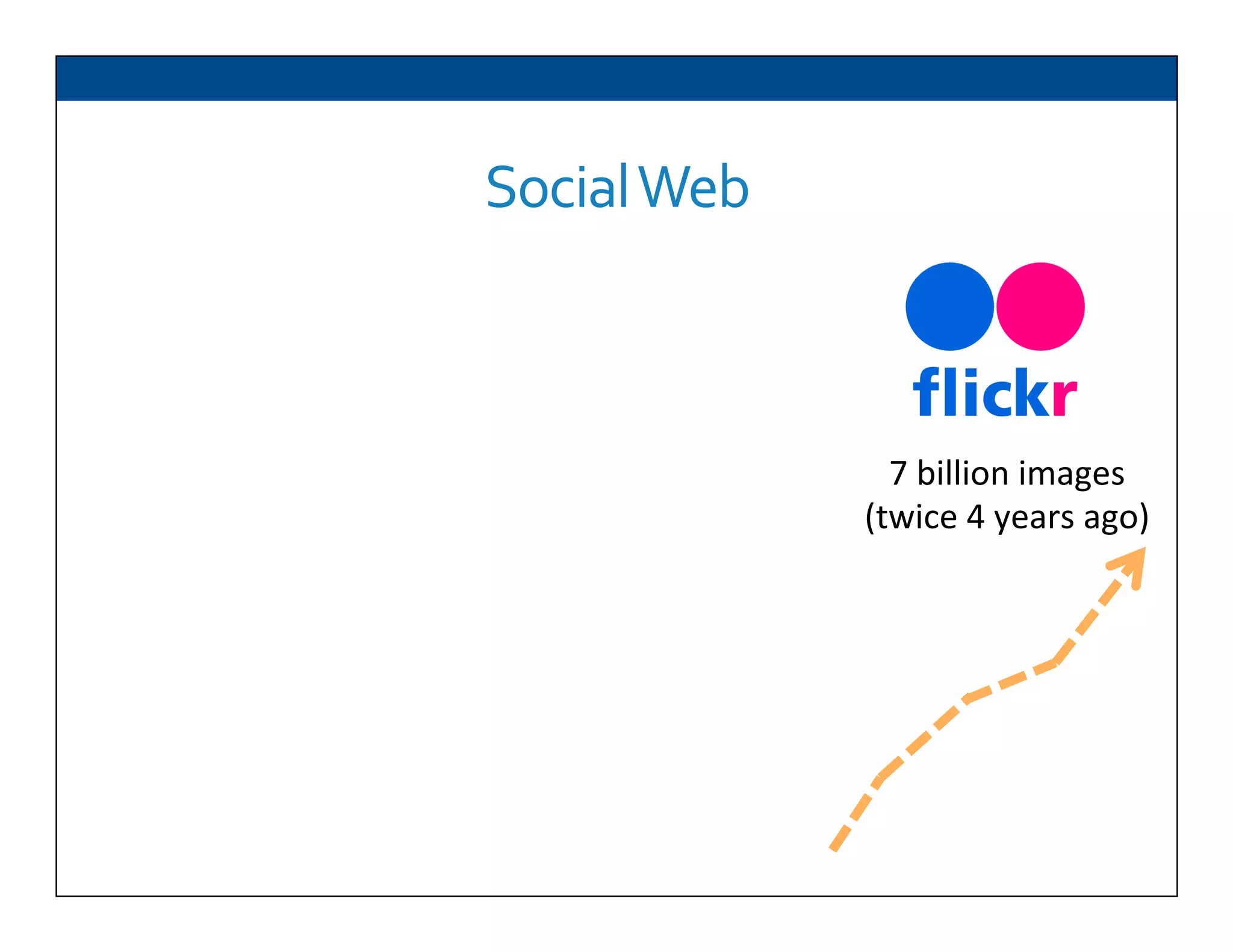
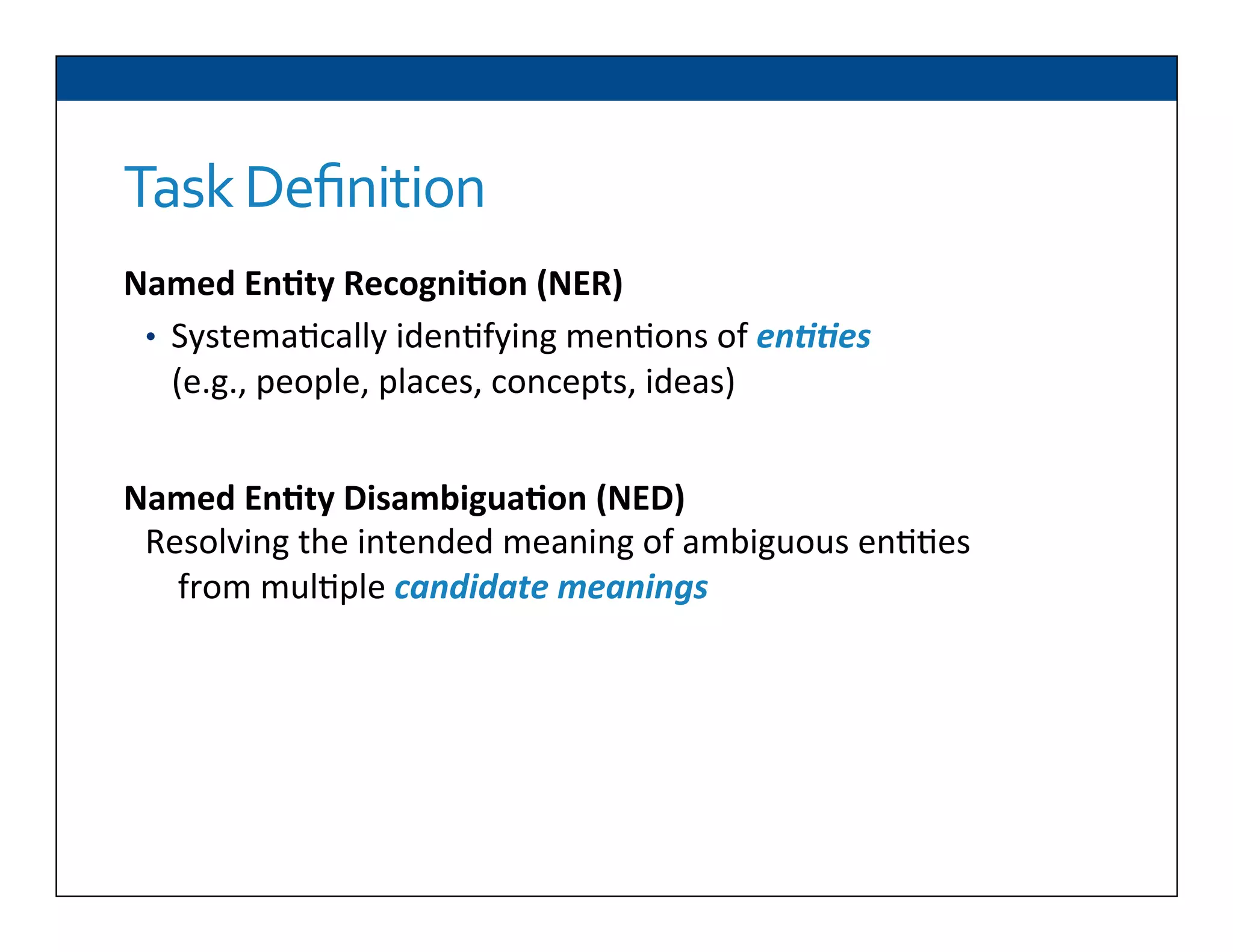
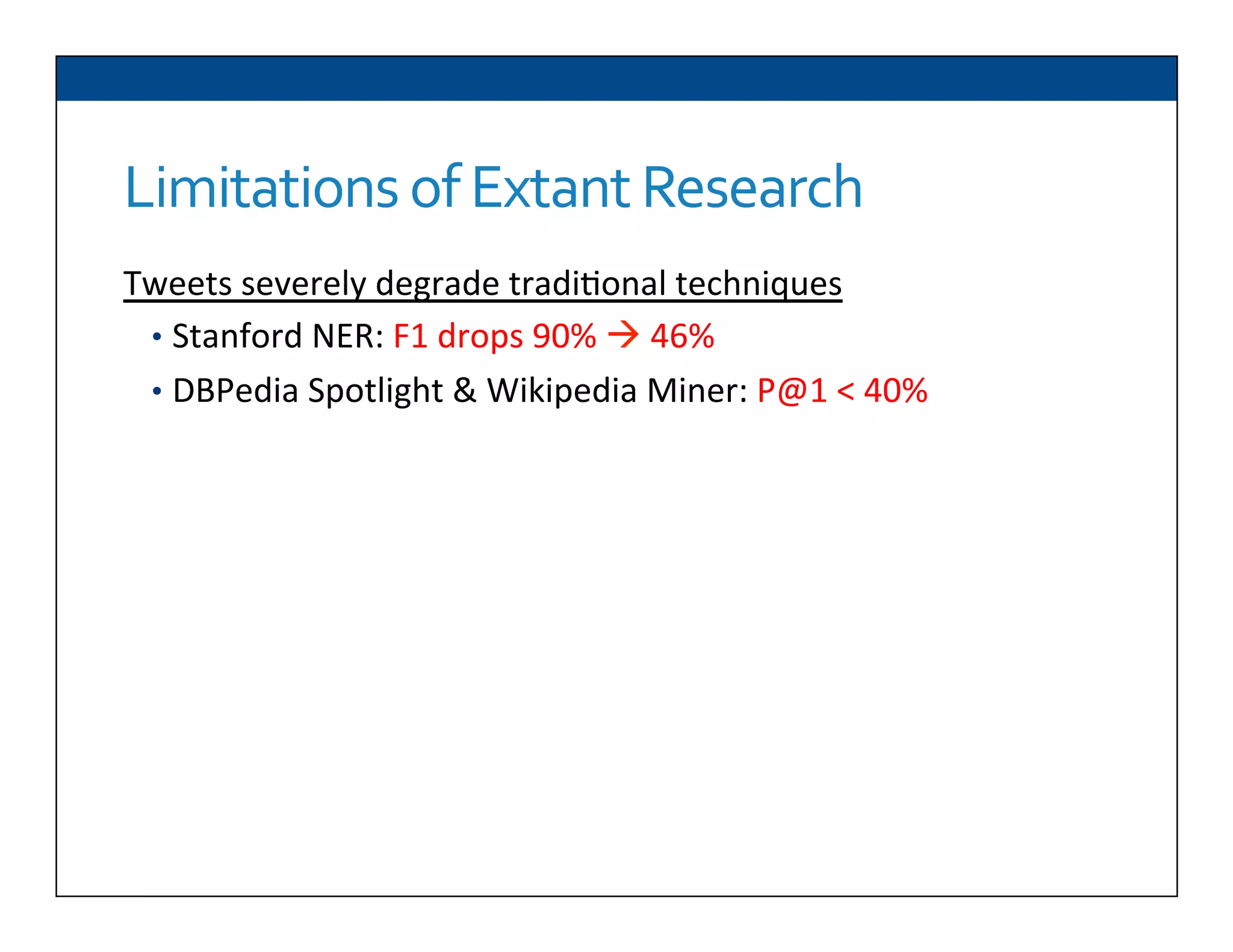
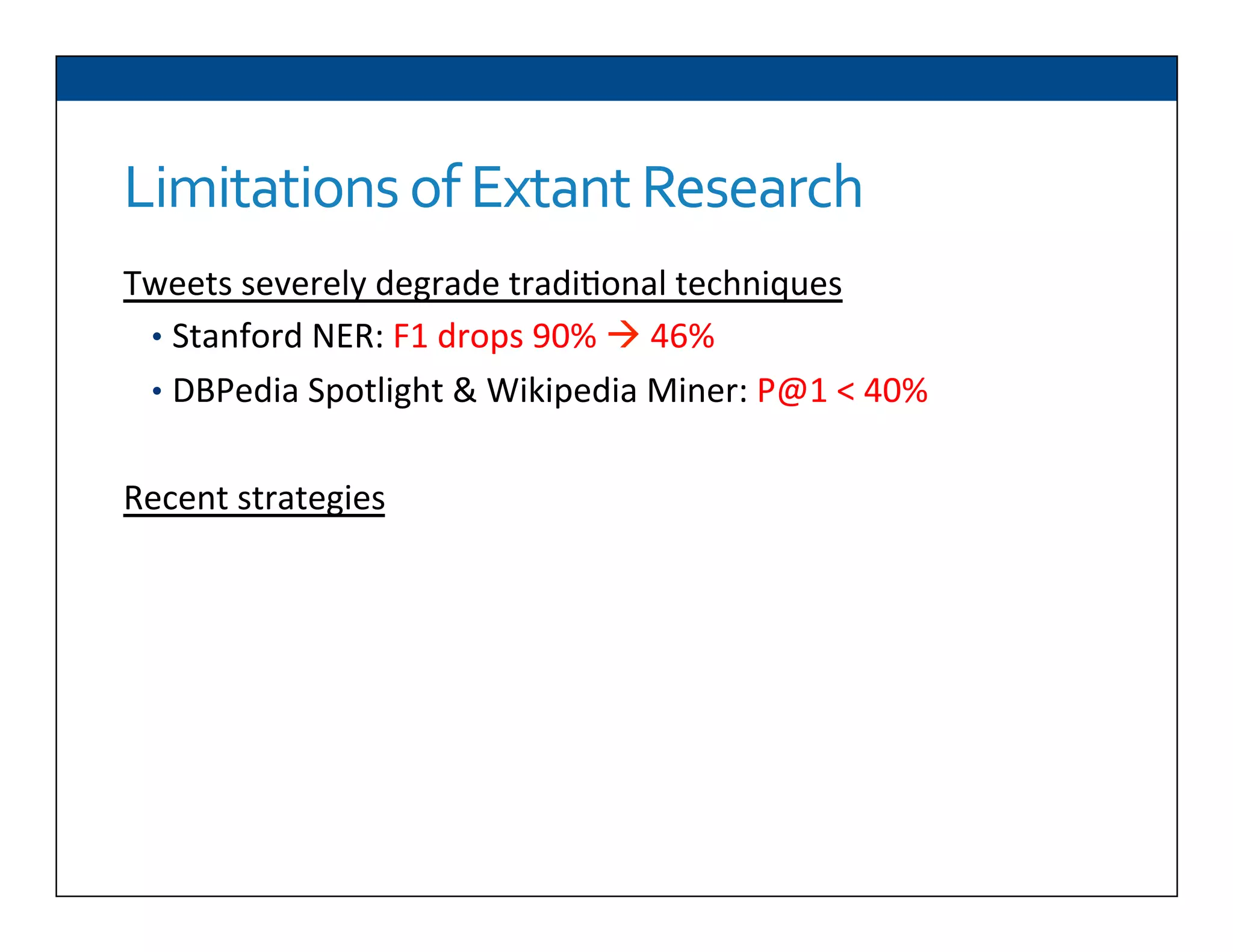
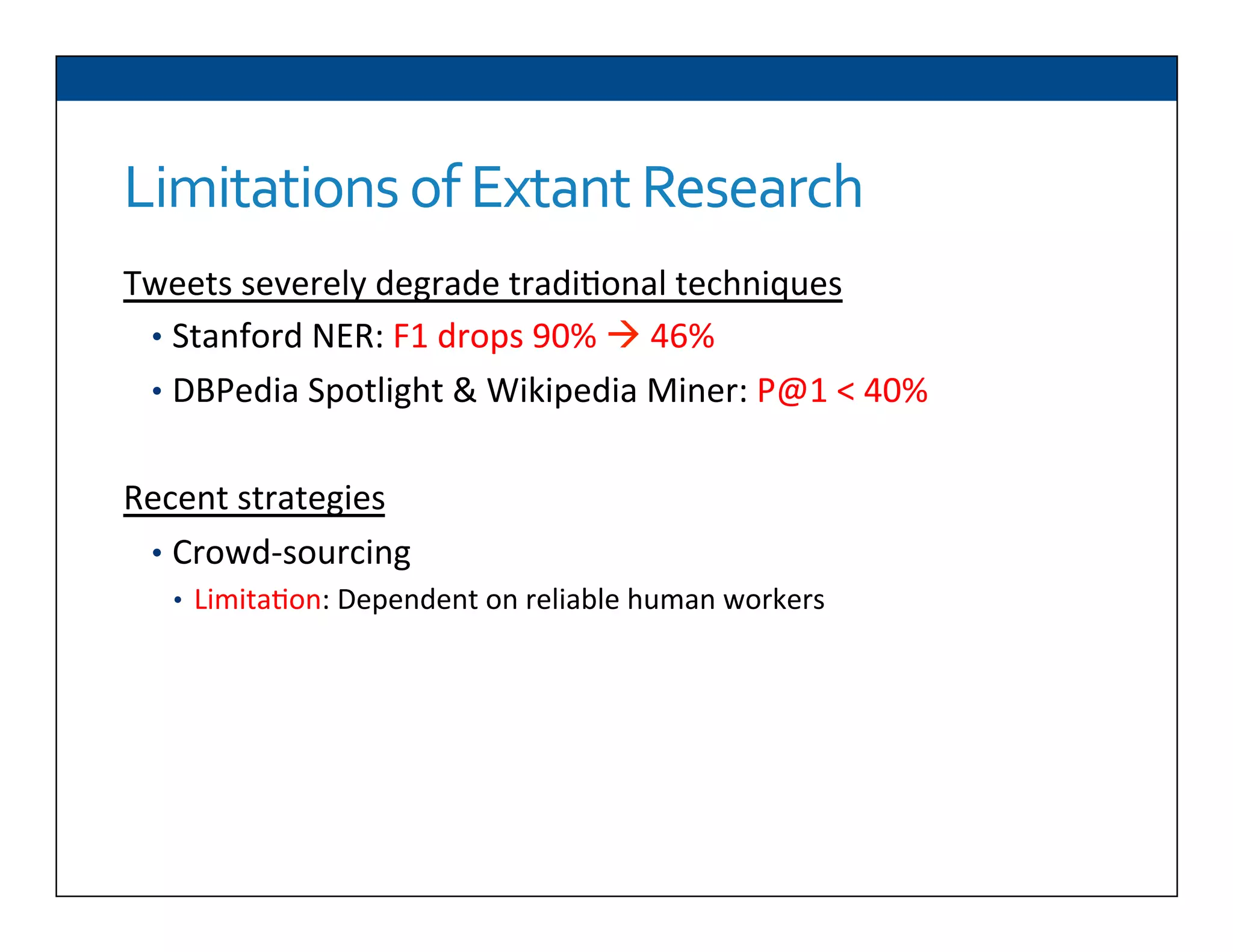
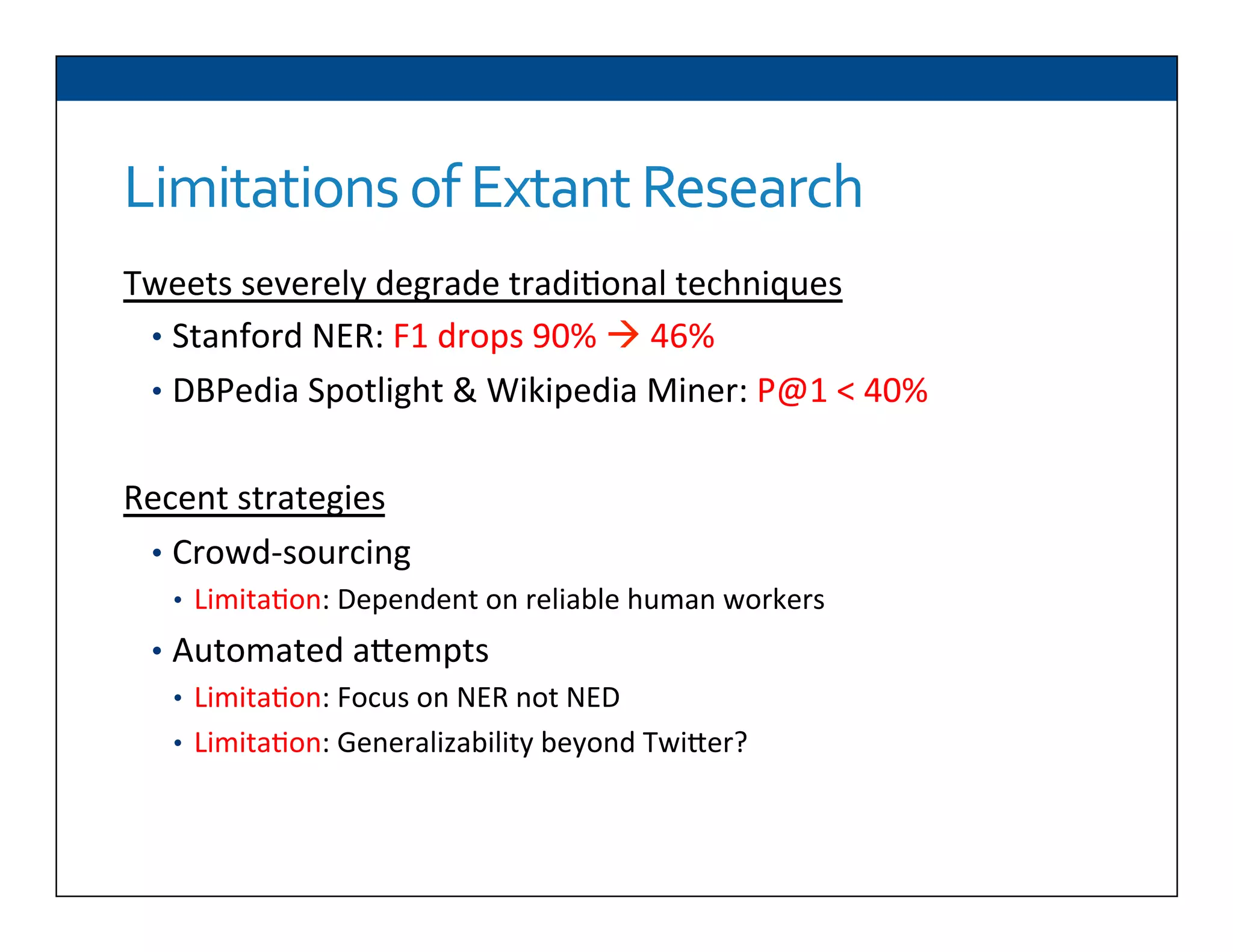
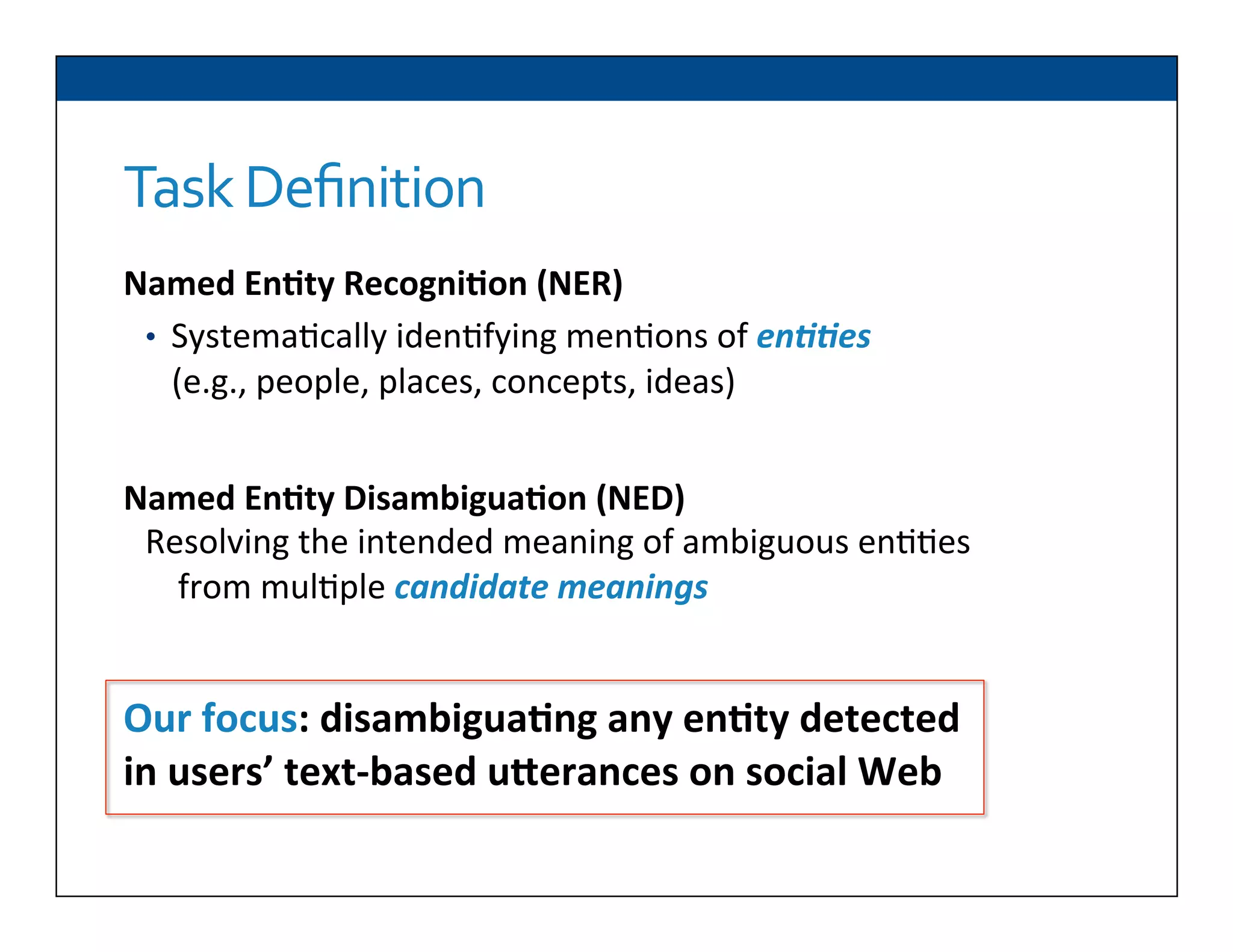
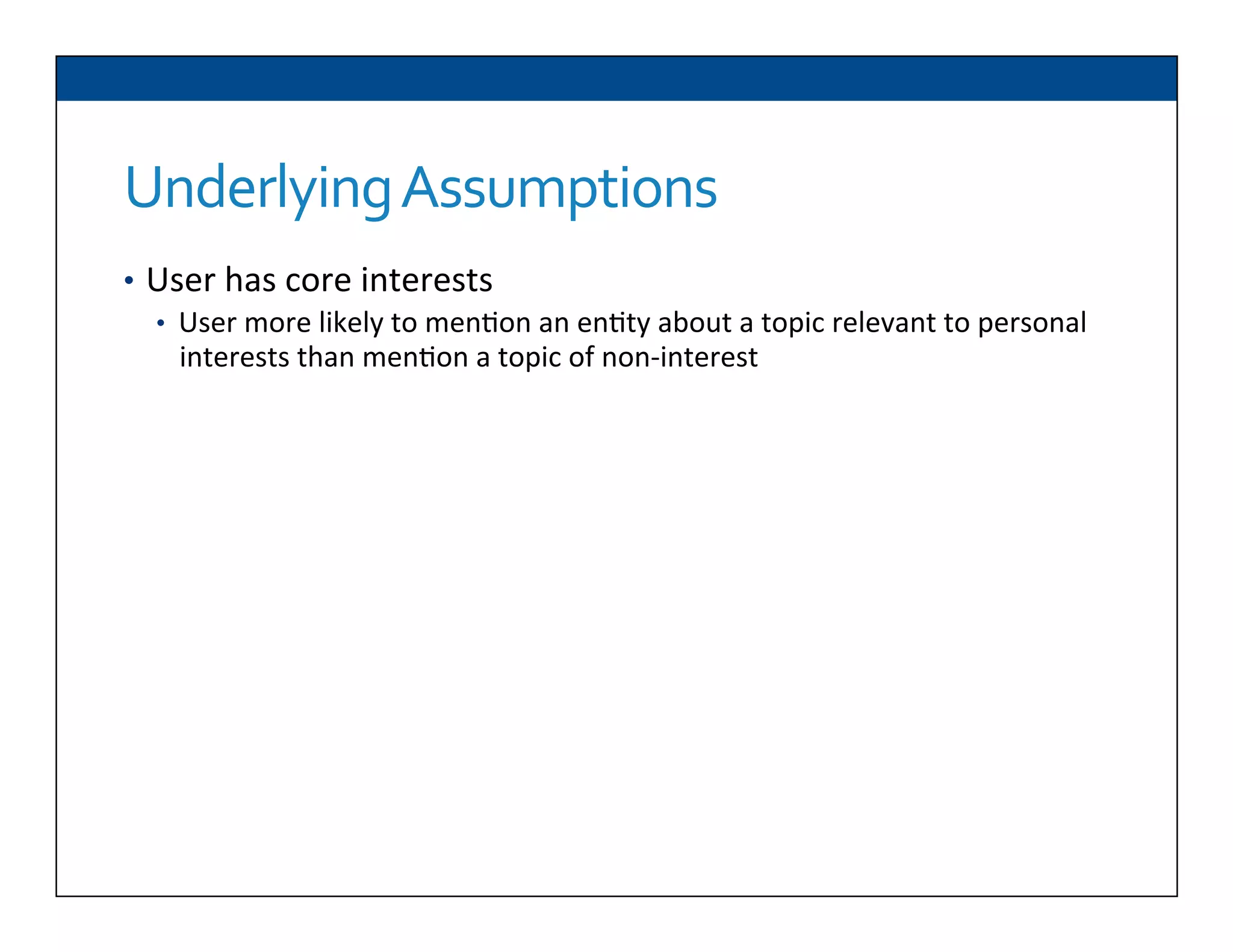
