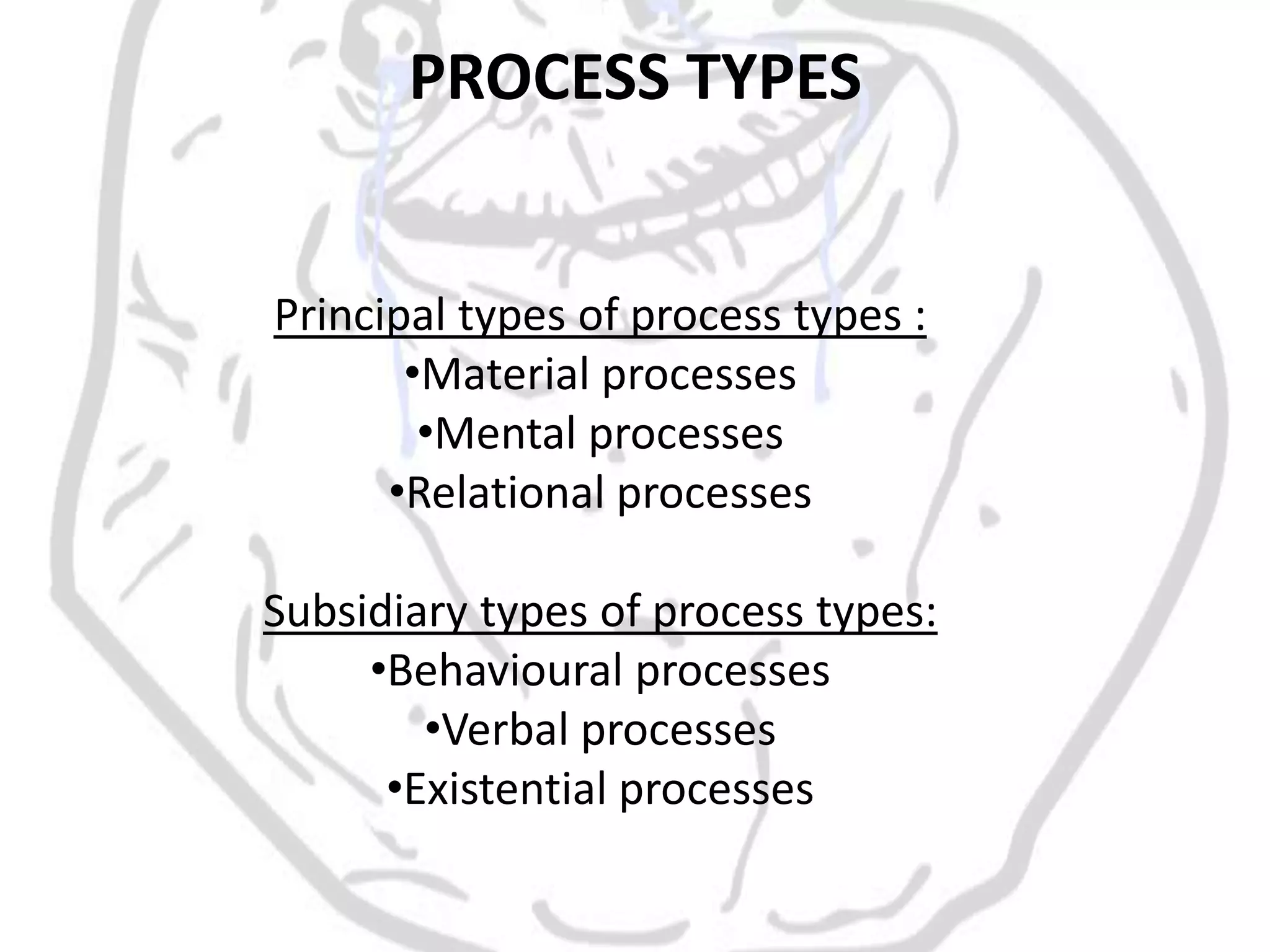
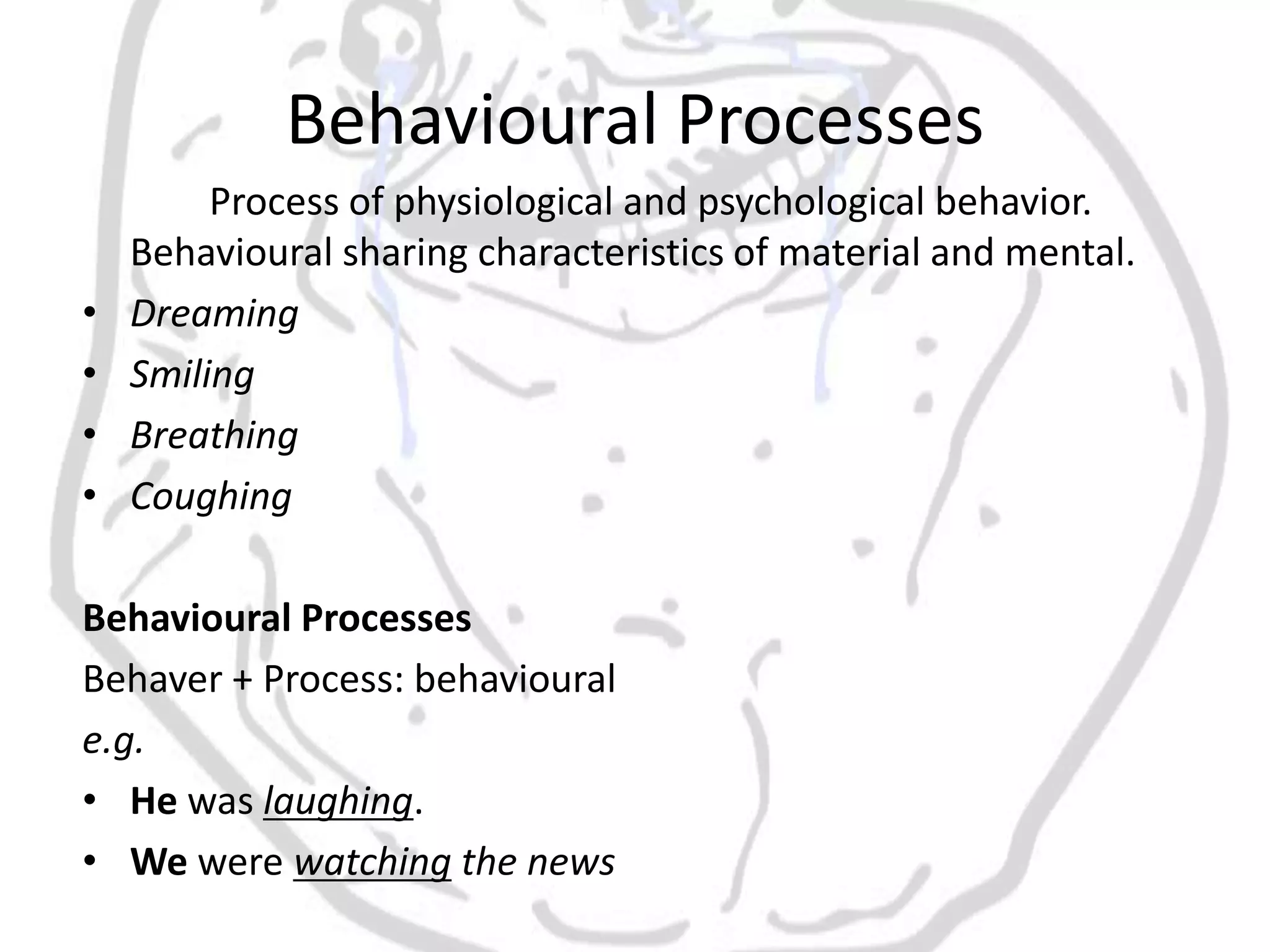
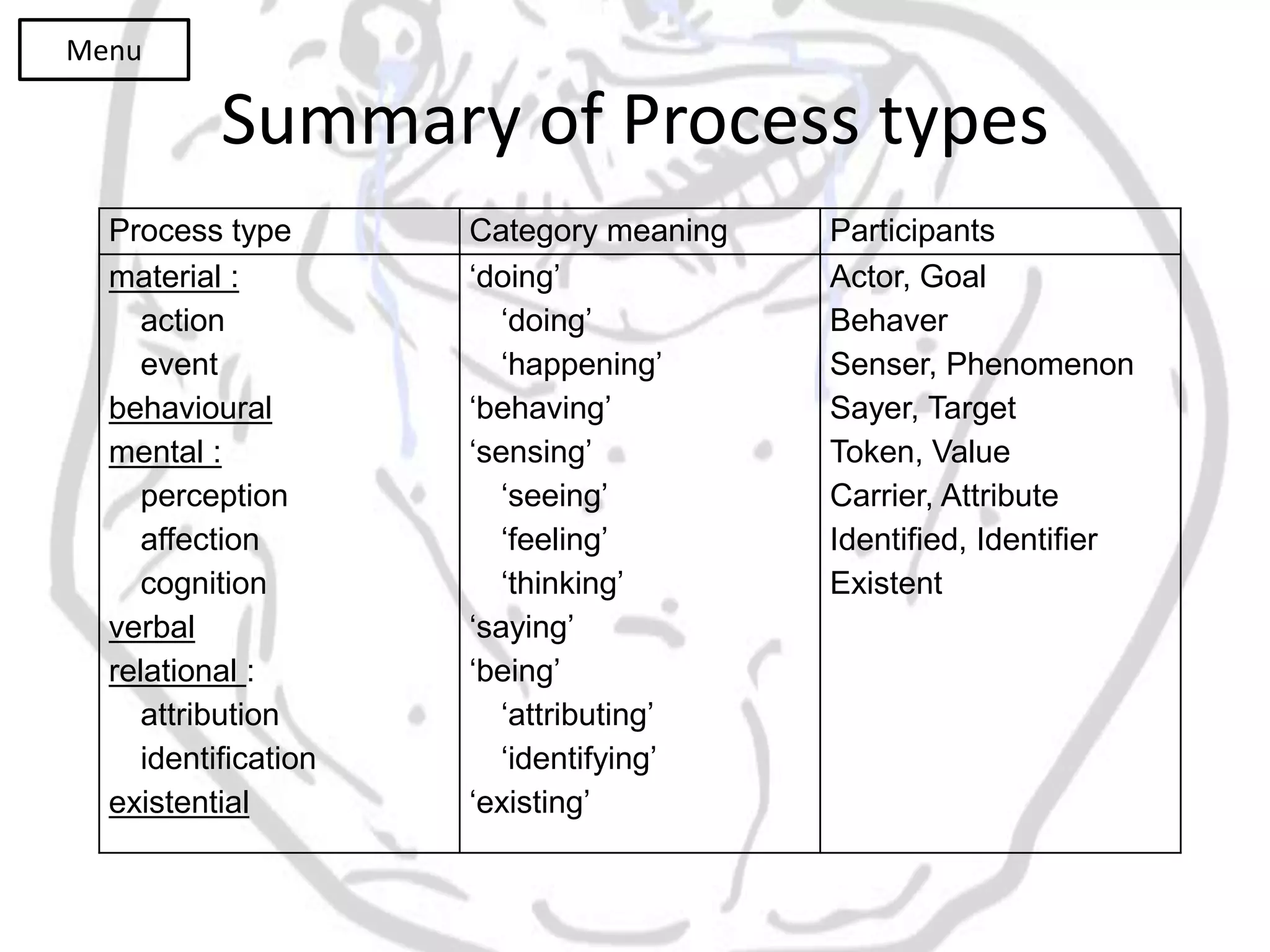
