This document discusses mathematical optimization and summarizes a presentation given by Dr. Stuart Mitchell on the topic. It provides an example problem of optimizing wedding guest seating assignments. The key points are:
1) Mathematical optimization provides a precise way to formulate problems with objectives and constraints to find optimal solutions.
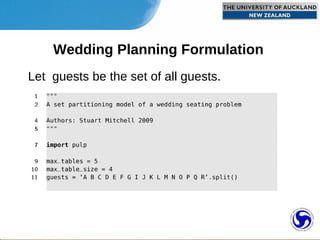
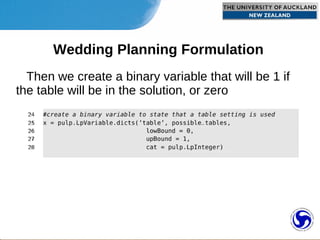
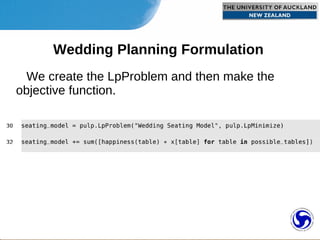
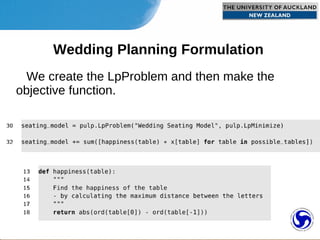
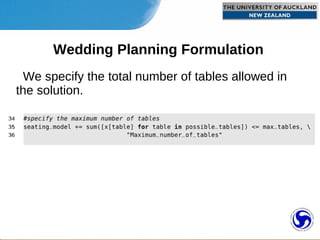
2) The wedding seating problem involves assigning guests to tables to maximize happiness based on relationships while ensuring each guest has a seat.
3) The problem is formulated as a set partitioning problem and implemented in Python code using the PuLP library to find the optimal seating arrangement.