This document provides an overview of C++ and object-oriented programming concepts. It discusses:
1. C++ is an object-oriented programming language introduced in the 1980s that retains the power of C and adds classes, inheritance, function overloading, and operator overloading.
2. OOP languages like C++ are well-suited for developing large, complex programs like editors, compilers, databases, and communication systems due to features like modularity and code reusability.
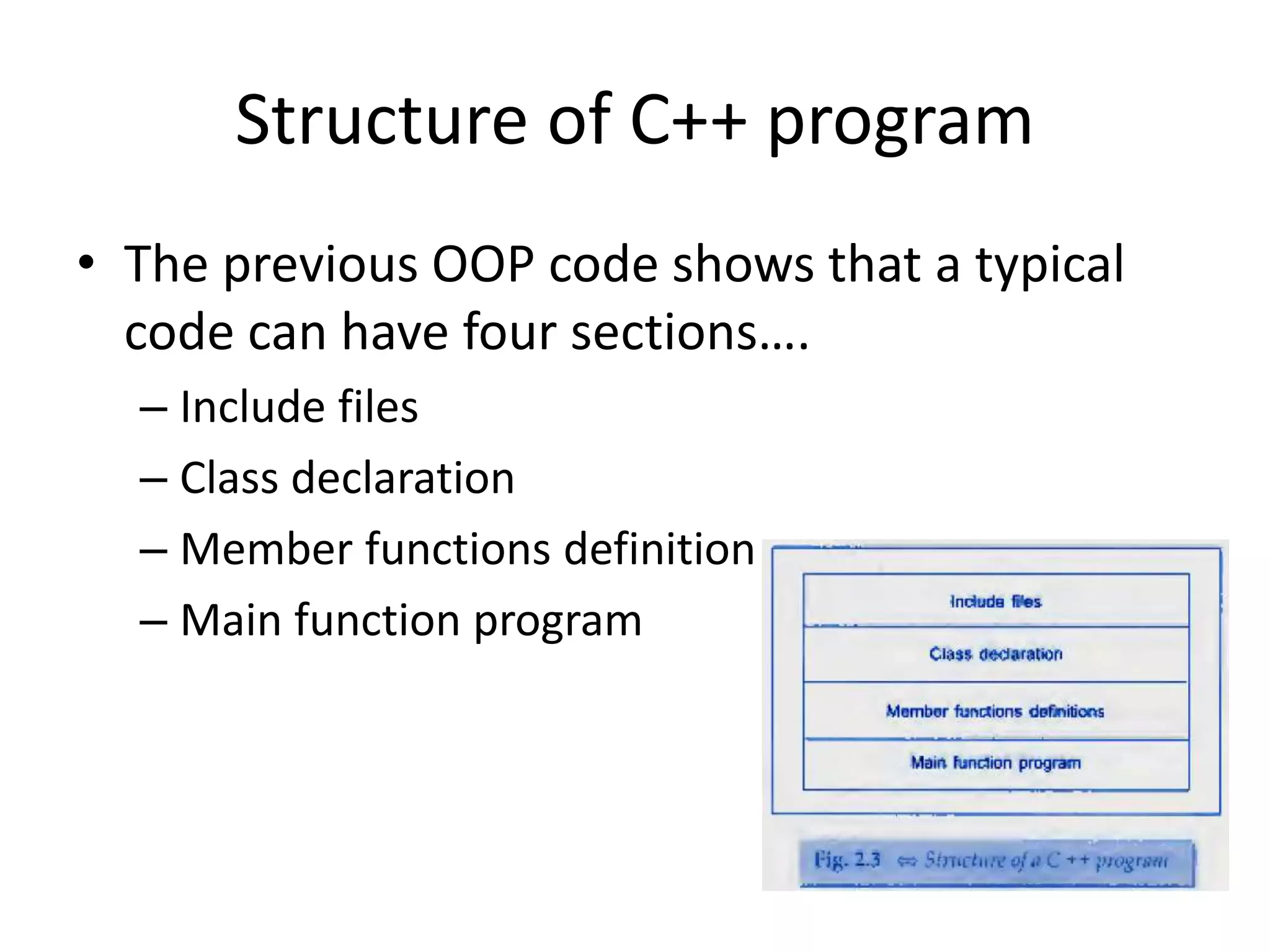
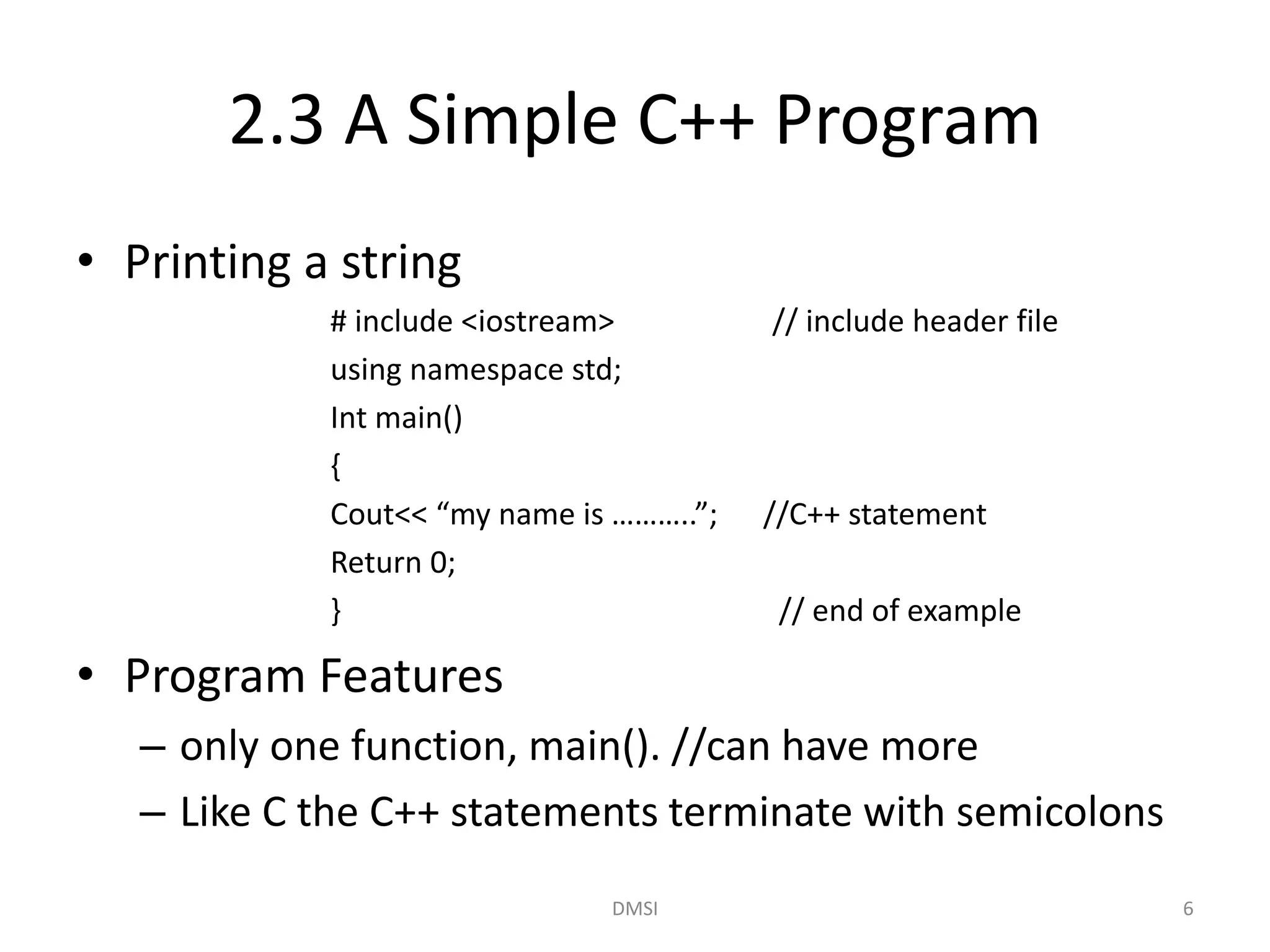
3. A simple C++ program is presented that demonstrates basic syntax like main(), comments, cout and << operators, and return type for main(). Classes and member functions are also introduced.









![Class
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class person
{
char name[30];
int age;
public:
void getdata(void);
void display(void);
};
void person:: getdata(void)
{
cout<<"enter the namen";
cin>> name;
cout<<"enter the agen";
cin>>age;
}
void person:: display(void)
{
cout<<"Name of the person:
"<<name<<"n";
cout<<"Age of the person:
"<<age<<"n";
}
int main()
{
person p;
p.getdata();
p.display();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-l2-151004165854-lva1-app6891/75/Oop-l2-13-2048.jpg)