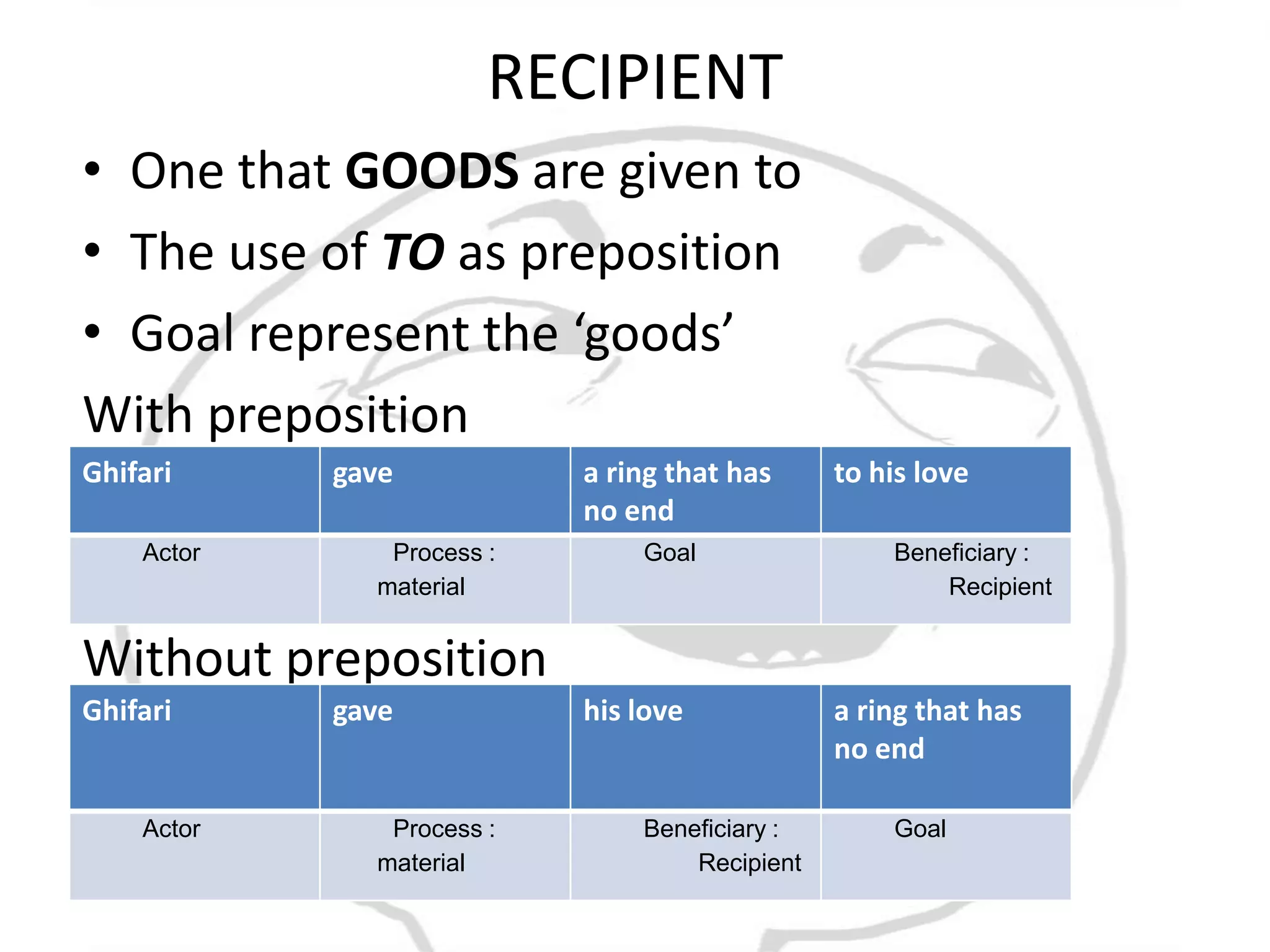
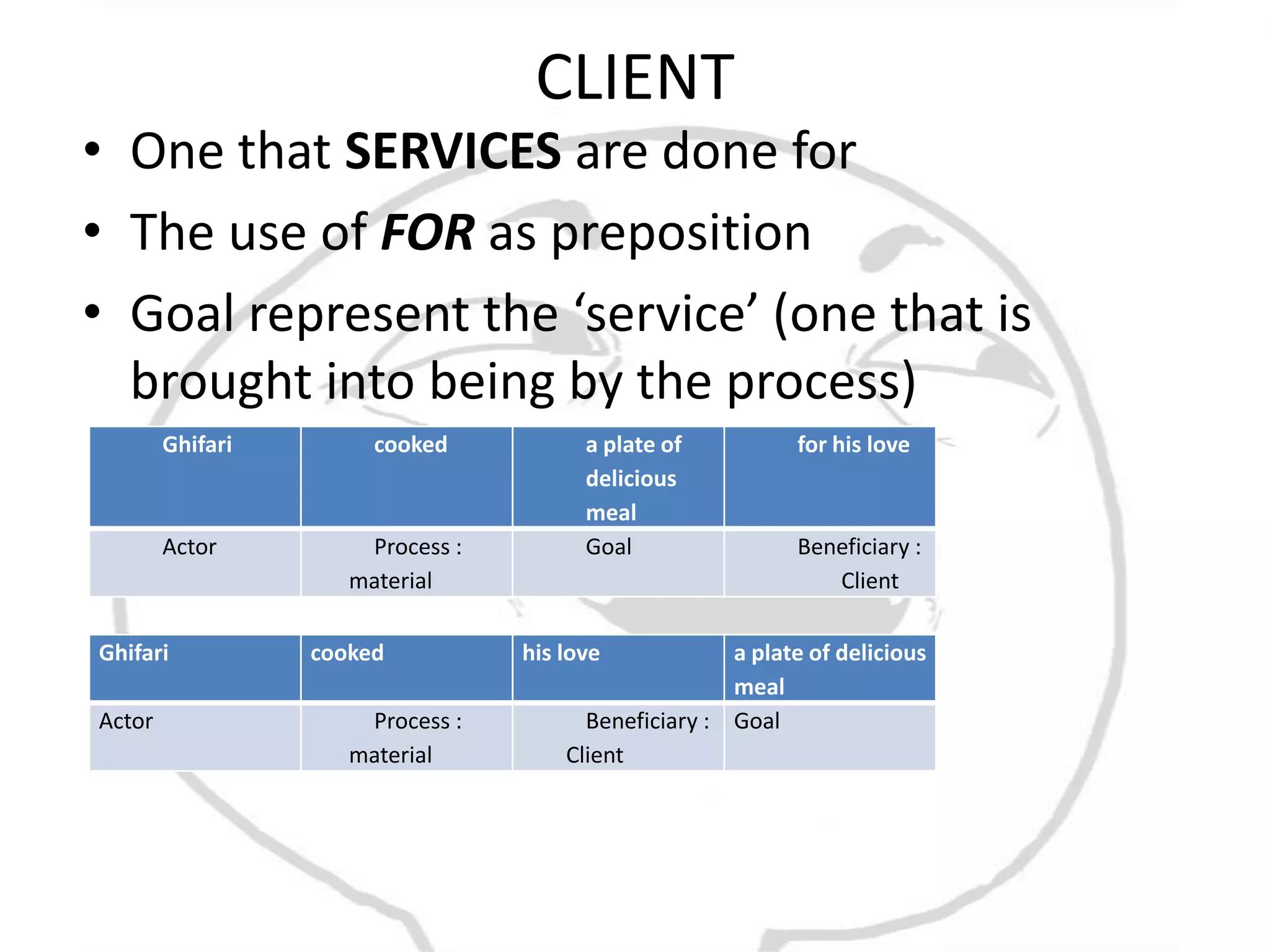
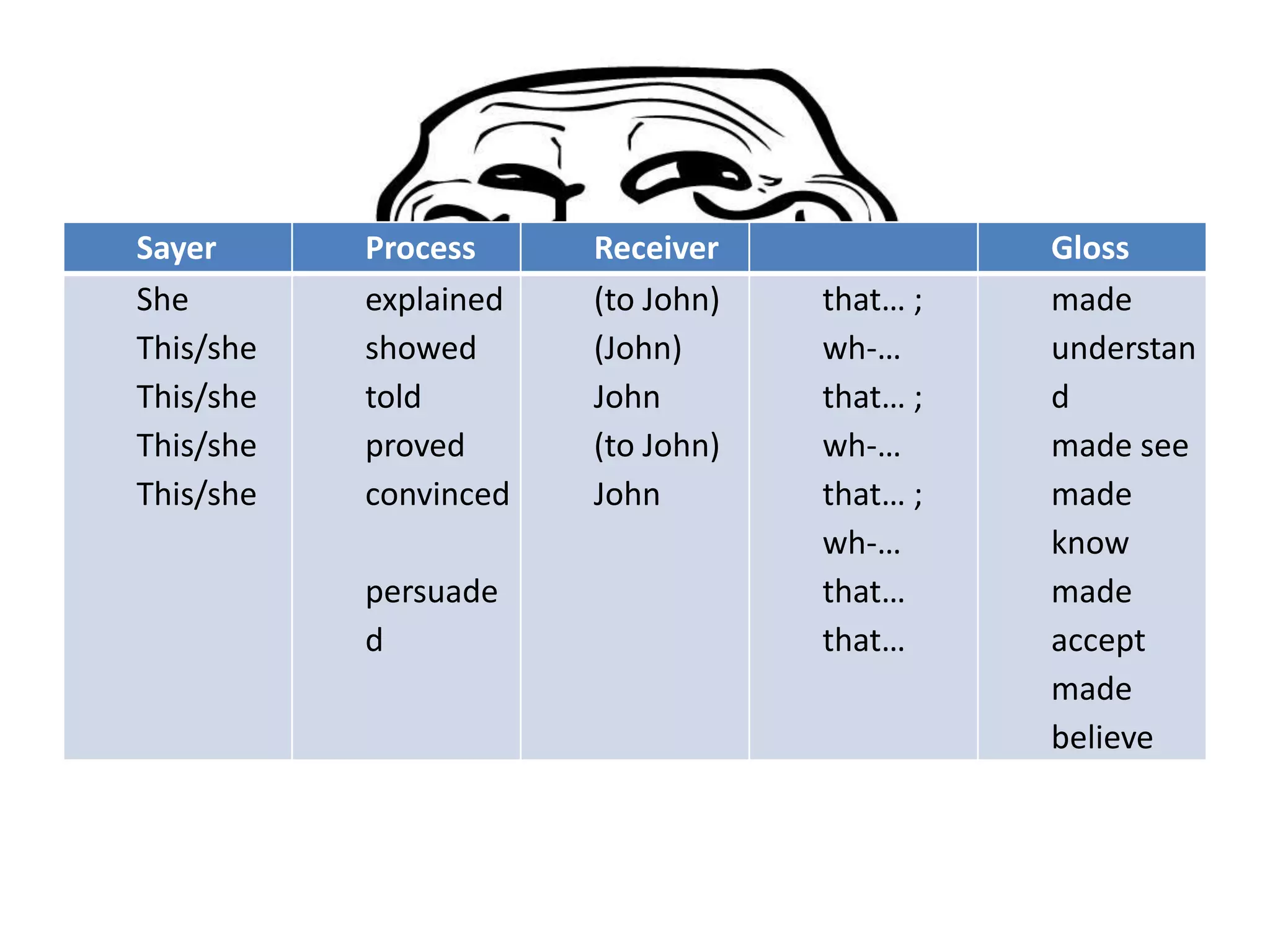
