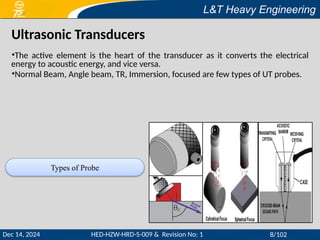
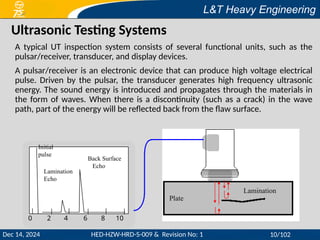
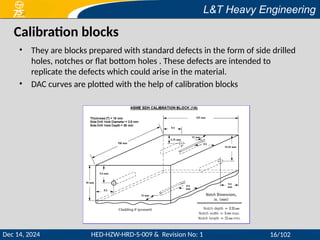
This document provides a comprehensive overview of ultrasonic testing (UT), detailing its principles, equipment, types of ultrasonic waves, and data presentation methods. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of UT, including operator qualifications and the importance of surface preparation. Additionally, the document references acceptance standards and calibration practices relevant to ultrasonic examination methods.