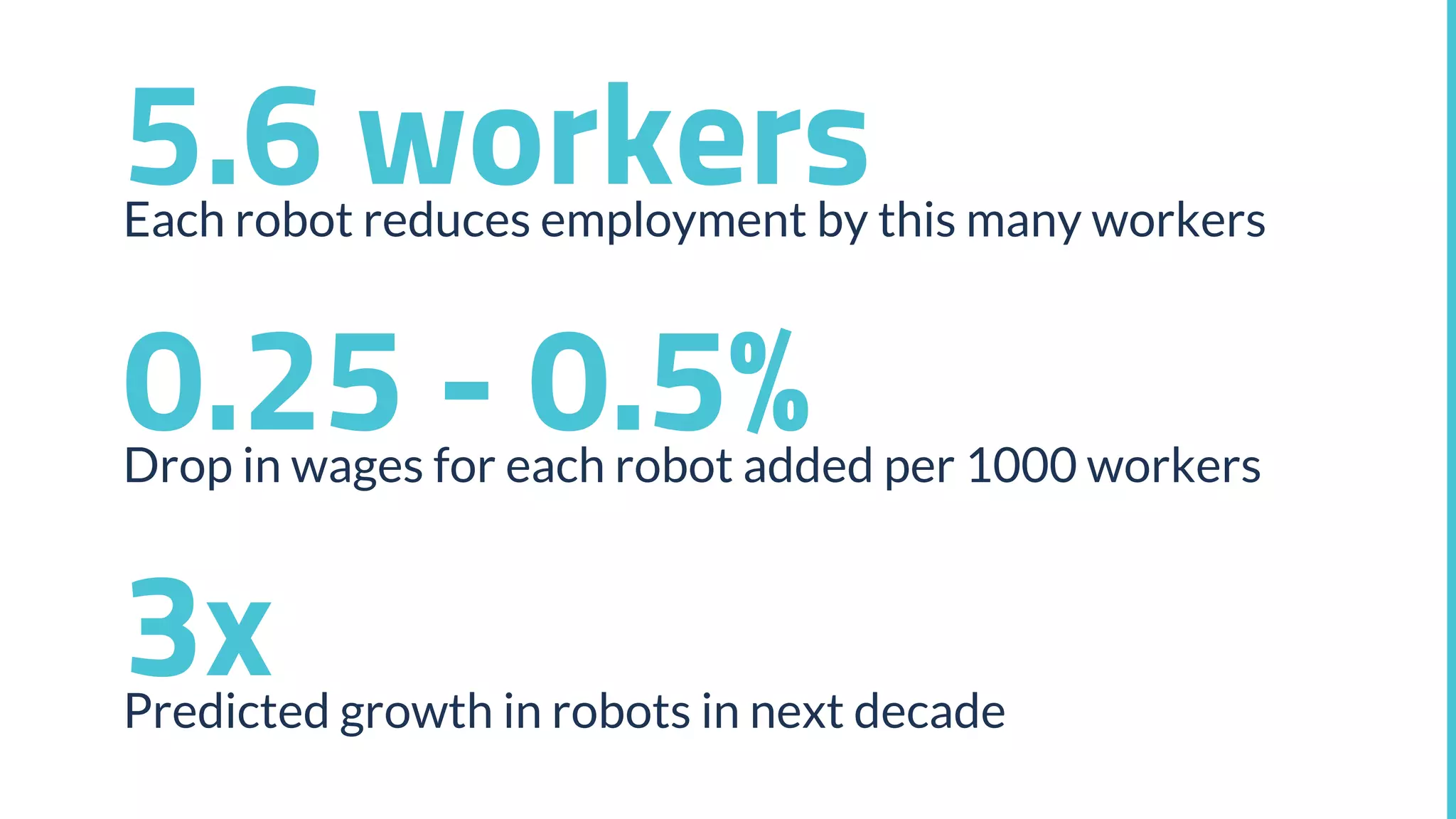
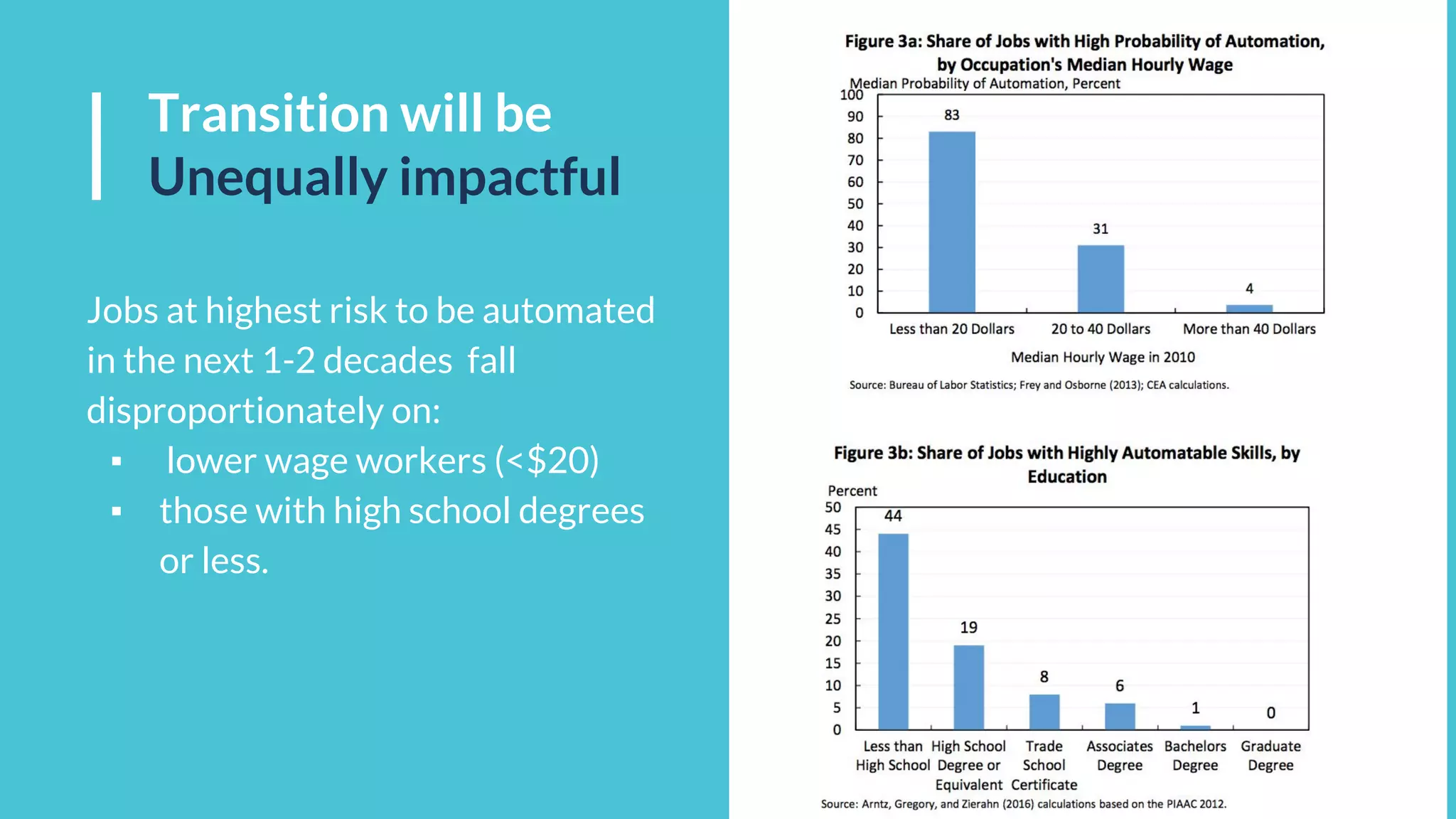
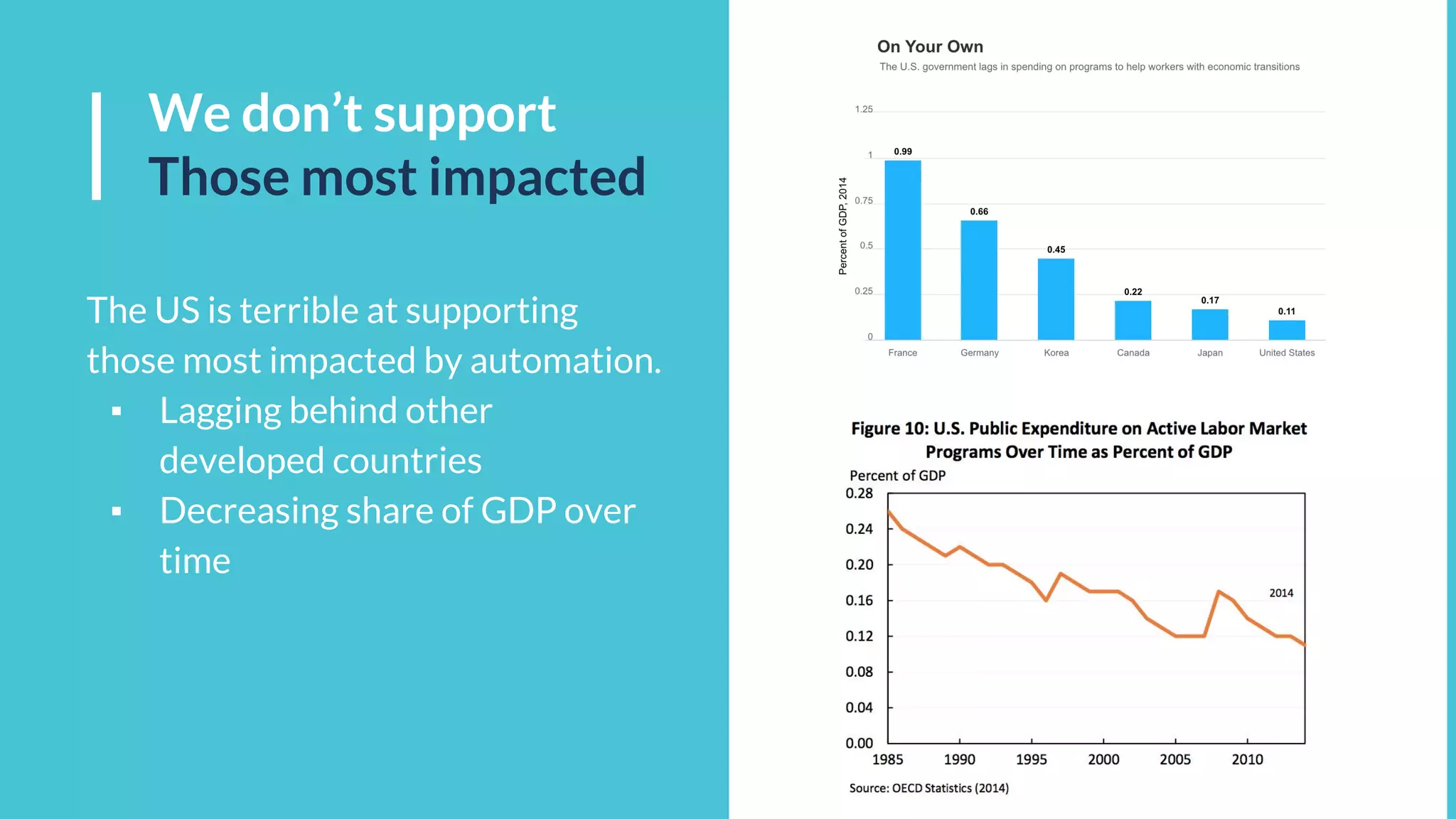
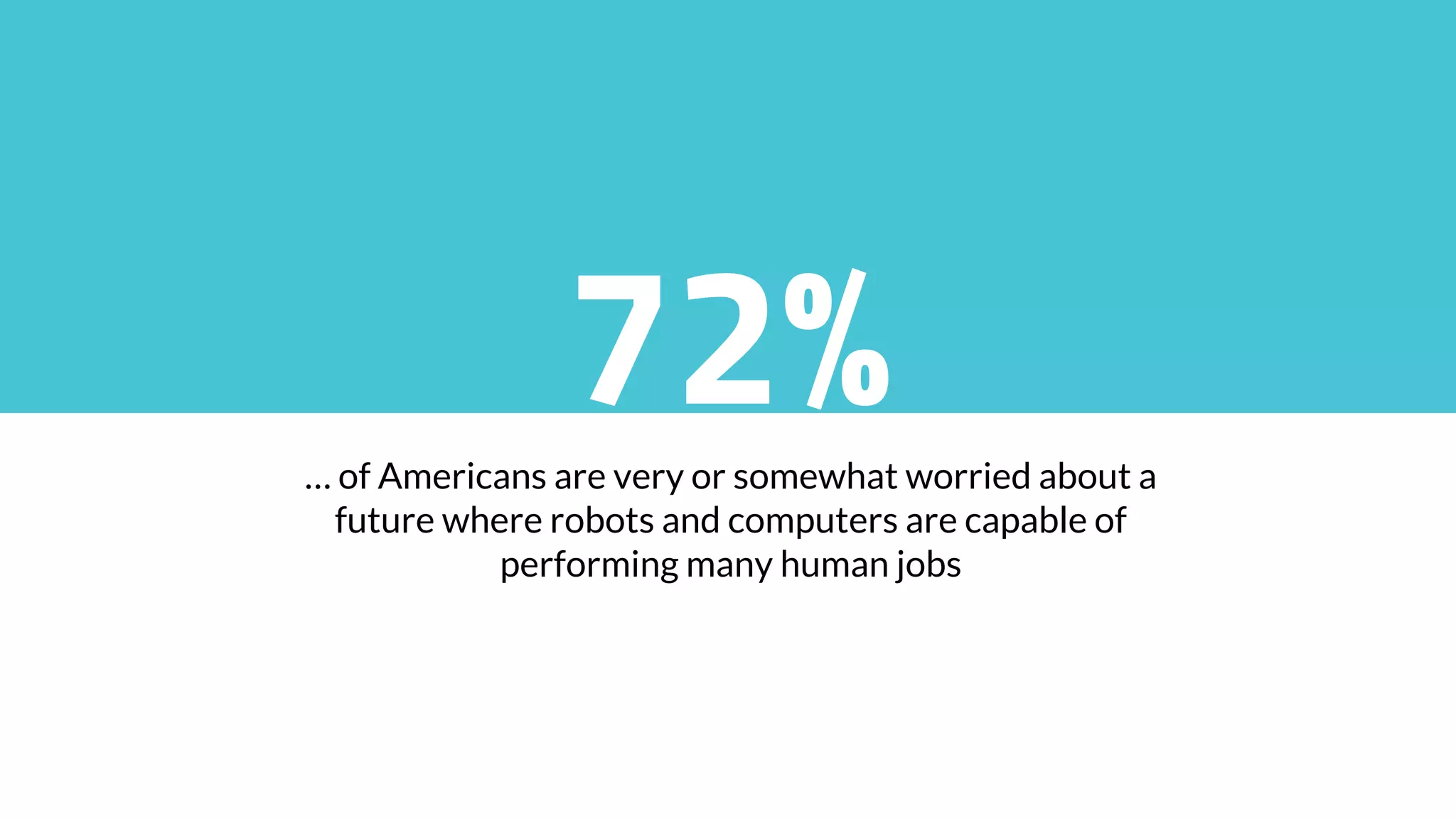
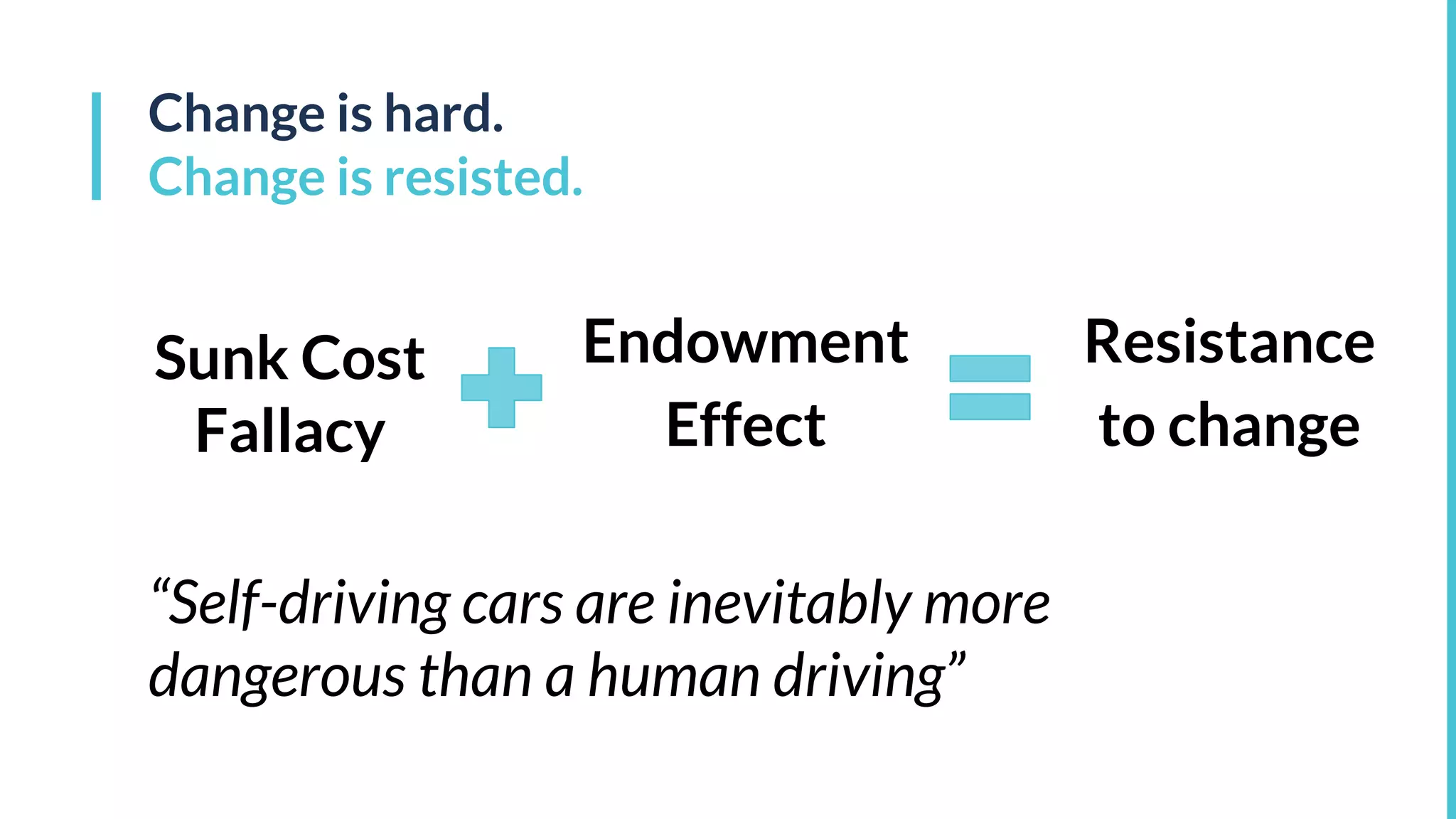
This document discusses the potential impacts of robotics and automation on employment, highlighting a significant projected job loss of 25 million by 2027, while robots are expected to create only 15 million new jobs. It emphasizes the need for society to adapt to a future where human labor may become less valuable, and raises concerns about the resulting loss of purpose for many individuals. The document advocates for changes in education, the consideration of universal basic income, and preparation for the socioeconomic shifts caused by automation.












![Future state
More hypotheses
“"It's probably hard to overstate how big of
an impact [automation] going to have on
society over the next twenty years,"”
- Jeff Bezos, Amazon
“The reality is that work has changed. Forty
percent of jobs are now contingent,
meaning they're part-time, independent
contractors, Uber drivers...”
- Chris Hughes, Facebook
“I’m fairly confident that at some point in the future, as
technology continues to eliminate traditional jobs and
massive new wealth gets created, we’re going to see some
version of [basic income] at a national scale.”
- Sam Altman, Y Combinator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nojobsforhumanshowtosurviveandthrivethetransitiontotheallrobotworkforce-180430170444/75/No-jobs-for-humans-How-to-survive-and-thrive-the-transition-to-the-all-robot-workforce-16-2048.jpg)