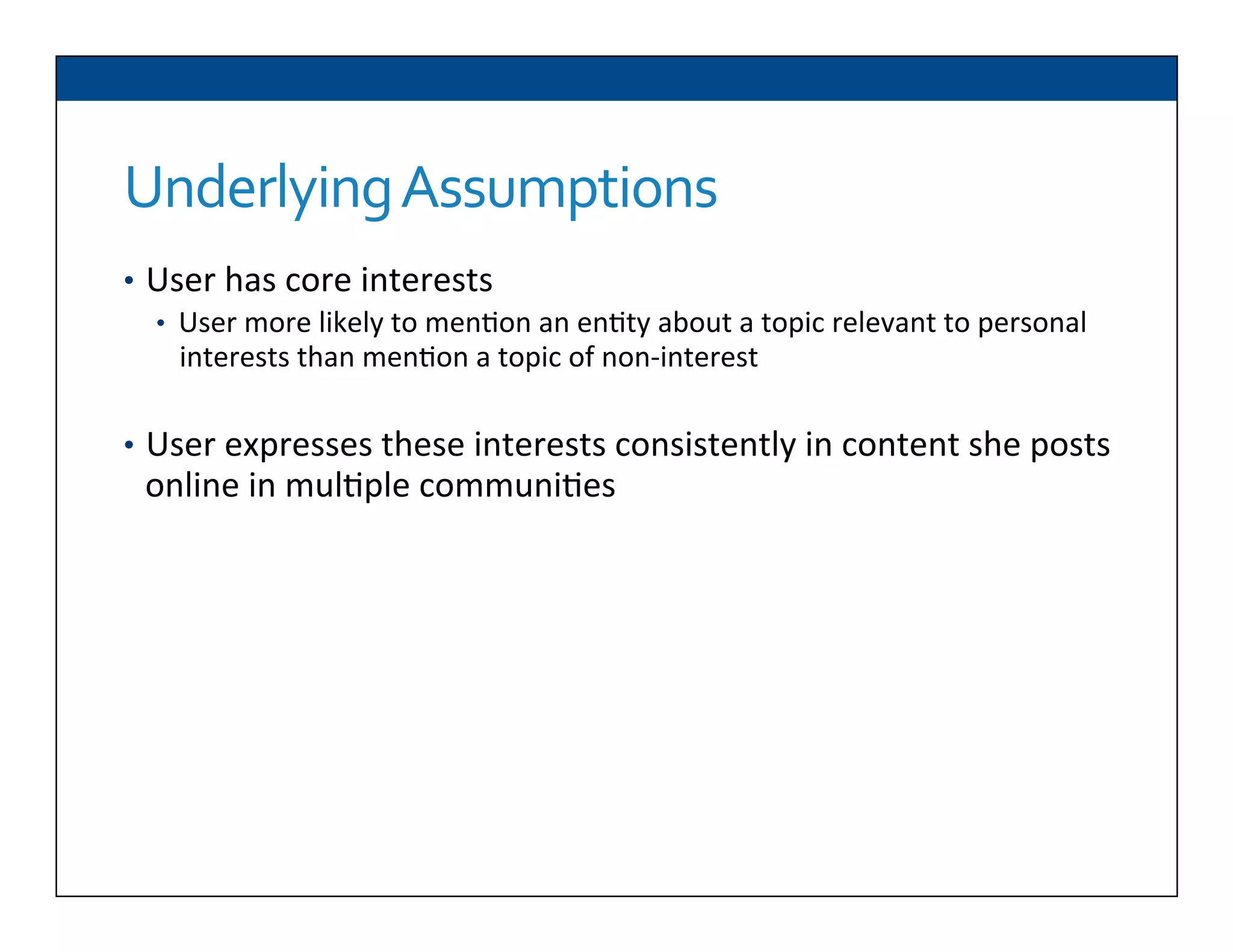
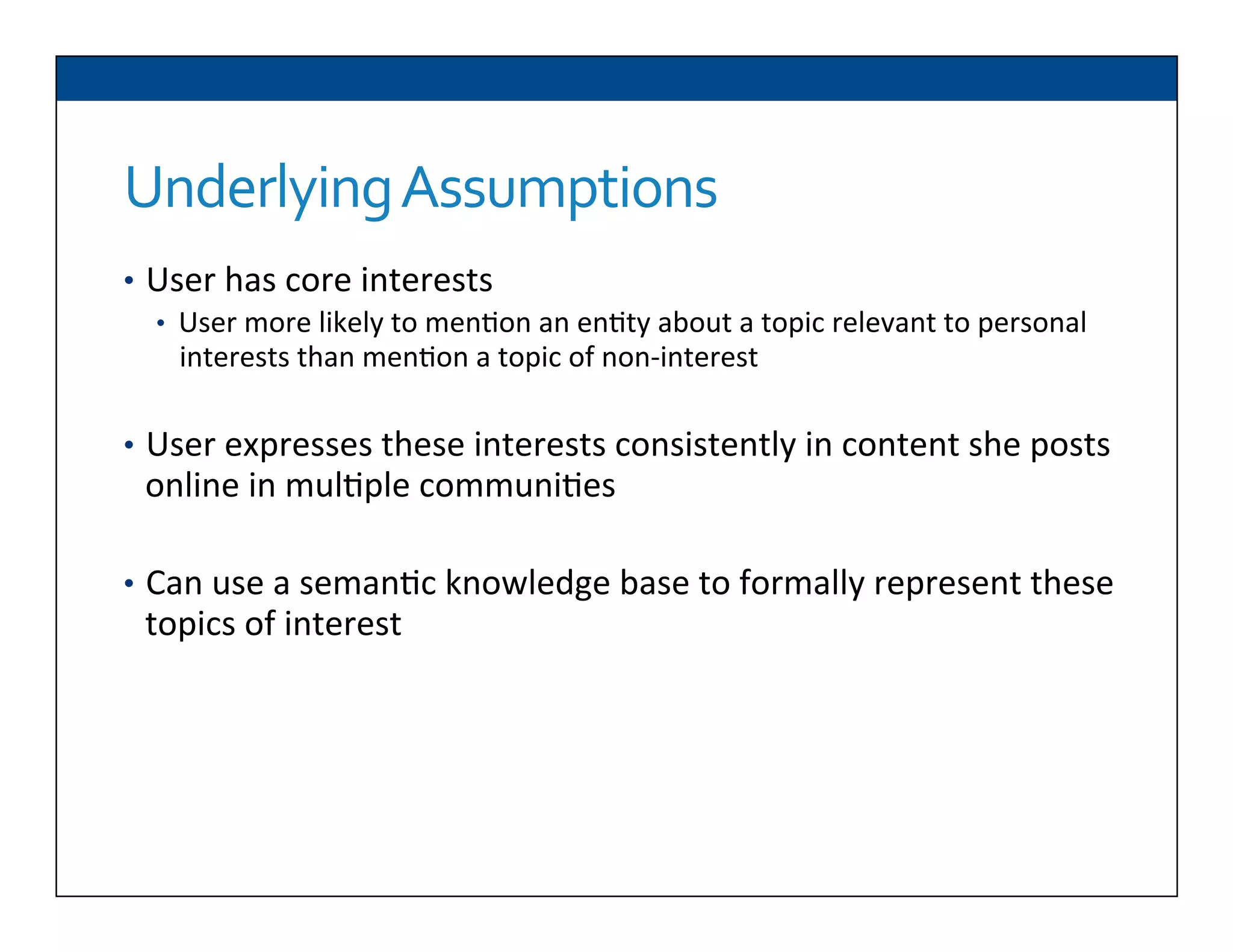
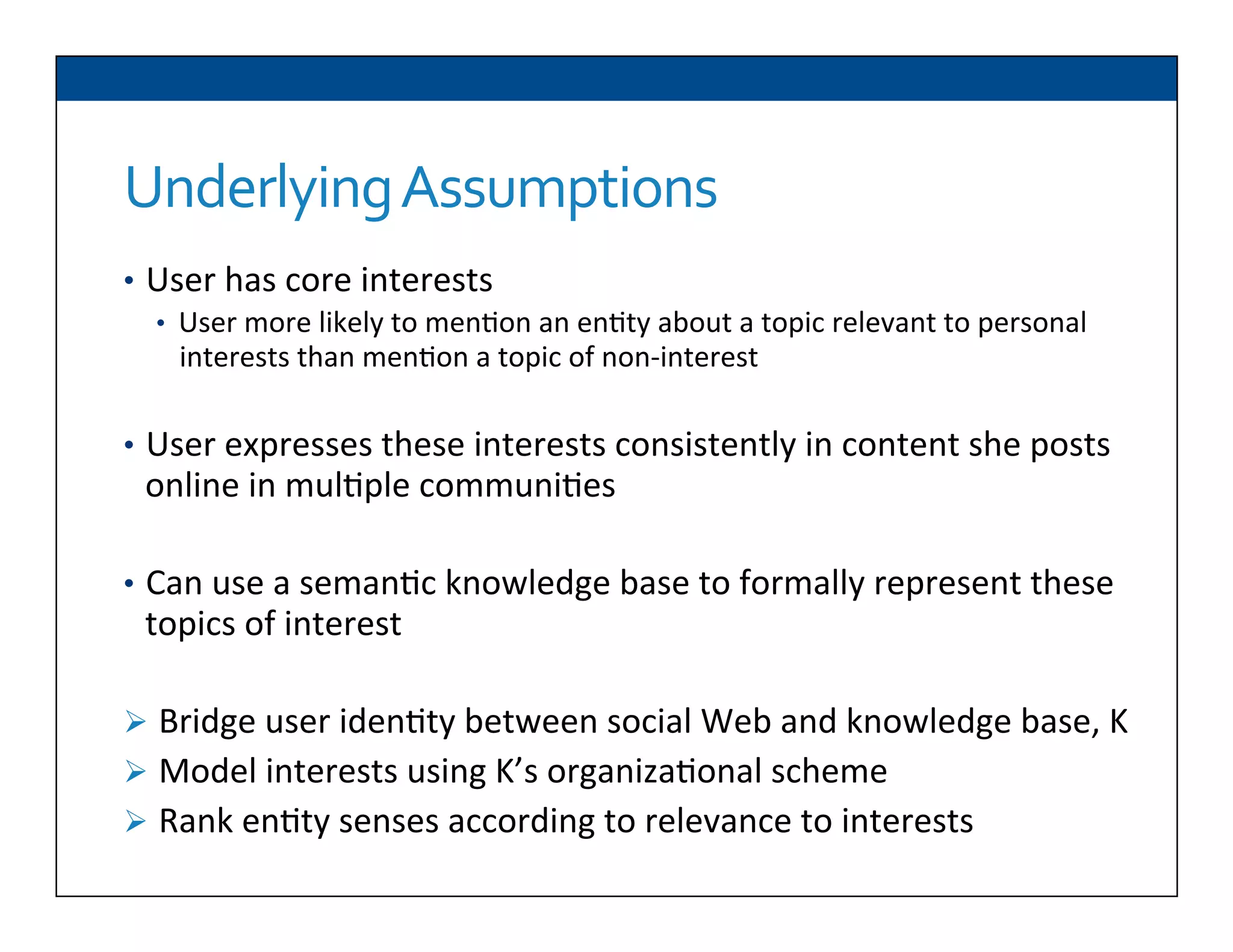
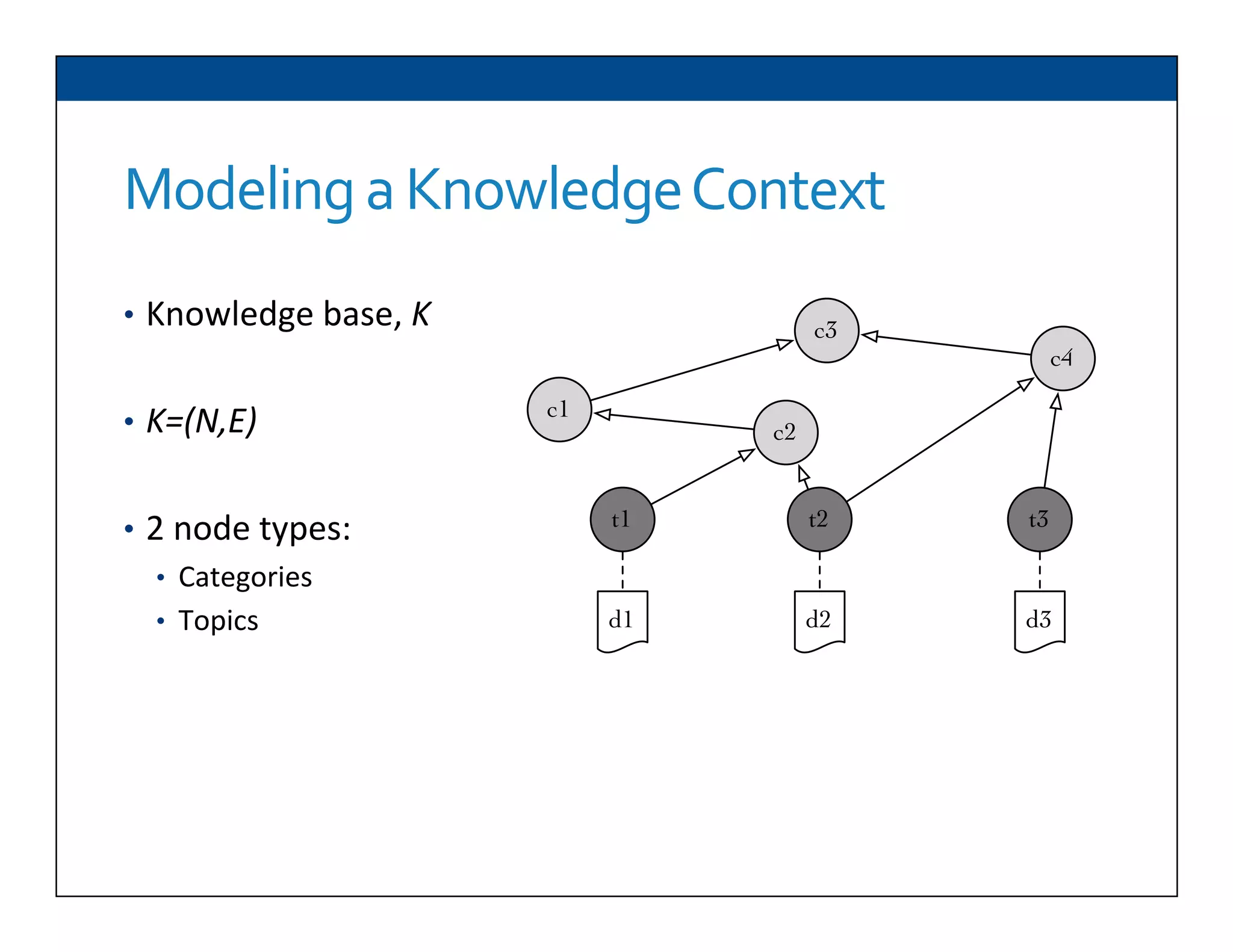
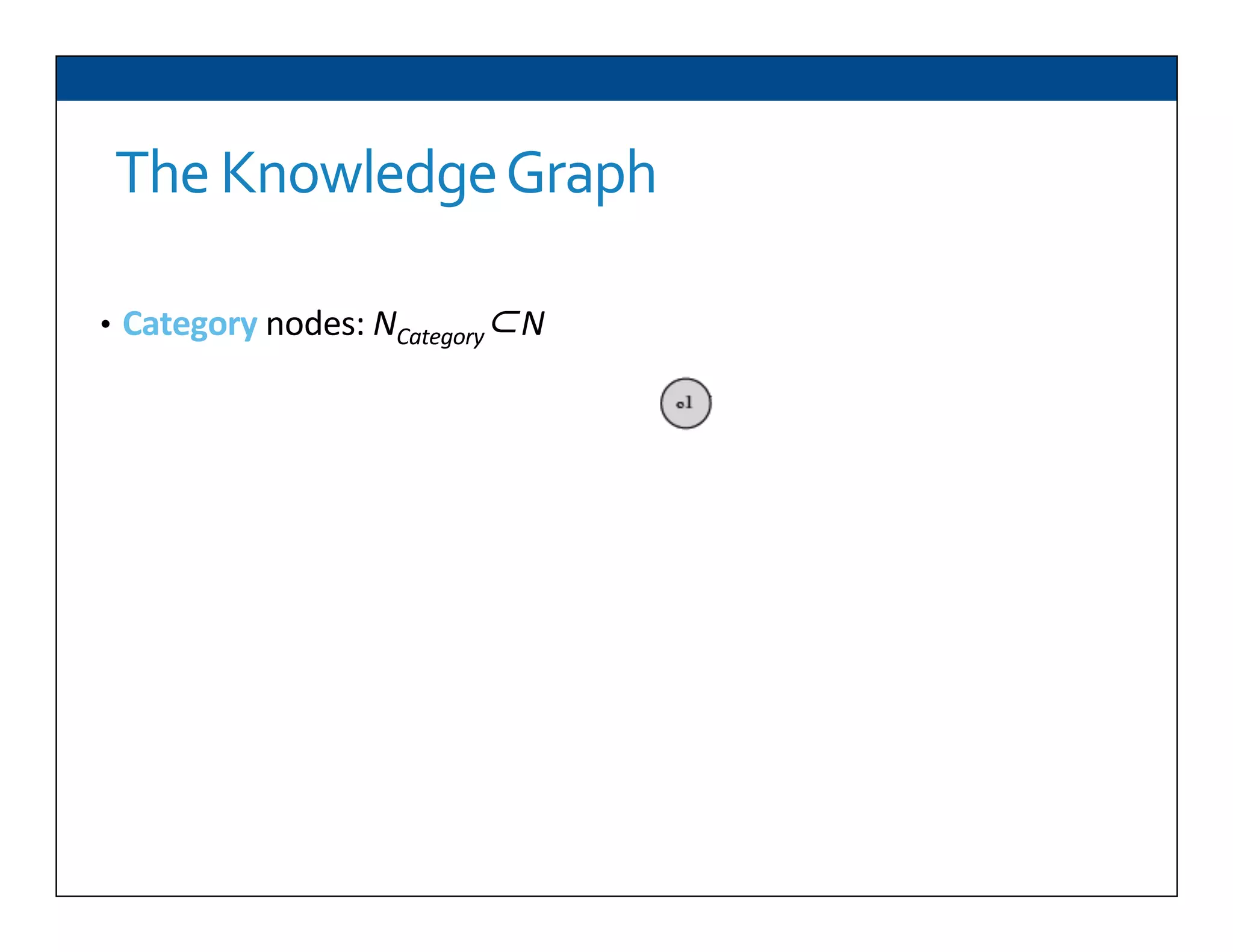
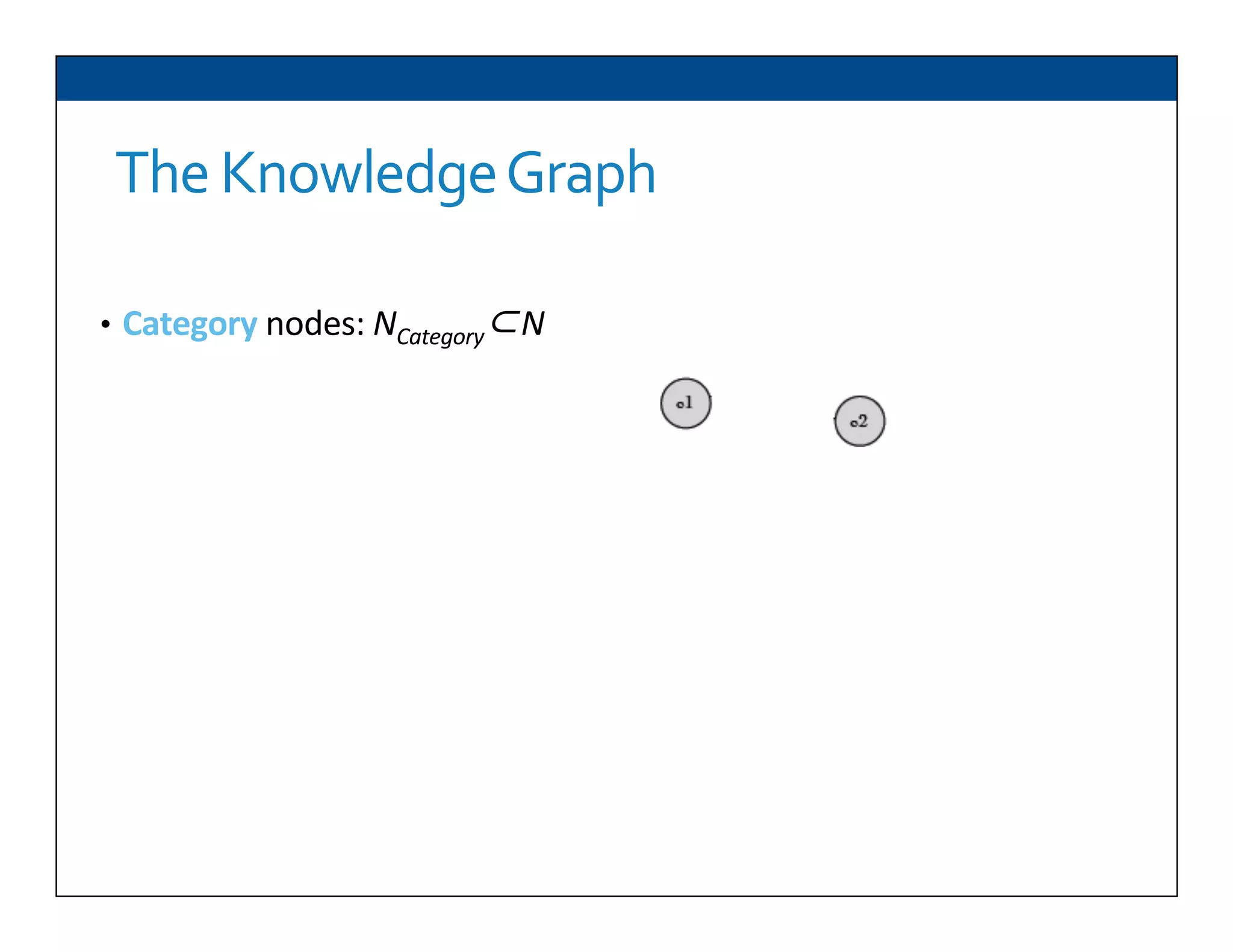
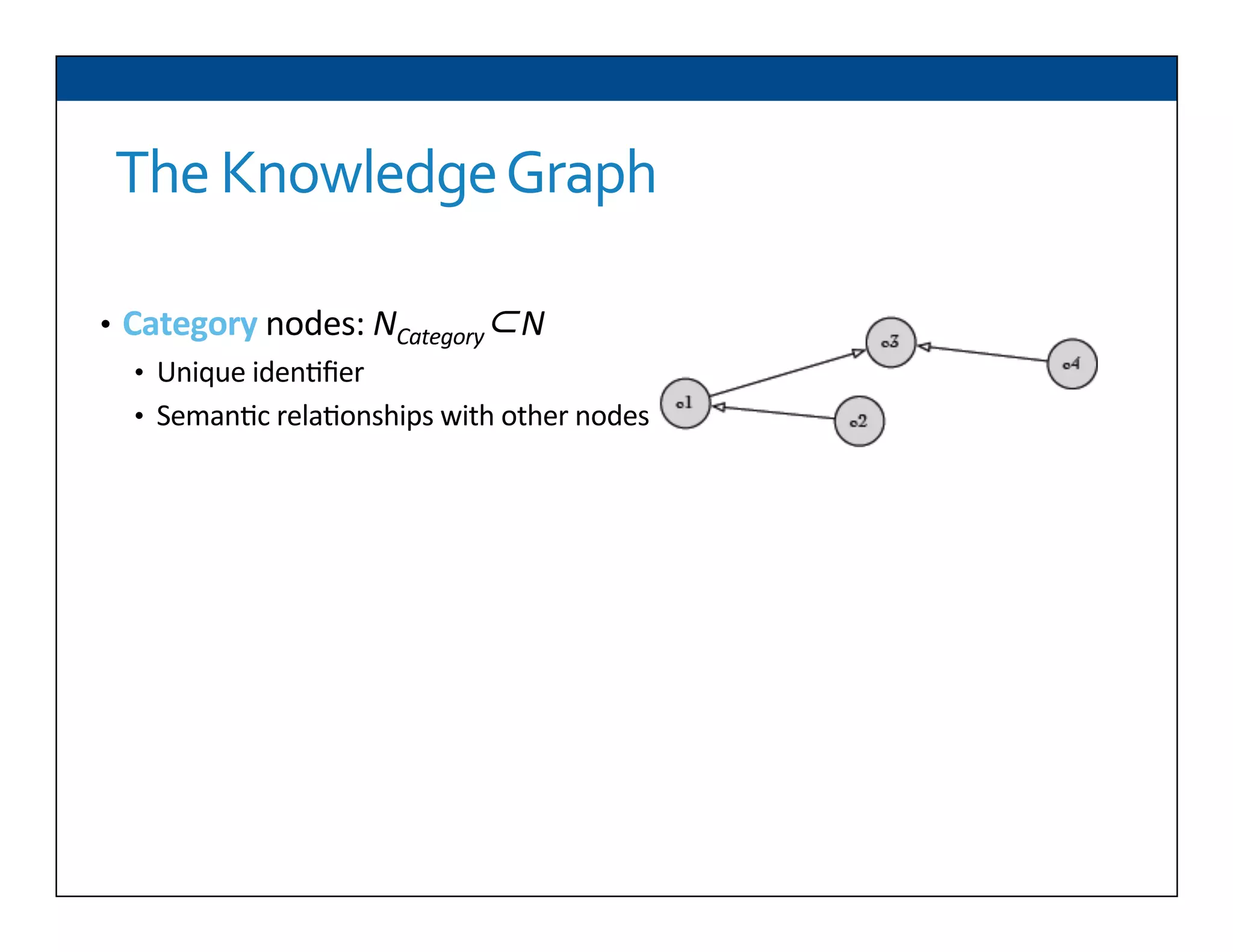
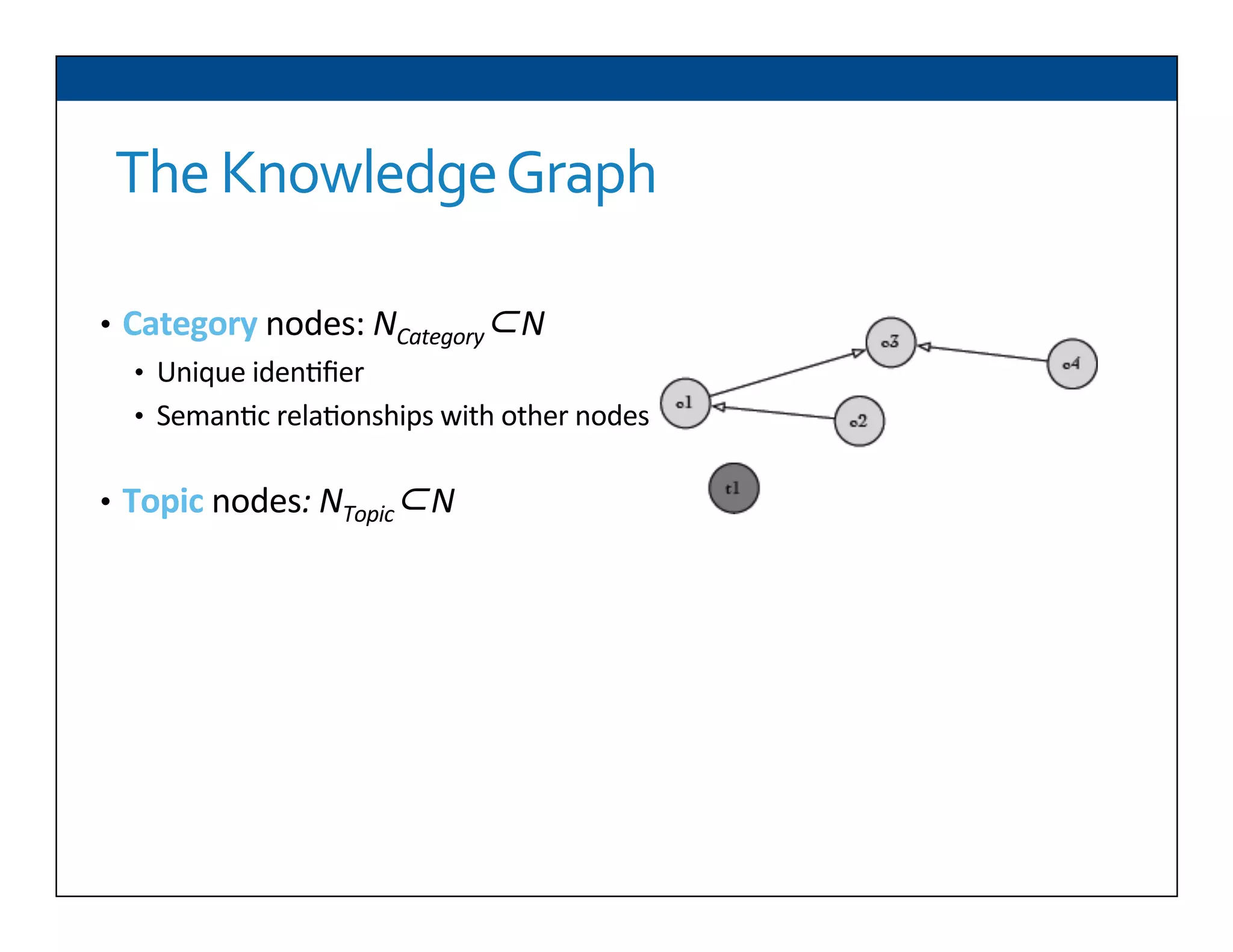
