This document discusses methods for rapid software development. It covers topics like agile methods, extreme programming, rapid application development, and software prototyping. Some key points made are:
- Rapid development is needed to quickly respond to changing business needs, even if it means lower initial quality.
- Agile methods focus on iterative development and early delivery of working software that can evolve rapidly based on changing requirements.
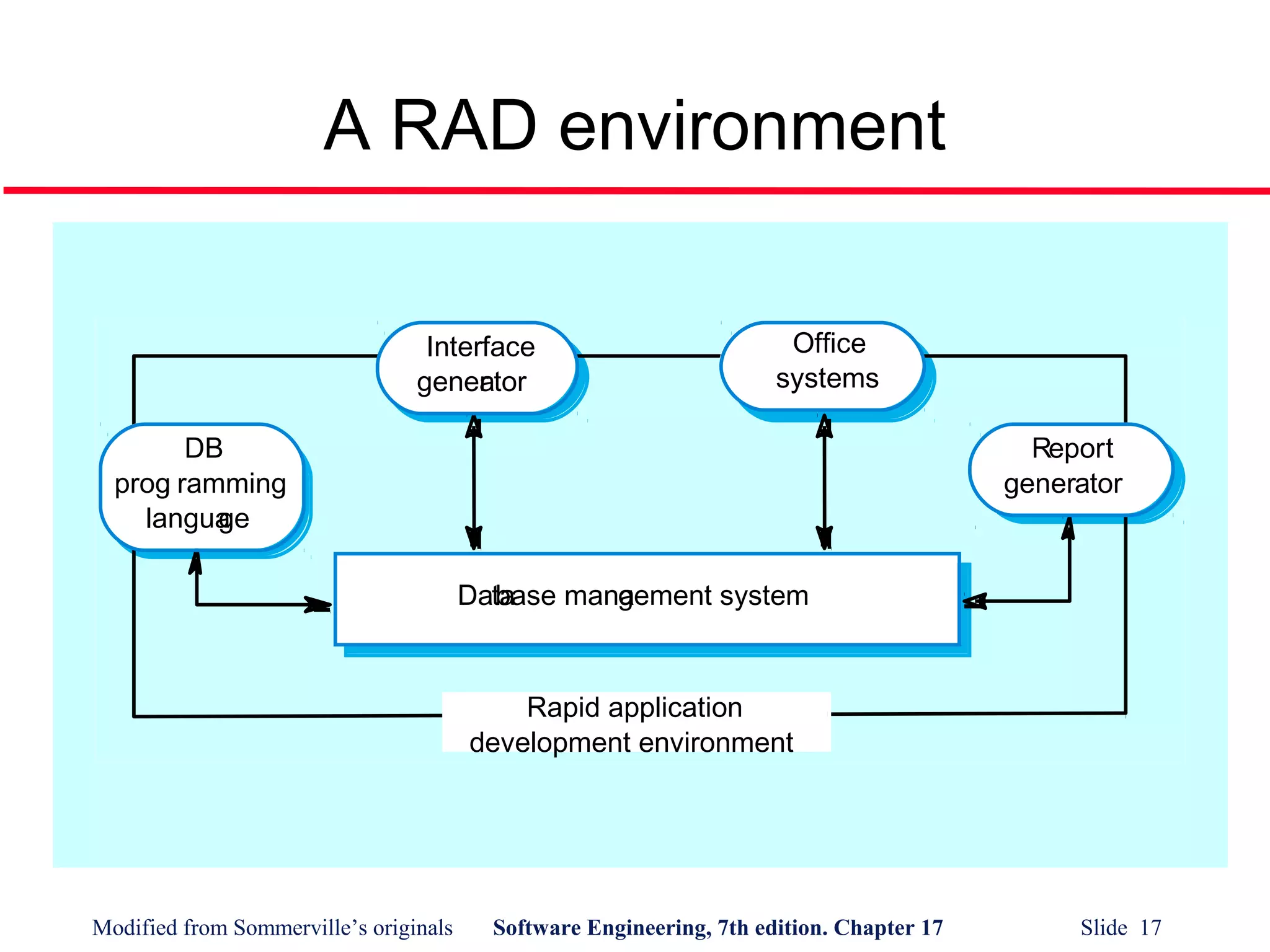
- Rapid application development uses tools that facilitate rapid creation of interfaces and reports linked to a database.
