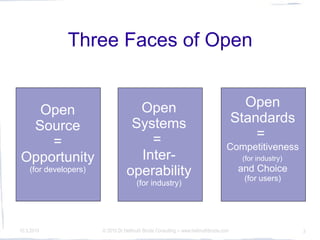
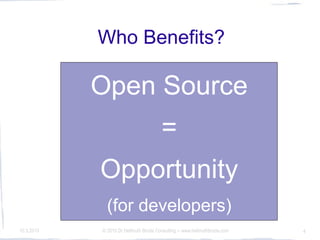
The conference discusses the significance of open source, open systems, and open standards in fostering innovation and competitiveness. It emphasizes a community-driven approach to create wealth and achieve interoperability while ensuring accessibility through open formats. The insights highlight the role of these elements in achieving digital sustainability.