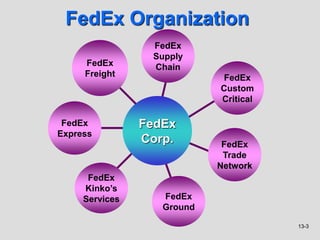
With all the acquisitions by FedEx, it adopted a multi-divisional structure to manage its growing operations. The structure delegates significant authority to specialized divisions like FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, and FedEx Freight, while corporate provides strategic direction and consolidated financial reporting. This allows each division to manage its own network of services. The document discusses how organizational structure and culture impact how employees interact and behave within an organization. It provides examples of how different companies structure themselves based on factors like strategy, environment, and technology.