Embed presentation









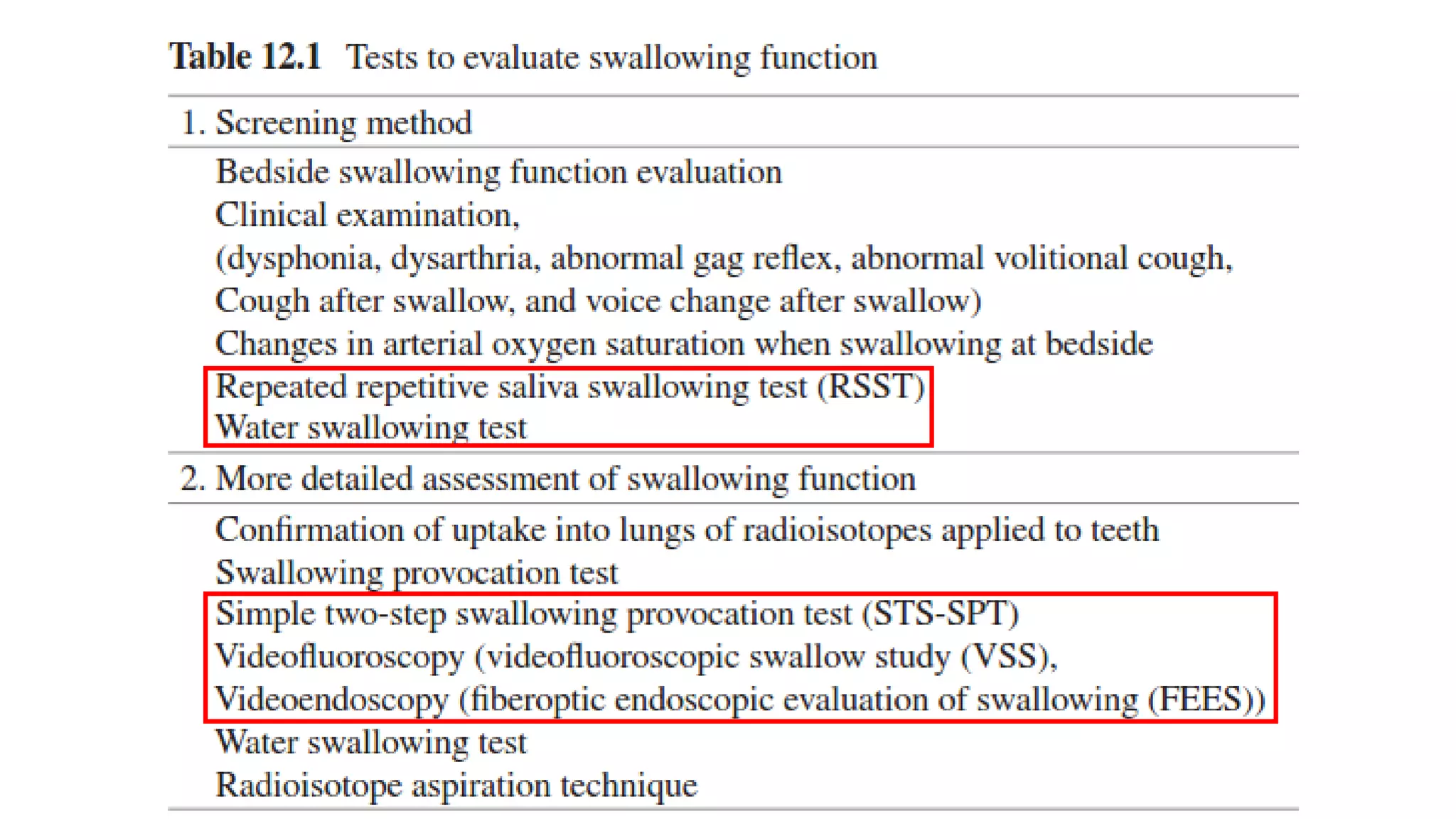
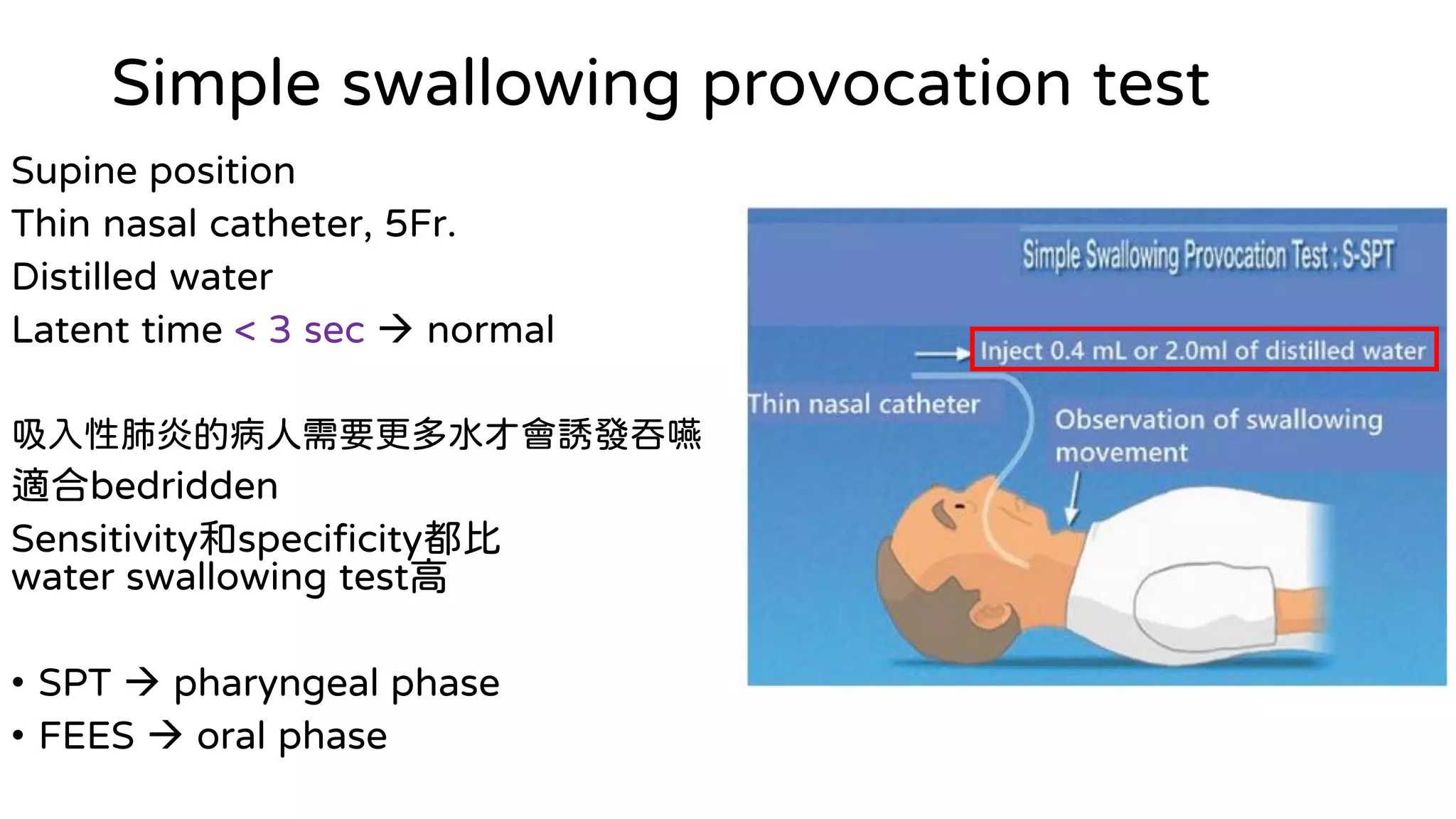

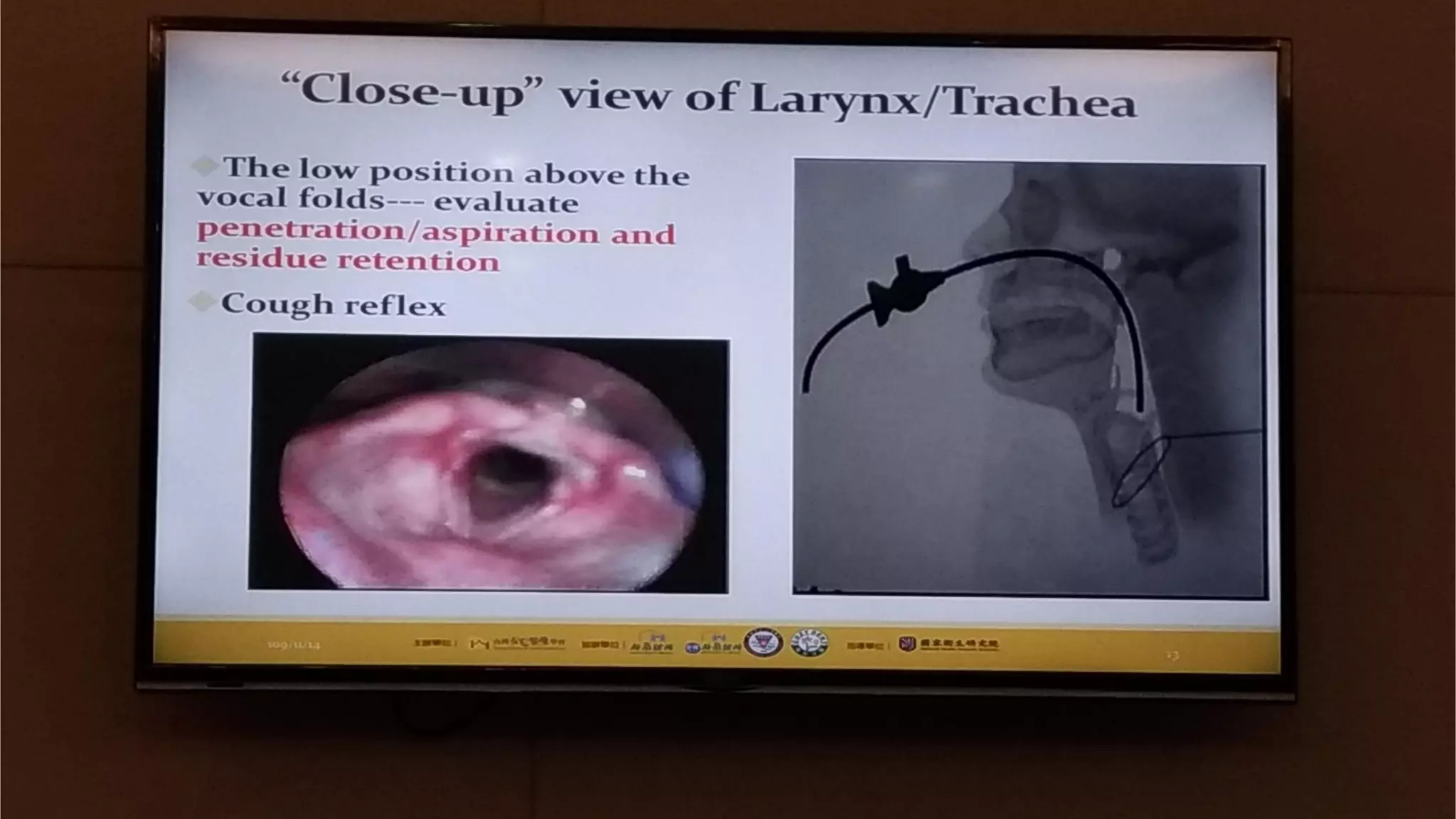