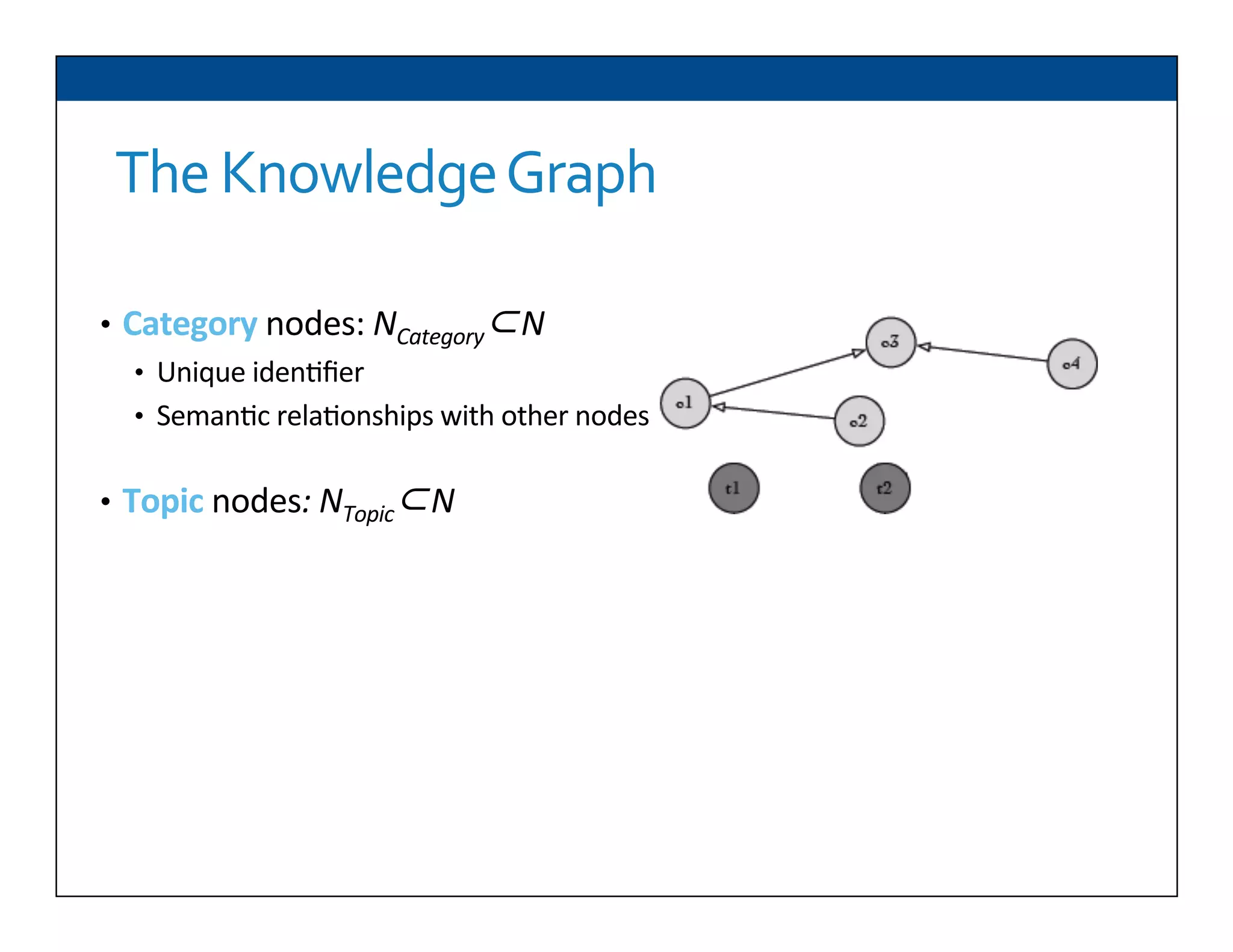
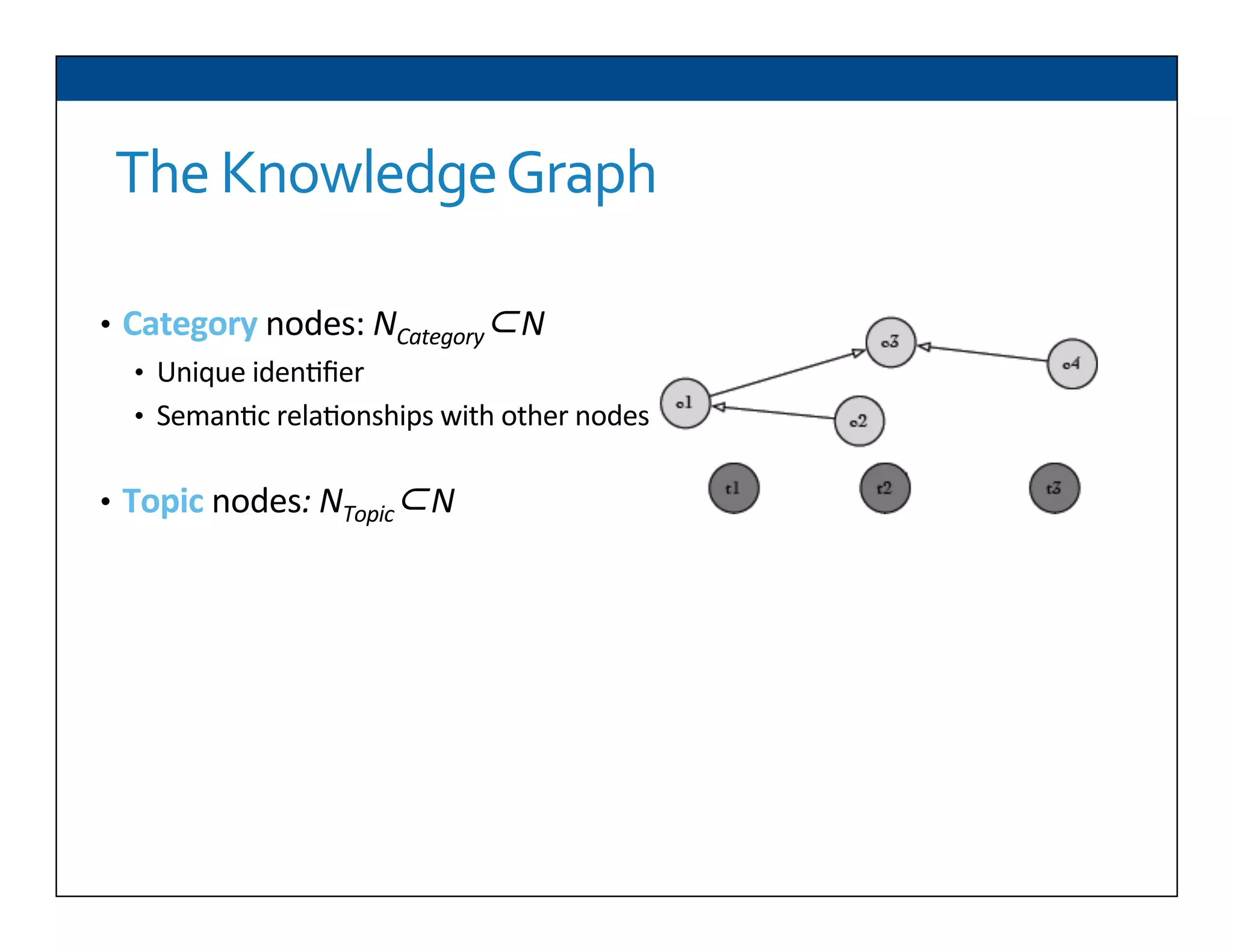
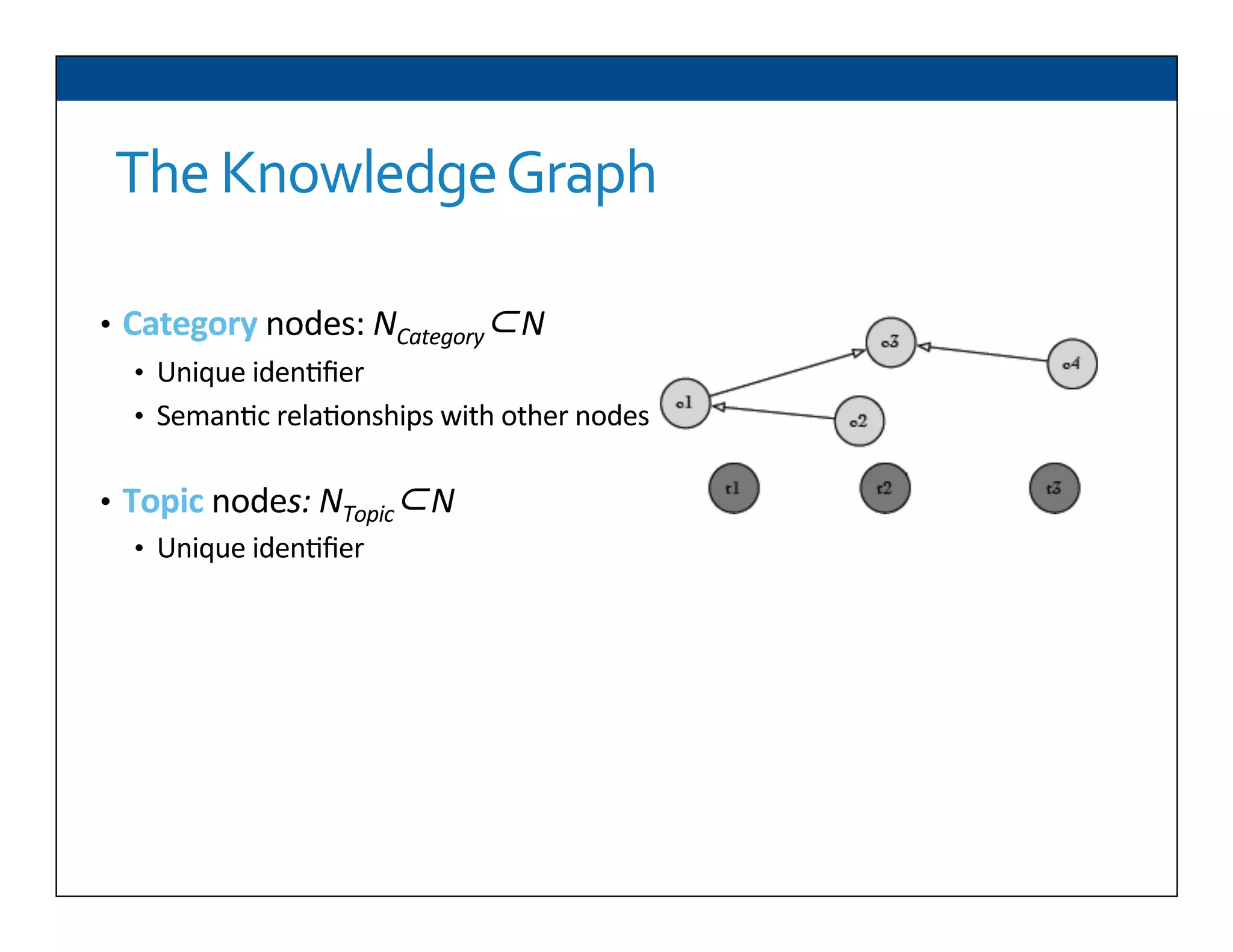
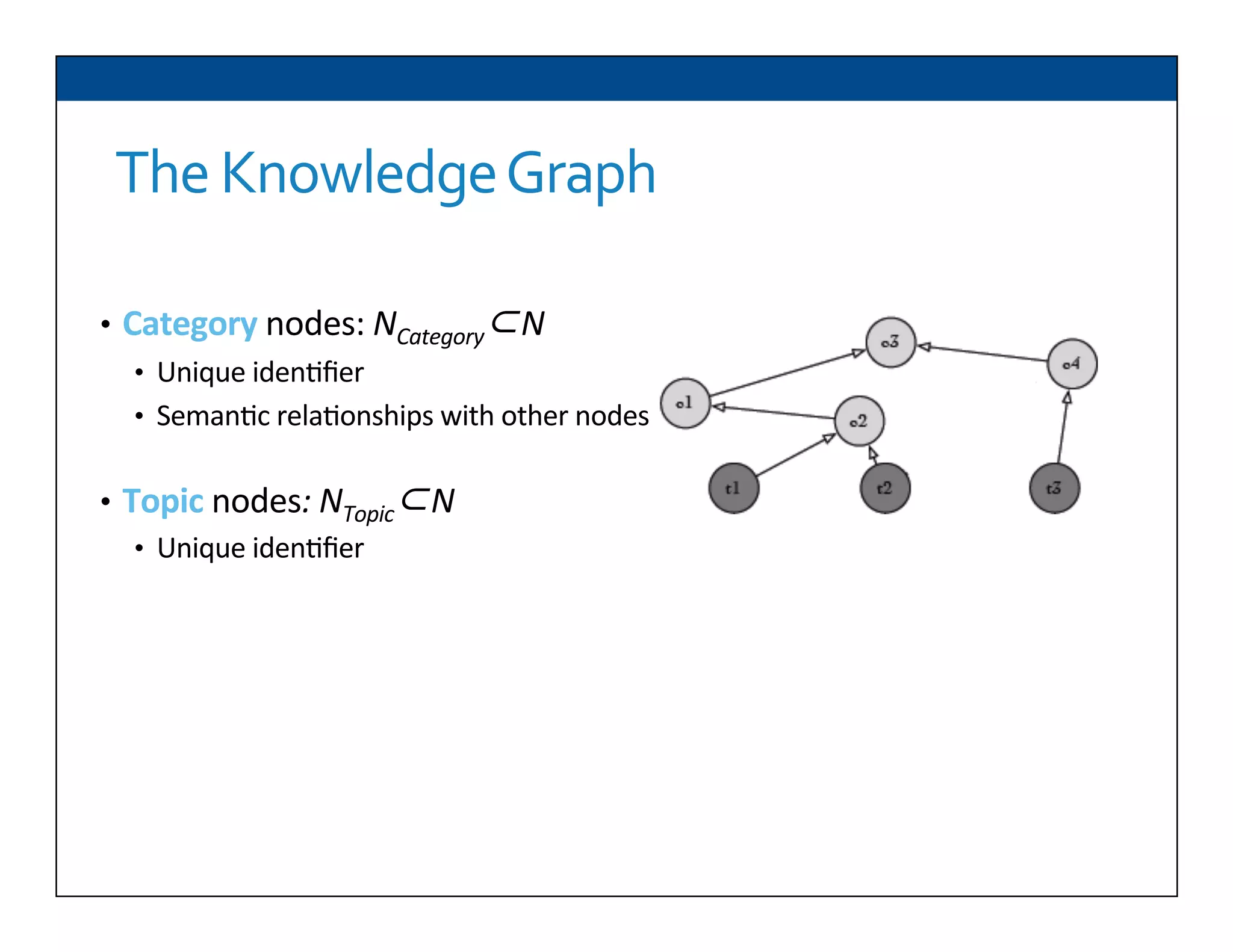
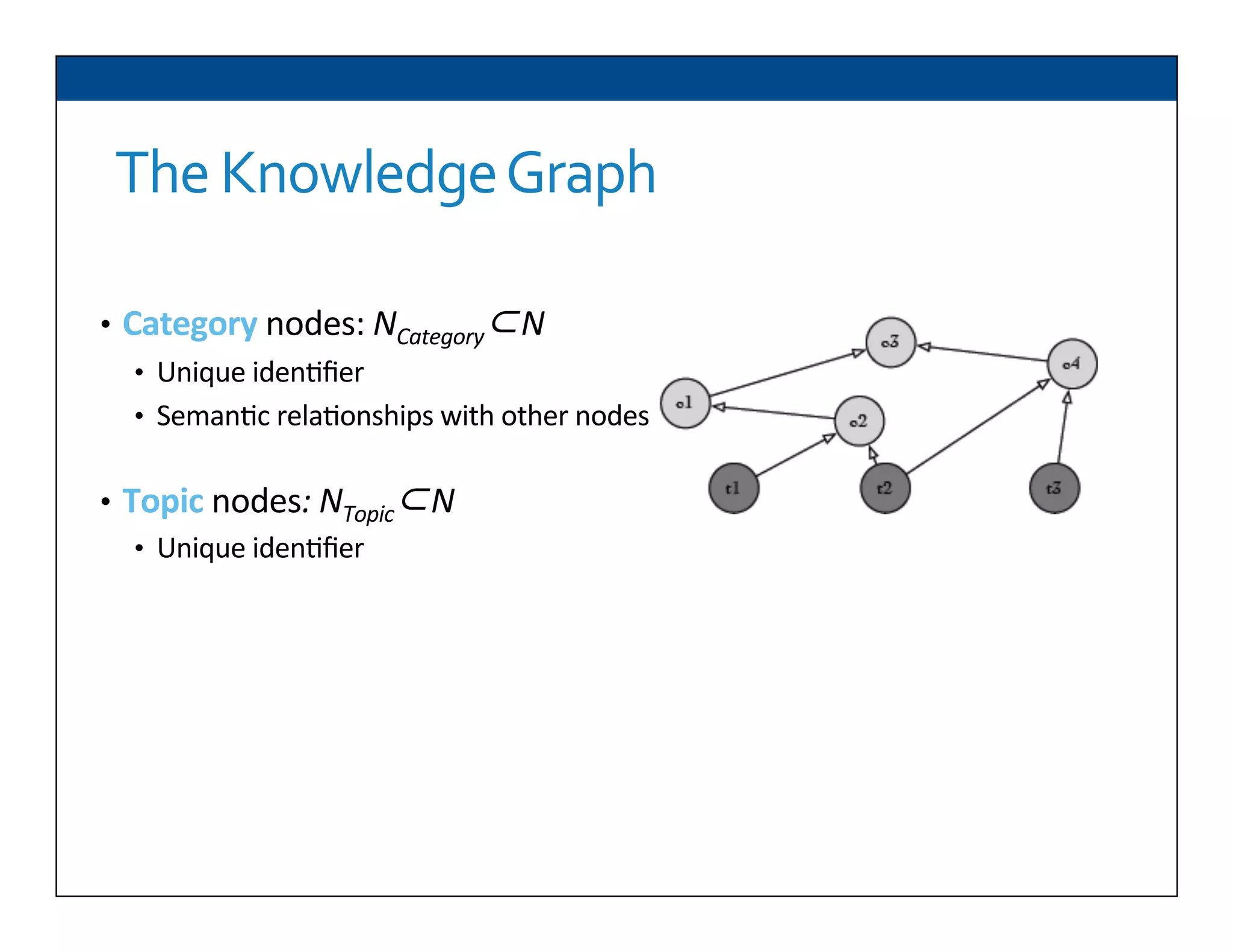
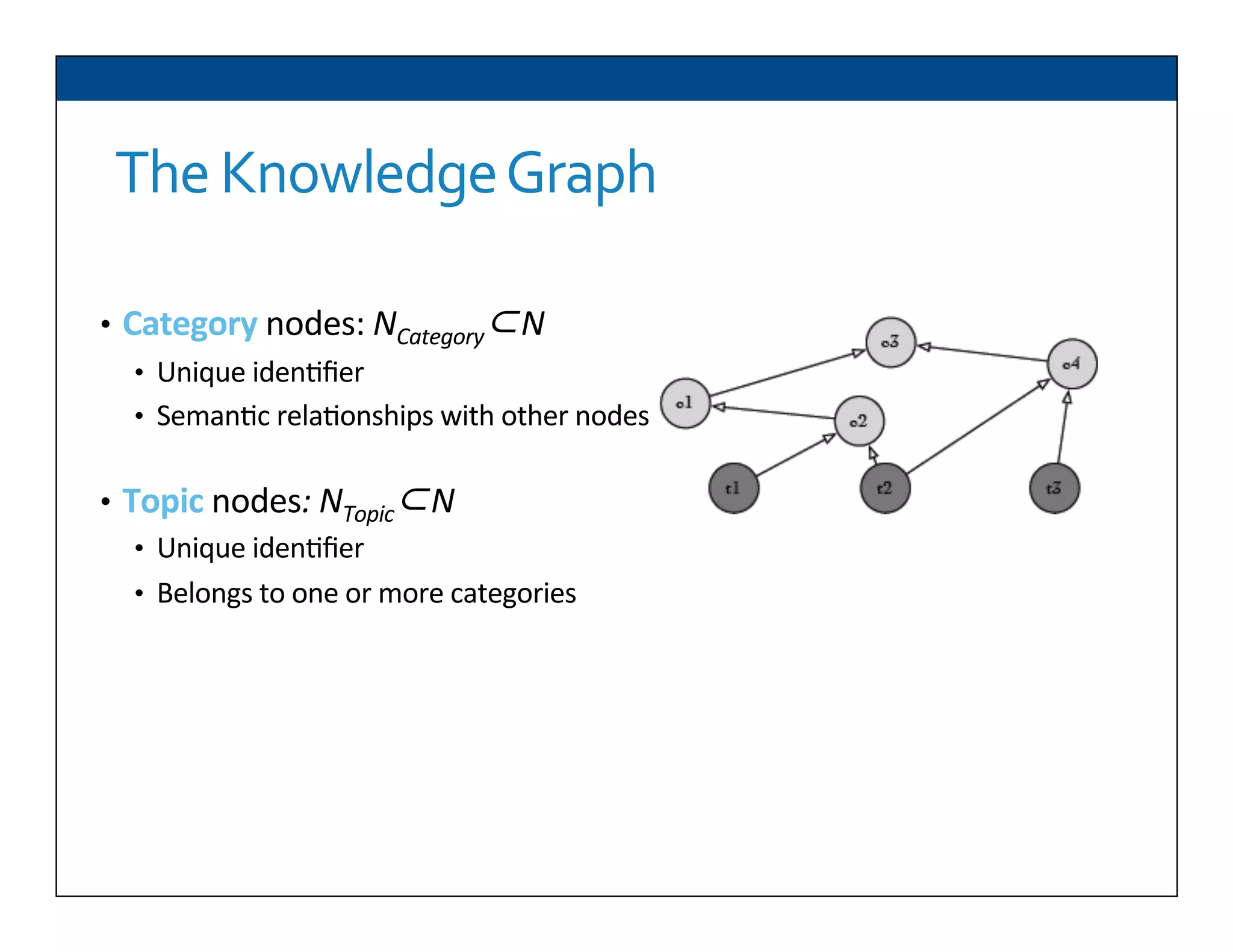
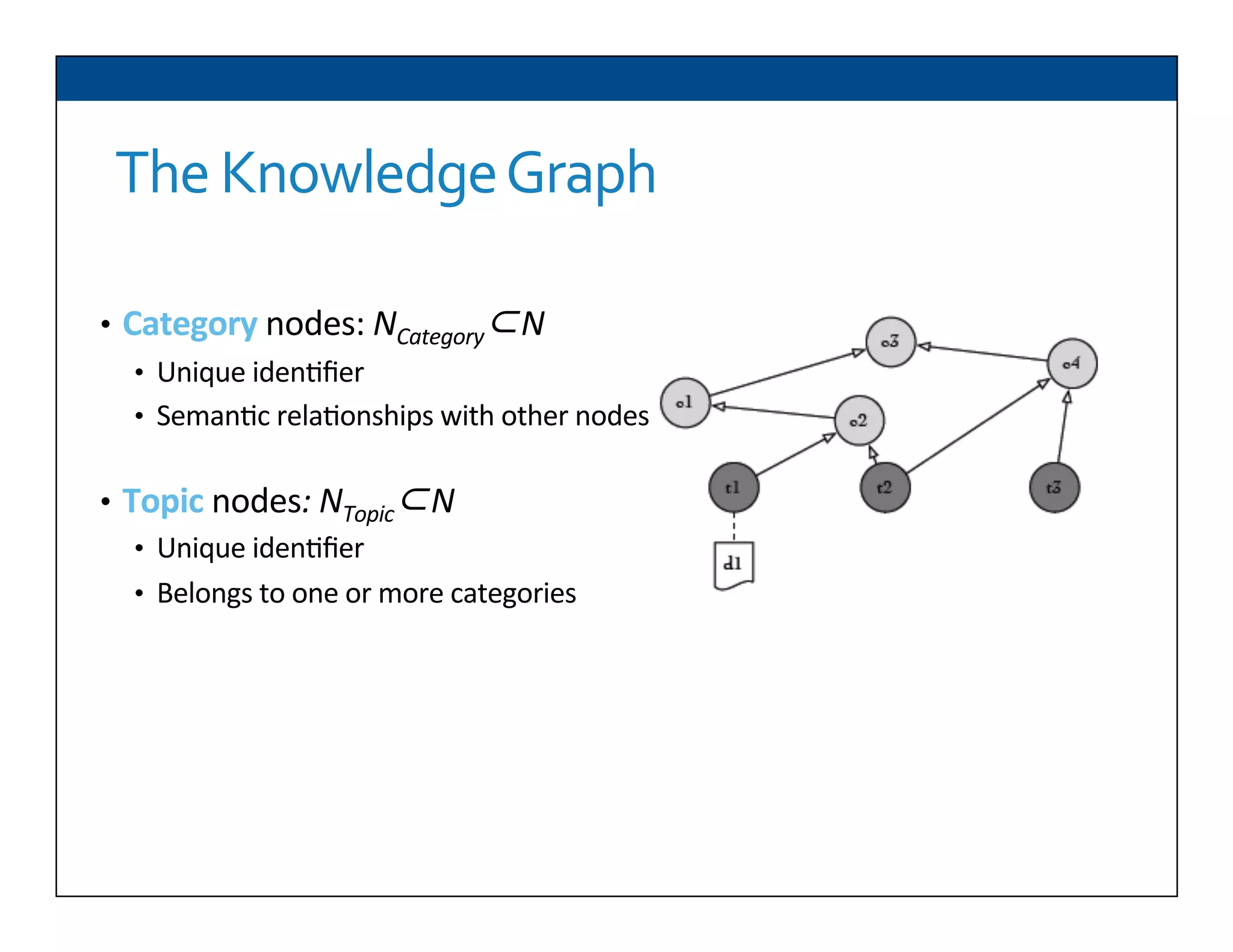
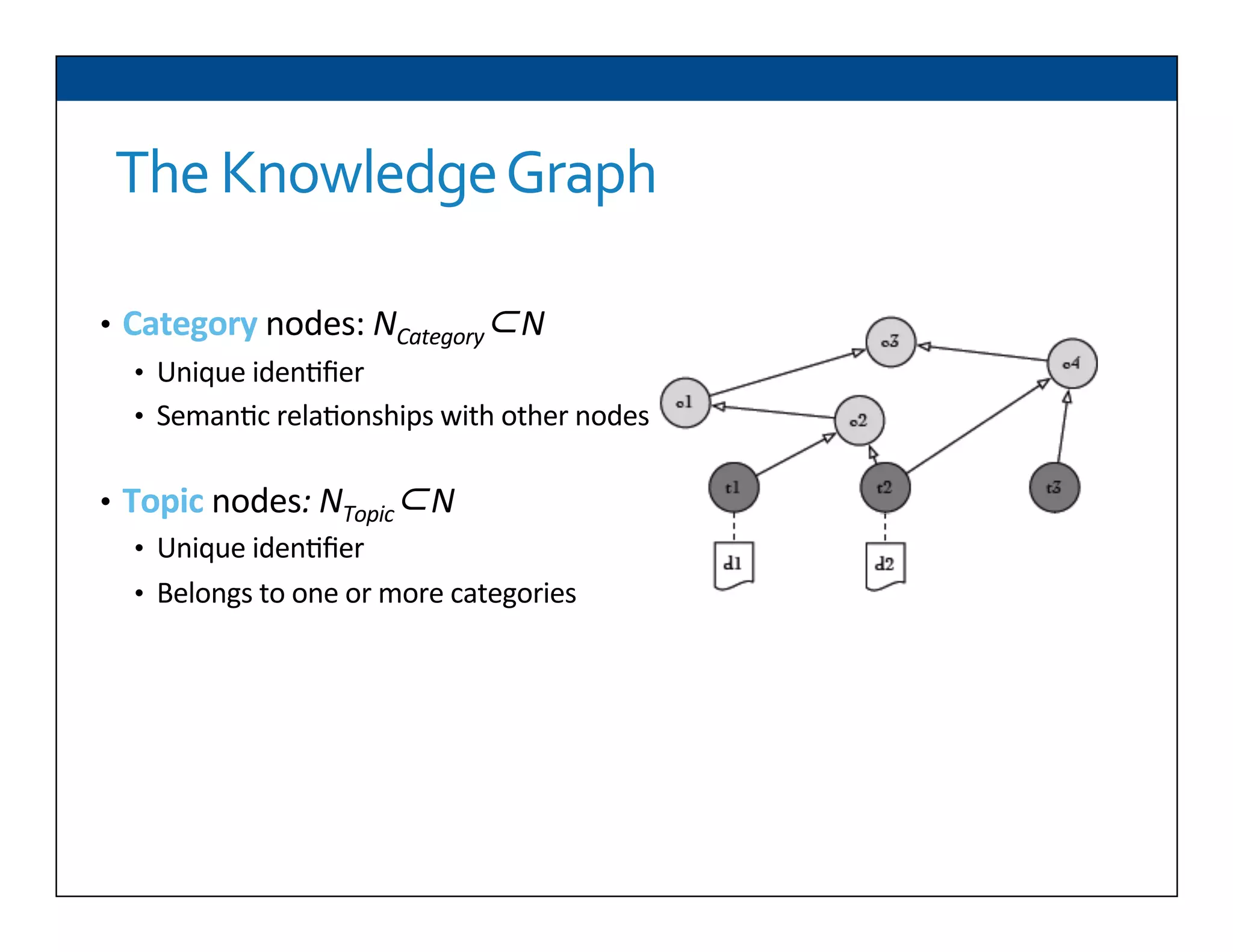
