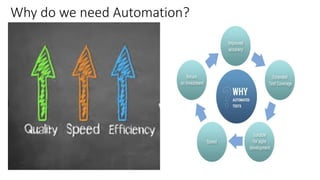
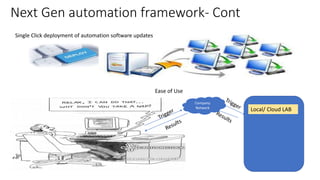
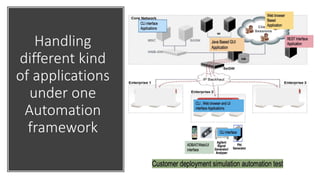
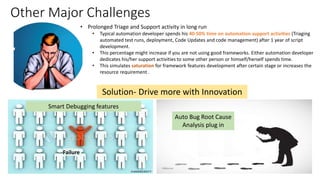
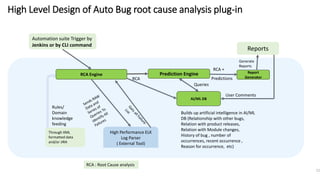
The document outlines next-generation automation frameworks focusing on three types of test automation: UI/web client-based, embedded systems testing, and a combination of both. It discusses the core qualities of effective automation frameworks and challenges such as prolonged support activities that consume developer time. Additionally, it proposes solutions like centralized logging, smart debugging features, and the use of AI/ML for root cause analysis to improve efficiency and effectiveness in automation processes.