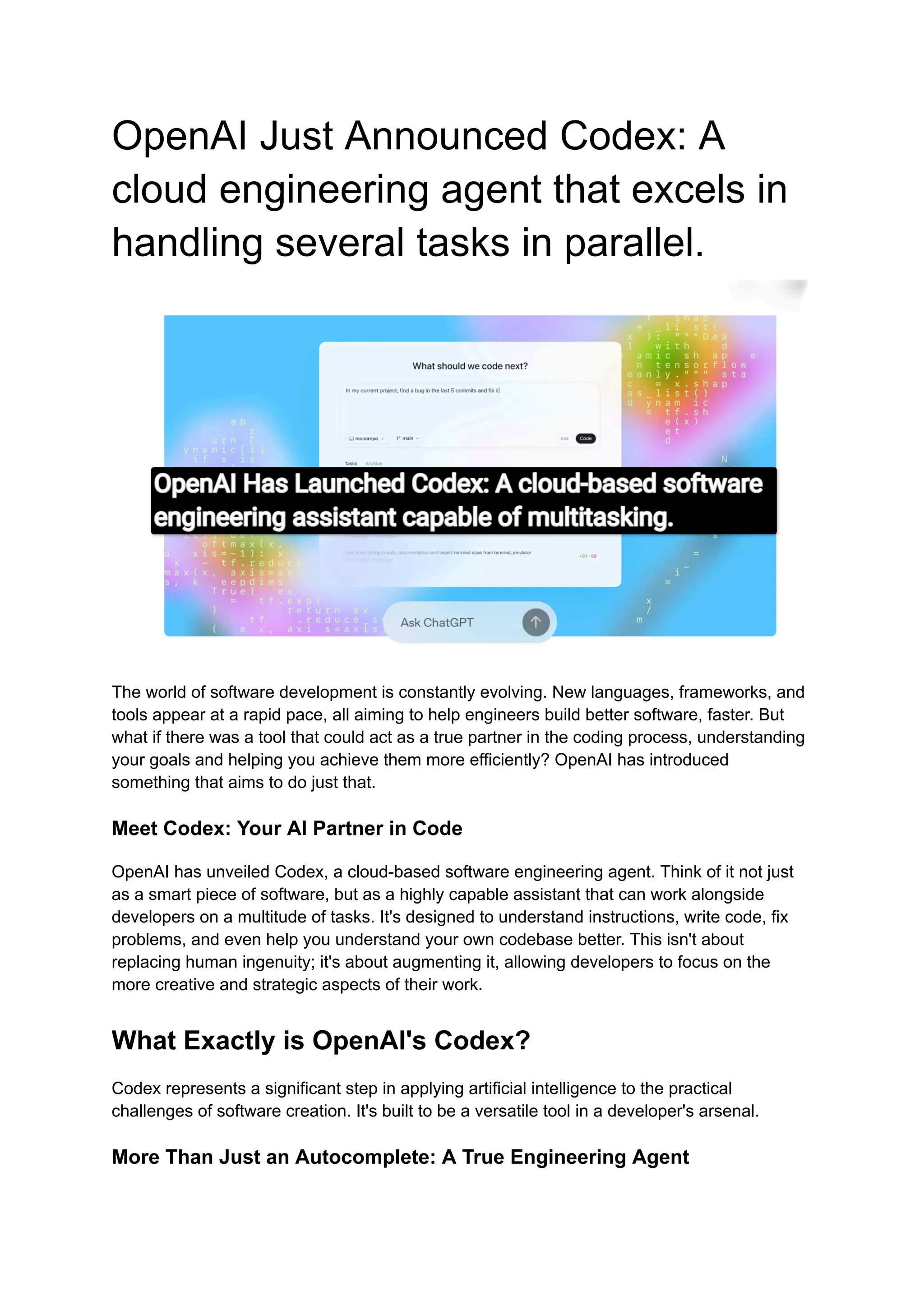
The world of software development is constantly evolving. New languages, frameworks, and tools appear at a rapid pace, all aiming to help engineers build better software, faster. But what if there was a tool that could act as a true partner in the coding process, understanding your goals and helping you achieve them more efficiently? OpenAI has introduced something that aims to do just that.