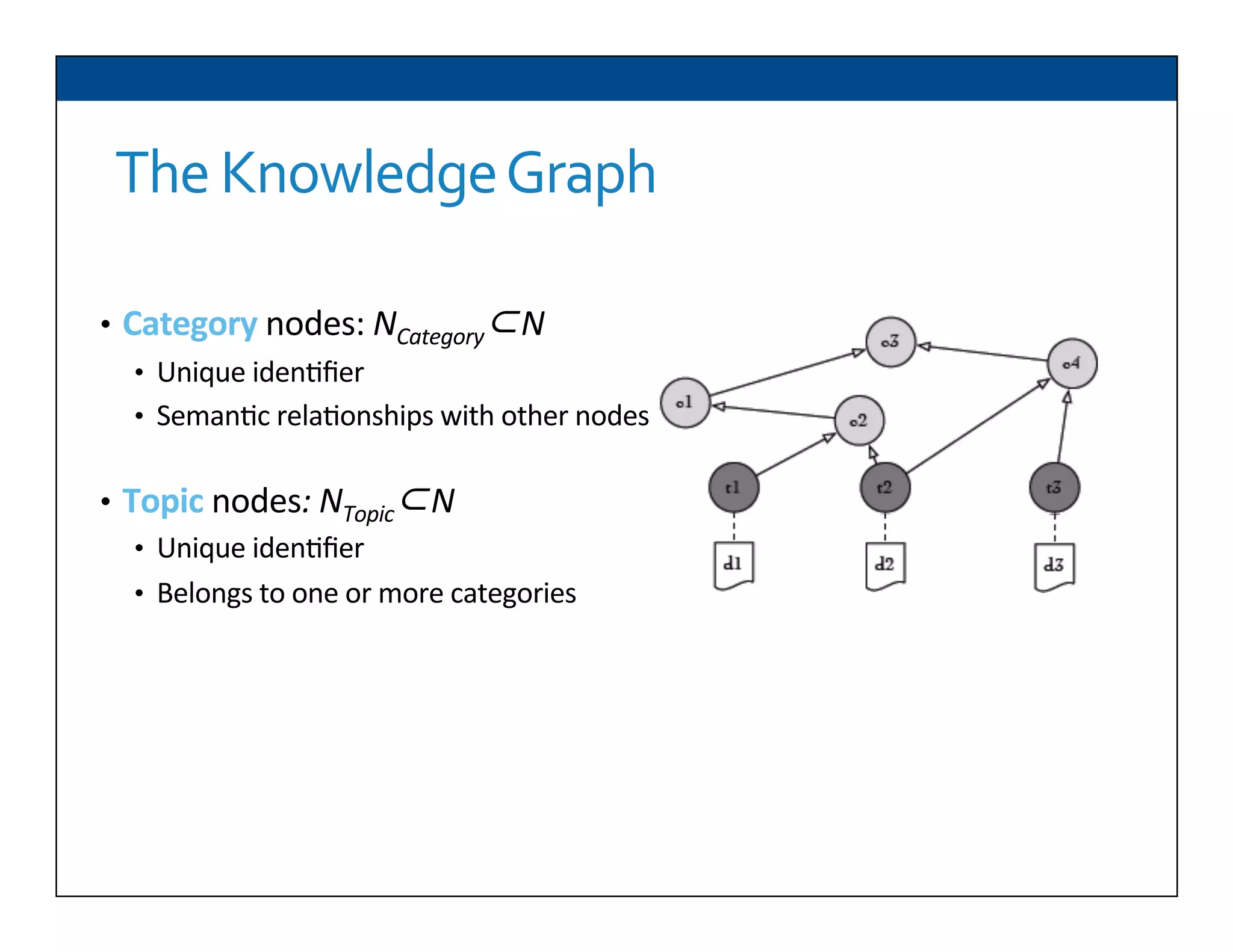
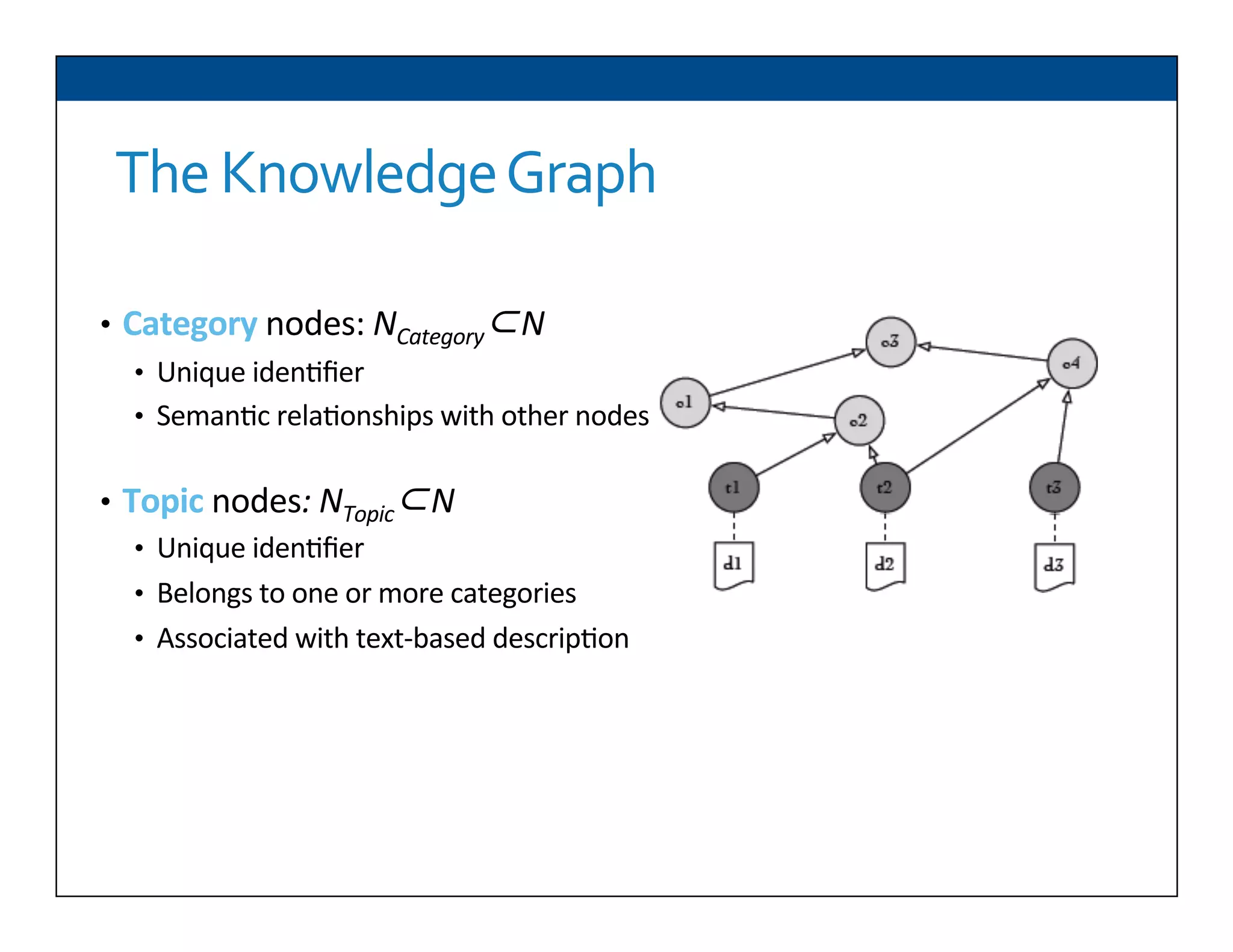
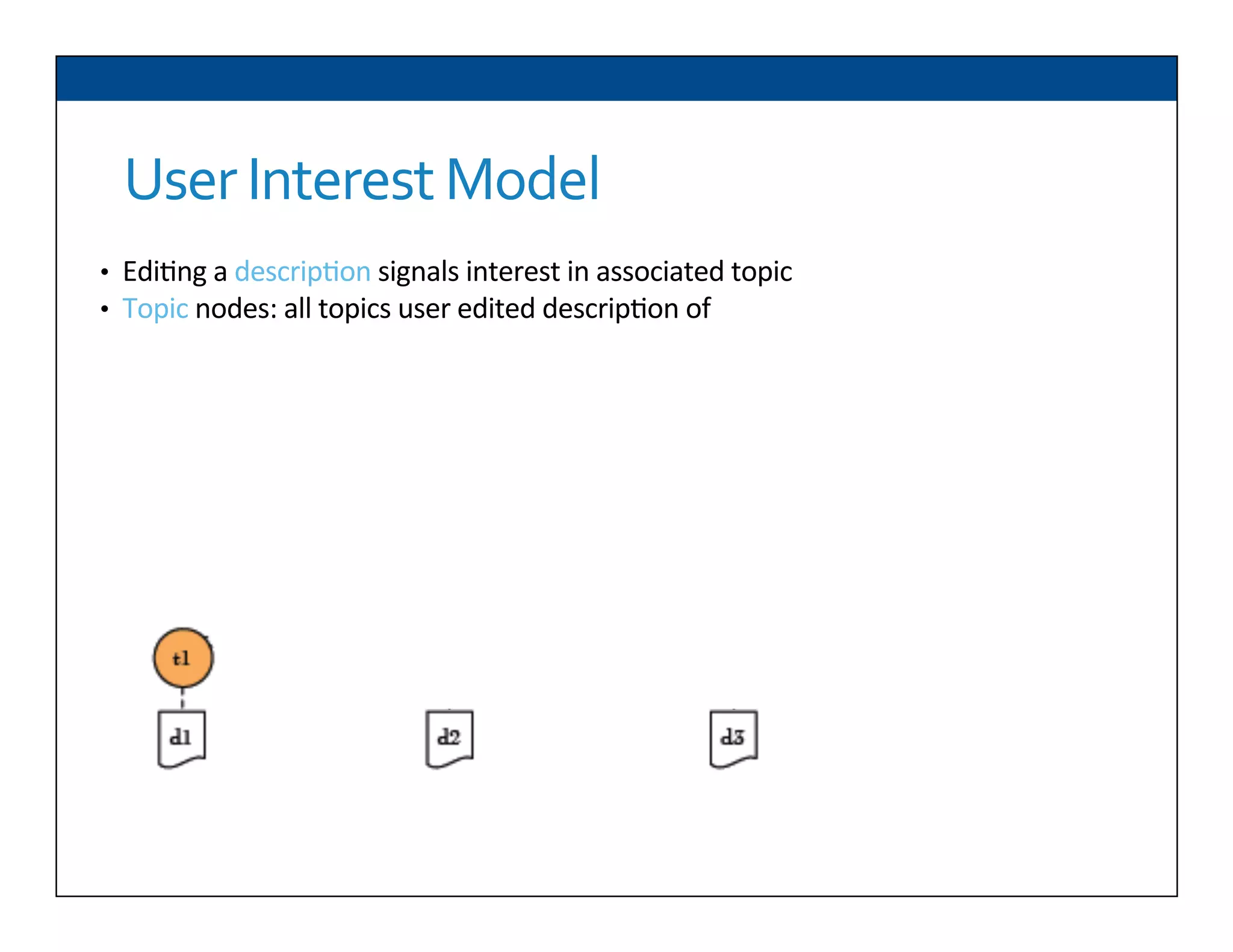
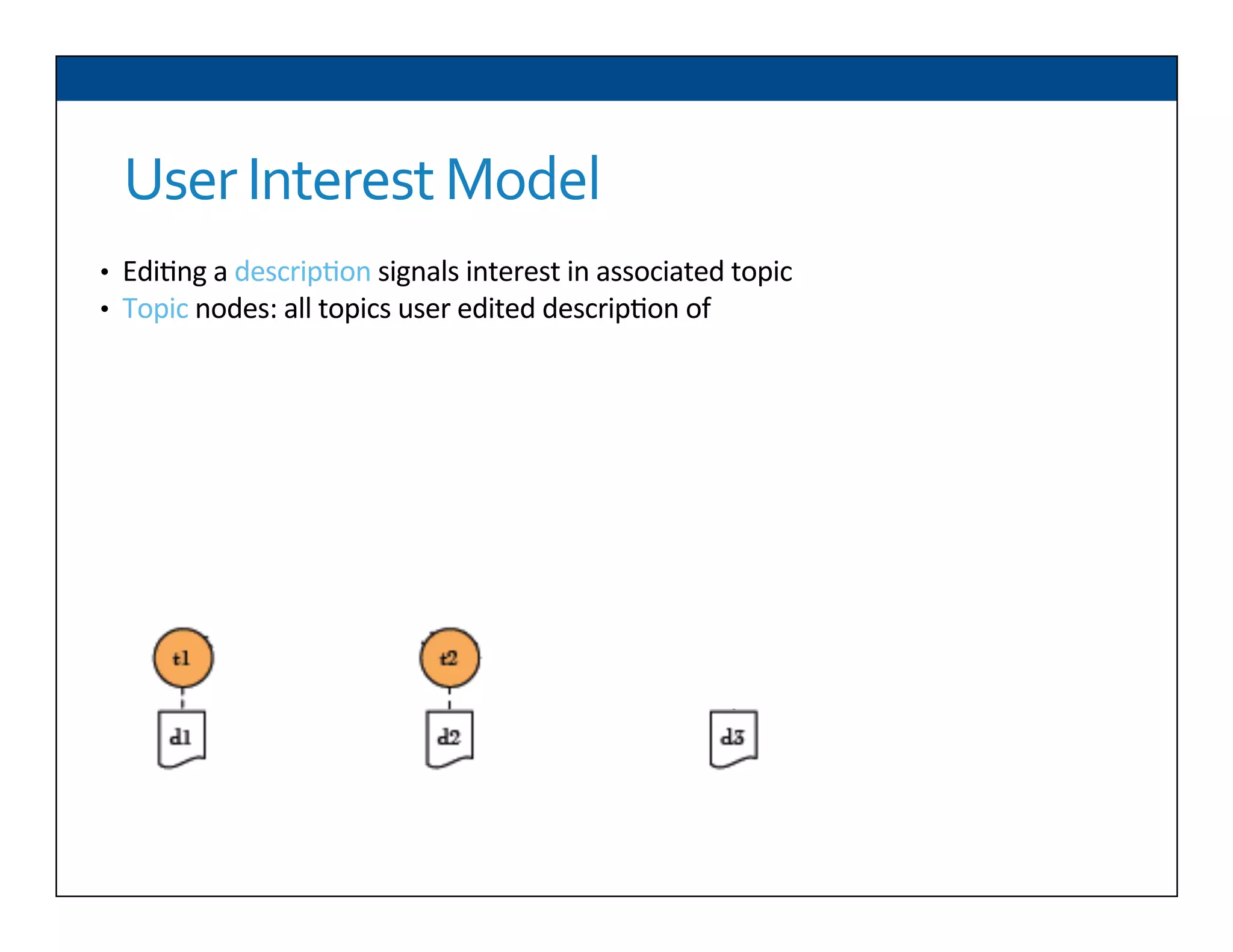
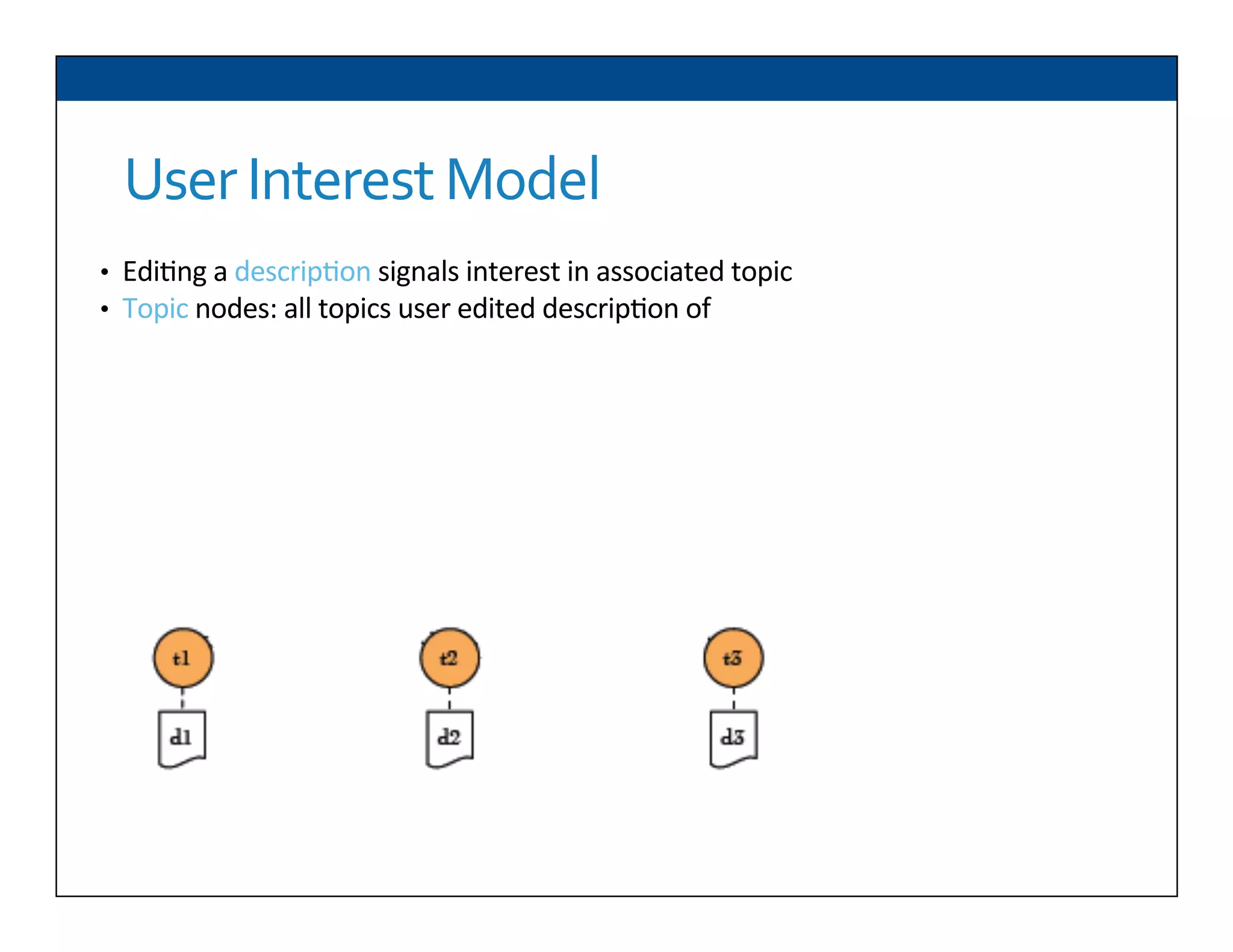
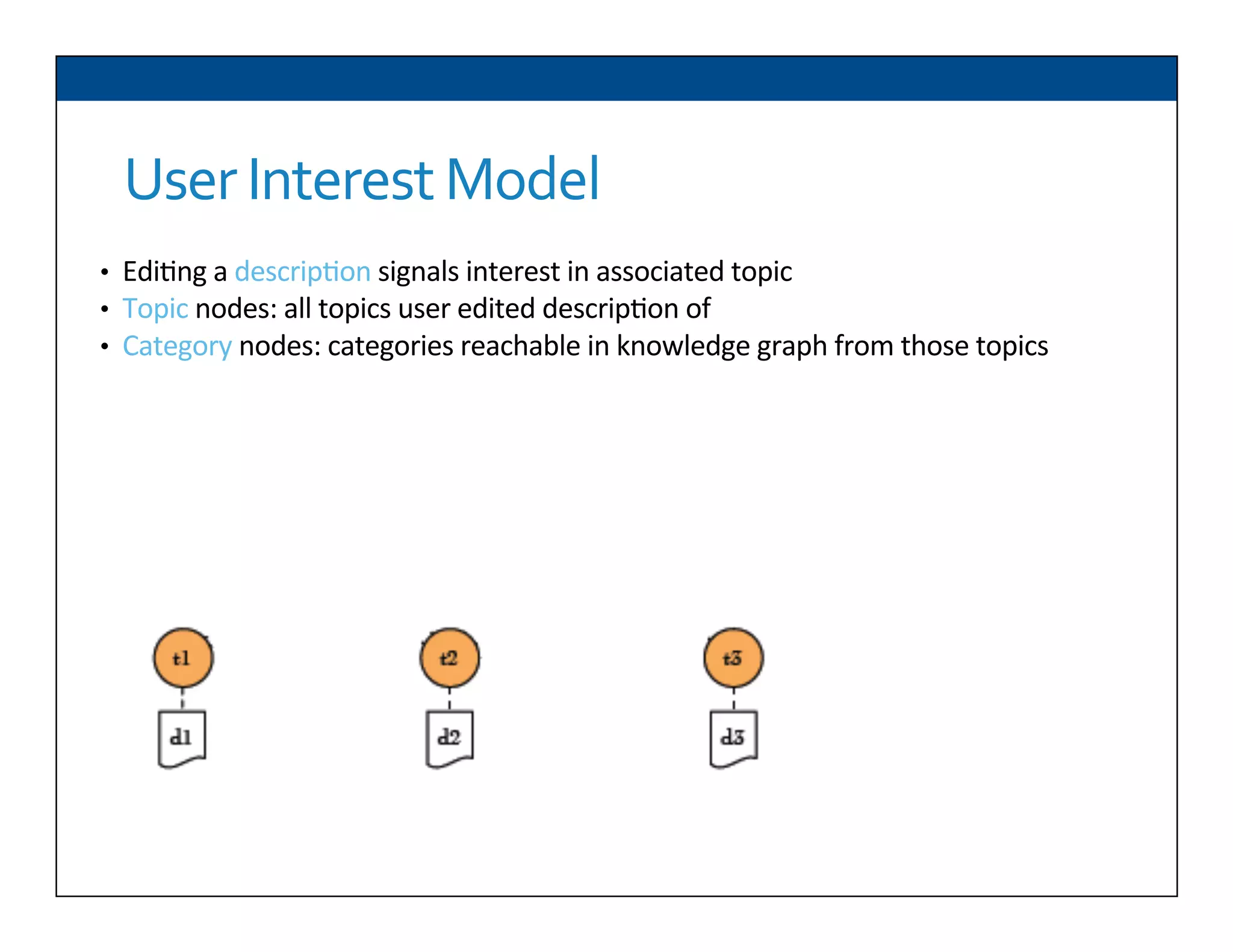
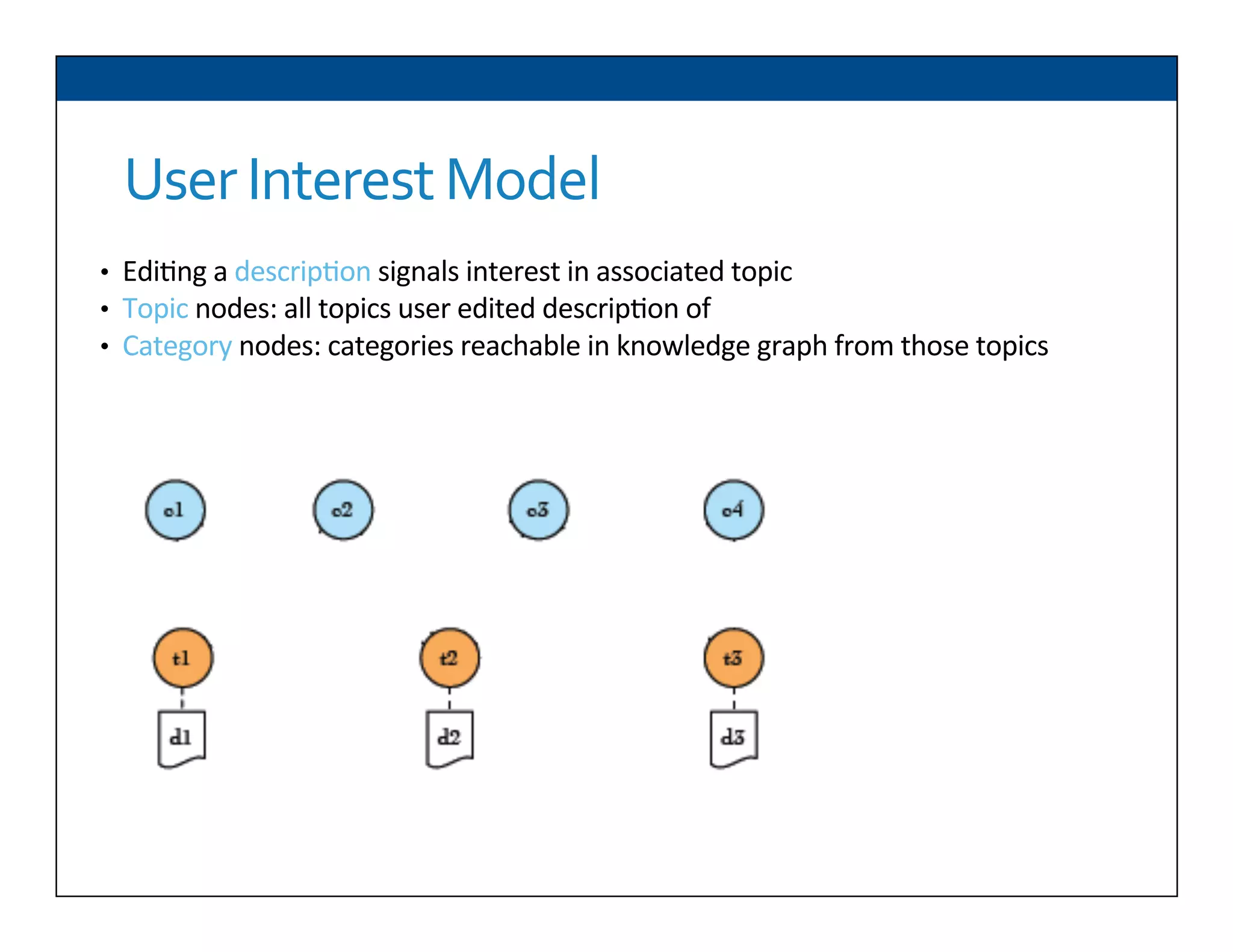
