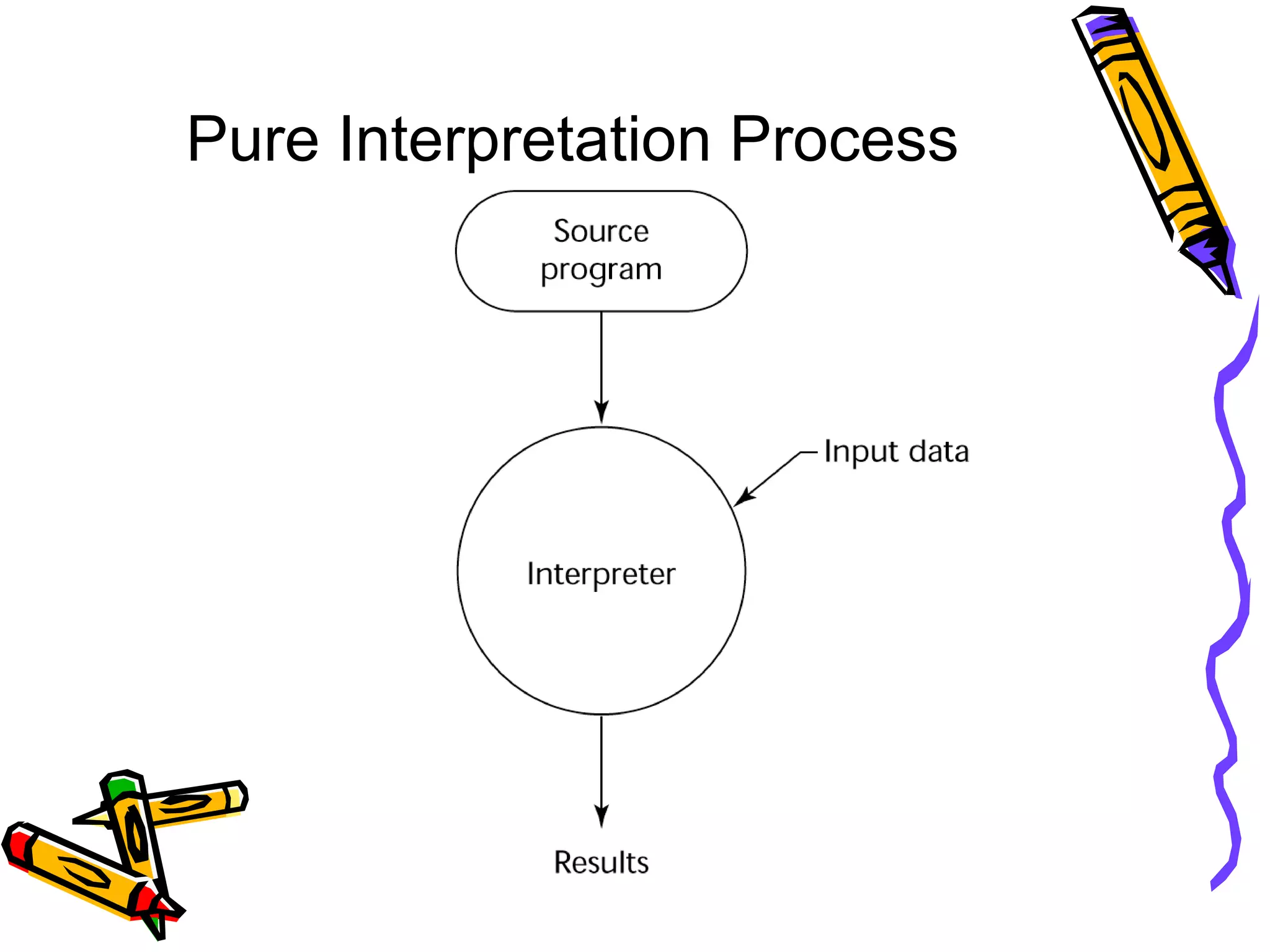
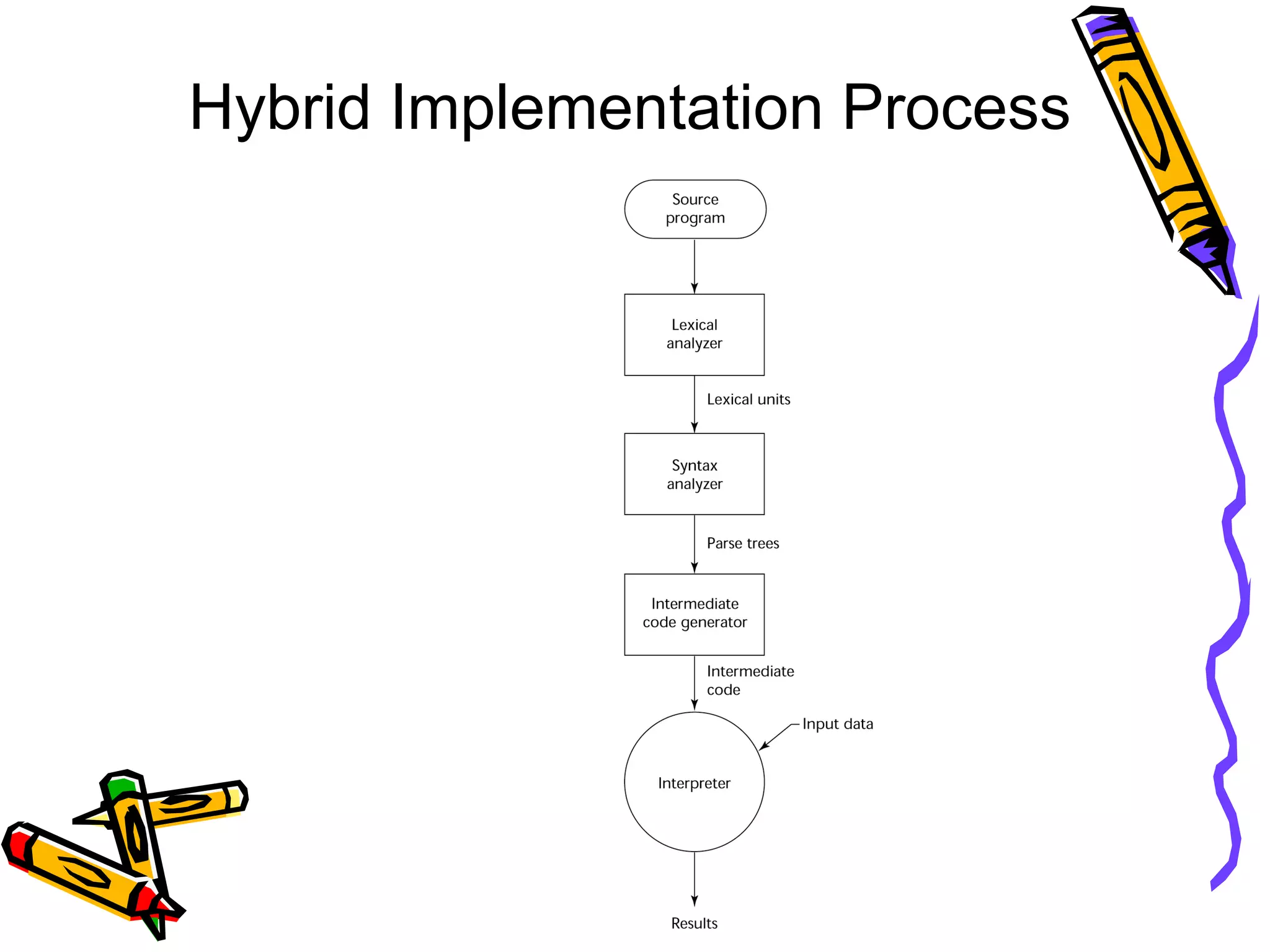
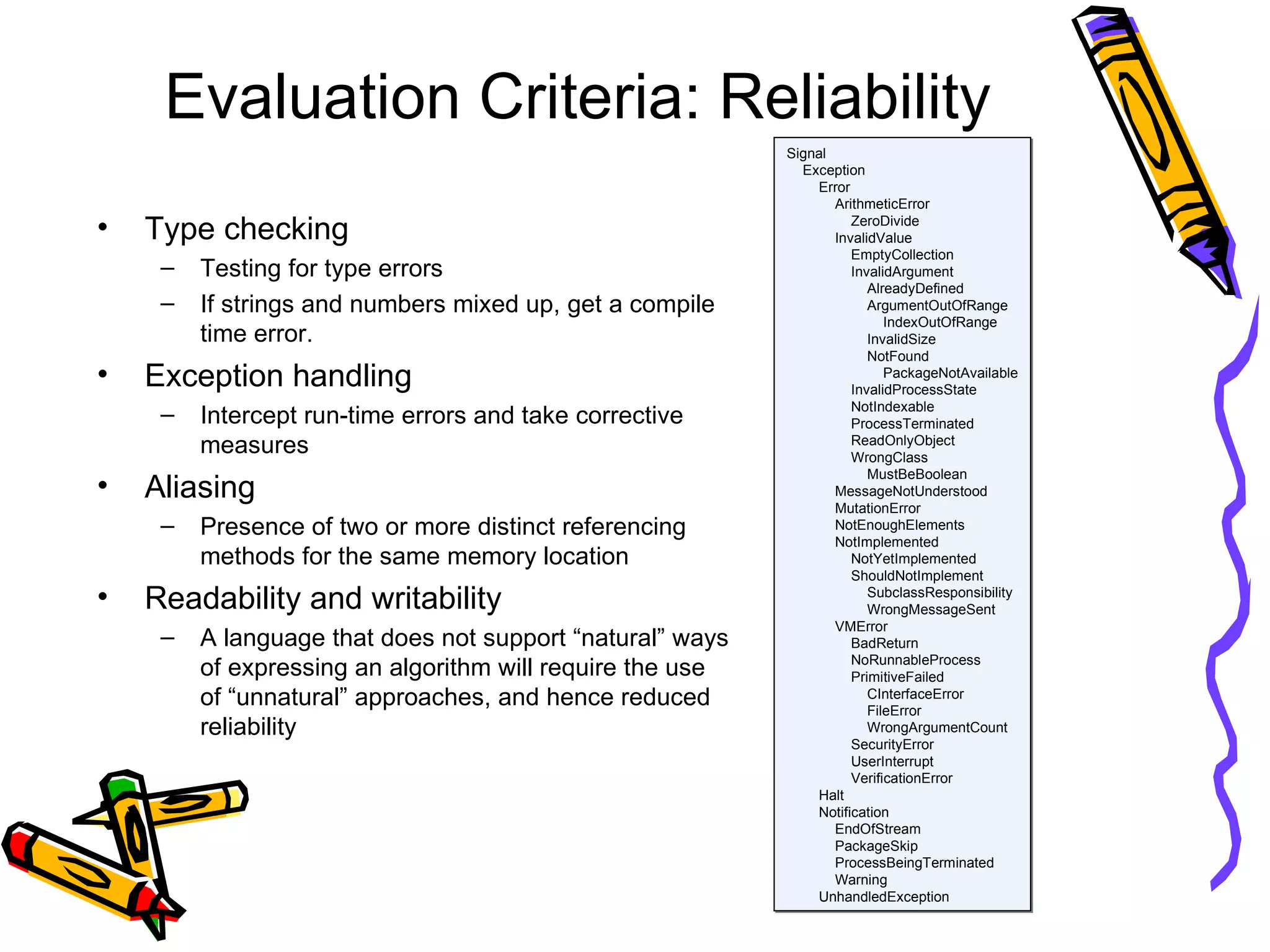
The document discusses various criteria for evaluating programming languages, including readability, writability, reliability, and cost. It examines factors such as syntax, data types, control structures, abstraction capabilities, type checking, and exception handling in relation to these criteria. The document also mentions other criteria like portability and generality.