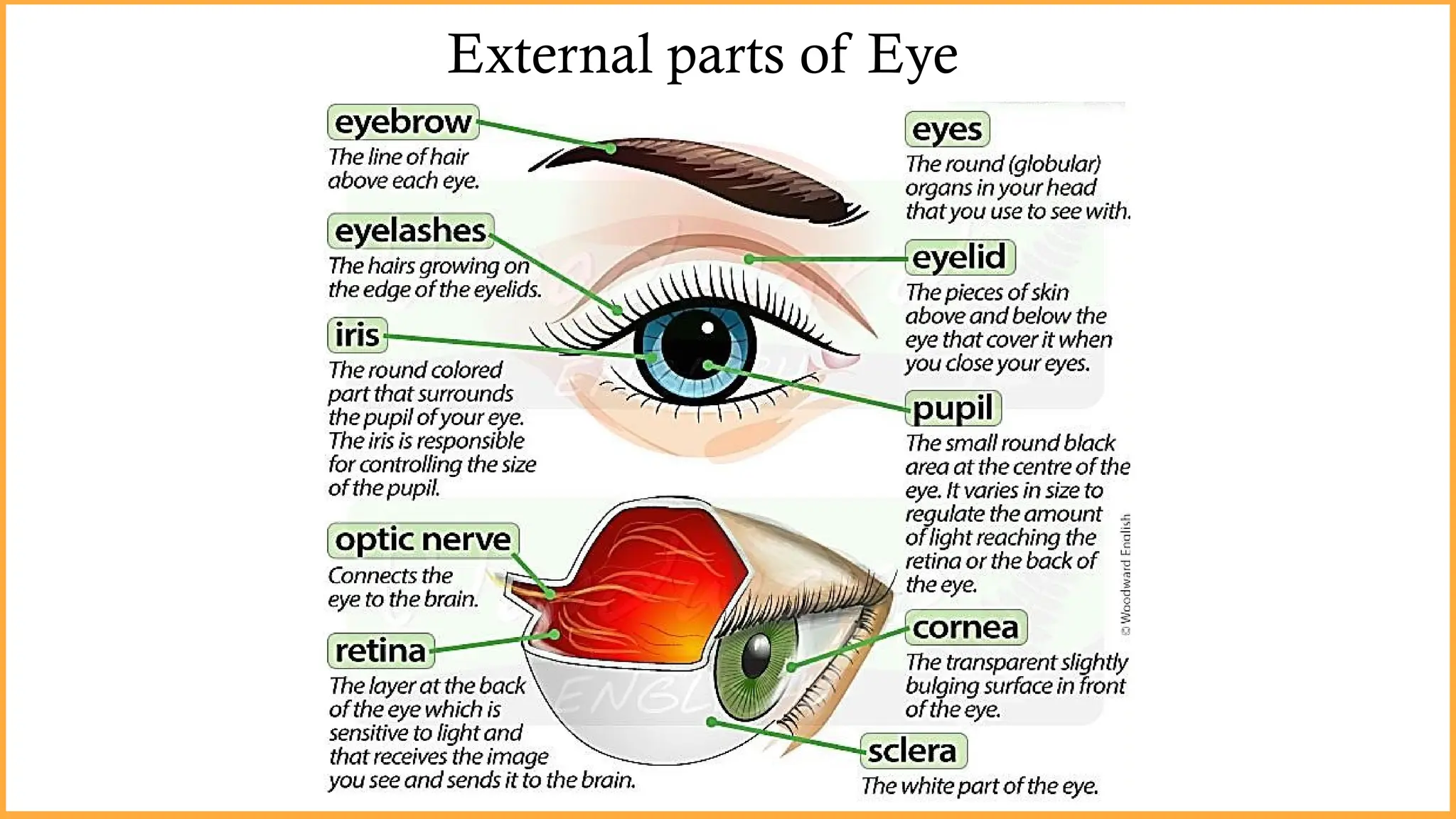
The document discusses the anatomy and functioning of the eye, explaining how light is processed into images by the brain, including concepts like the blind spot. It also covers optical principles such as light dispersion, rainbow formation, and atmospheric refraction, explaining phenomena like twinkling stars and double rainbows. Overall, it emphasizes the interplay between light and perception through various optical instruments and natural occurrences.