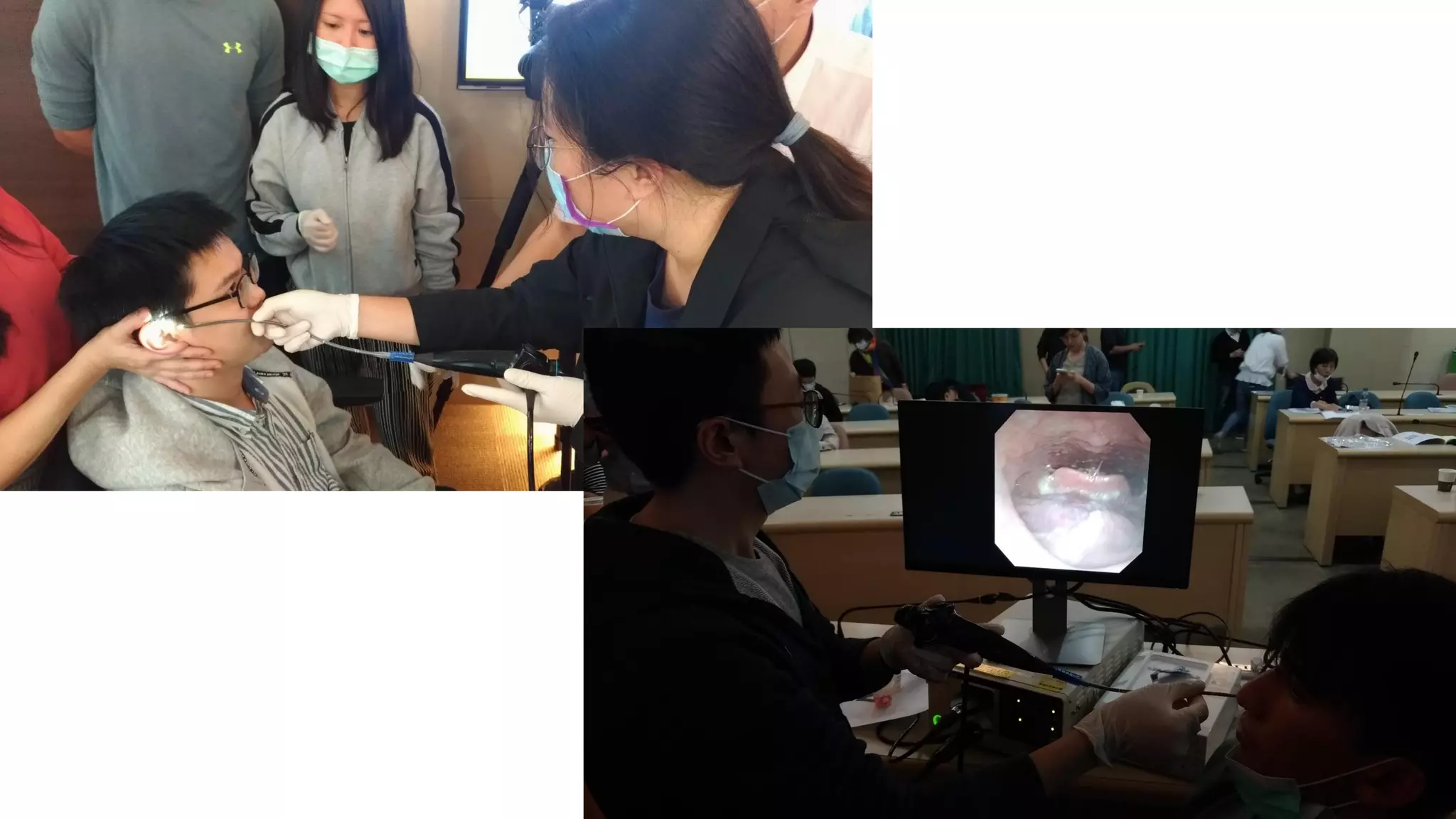



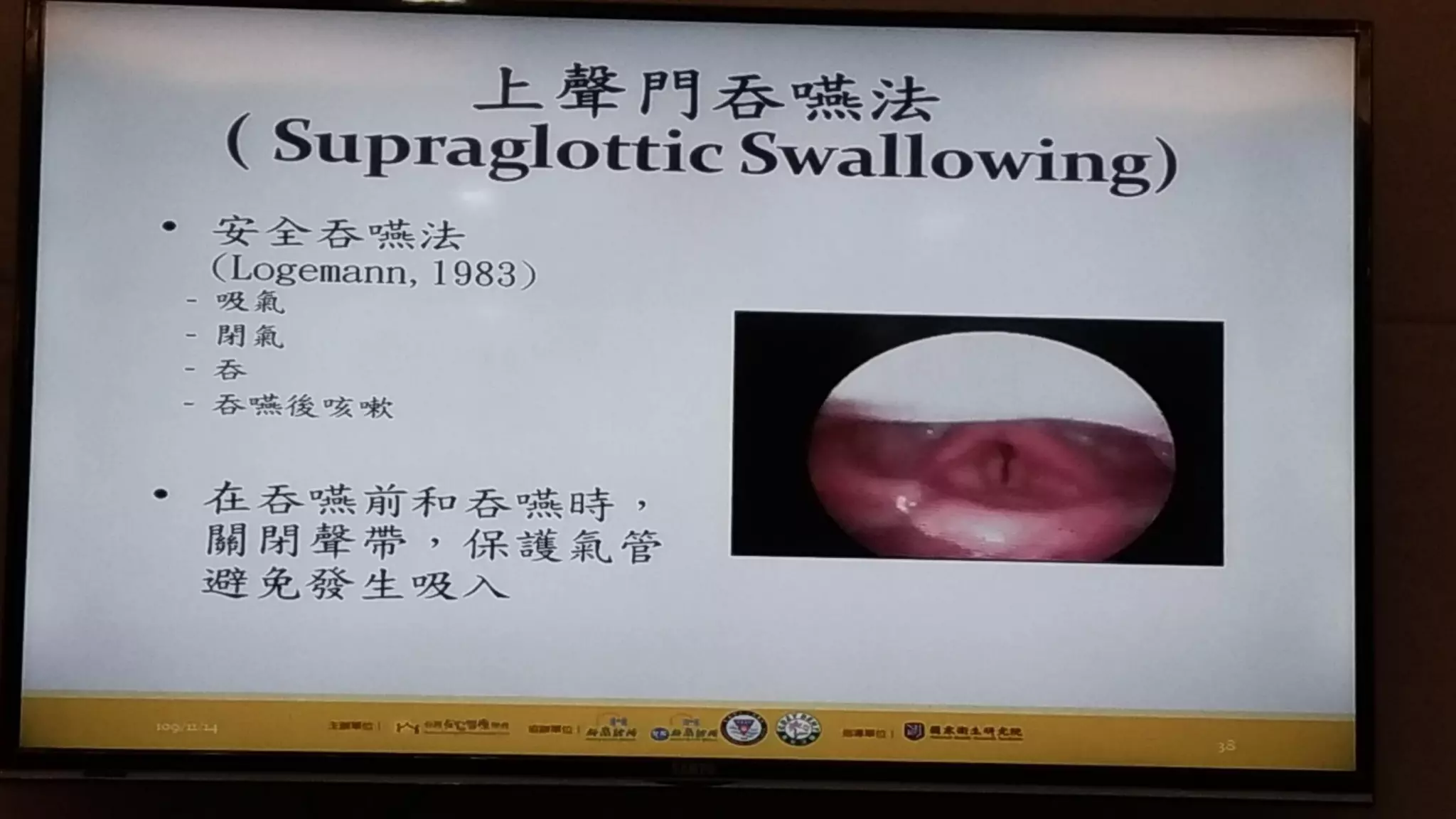
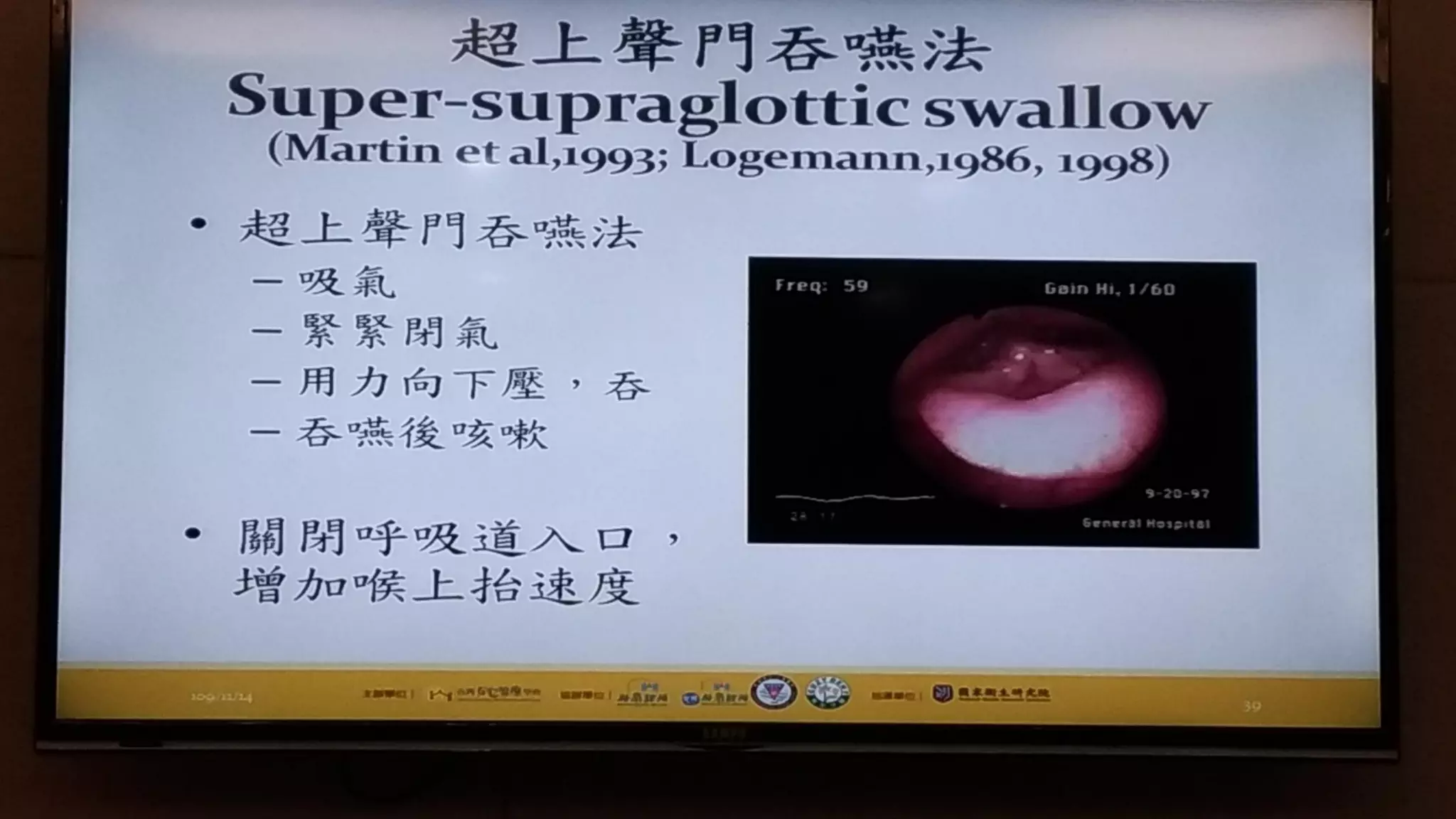






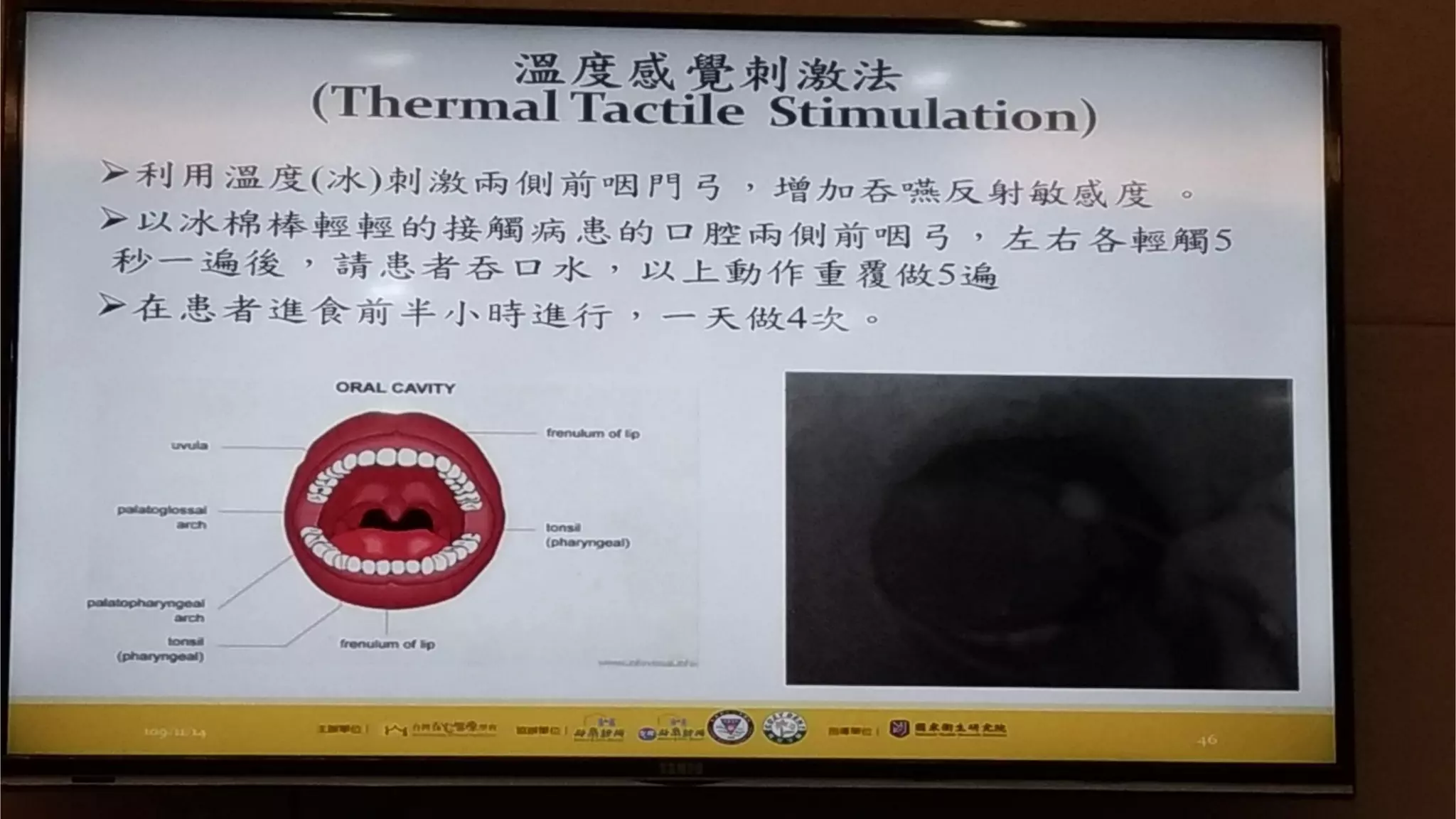

This document summarizes information about oral frailty and a swallowing provocation test. It discusses how oral frailty is indicative of sarcopenia and related to poor grip strength, walking speed, and head lifting strength. It recommends treatments for oral frailty including dental care, treating dry mouth, increasing protein intake, resistance training, and early activity. It also notes that 60% of hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia should be diagnosed with aspiration pneumonia, which is a risk for the elderly due to silent aspiration at night. The document introduces a simple swallowing provocation test using a thin nasal catheter that can identify aspiration risk, with a latent time of less than 3 seconds to trigger swallowing considered normal


























