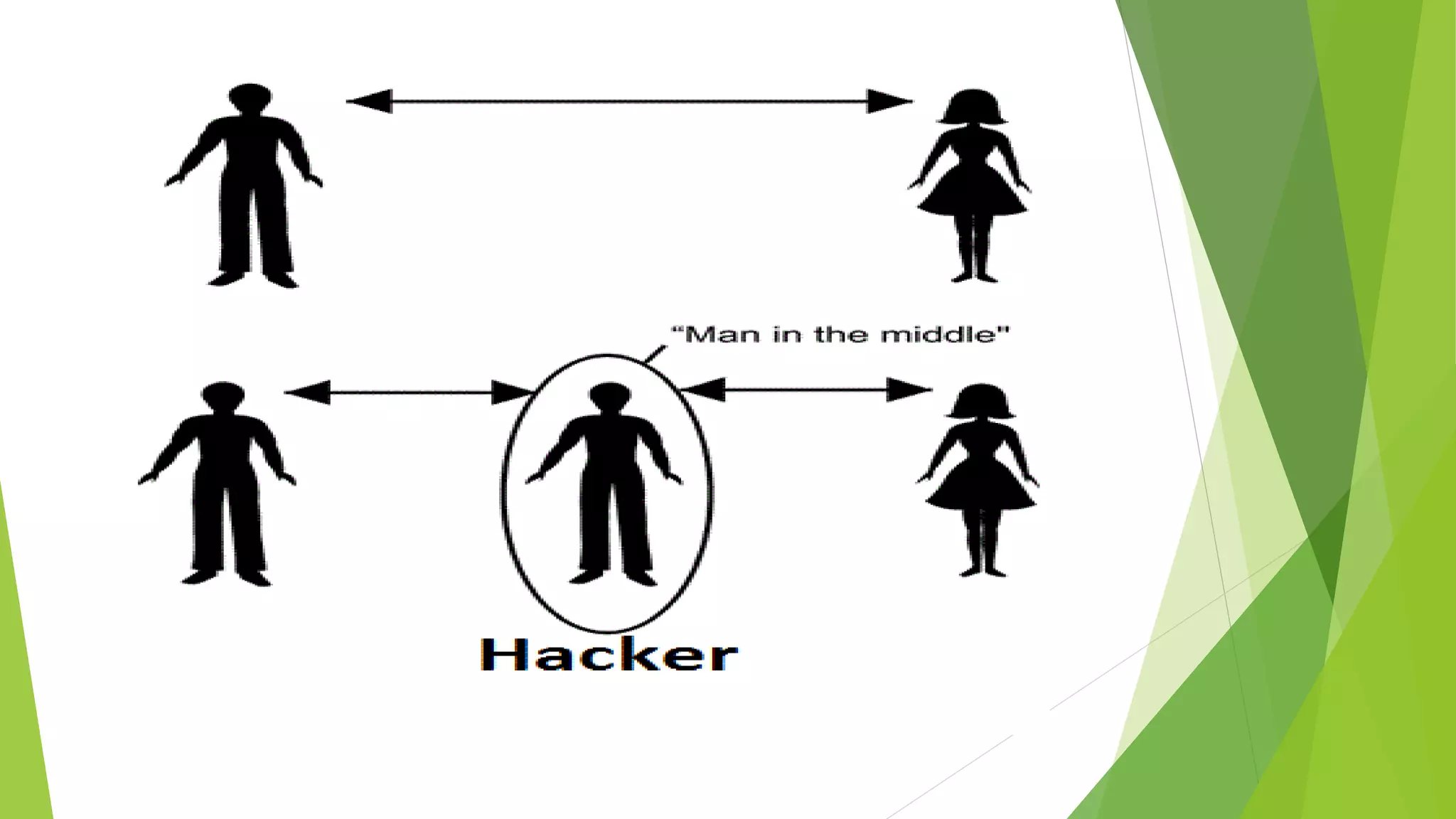
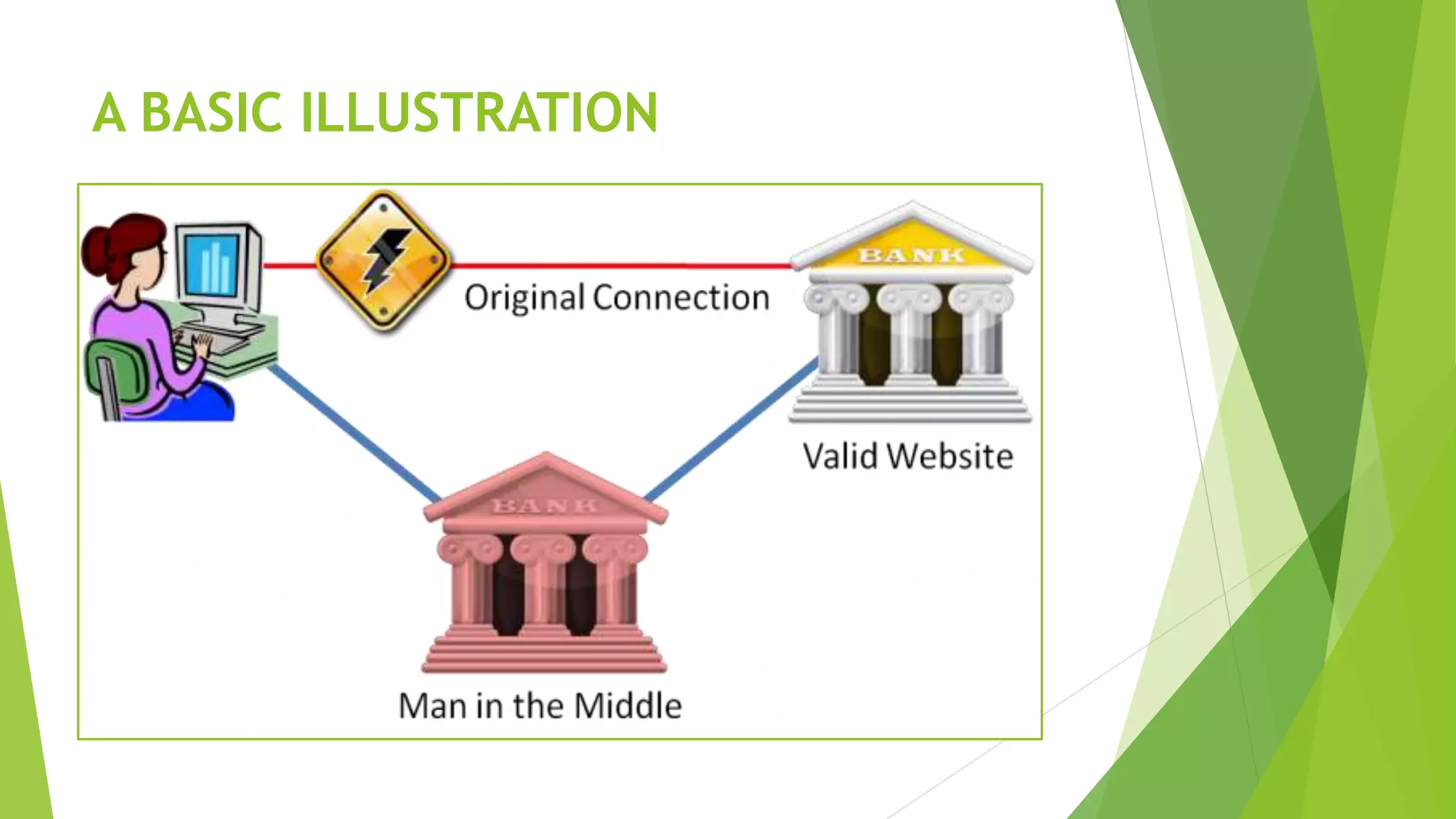
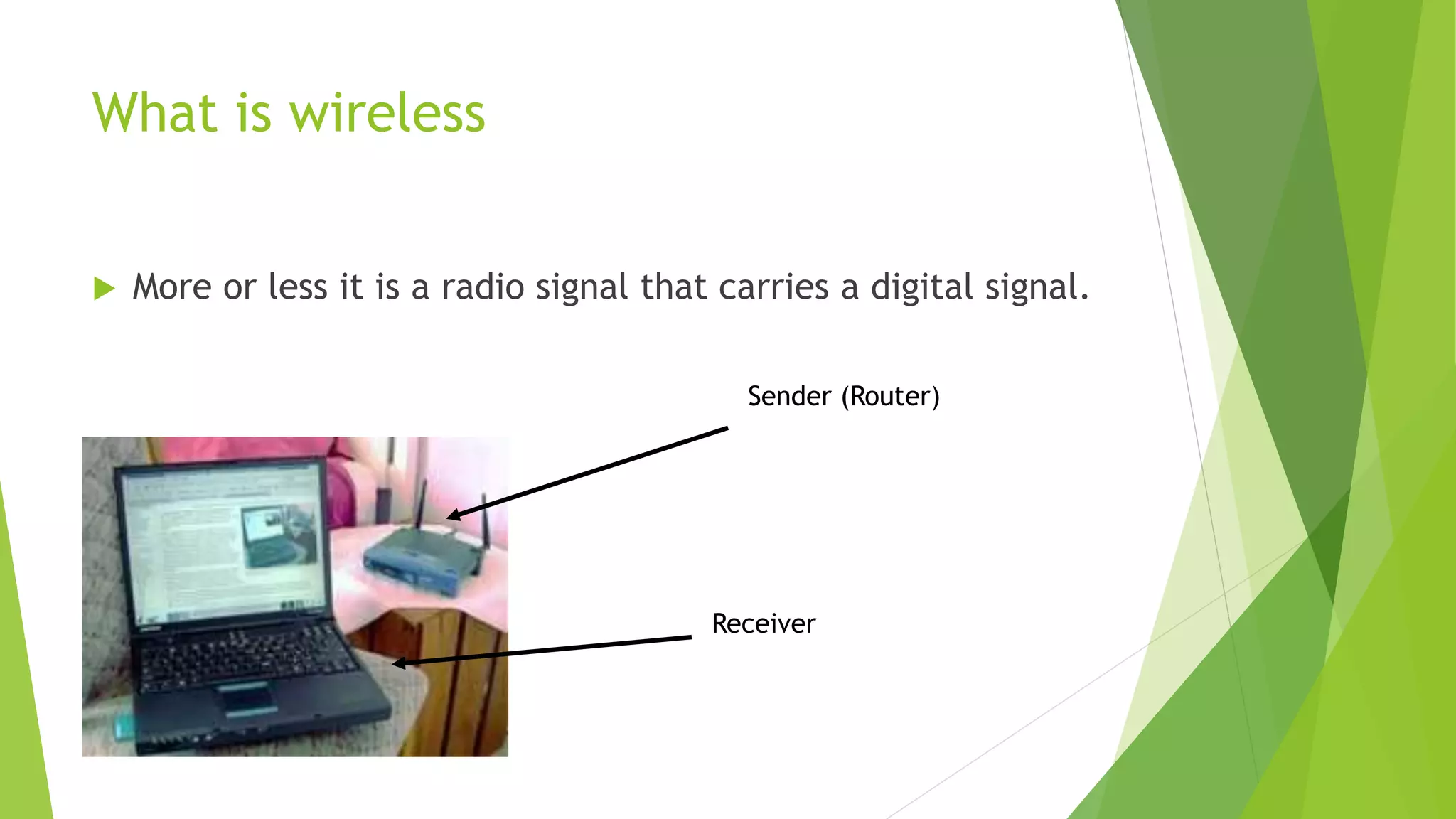
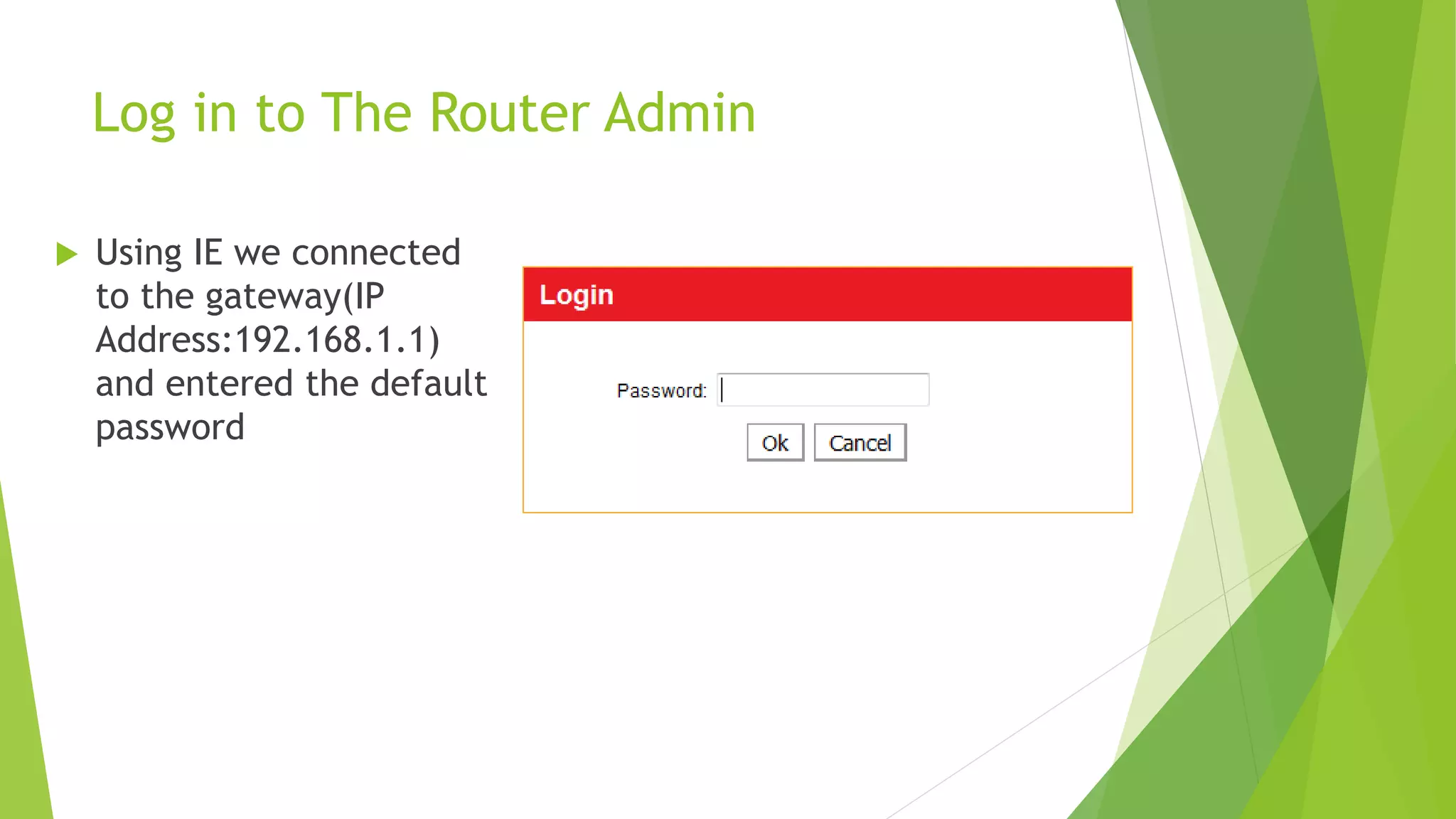