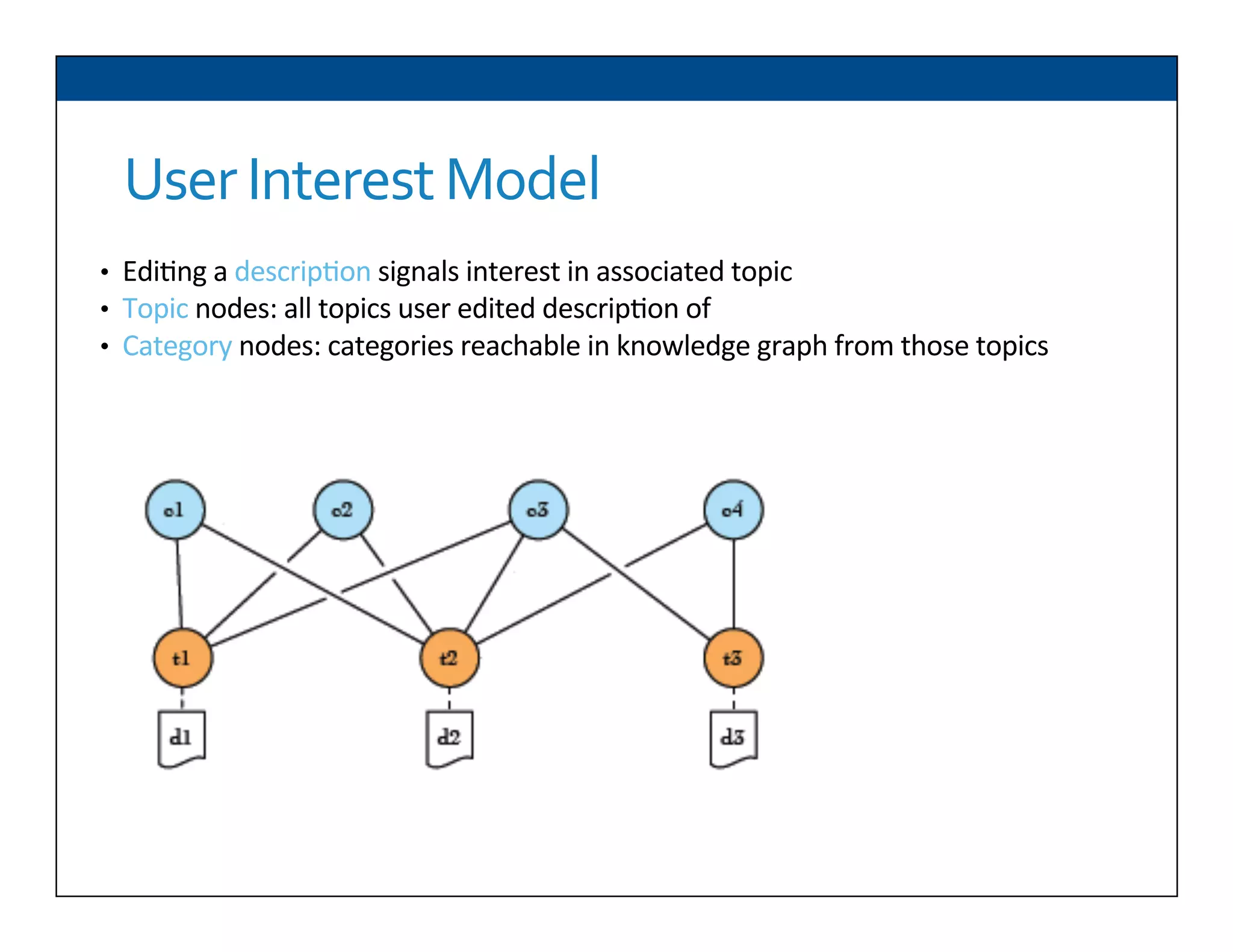
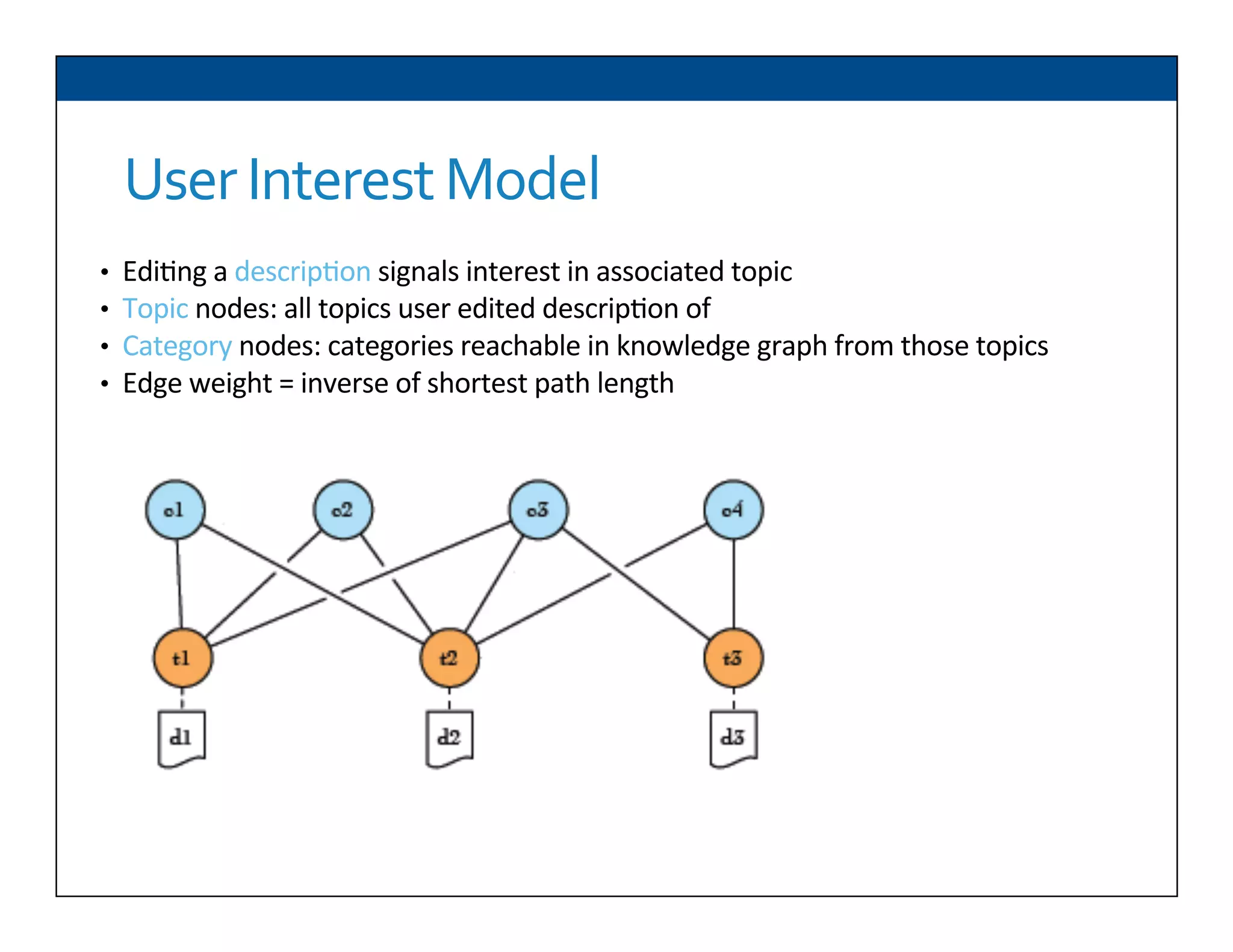
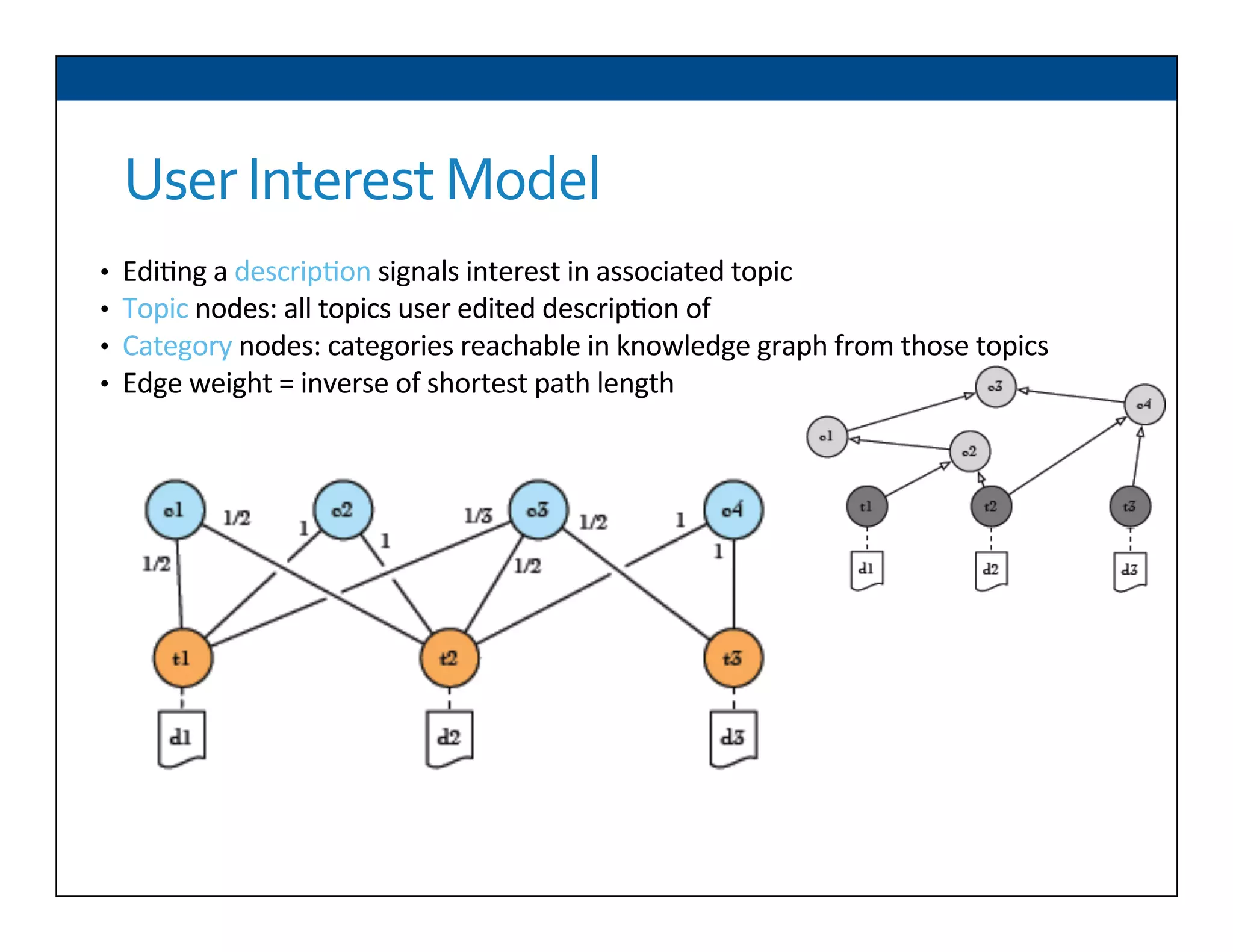
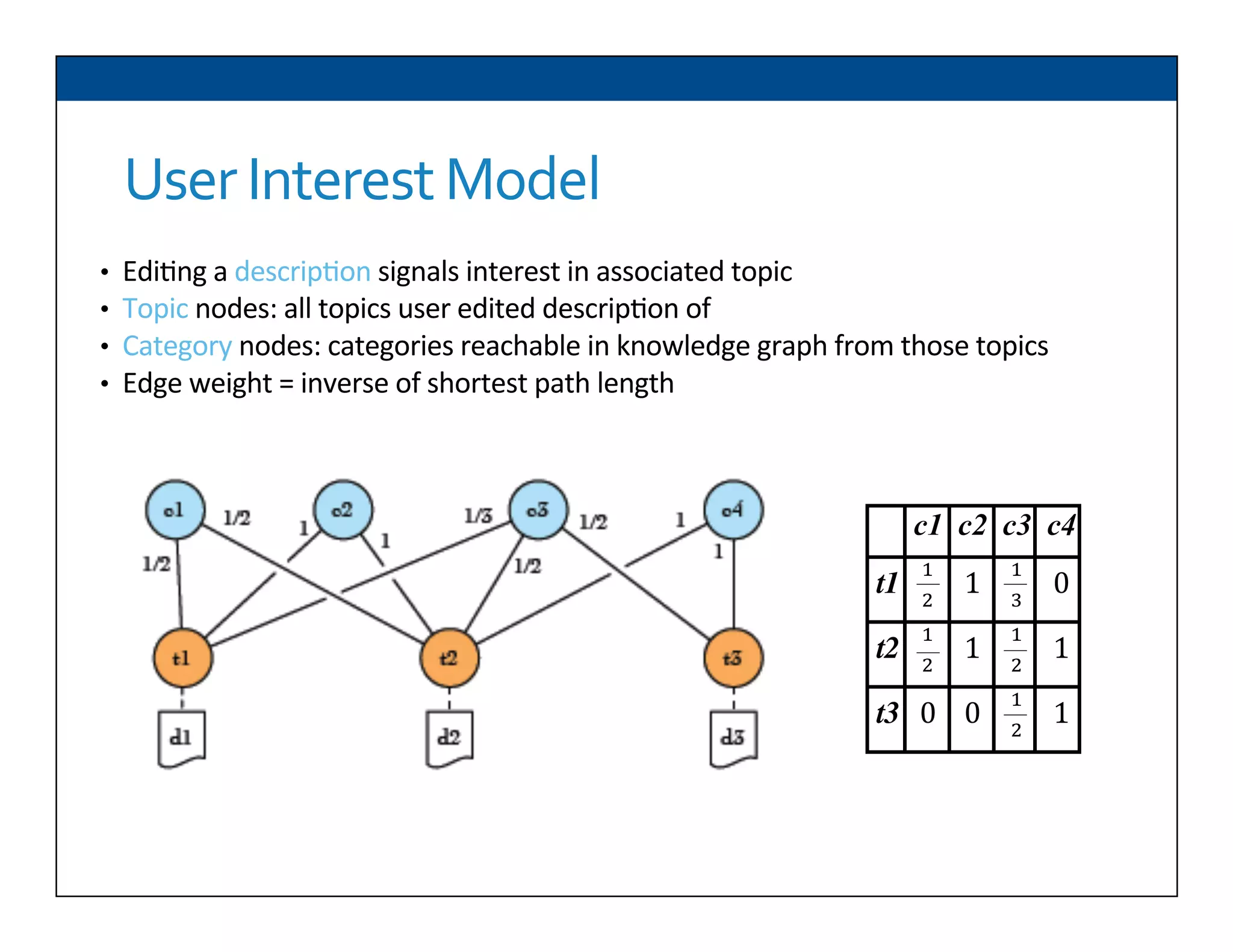
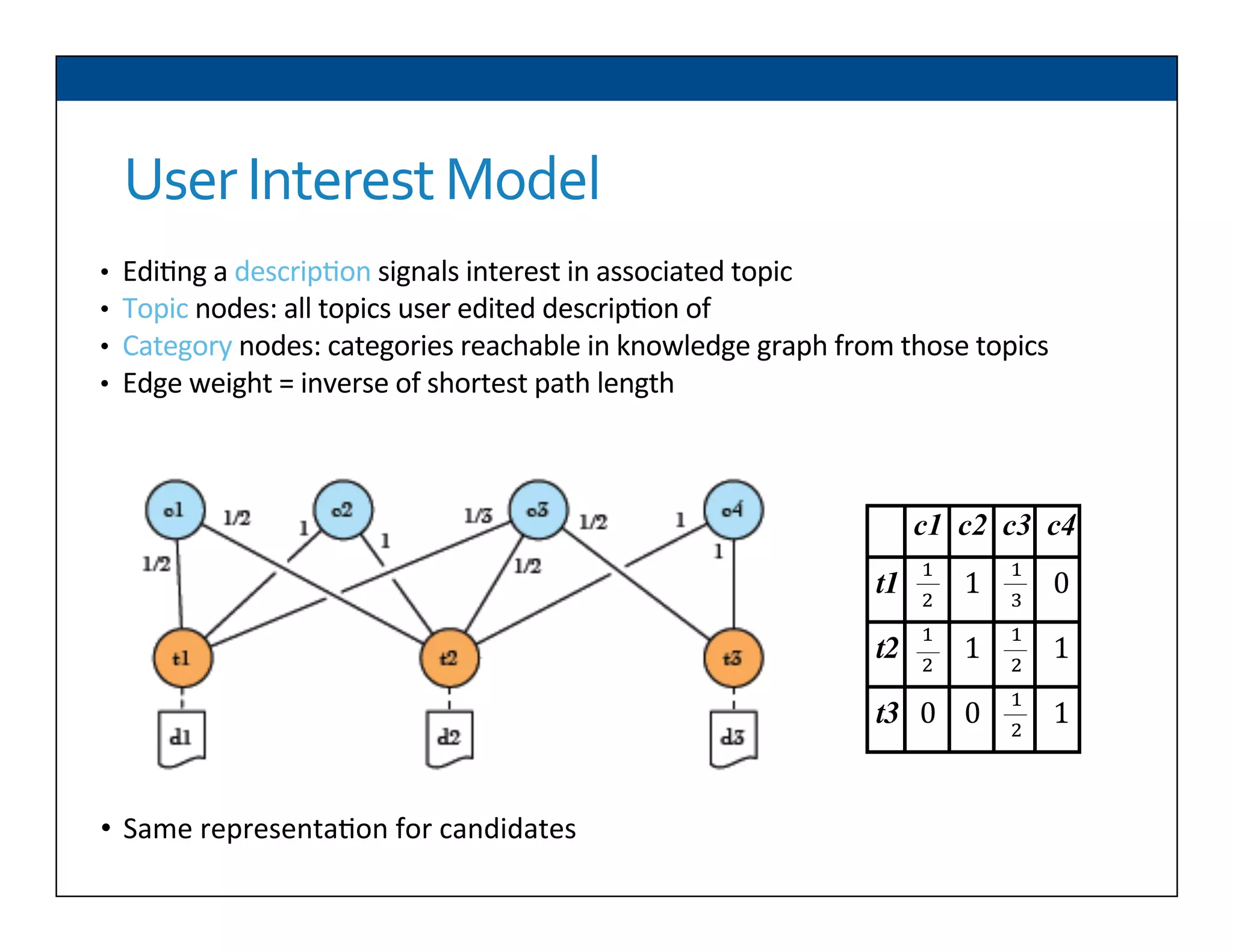
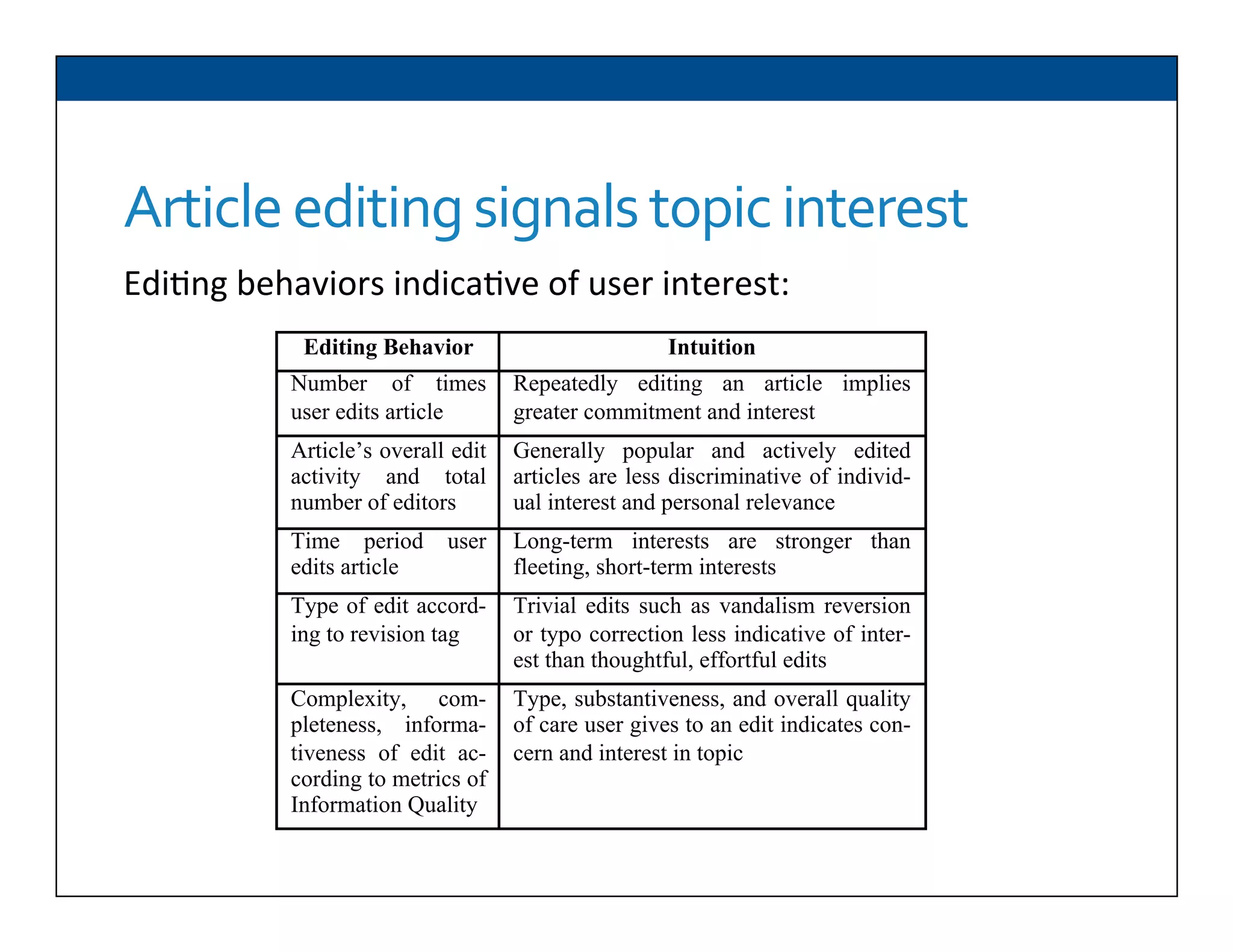
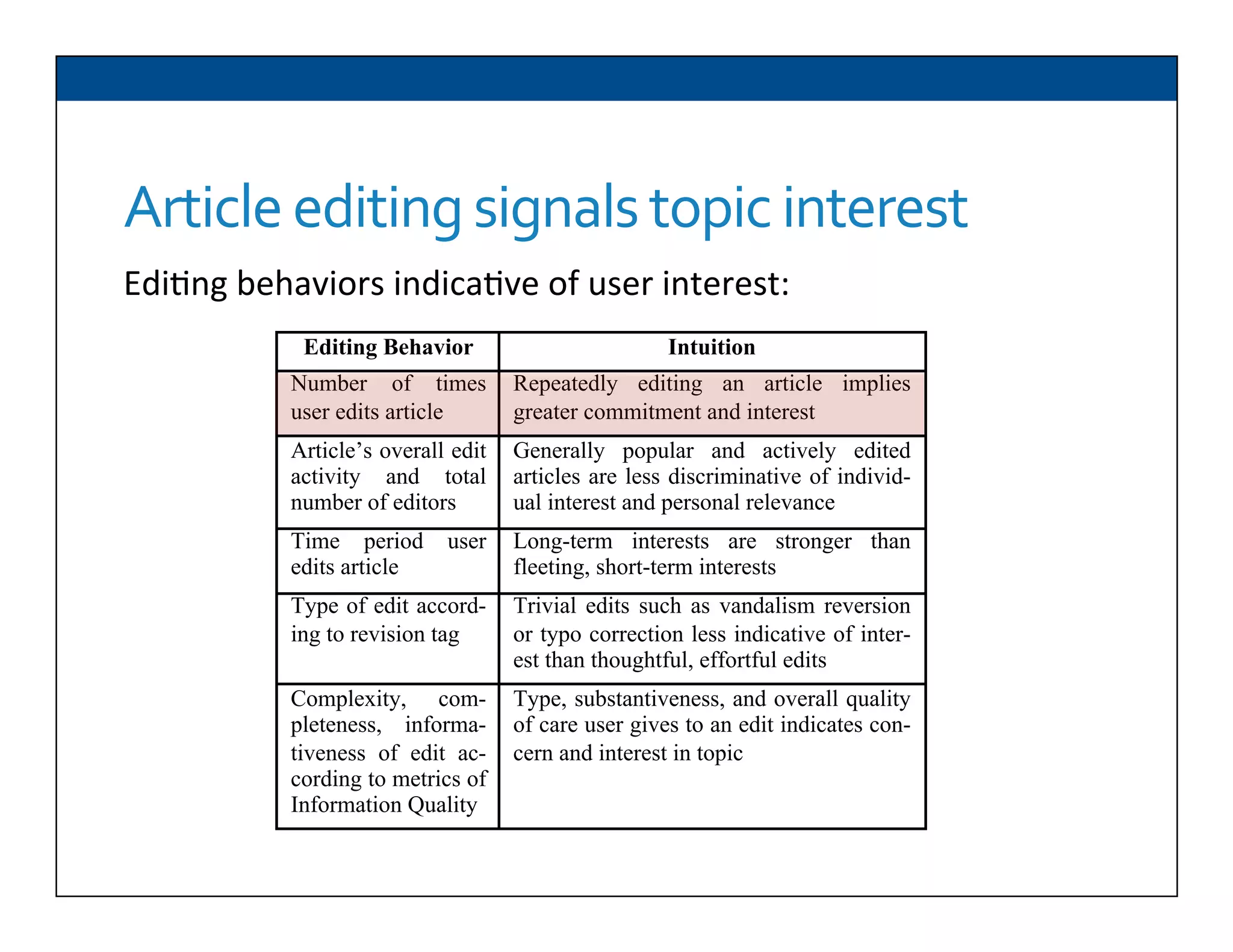
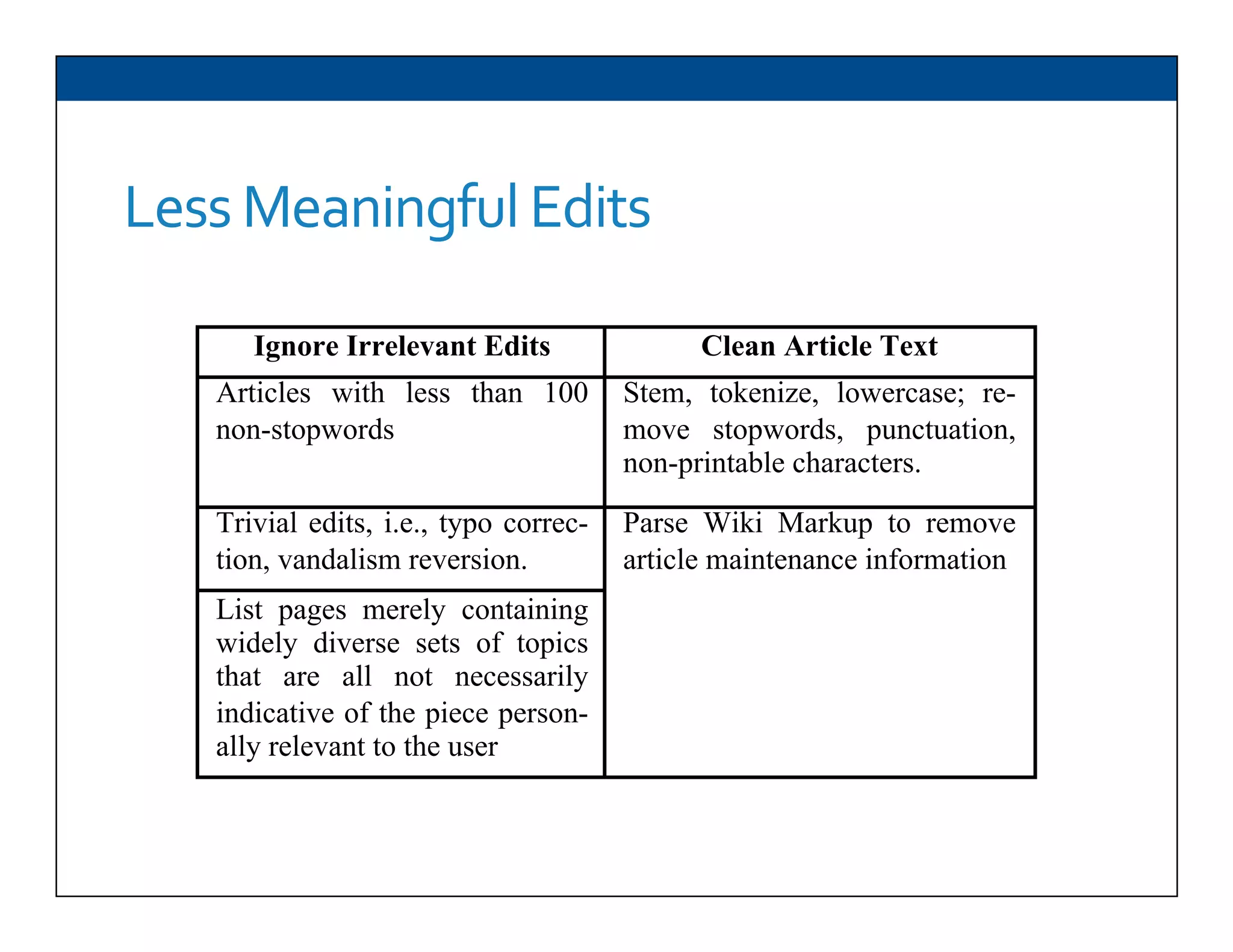
