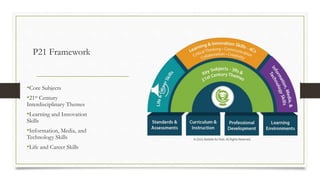
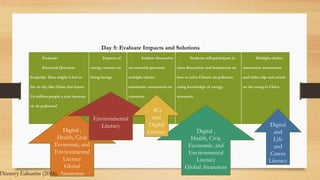
The document discusses the importance of integrating the Partnership for 21st Century Learning (P21) framework into education to equip students with essential skills for success in a competitive global economy. It highlights strategies for aligning curriculum, instruction, and assessment with 21st century themes such as global awareness and financial literacy, while emphasizing critical skills like creativity, communication, and collaboration. Through practical examples and essential questions, it outlines how educators can foster student-centered learning and enhance digital literacy among learners.















![References
• Andrade, M. (2016). Curricular elements for learner success – 21st century skills. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 4(8), 143-149
• Bali, M. (2016). Digital skills and digital literacy. Literacy Today, 33(4), 24-25
• Blackhurst, Kathryn. (2015). Common core: What is international benchmarking? Newsmax. Retrieved from https://www.newsmax.com/fastfeatures/common-core-
international-benchmarking/2015/06/02/id/648150/
• Cleaves, P. (2015). Collaboration – How do we actually develop this essential 21st century skill in students? Australian Educational Leader, 37(3), 79-82
• Discovery Education. (2016). Value of renewable resources. Discovery Education, California. Retrieved from
https://app.discoveryeducation.com/learn/techbook/courses/science
• Dutton, C. (Course Lecturer). (2018). 21st Century skills for the digital educator review: Module 1 [Video]. American College of Education. Retrieved from http://ace.edu
• P21 Partnership for 21st Century Learning. (2019). Framework for 21st century learning. Battle for Kids. Retrieved from
http://www.battelleforkids.org/networks/p21/frameworks-resources
• P21 Partnership for 21st Century Learning. (2019). Framework for 21st century learning definitions. Battle for Kids. Retrieved from
http://www.battelleforkids.org/networks/p21/frameworks-resources
• Ross, D. (2017). Empowering students with 21st century skills for today. Getting Smart. Retrieved from https://www.gettingsmart.com/2017/04/empowering-students-21st-
century-skills/
• Watanabe-Crockett, L. (2017, November). 5 Reasons why you should be teaching digital citizenship. Global Digital Citizenship Foundation. Retrieved from
https://globaldigitalcitizen.org/5-reasons-teaching-digital-citizenship](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/originalcontribution-190612225820/85/Original-Contribution-18-320.jpg)