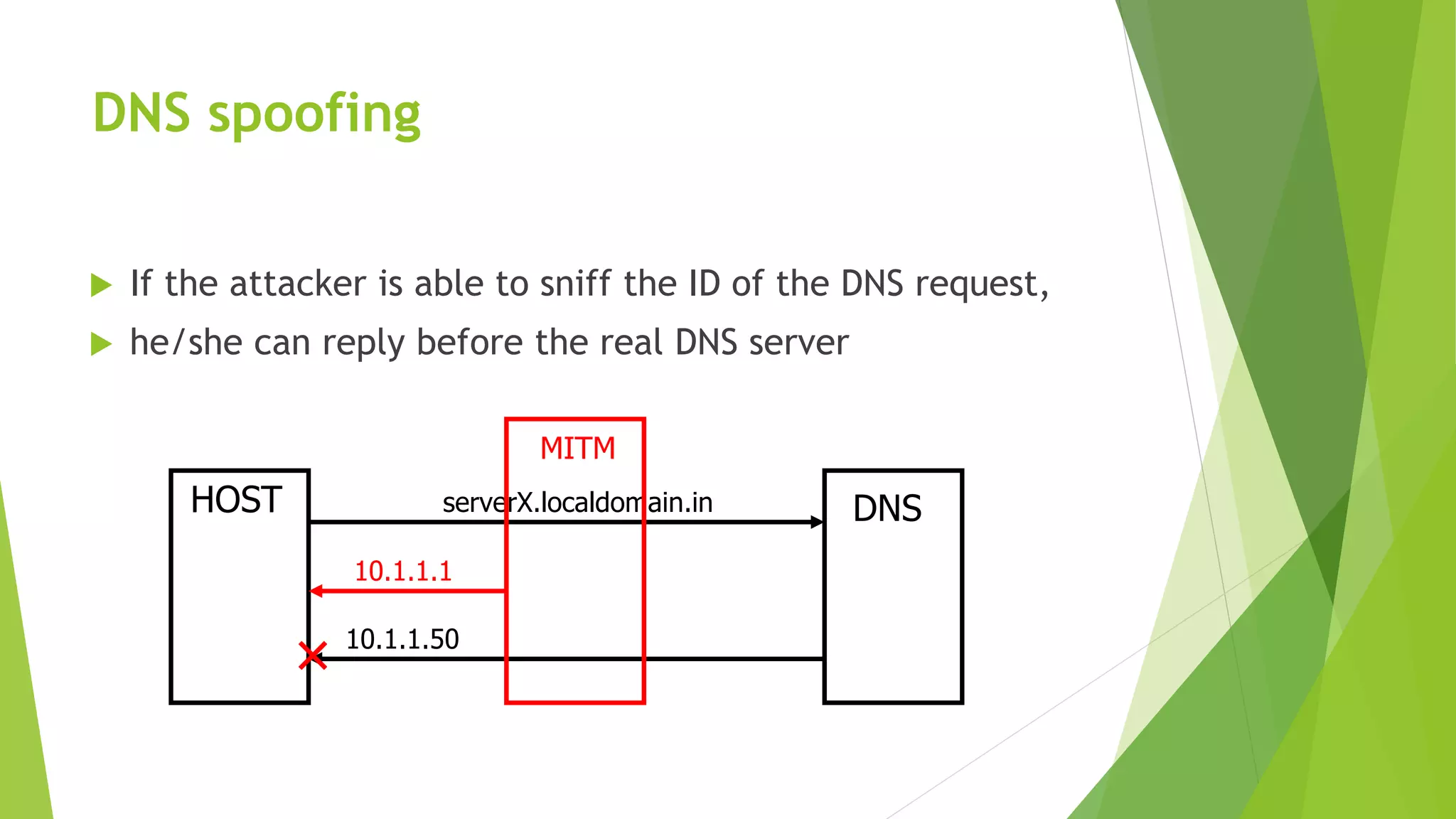
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack intercepts communications between two parties by relaying and controlling messages between them. The attacker eavesdrops and potentially modifies the communication by replacing the keys for their own. This allows them to intercept sensitive transmissions like passwords or financial transactions. A MITM works by spoofing the MAC address of the target to intercept and manipulate traffic between the target and other devices on the network, such as a router. Encrypted connections and careful certificate verification can help prevent MITM attacks.