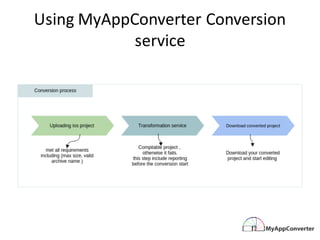
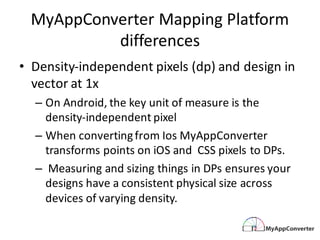
MyAppConverter is a service that enables seamless native code conversion from iOS to Android without the need for an SDK or runtime, providing developers with fully documented and scalable code. The transformation engine facilitates semantic-driven conversions while adhering to the native structures and lifecycle of both platforms. It simplifies language syntax mappings and addresses platform-specific differences, ensuring an optimal development experience across mobile platforms.