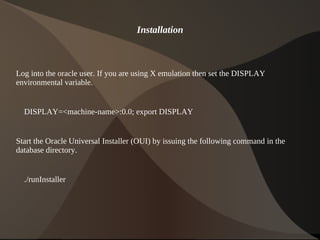
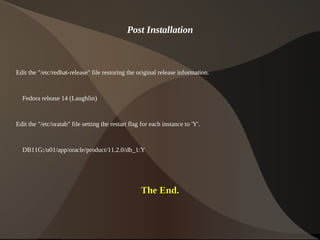
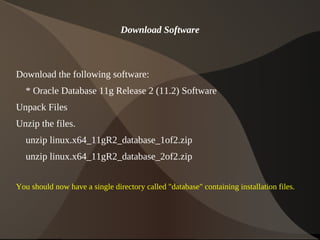
This document provides instructions for installing Oracle 11g Release 2 on Fedora 14. It describes downloading and unpacking the required software, configuring kernel parameters and firewall settings, installing prerequisite packages, creating user groups and directories for the installation, and running the Oracle Universal Installer to complete the database installation. Post-installation steps involve restoring the original "/etc/redhat-release" file and setting the restart flag in "/etc/oratab".



















![Cont. Editing .bash_profile file
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib:/usr/lib; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
CLASSPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/JRE:$ORACLE_HOME/jlib:$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib; export
CLASSPATH
if [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then
if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then
ulimit -p 16384
ulimit -n 65536
else
ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536
fi
fi](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracle11gonfedora14-12950165620183-phpapp02/85/Oracle11g-On-Fedora14-21-320.jpg)