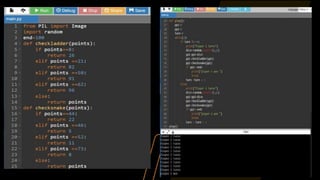
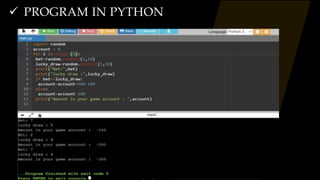
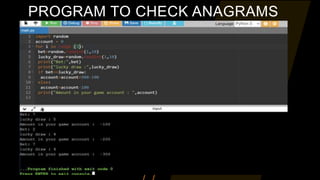
The document provides an overview of a Python programming presentation on the Joy of Computing with Python. It discusses why programming is important, the importance of clear instructions, and introduces concepts like Scratch and loops. The presentation is split into 8 weeks, with topics covered including crowd computing, genetic algorithms, searching and sorting algorithms, recursion, and simulations of games like snakes and ladders and the lottery.

































![ COMMANDS IN NUMPY
1. Importing
NumPy:
import numpy as np
2. Creating a 1D array:
arr_1d = np.array([1, 2, 3])
3. Creating a 2D array (matrix)
arr_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5,
6]])
4. Creating arrays with zeros or
ones:
zeros_arr = np.zeros((3, 4))
ones_arr = np.ones((2, 2))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nptelcomplete-231029094050-f1eb53ee/85/NPTEL-complete-pptx-pptx-37-320.jpg)
![ COMMANDS IN NUMPY
5. Element-wise operations:
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
c = a + b
6. Matrix multiplication:
matrix_a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
matrix_b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
result = np.dot(matrix_a, matrix_b)
7. Indexing and Slicing:
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7,8,9]])
element = arr[0, 1] # Accessing an element
row = arr[1] # Accessing a row
column = arr[:, 2] # Accessing a column](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nptelcomplete-231029094050-f1eb53ee/85/NPTEL-complete-pptx-pptx-38-320.jpg)