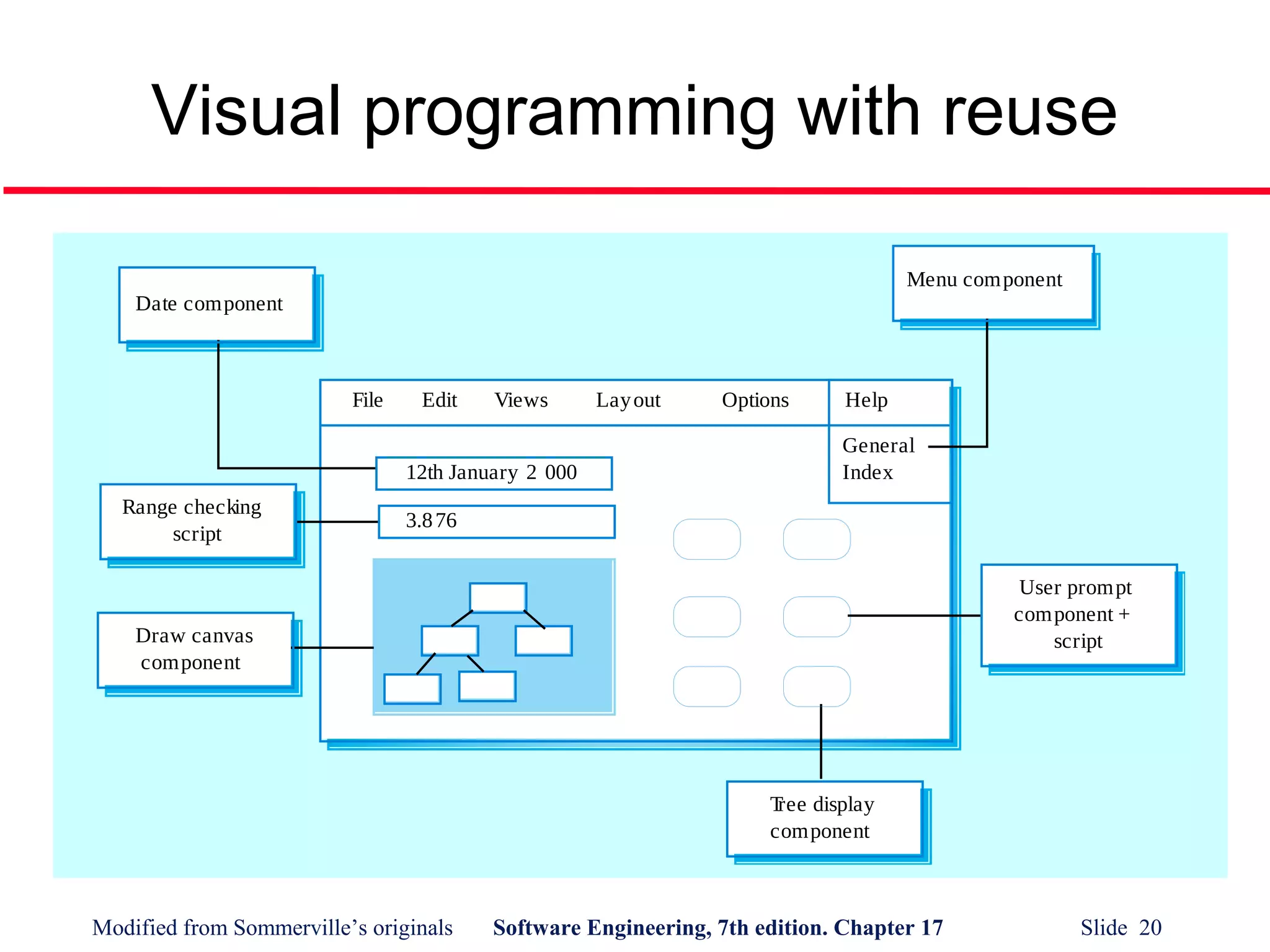
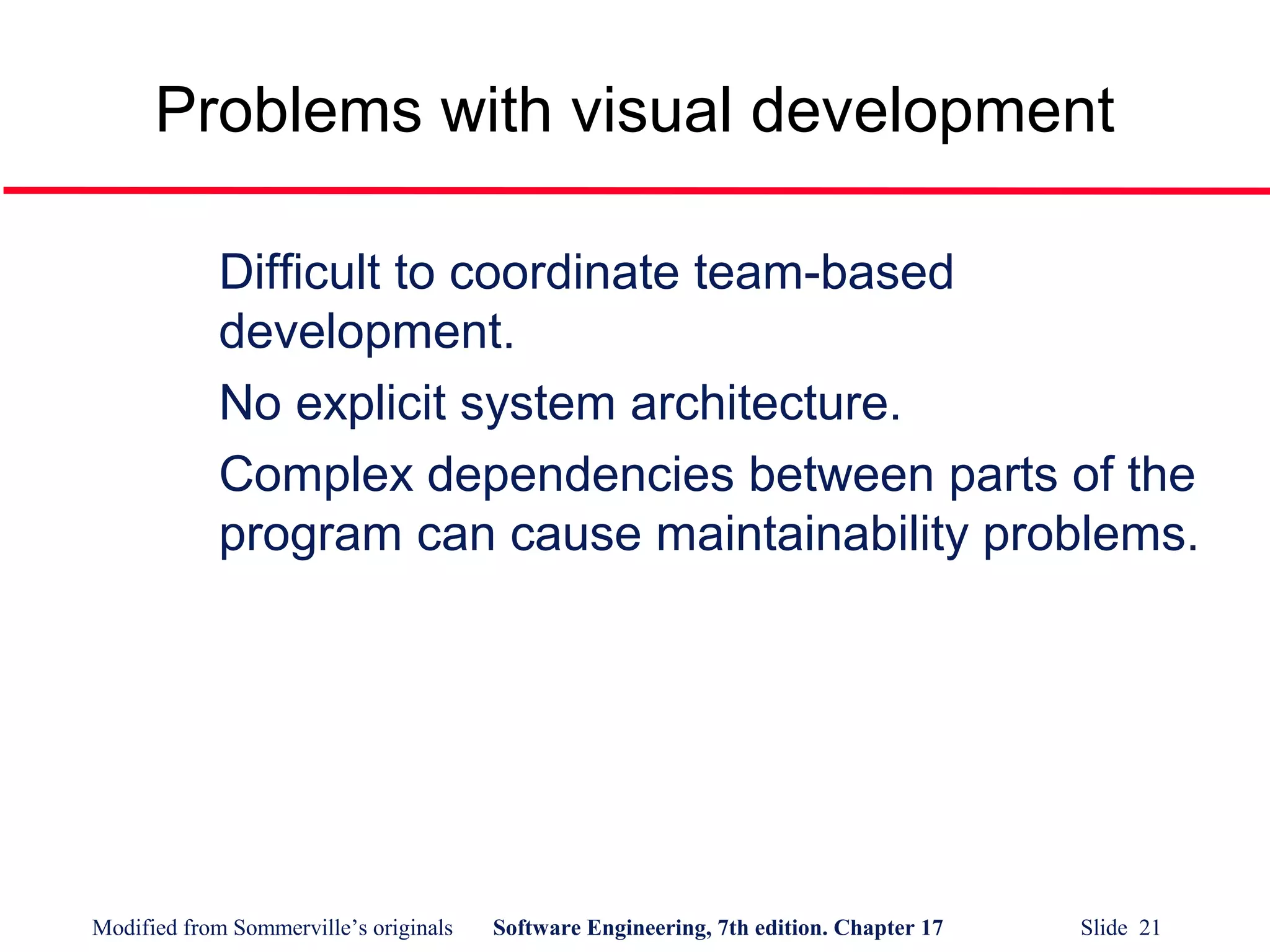
- Visual programming allows rapid prototyping through a graphical interface but can cause coordination and maintenance issues for large projects.