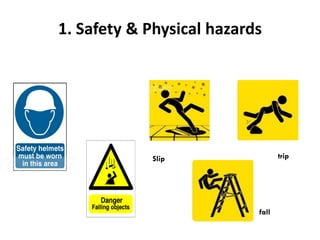
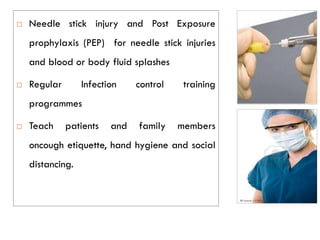
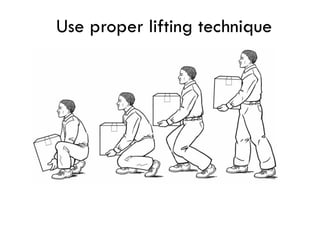
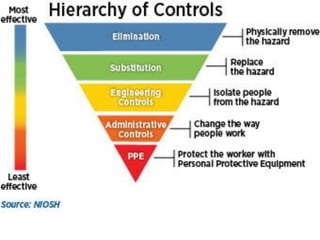
This document outlines occupational health hazards in hospitals. It categorizes common hazards as physical, ergonomic, biological, radiological, chemical, and psychosocial. Potential hazard areas in different hospital departments are described. The document then outlines safety measures and protocols for managing key hazards like slips/trips/falls, radiation, biological agents, chemicals, ergonomics, and psychosocial stressors. It stresses training for staff on hazard identification and safety protocols. Risk assessment and management workflows are to be outlined separately.