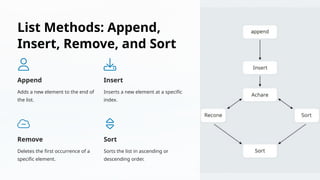
This presentation covers essential operations for four key Python data structures: strings, lists, tuples, and dictionaries. It includes techniques for manipulating these structures, such as slicing, concatenation, and using methods like append and sort for lists, and get and keys for dictionaries. The goal is to enhance Python proficiency through practical examples and applications of each data structure.



![List Operations: Creation,
Indexing, and
Manipulation
Creating a List
Lists are ordered collections of
items, enclosed in square
brackets [].
Accessing Elements
Accessing individual items in a
list using their index, starting
from 0.
Manipulating Lists
Modifying lists by adding, removing, or changing elements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operations-of-strings-lists-tuples-and-dictionaries-in-python1-241205125240-0aee2e3d/85/Operations-of-Strings-Lists-Tuples-and-Dictionaries-in-Python-1-pptx-4-320.jpg)