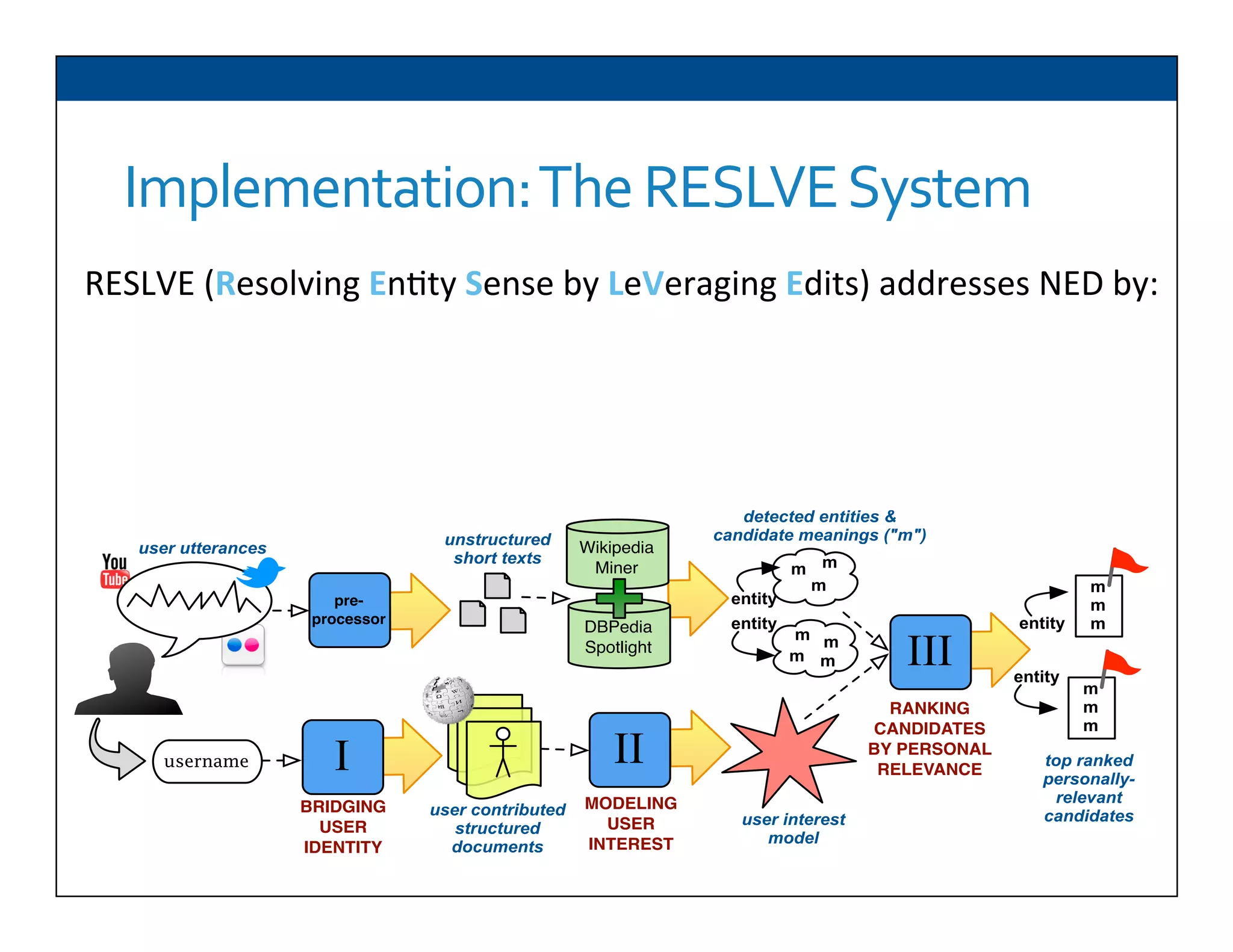
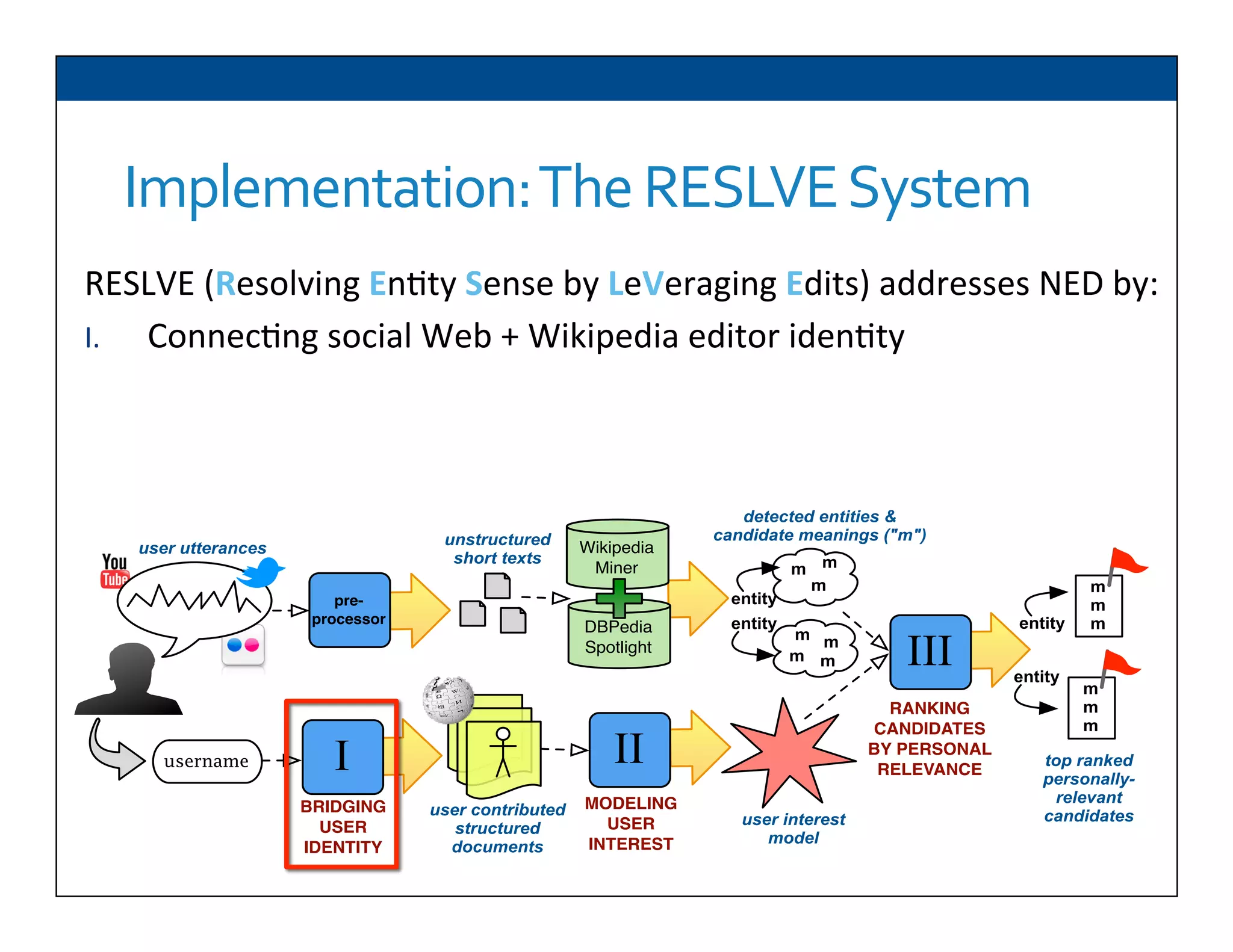
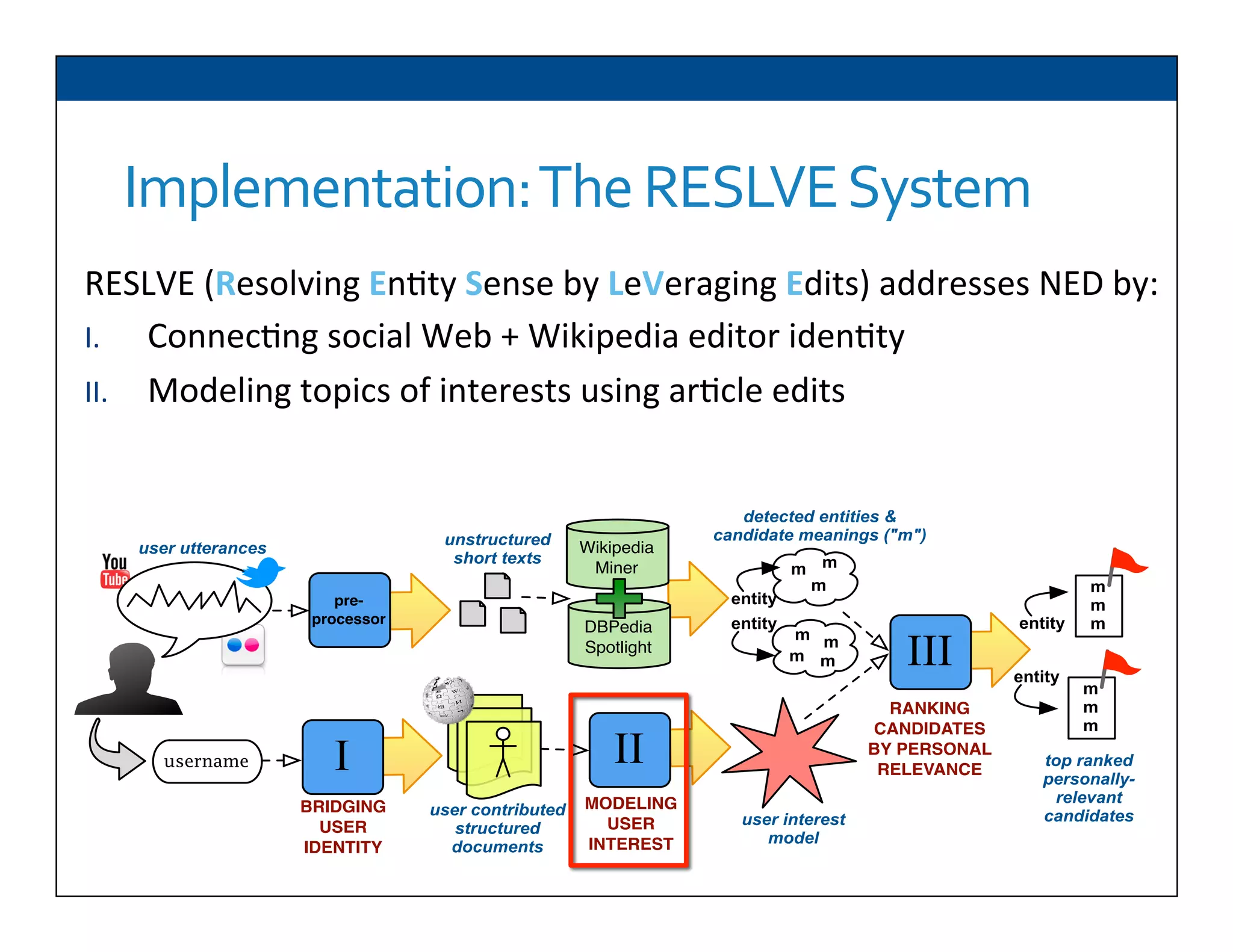
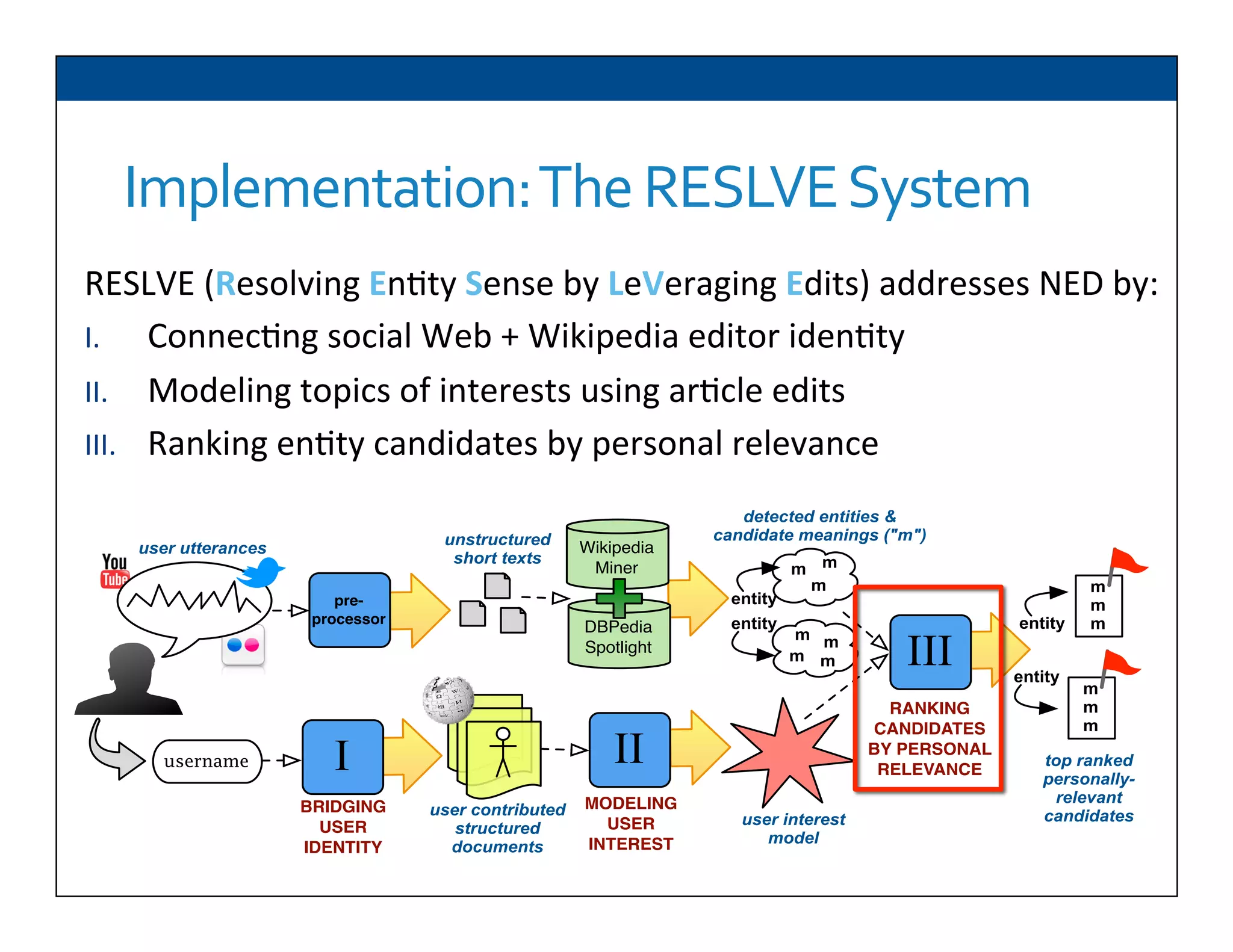
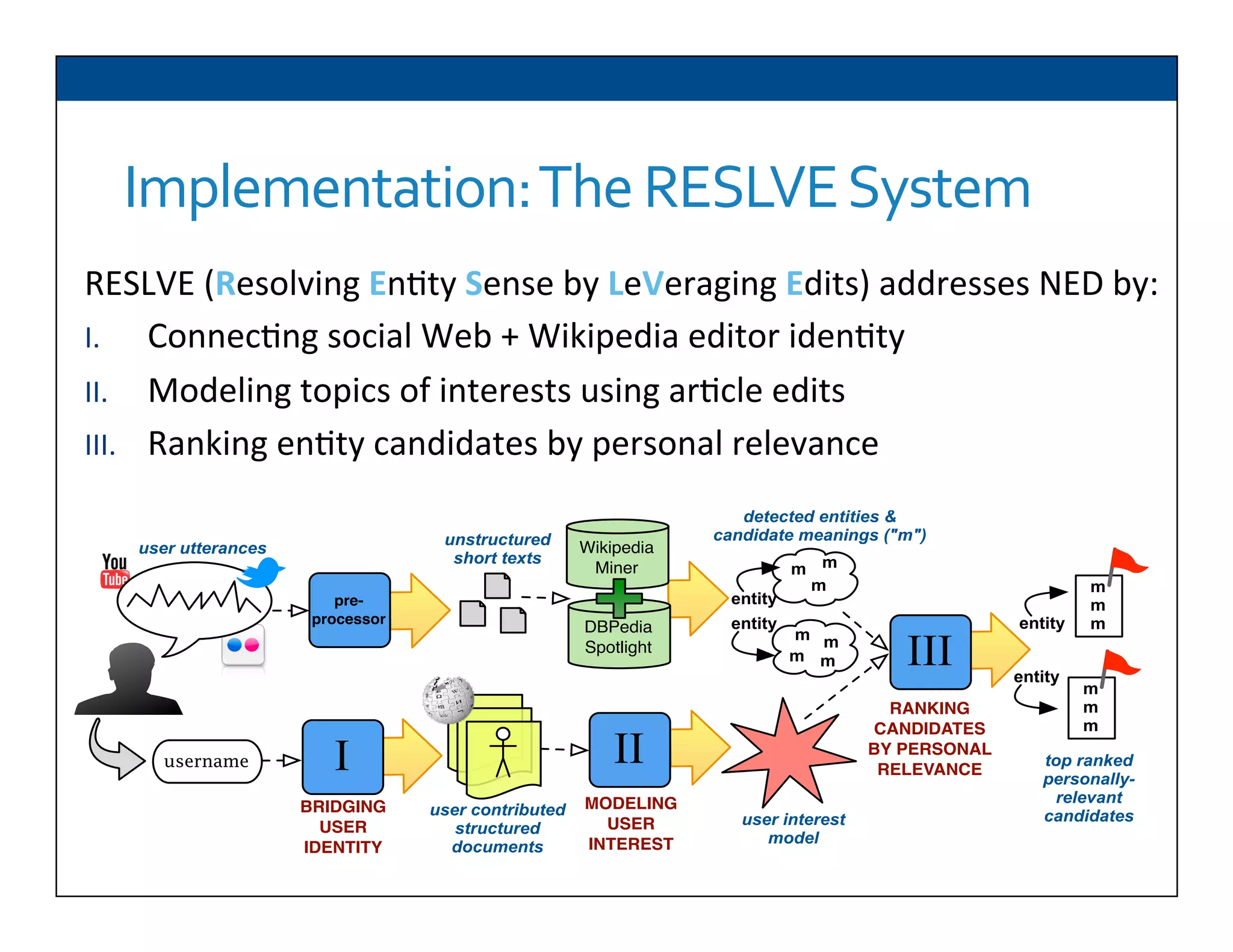
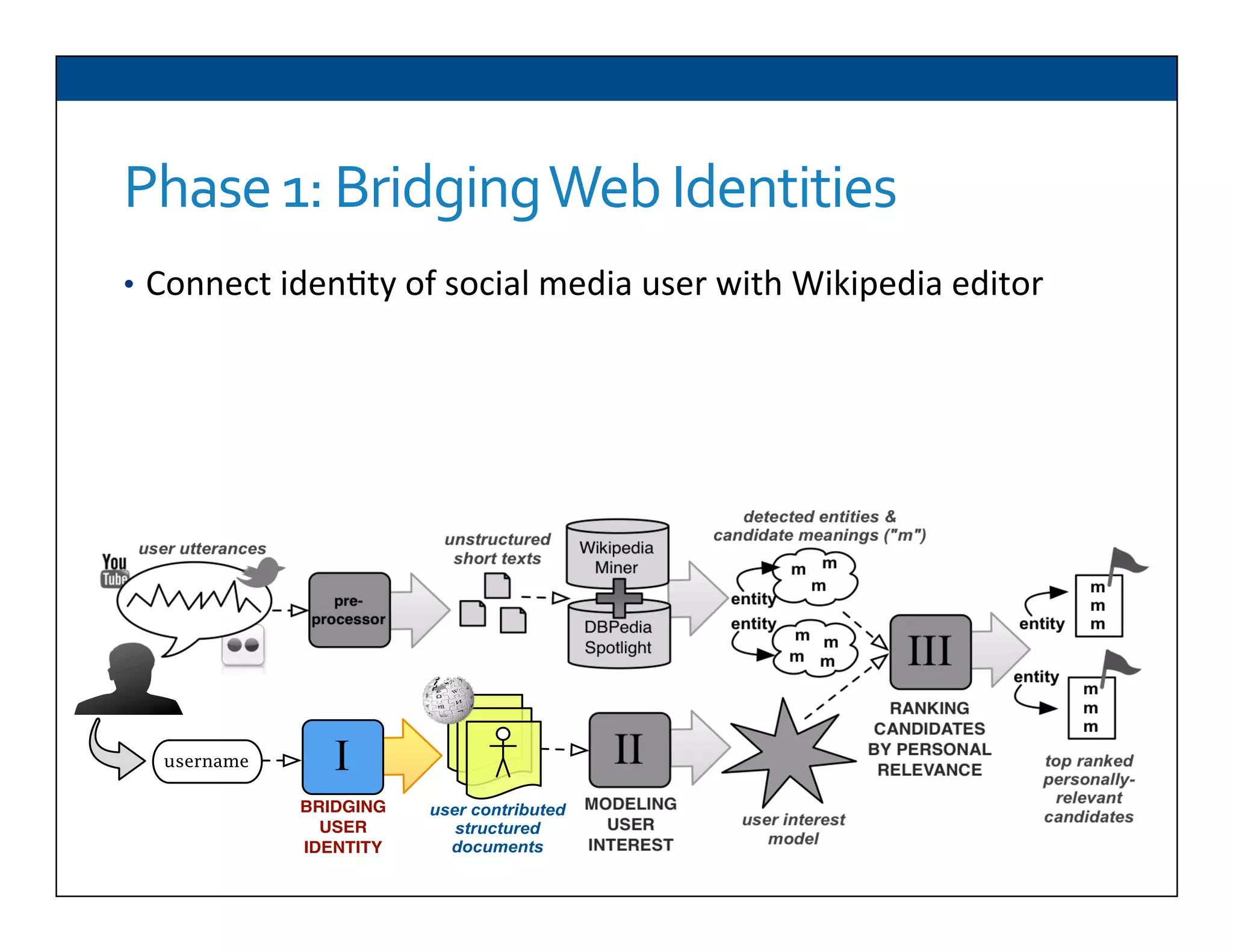
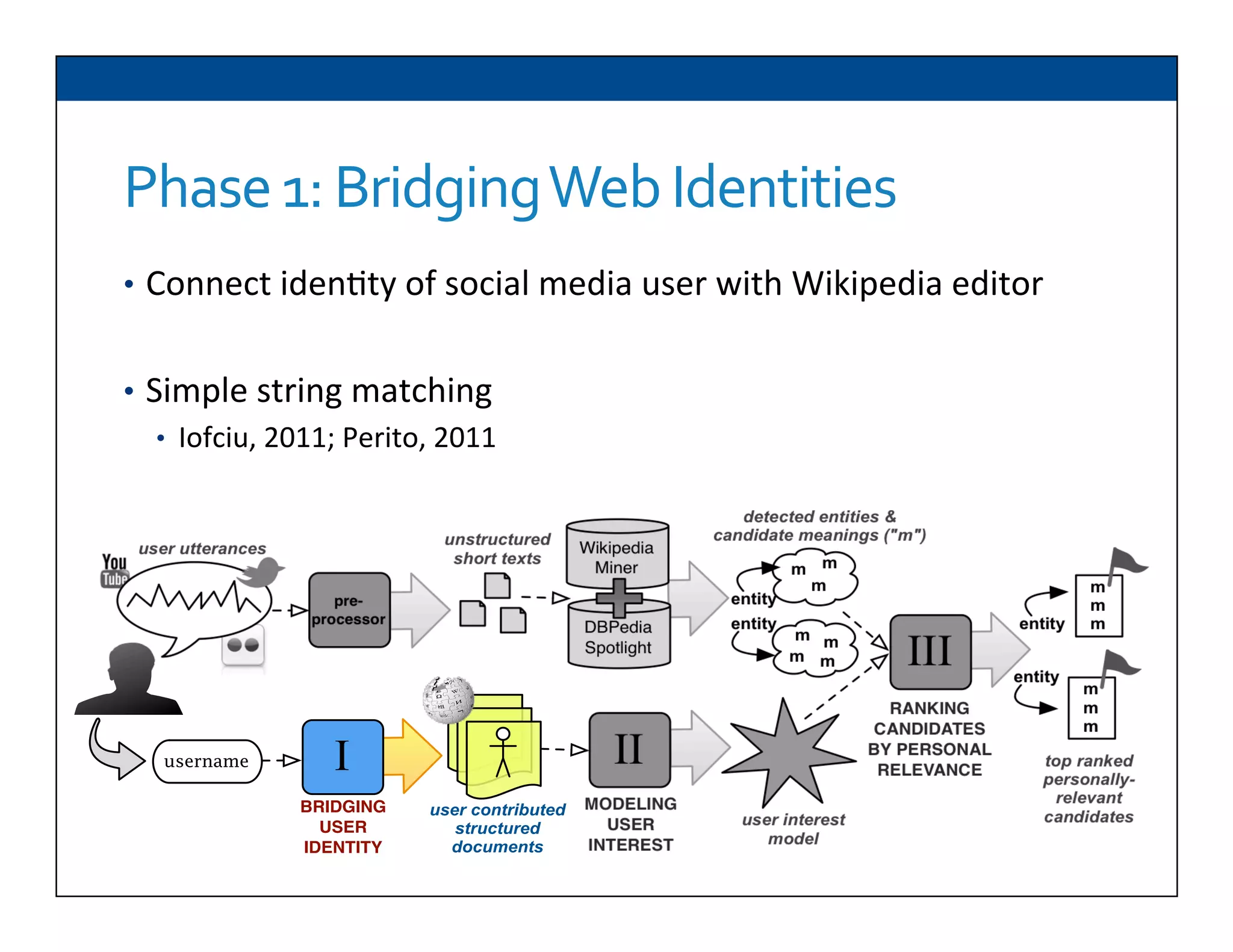
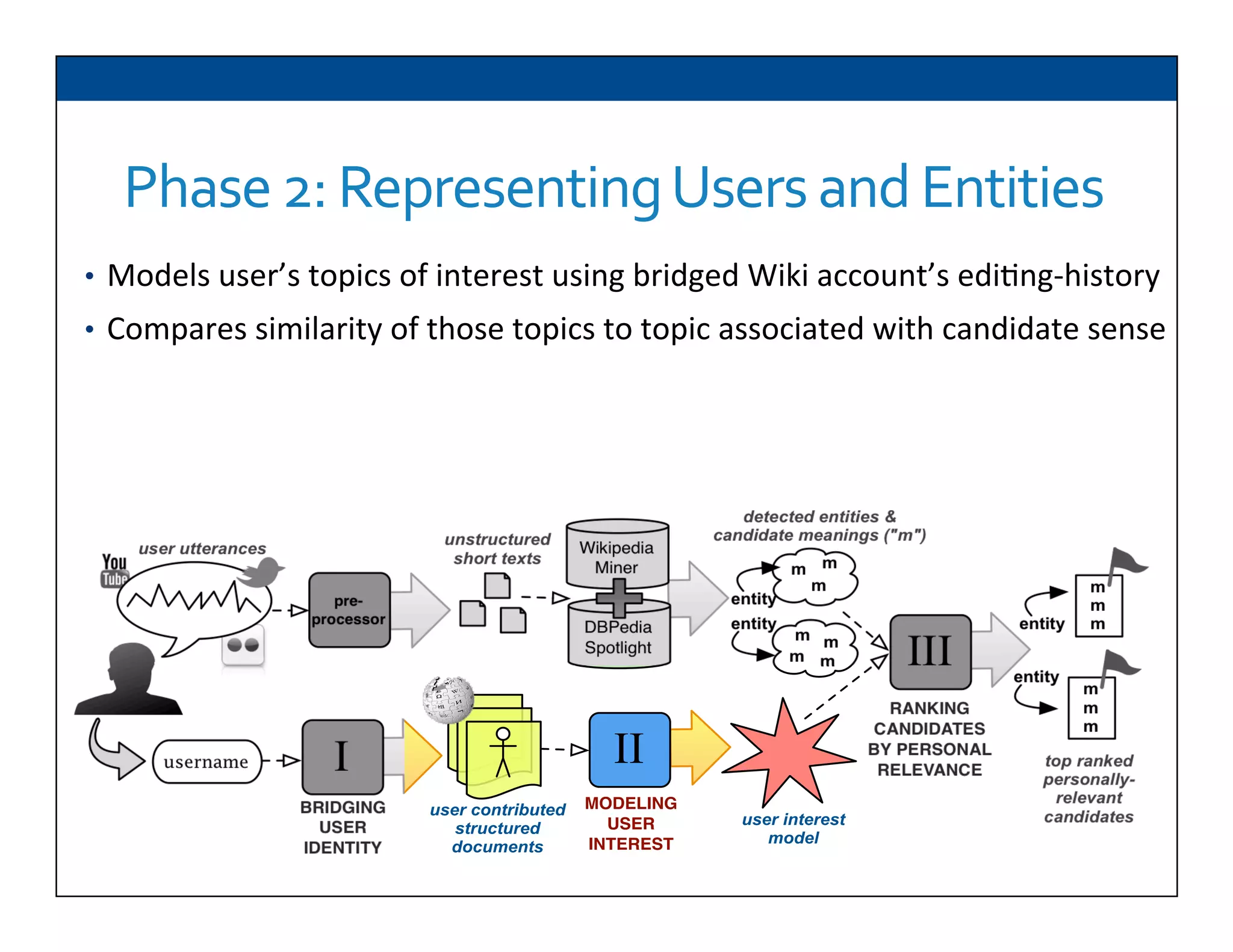
