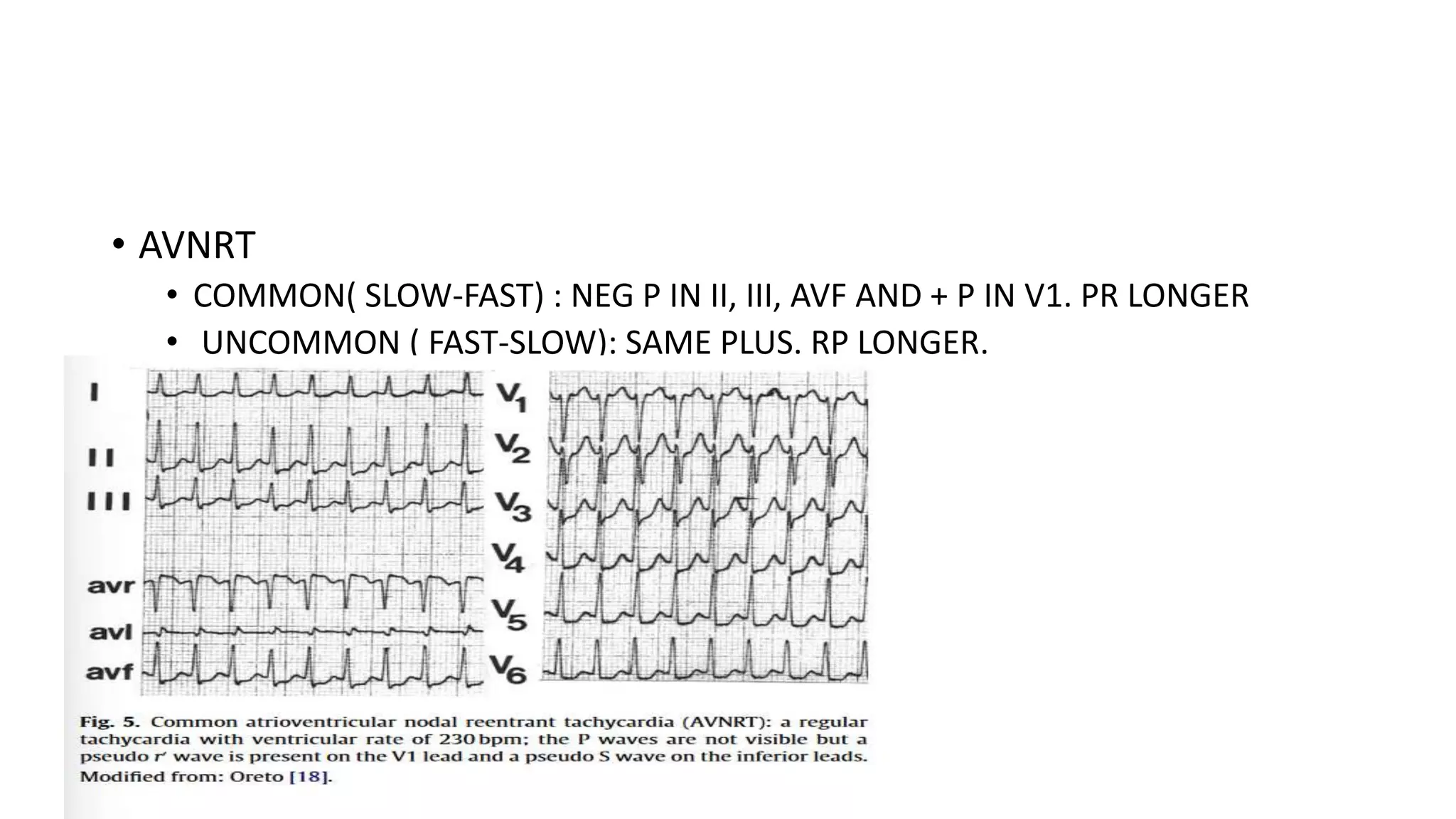
The document discusses various types of narrow complex tachycardia (NCT), which are defined as having a QRS duration less than 120 ms and a heart rate over 100 bpm on an ECG. It describes several supraventricular origins for NCT including sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, focal atrial tachycardia, junctional tachycardia, atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), and atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT). The document provides details on characteristics such as rates, rhythms, and ECG patterns for each type of NCT.