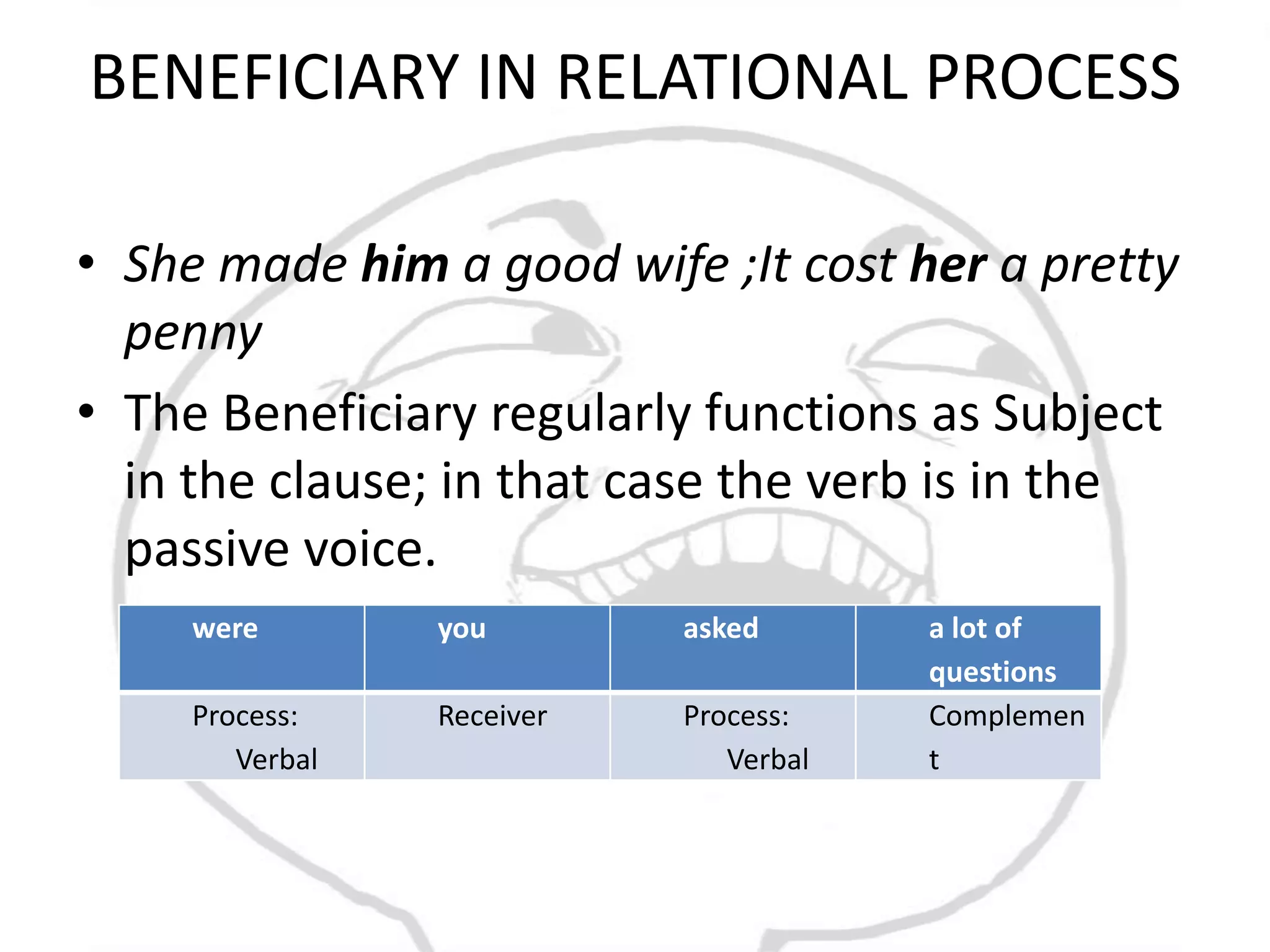
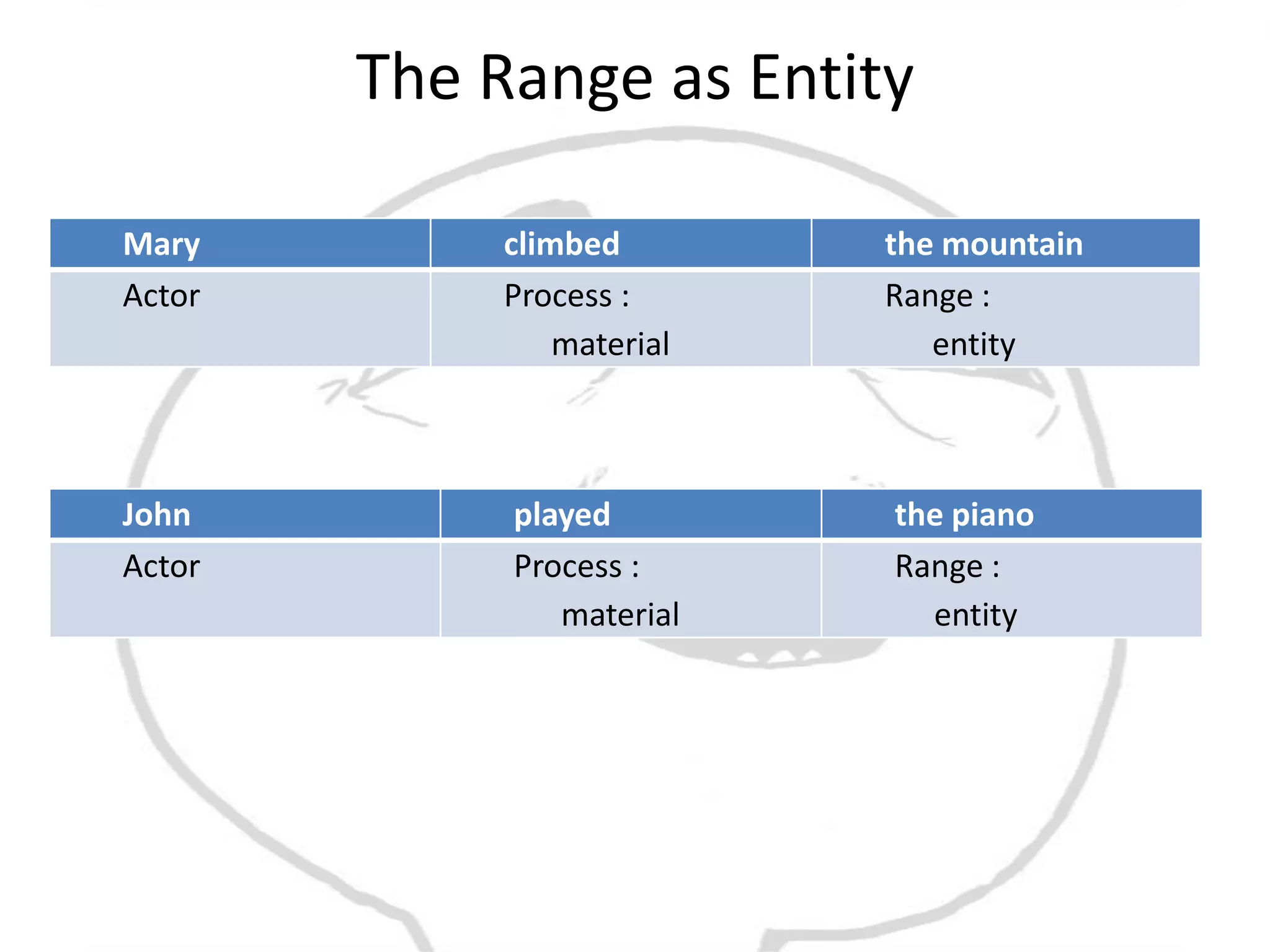
