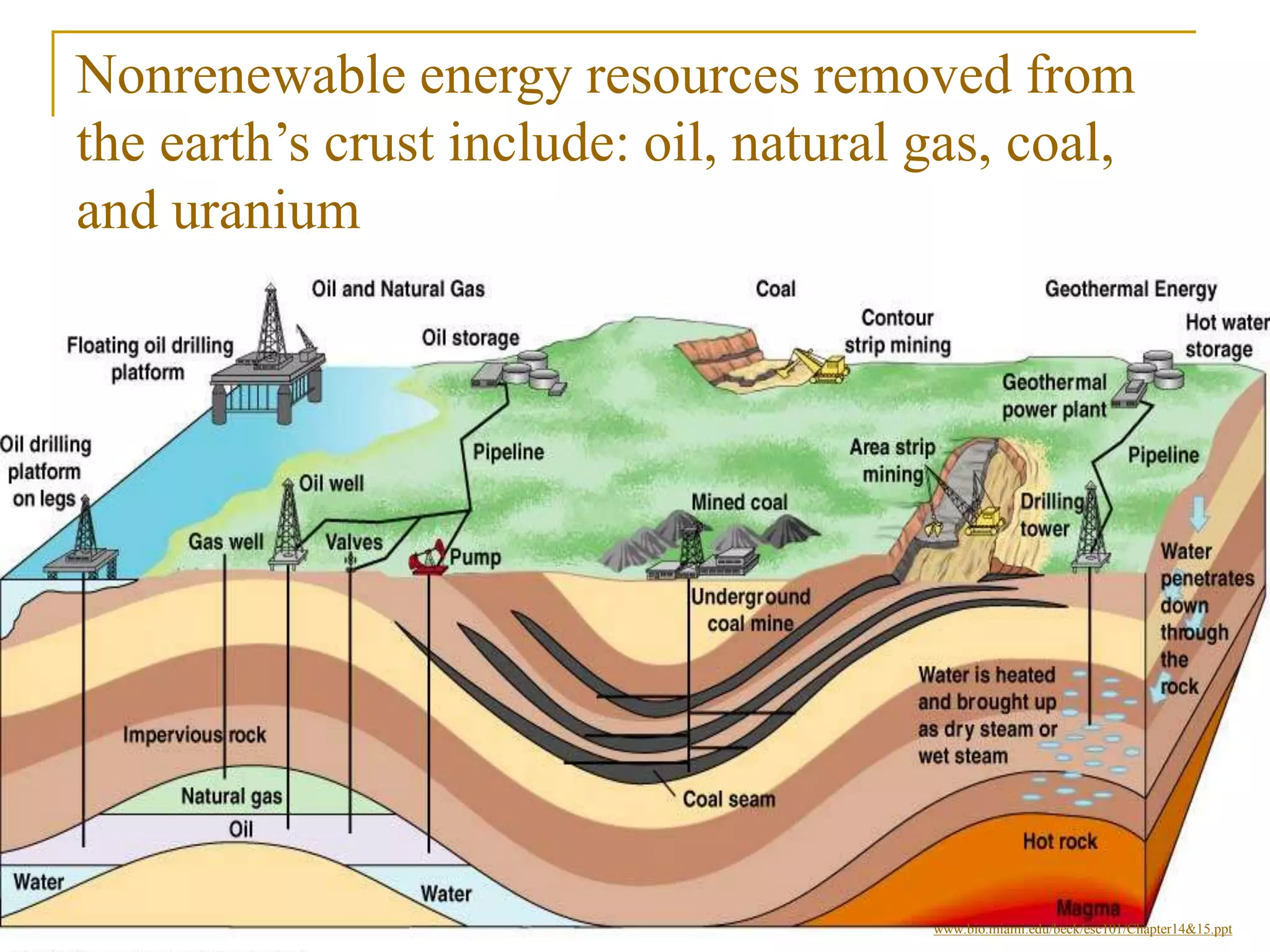
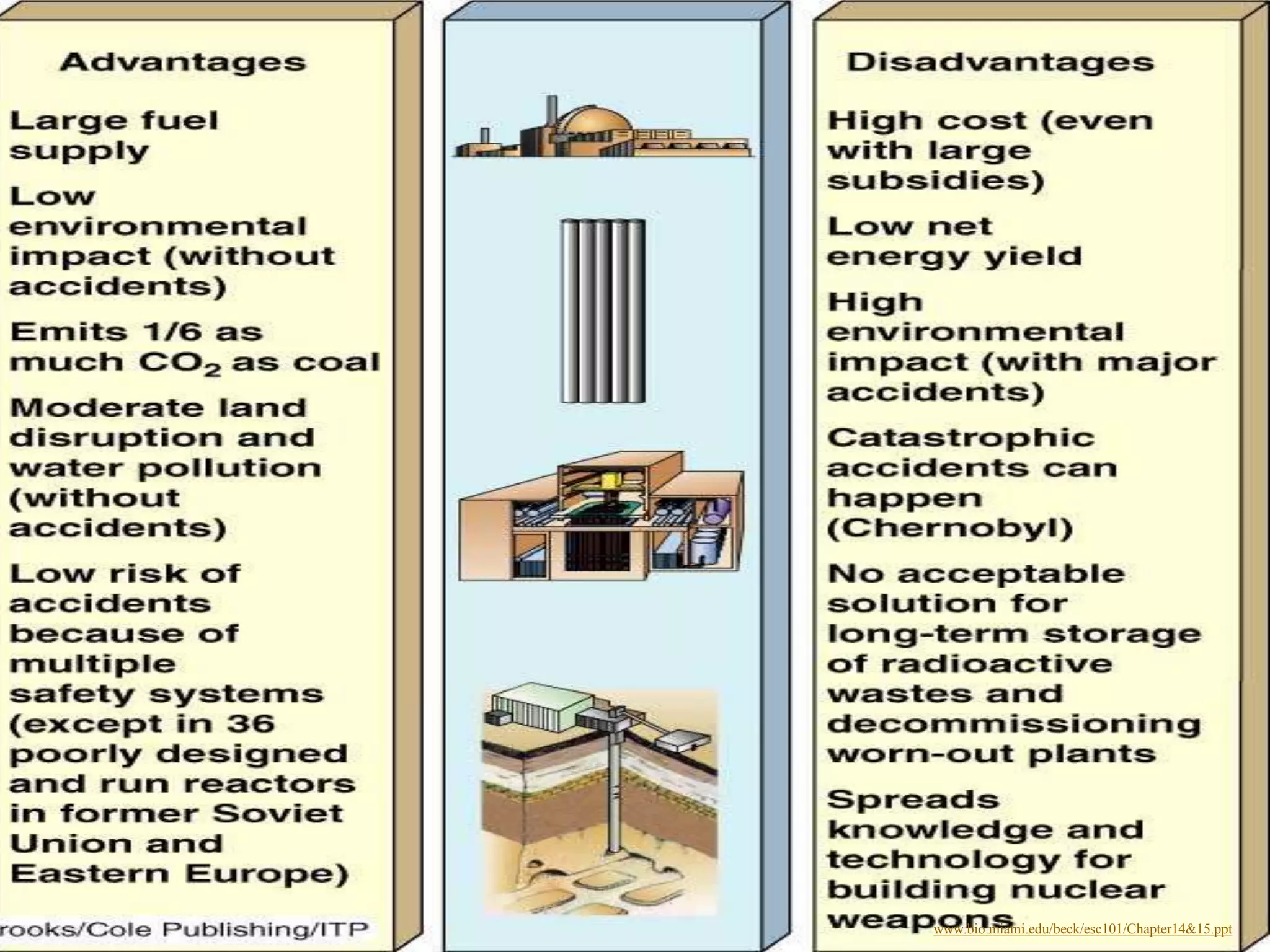
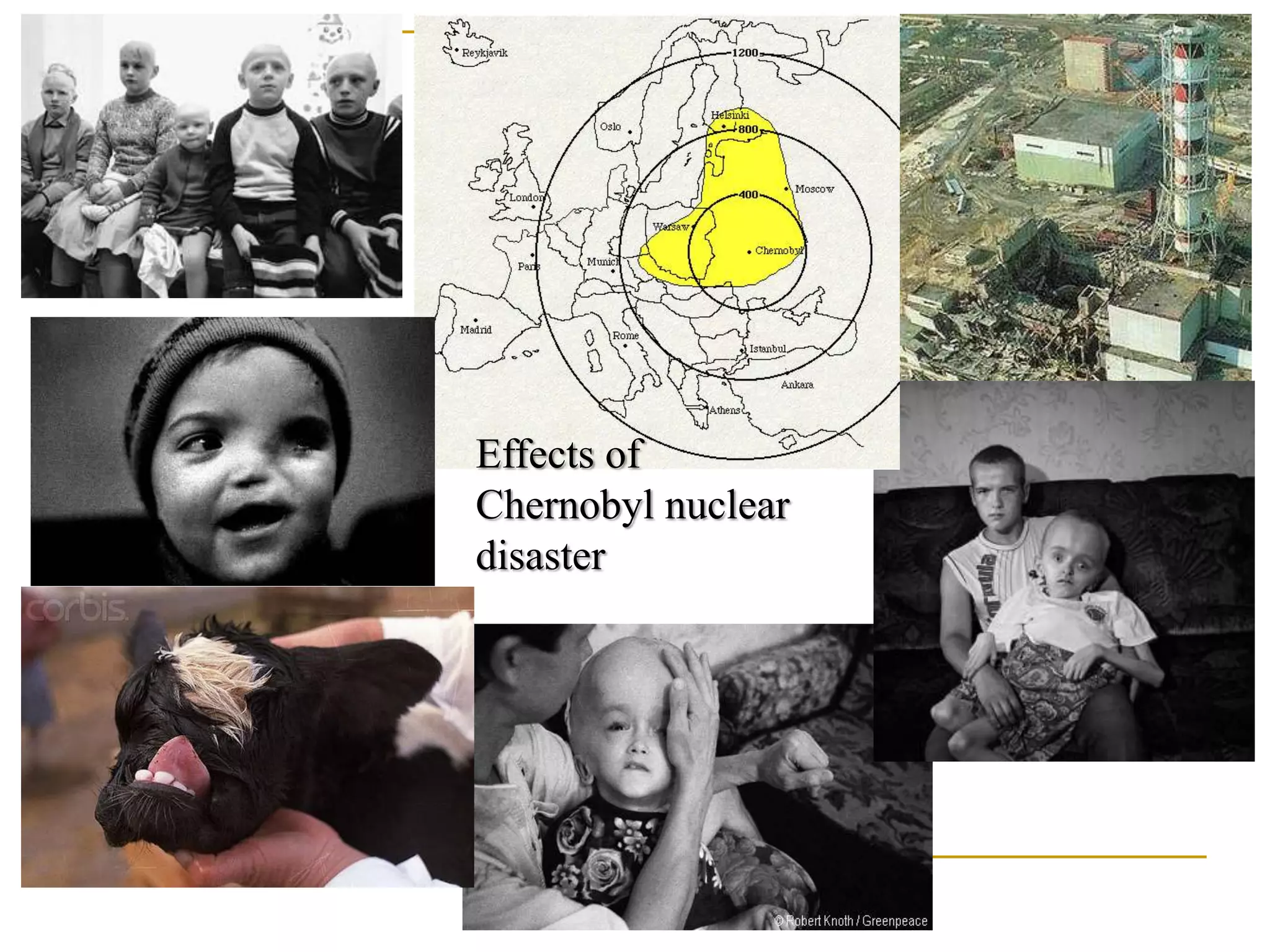
