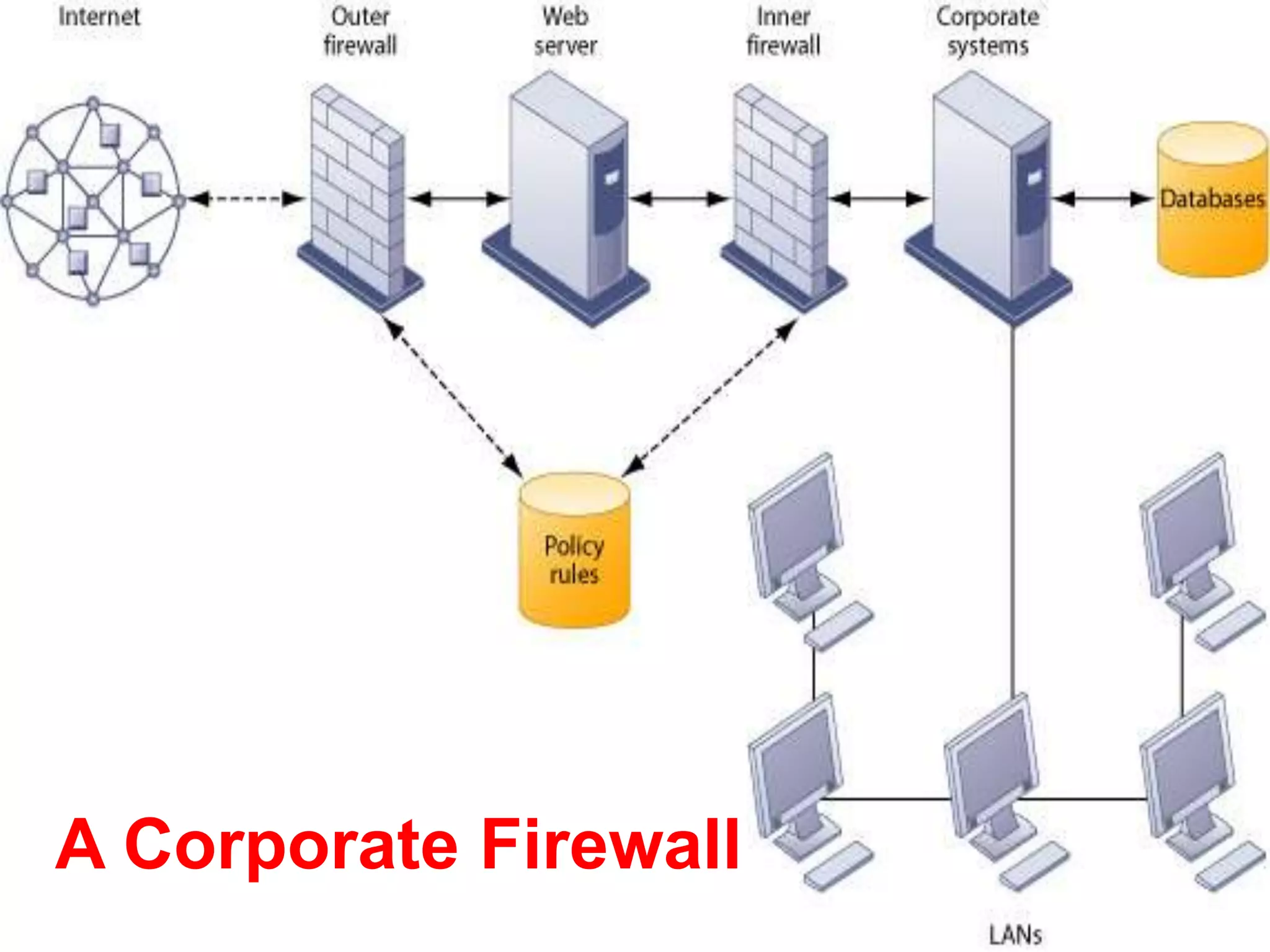
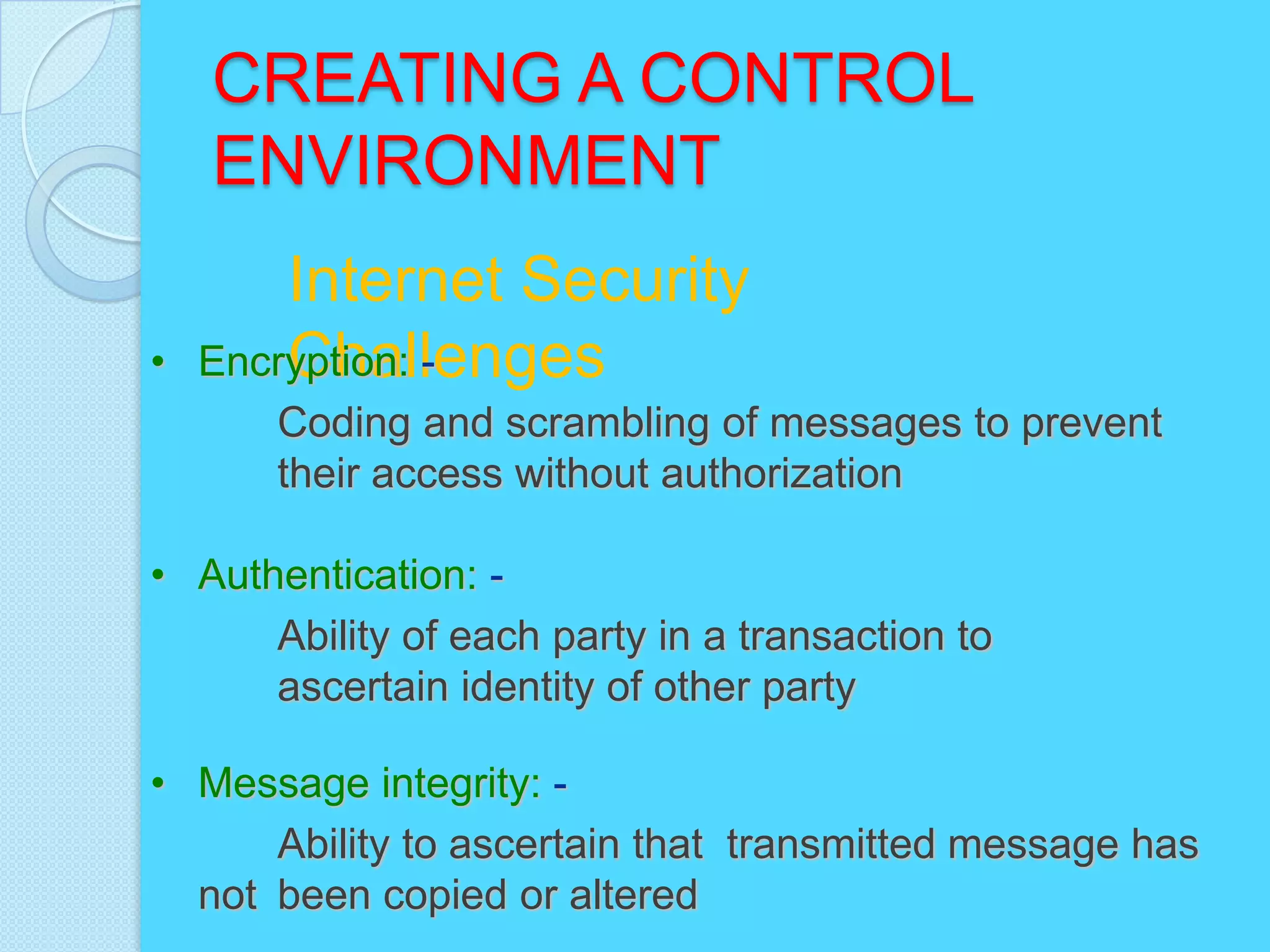
This document discusses information systems security and control. It defines security and explains why systems need protection from threats like destruction, error and abuse. The objectives are to explain why security is important and to evaluate frameworks for security and control. The document identifies challenges like vulnerability and discusses various security strategies and controls like firewalls, encryption and disaster recovery plans. It emphasizes that security is a management priority that requires commitment from all levels.