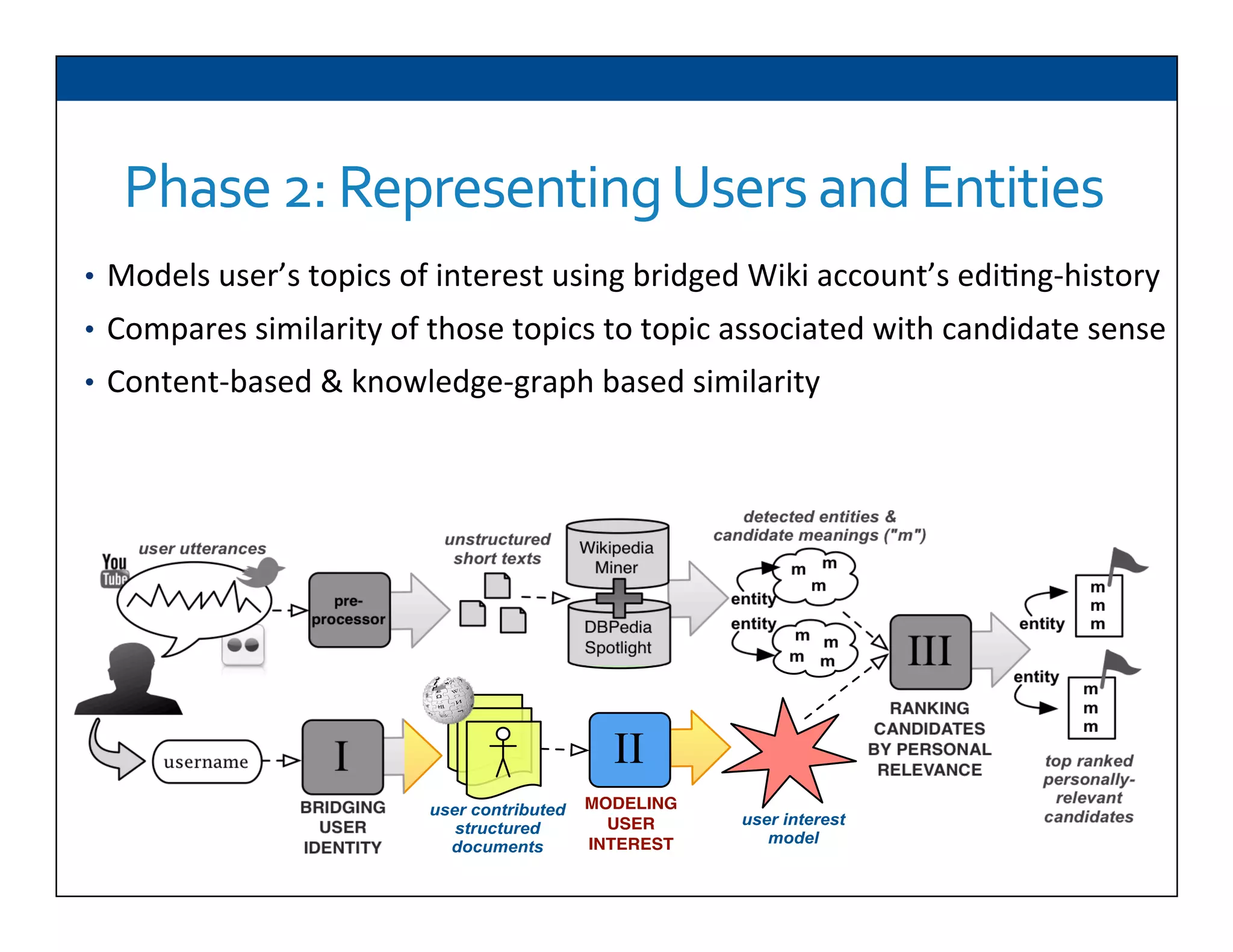
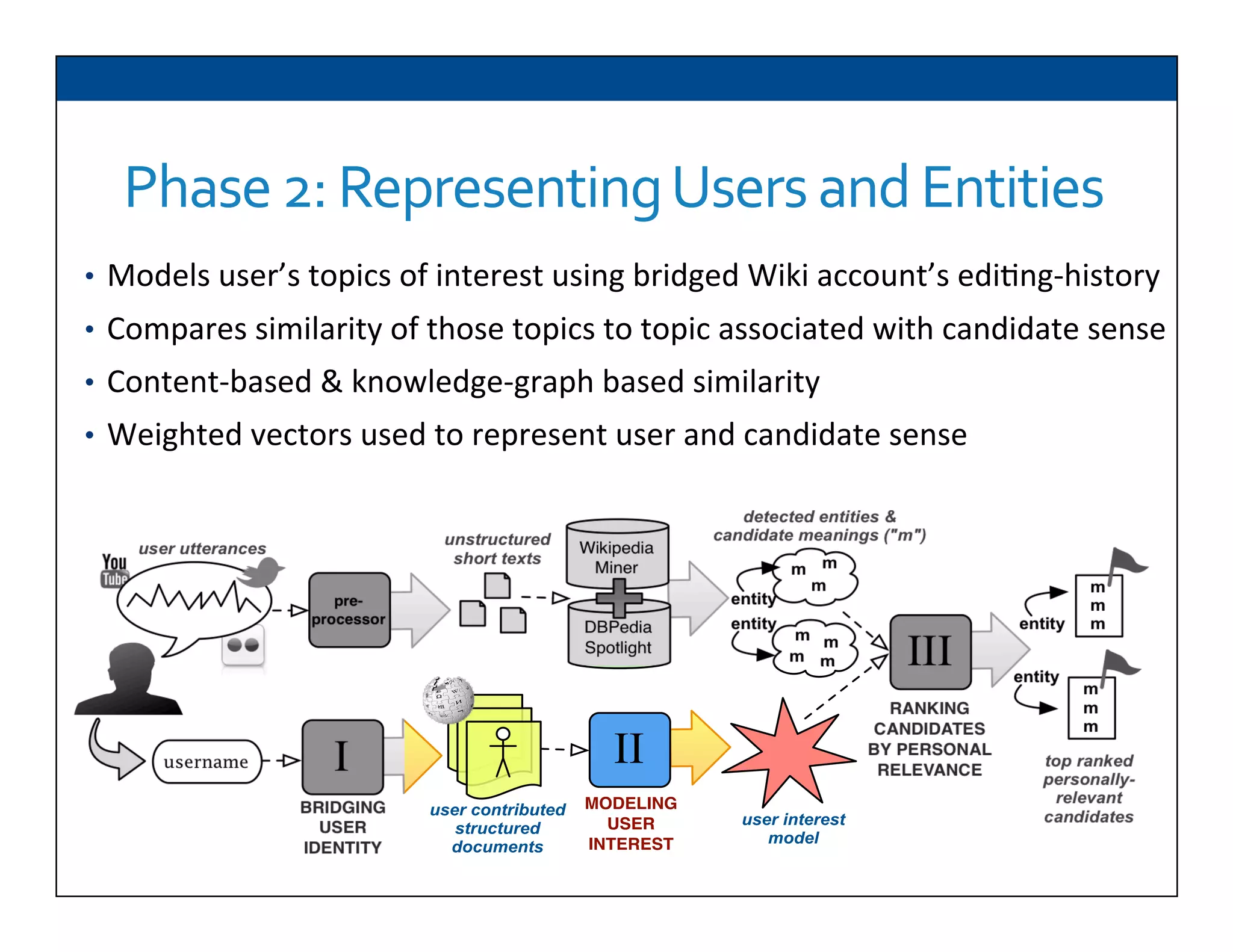
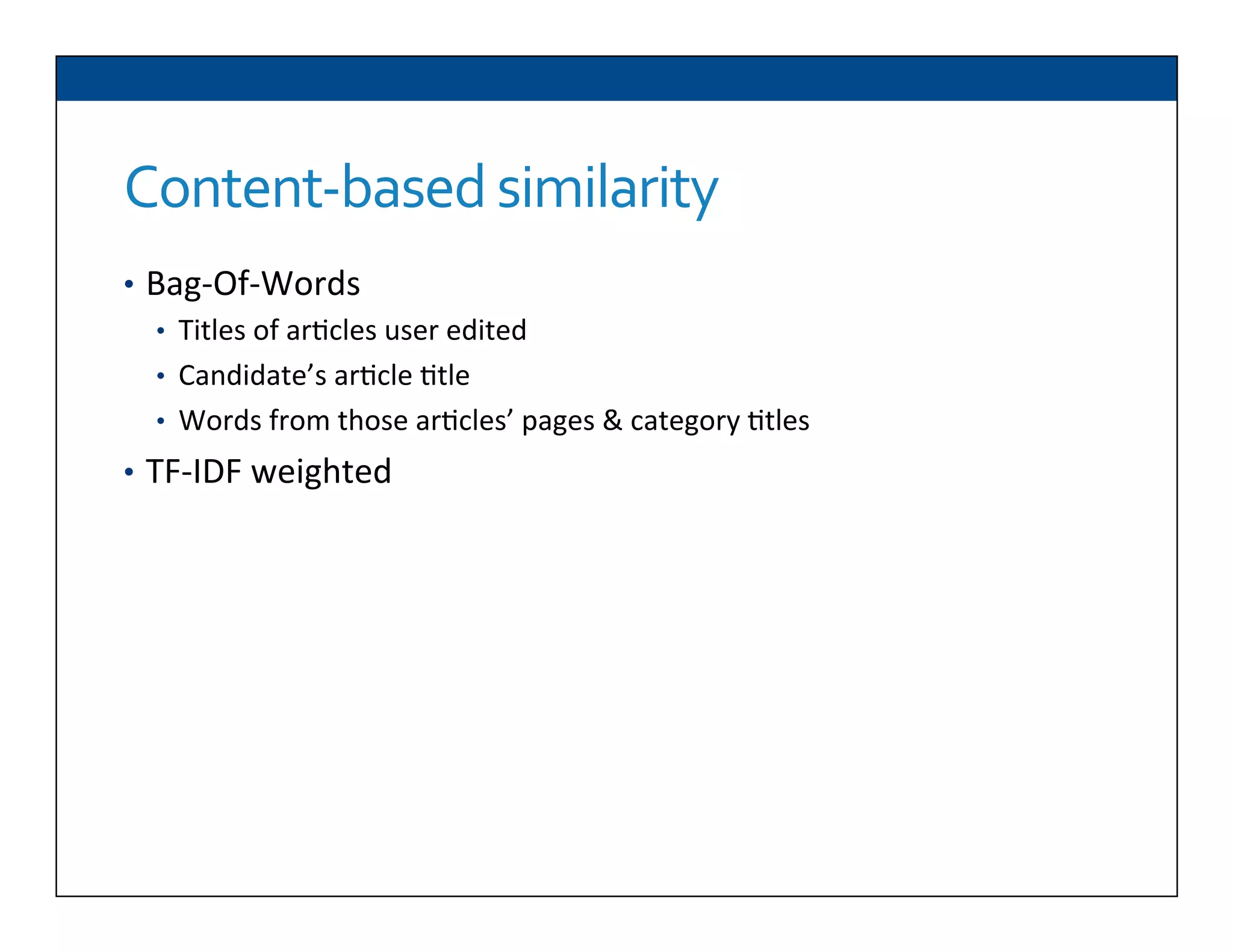
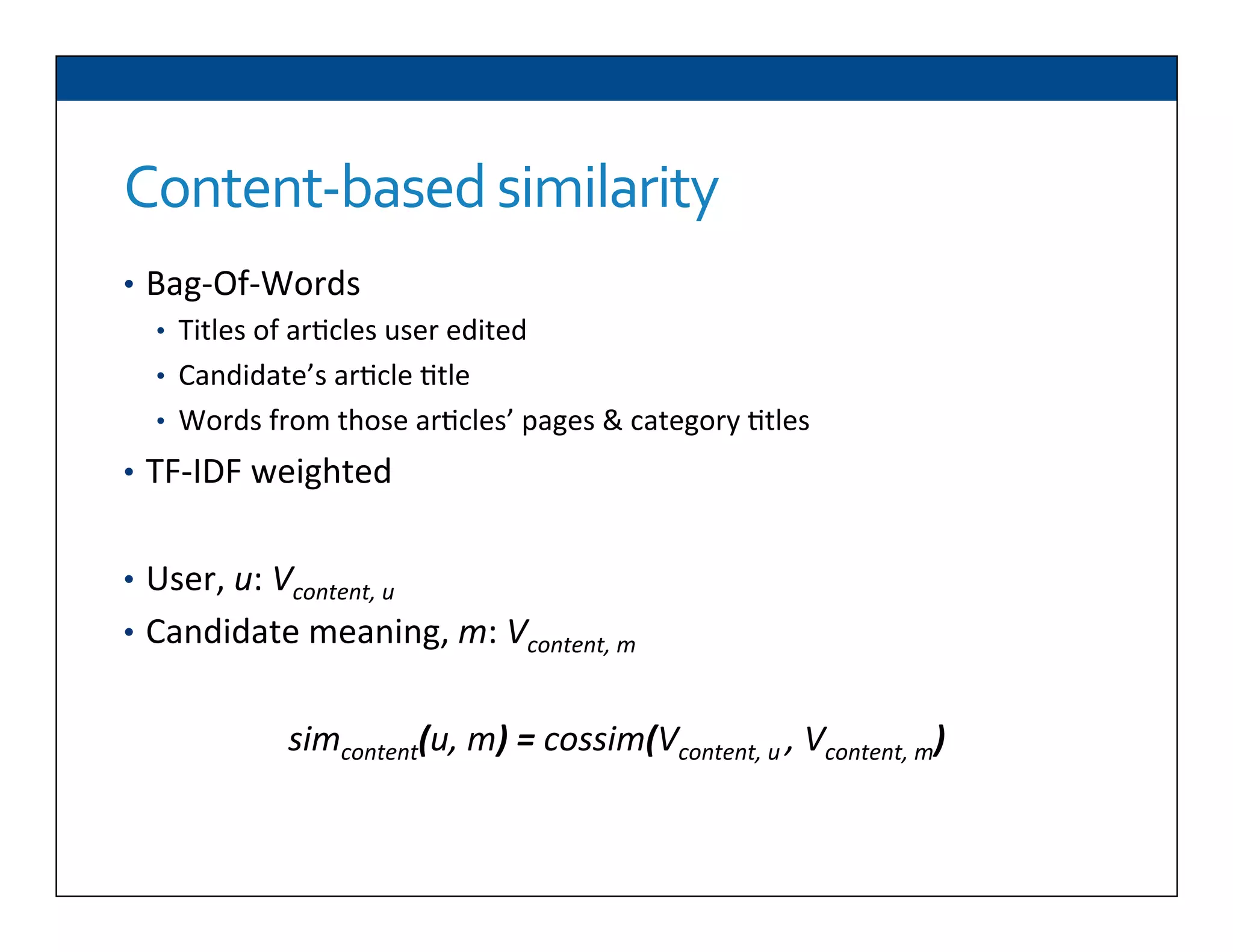
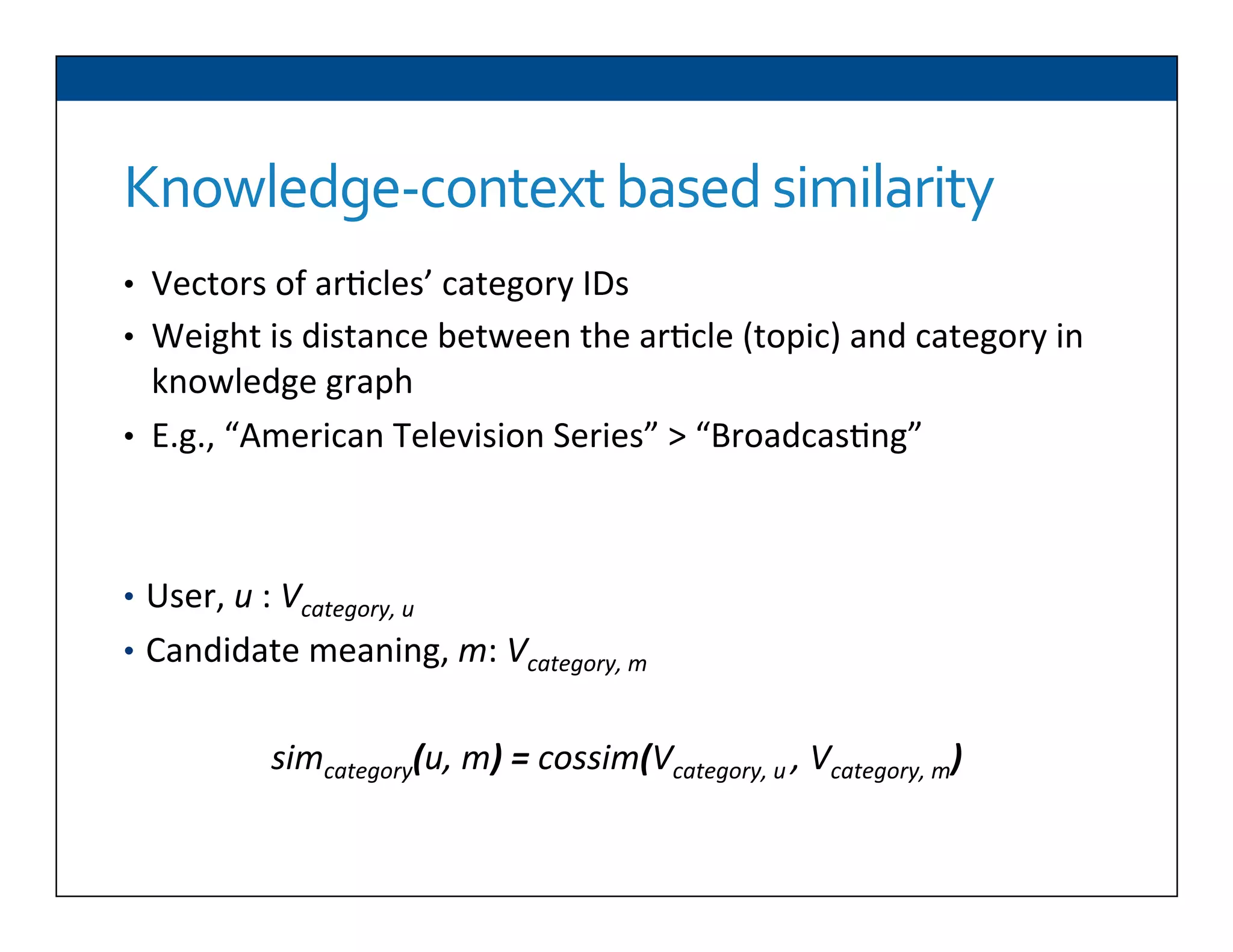
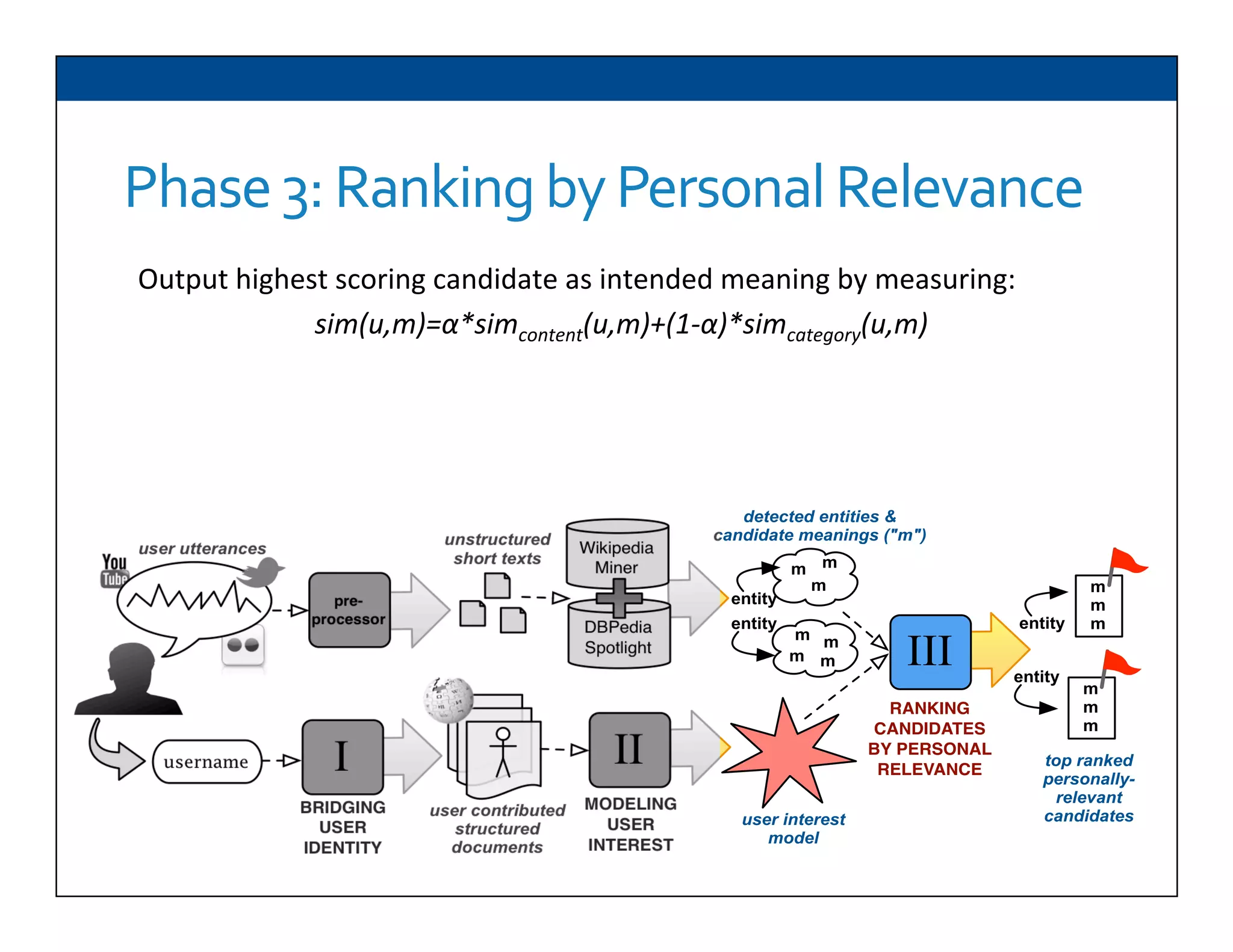
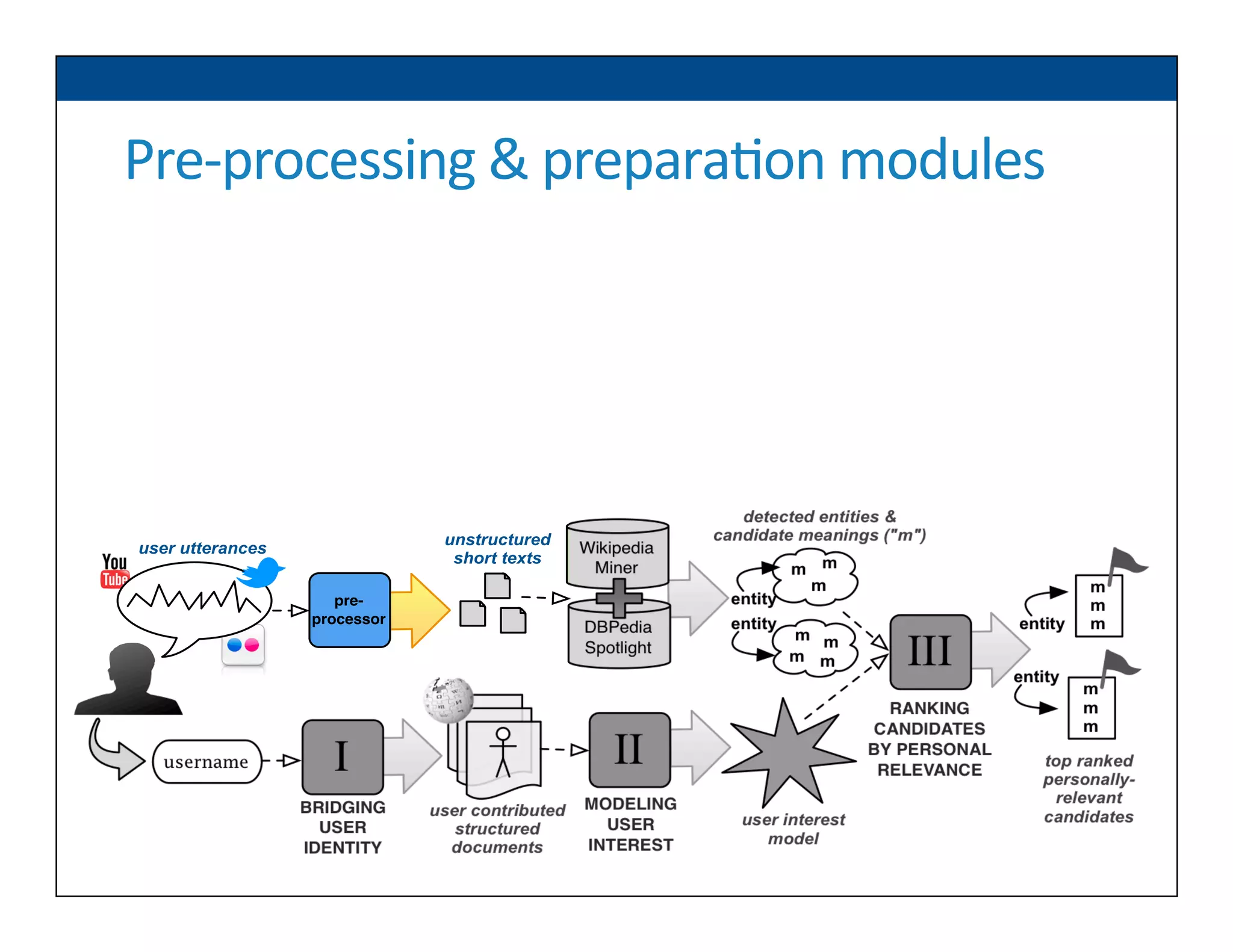
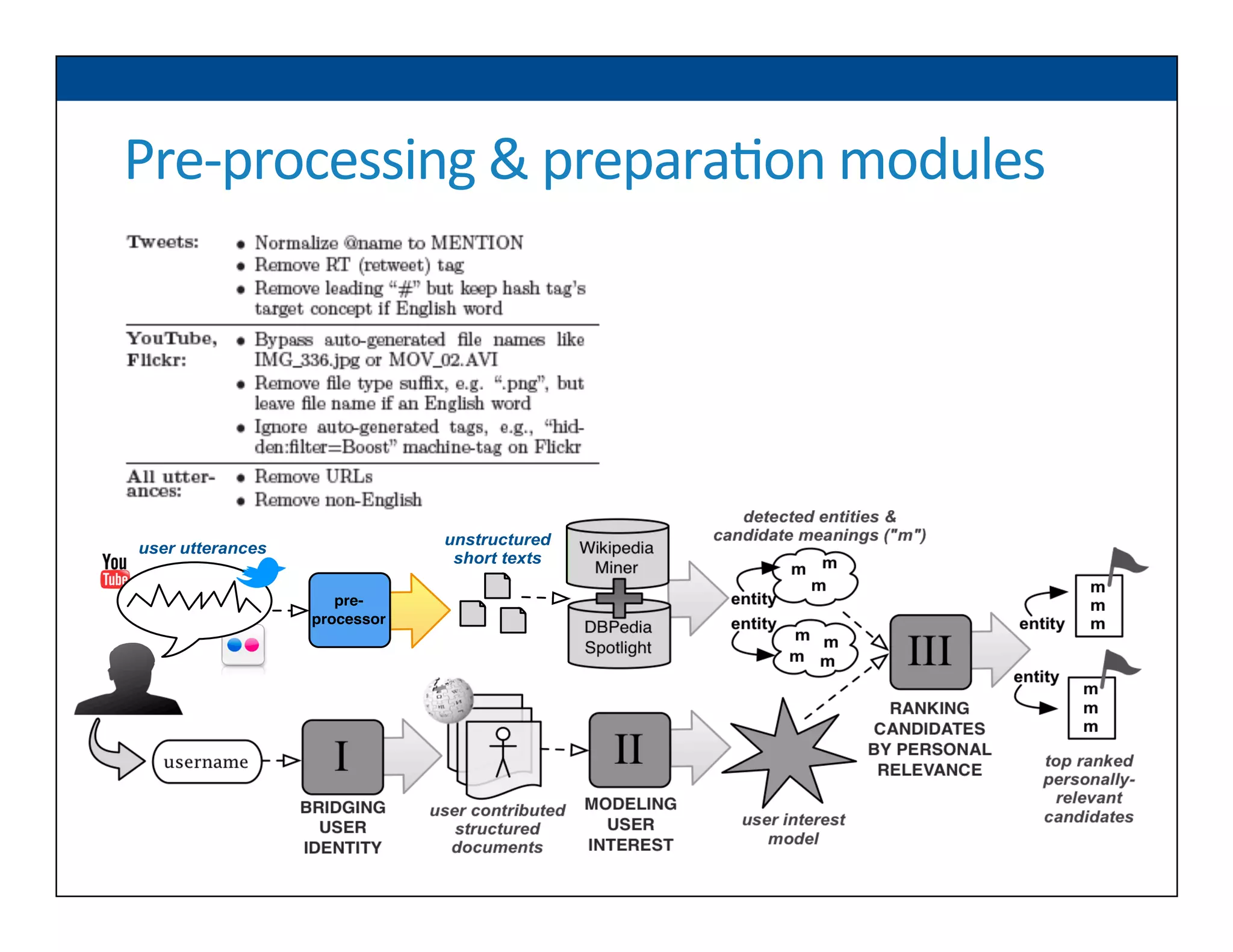
