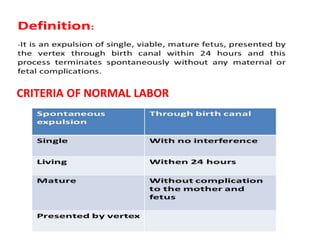
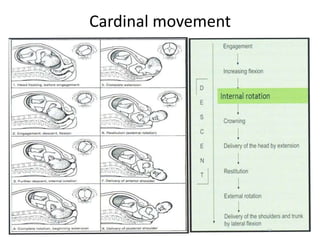
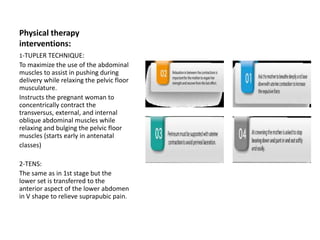
This document discusses normal labor and delivery. It begins by outlining the criteria for normal labor versus prolonged or precipitate labor. The three stages of labor are then described: cervical dilation in stage one, delivery of the baby in stage two, and delivery of the placenta in stage three. Key physical therapy interventions to assist with labor and delivery include the Tupler technique to maximize abdominal muscle use during pushing and TENS to relieve pain. Post-partum exercises are also outlined to aid recovery.