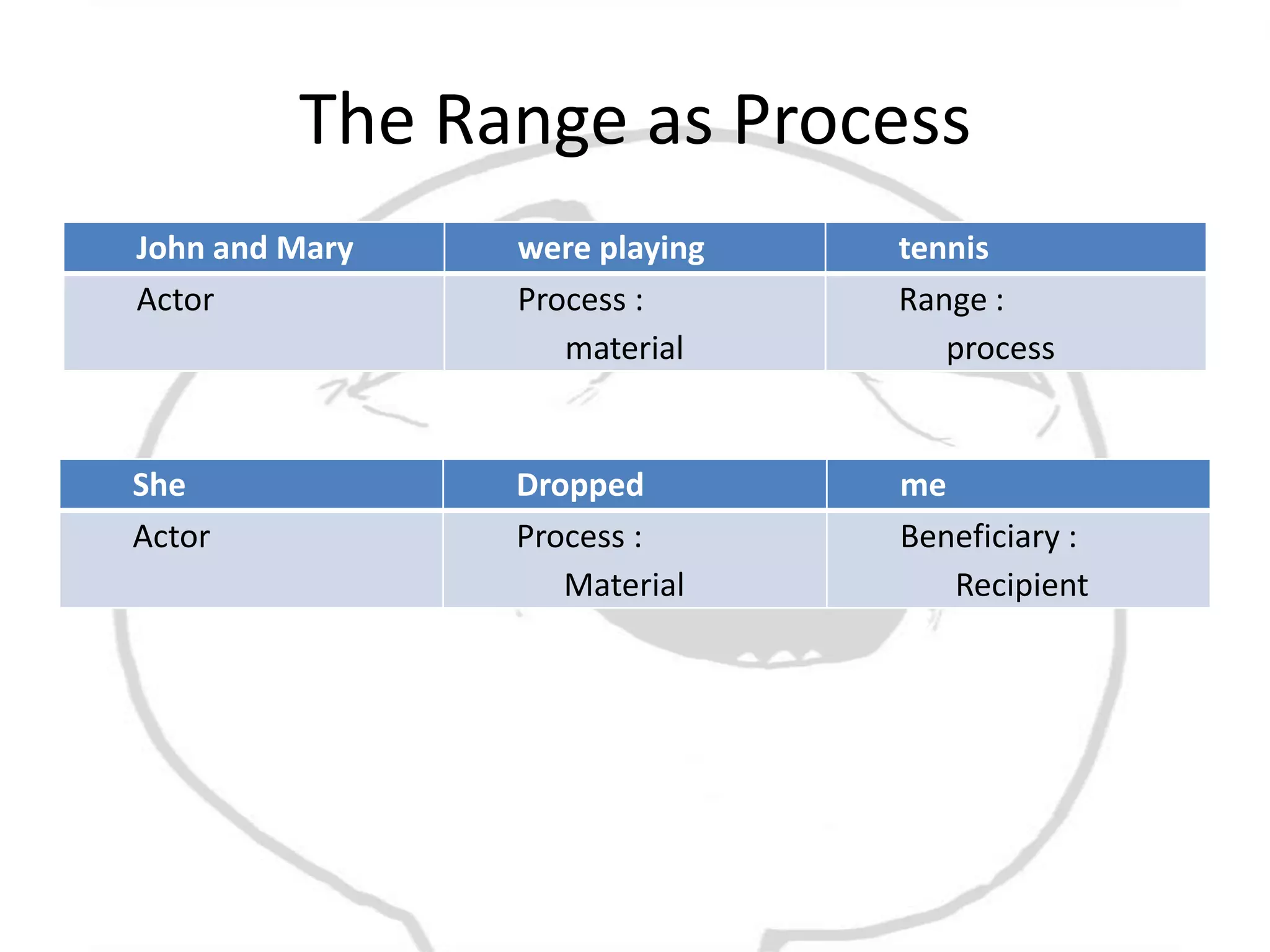
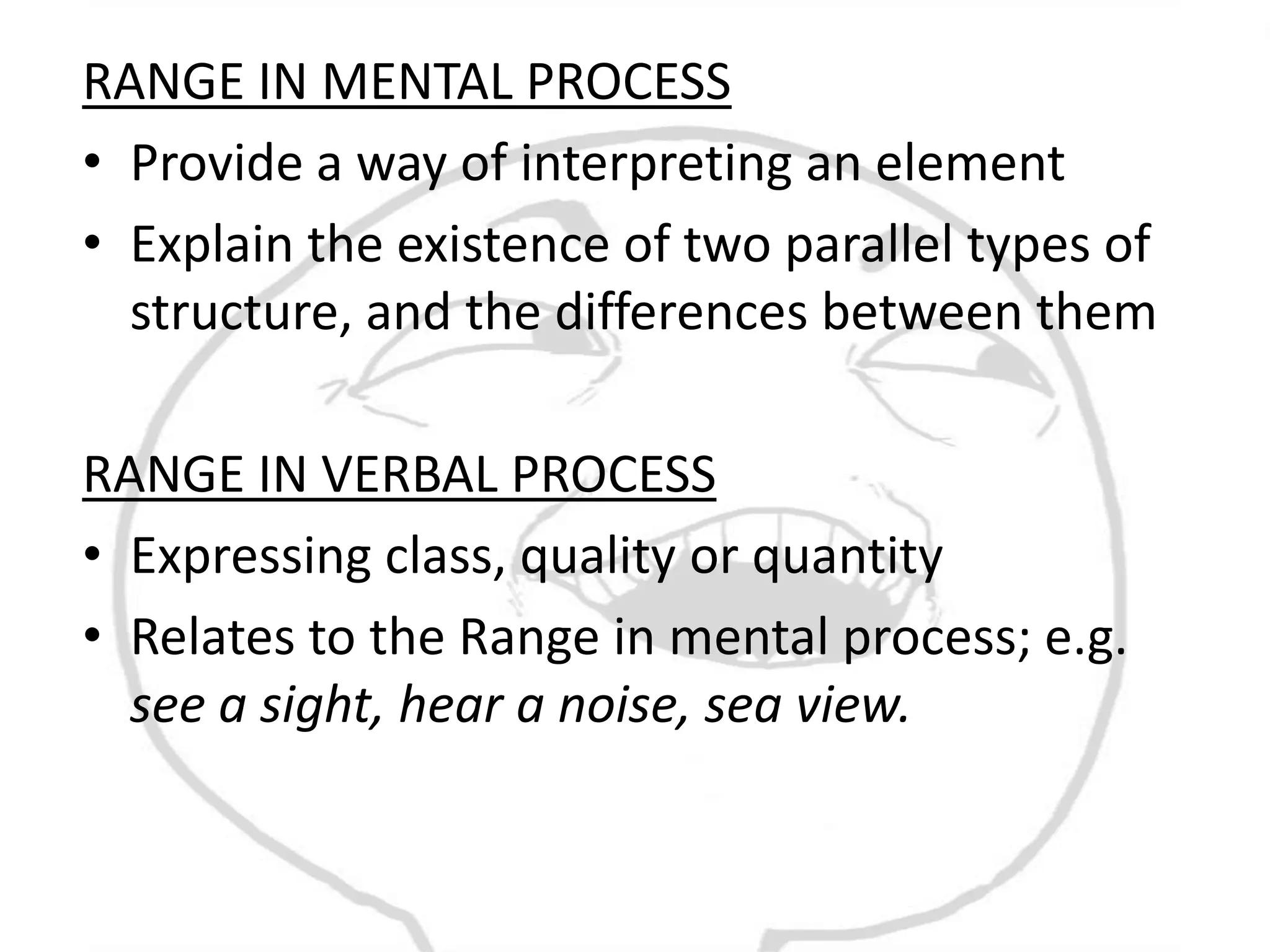
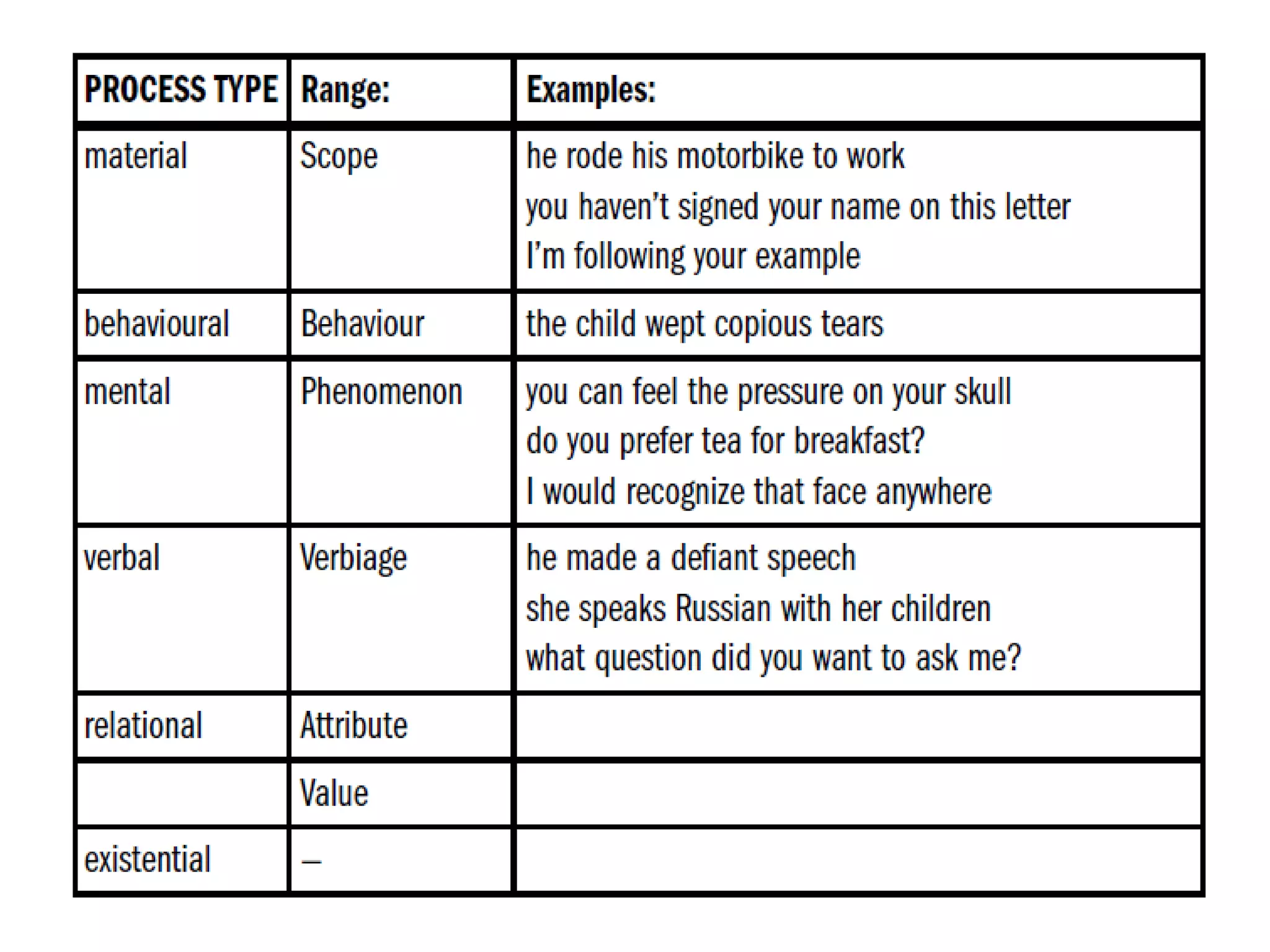
The document discusses different types of processes and participants in processes. There are three main types of processes: material, mental, and relational. There are also subsidiary process types: behavioural, verbal, and existential. The document also describes different participant functions including beneficiary, recipient, client, receiver, and range. Beneficiaries are participants that processes are done for or to. Ranges specify the scope or domain of a process.