Embed presentation
Downloaded 238 times




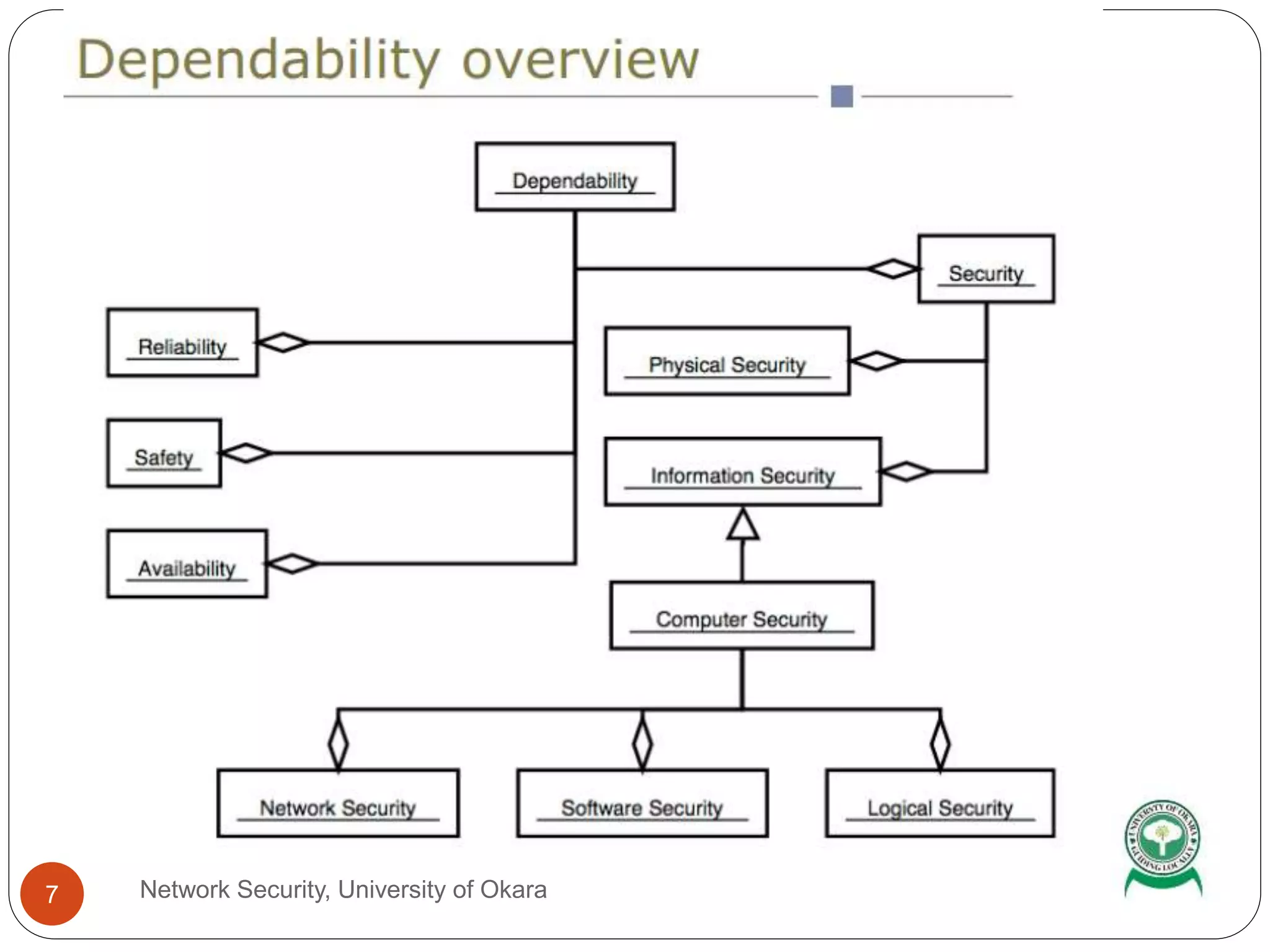



The document discusses network security terminology such as threats, attacks, risk analysis, and cryptography. It defines common threats like spoofing, tampering, repudiation, and denial-of-service attacks. The document also outlines the steps for performing risk analysis and includes an exercise asking questions about finding, removing, and preventing vulnerabilities.









Introduction by Inam Ul Haq, MS in Computer Science, outlining the discussion forum and memberships.
Overview of lecture contents including Terminologies, White Hacking, and Exercise.
Discussion of essential terms including Threats, Attacks, Risk Analysis, and Cryptographic terms.
Definition of threats and attacks, emphasizing the importance of security in all systems.
Four common threats: Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, and Denial-of-Service.
Five steps in risk analysis: Identifying assets, threats, prioritizing risks, implementing controls, and monitoring.
(No content provided for this slide)
(No content provided for this slide)
Discussion on identifying and removing vulnerabilities, with specifics on Windows XP exploitation.