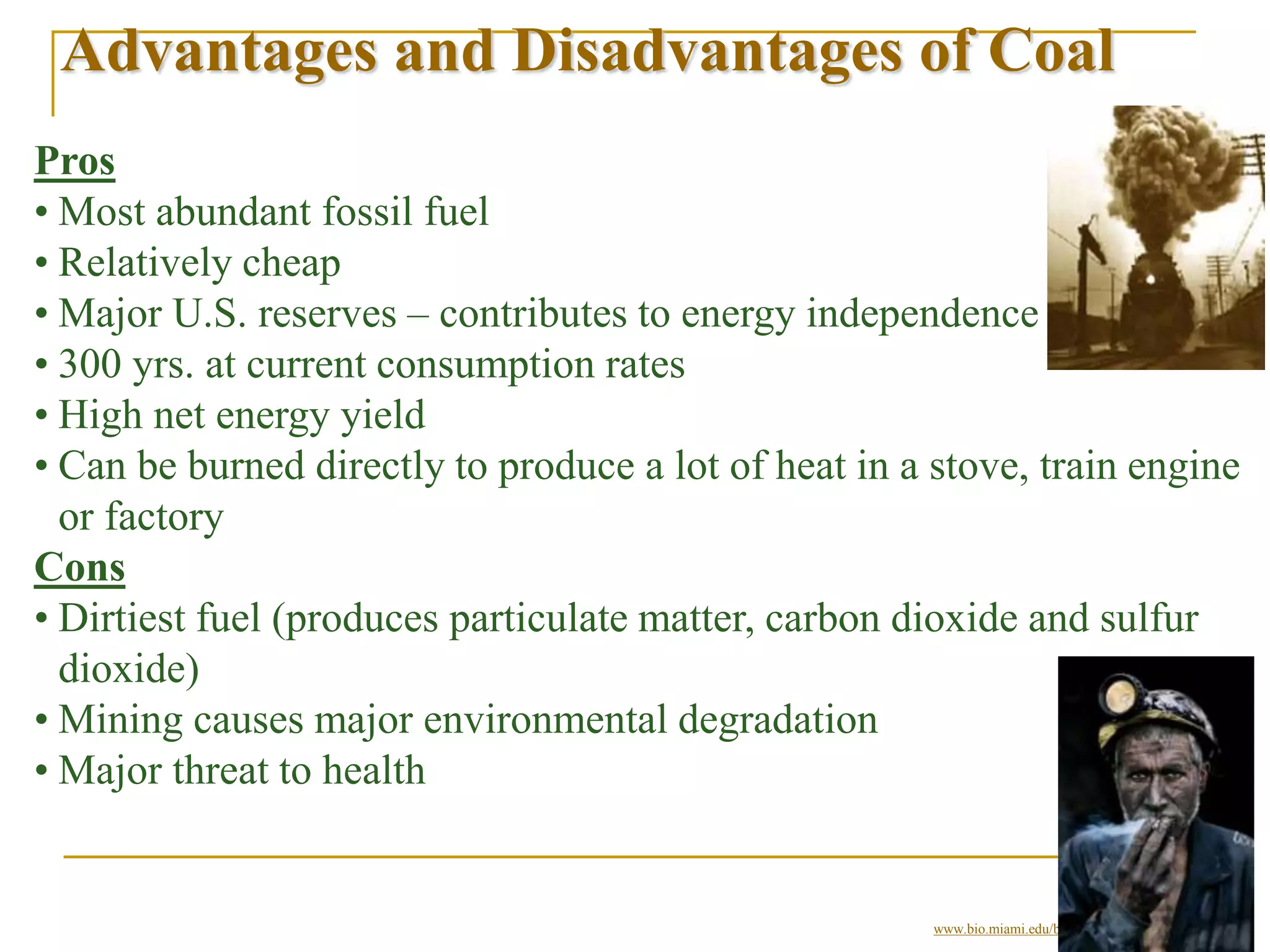
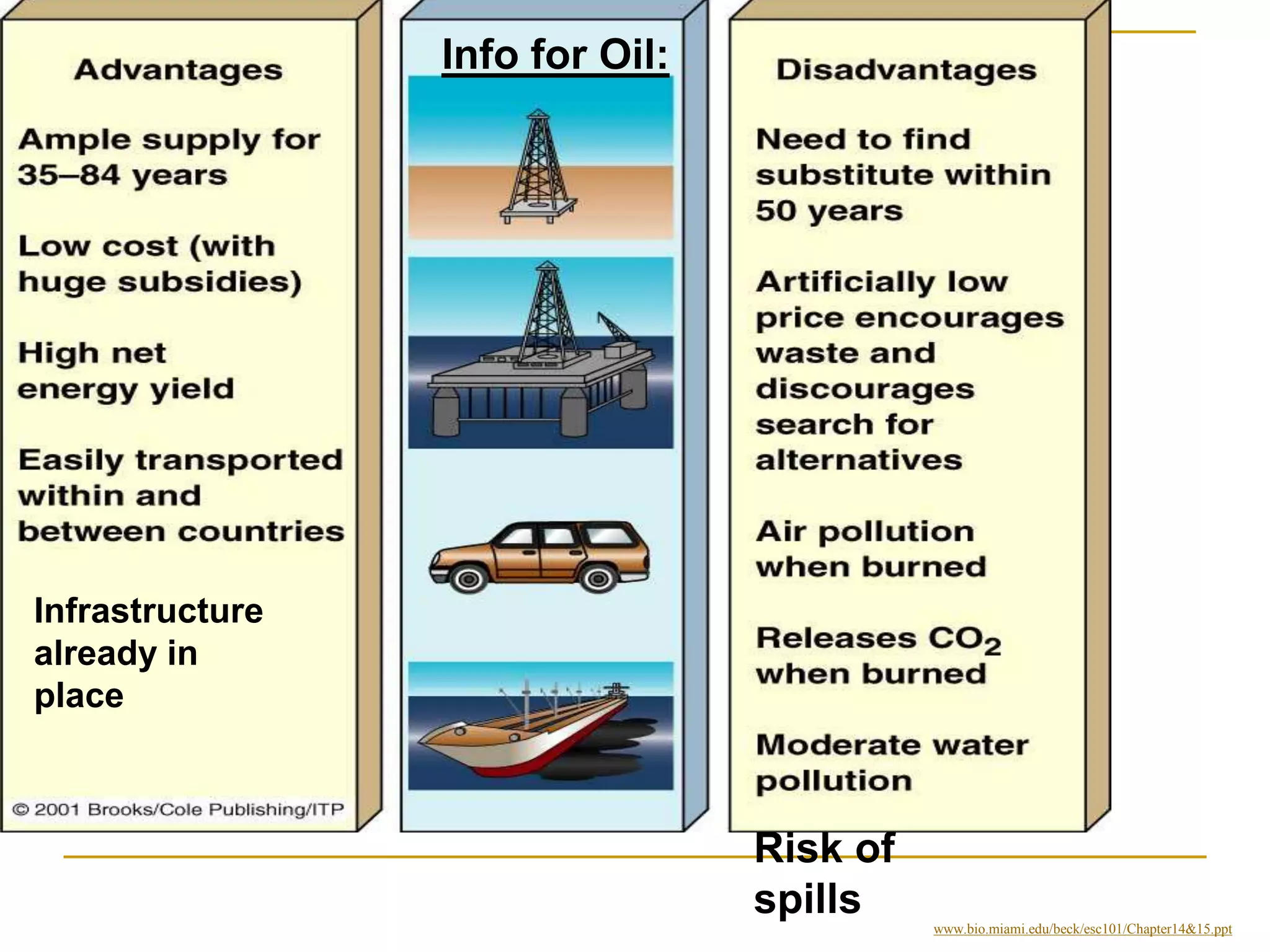
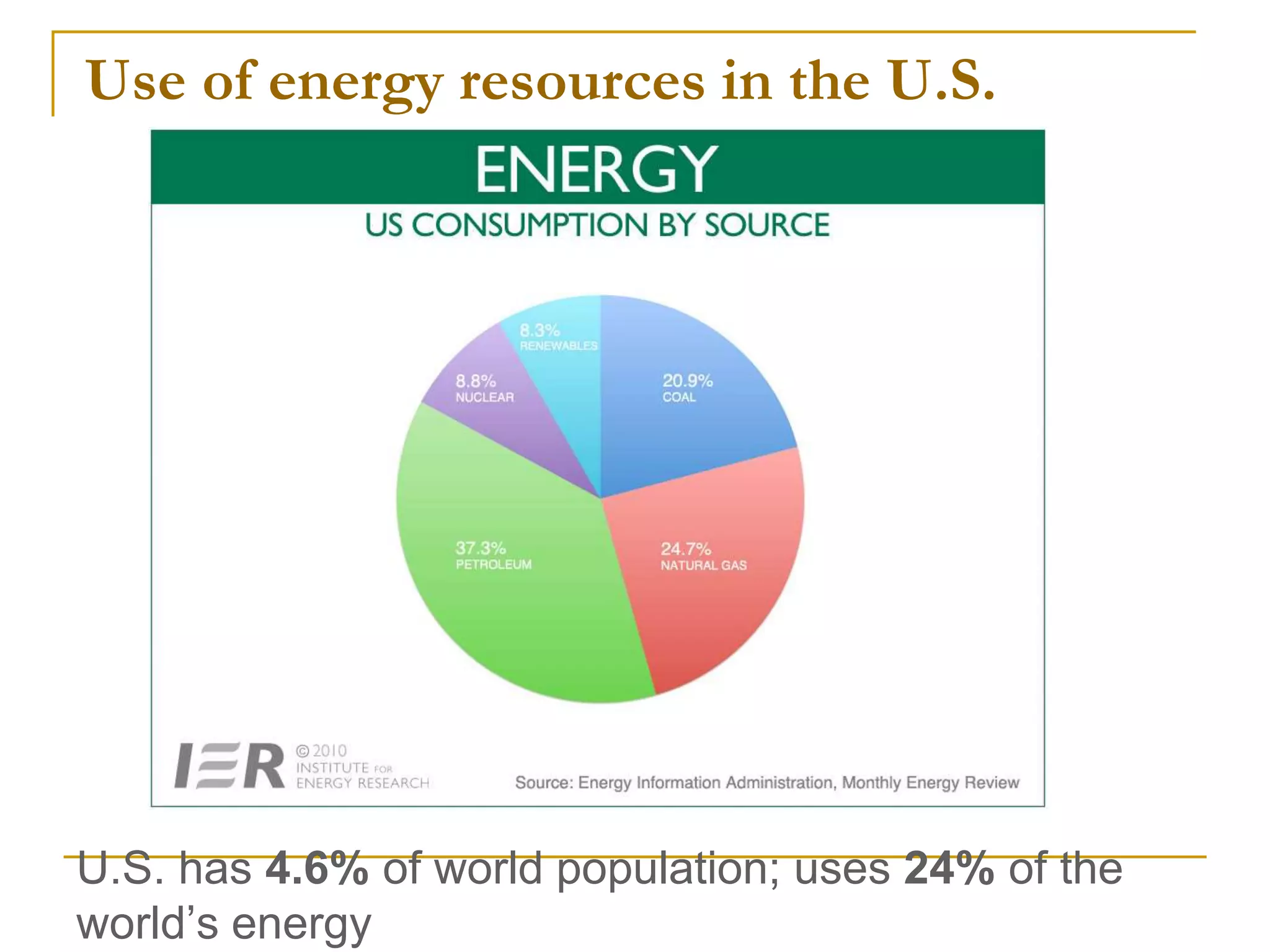
Nonrenewable resources like coal, petroleum and uranium are finite and cannot be replenished within human timescales, while renewable resources like solar, wind and water can be replenished naturally and sustainably. The document provides examples of some major nonrenewable resources that powered industrialization but also caused environmental disasters when accidents occurred at nuclear power plants. In contrast, renewable resources like sunlight, wind and flowing water provide sustainable alternatives to reduce reliance on finite fossil fuels.