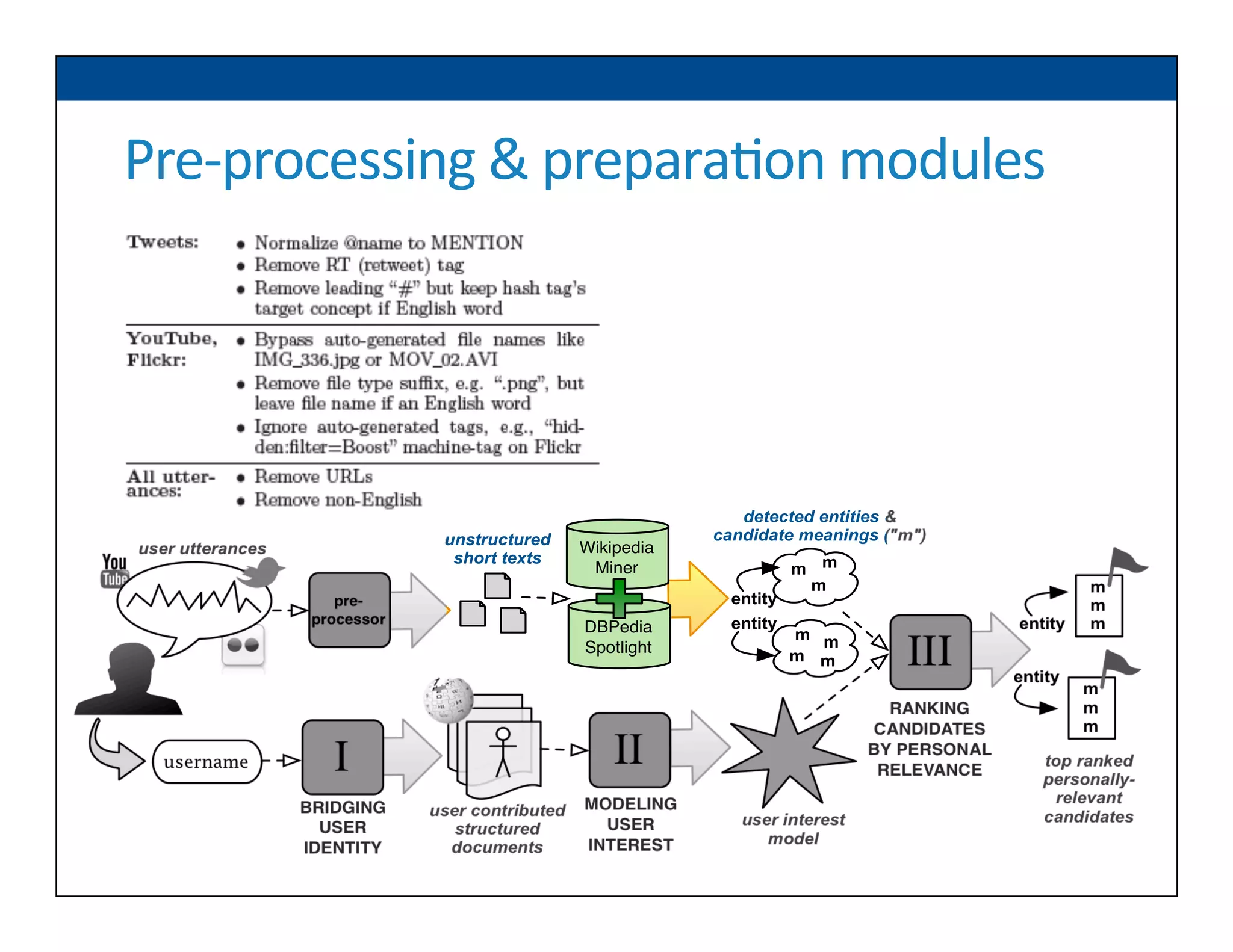
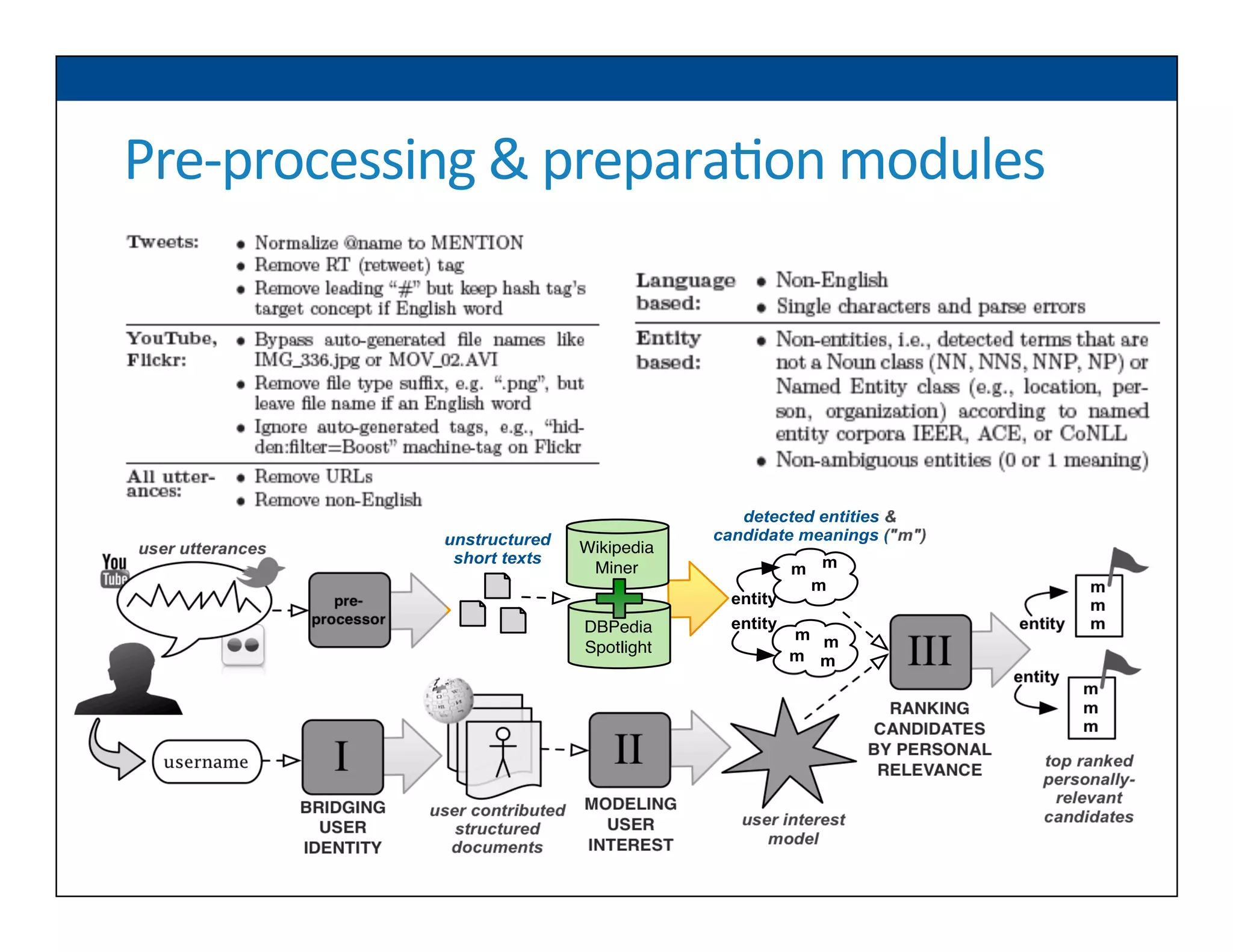
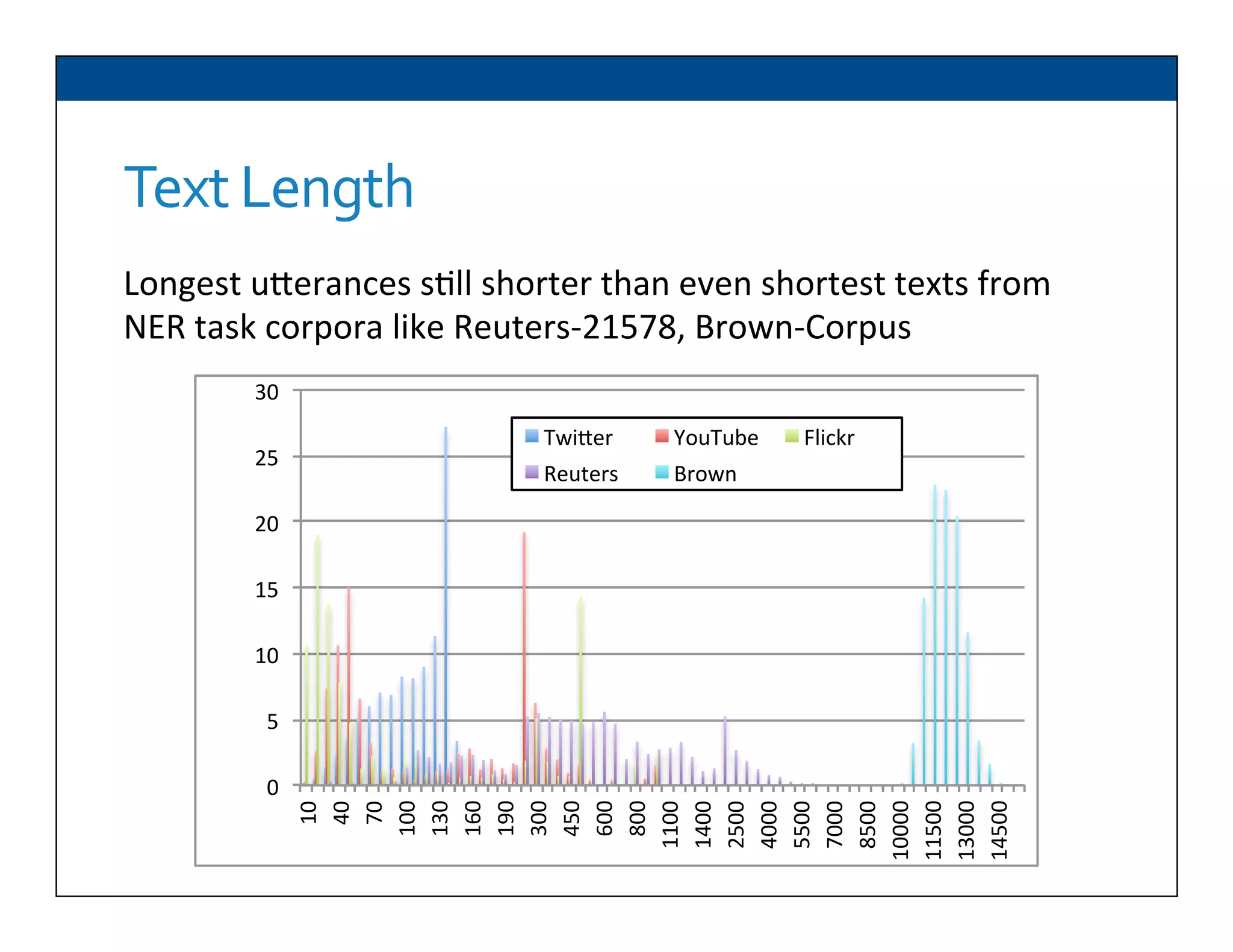
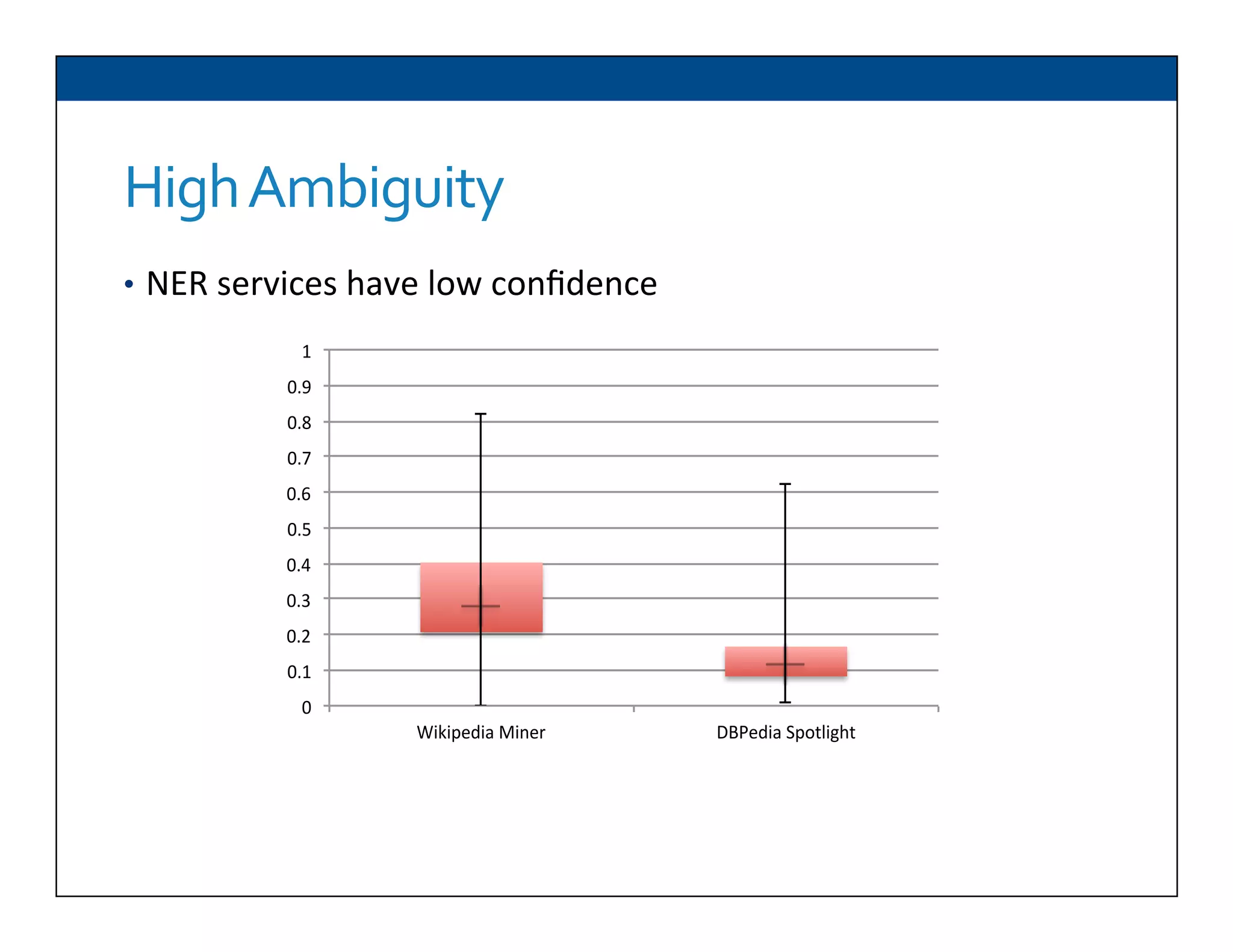
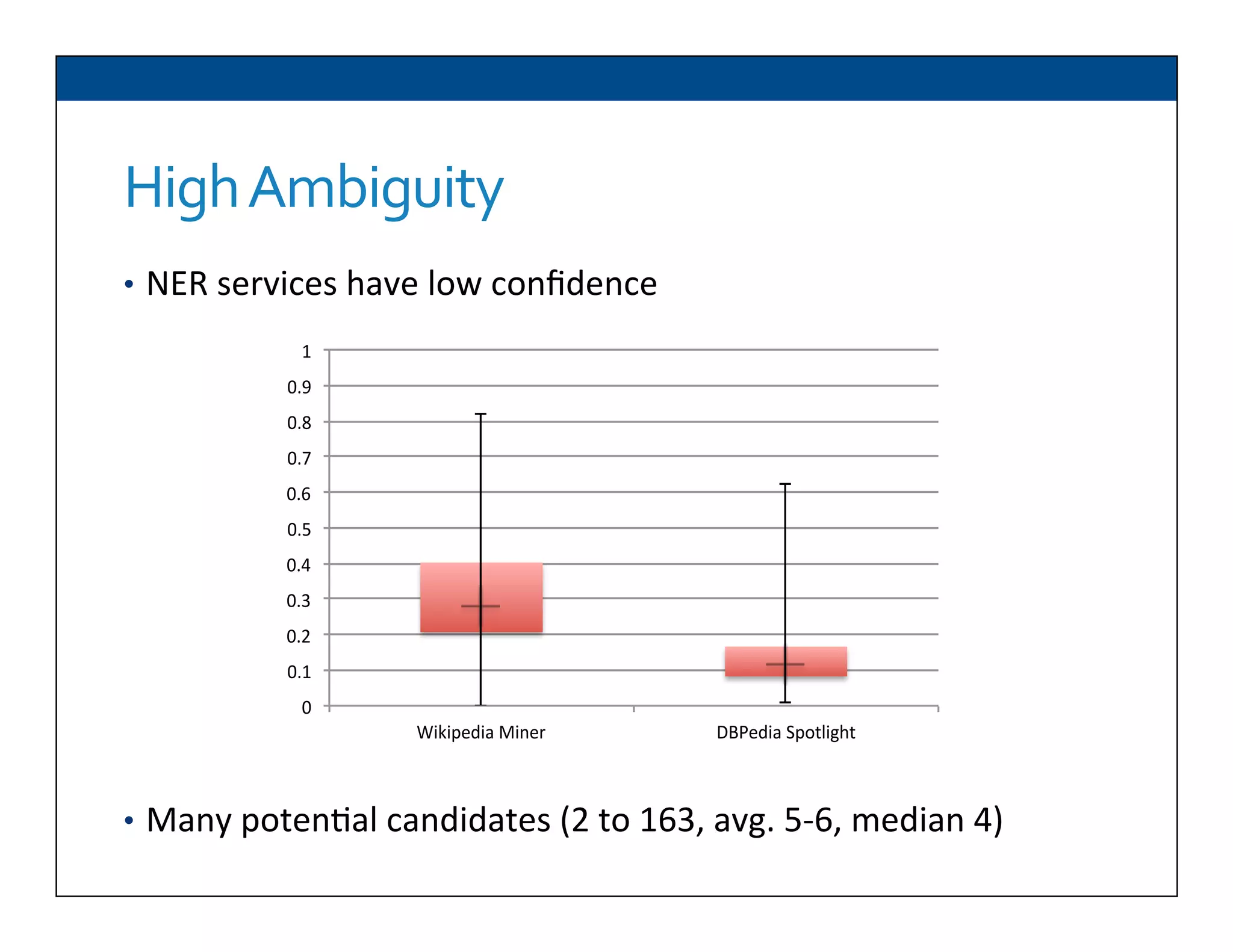
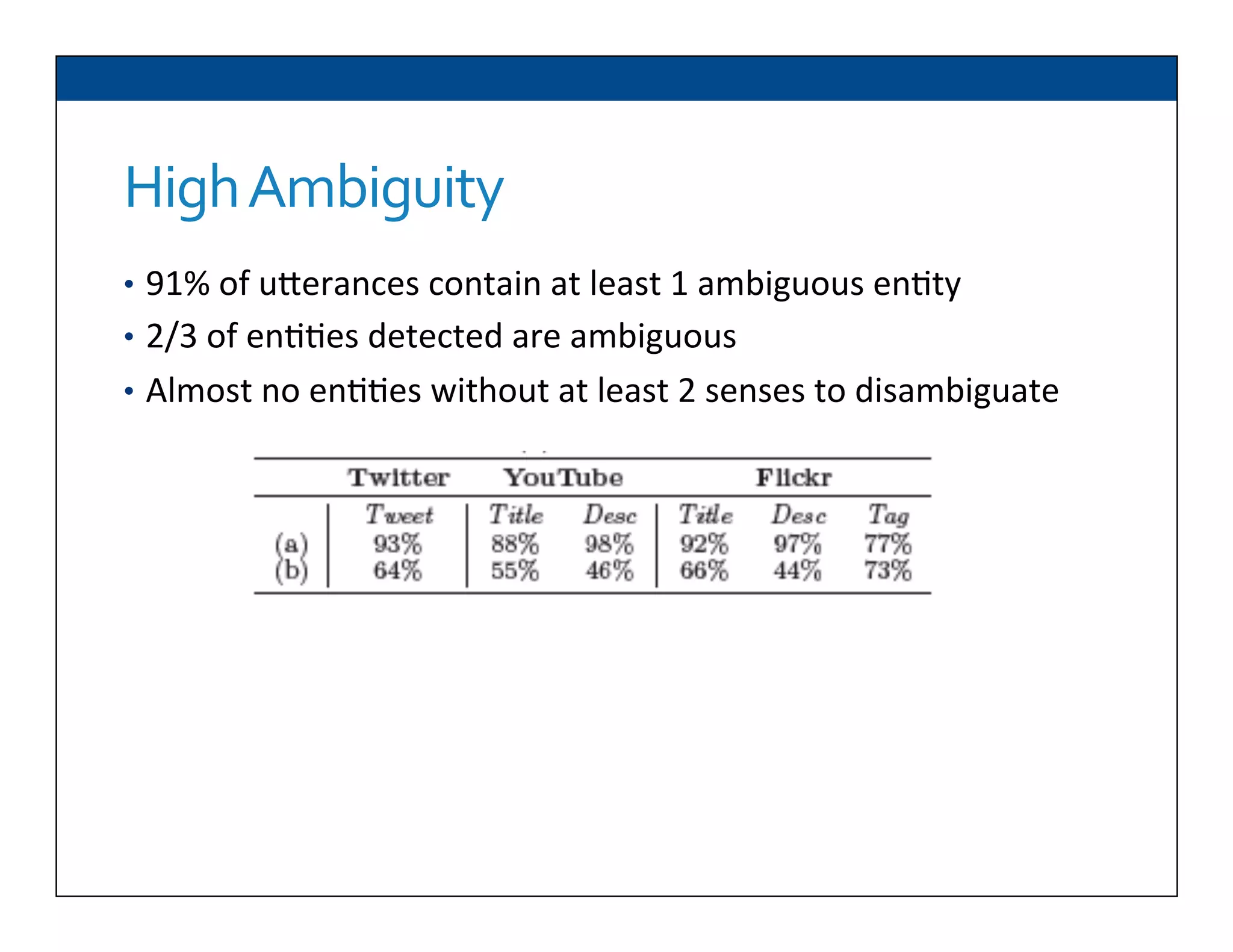
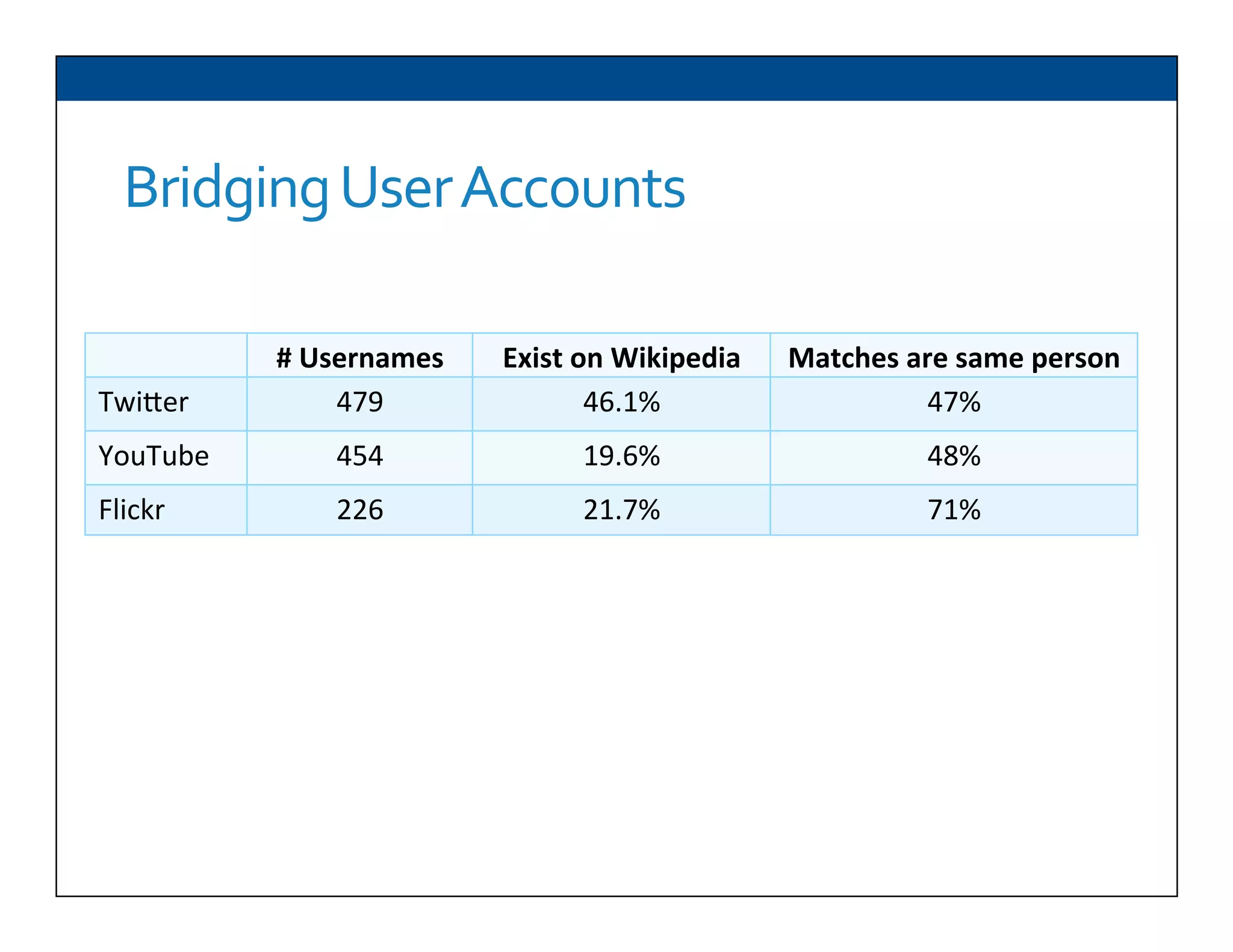
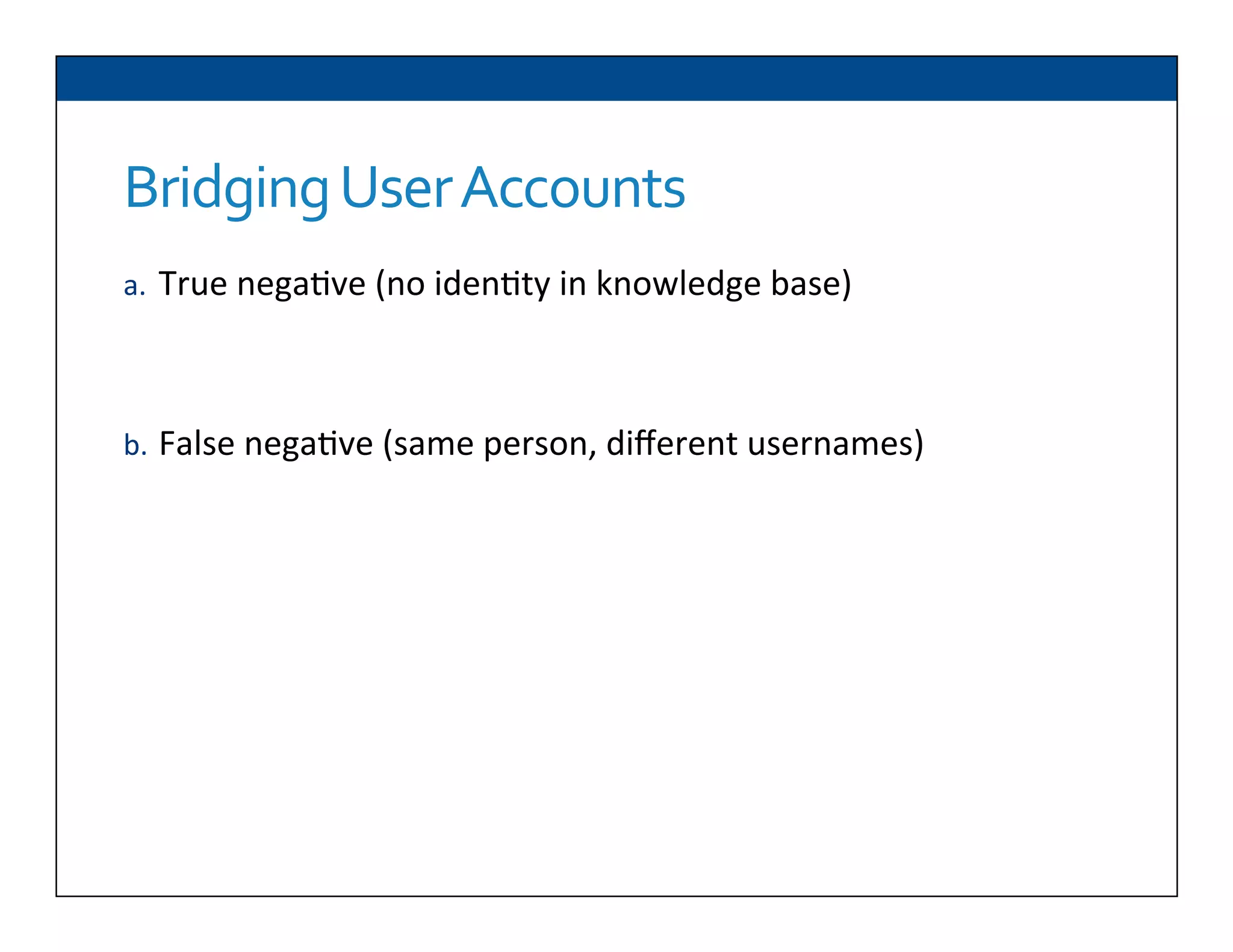
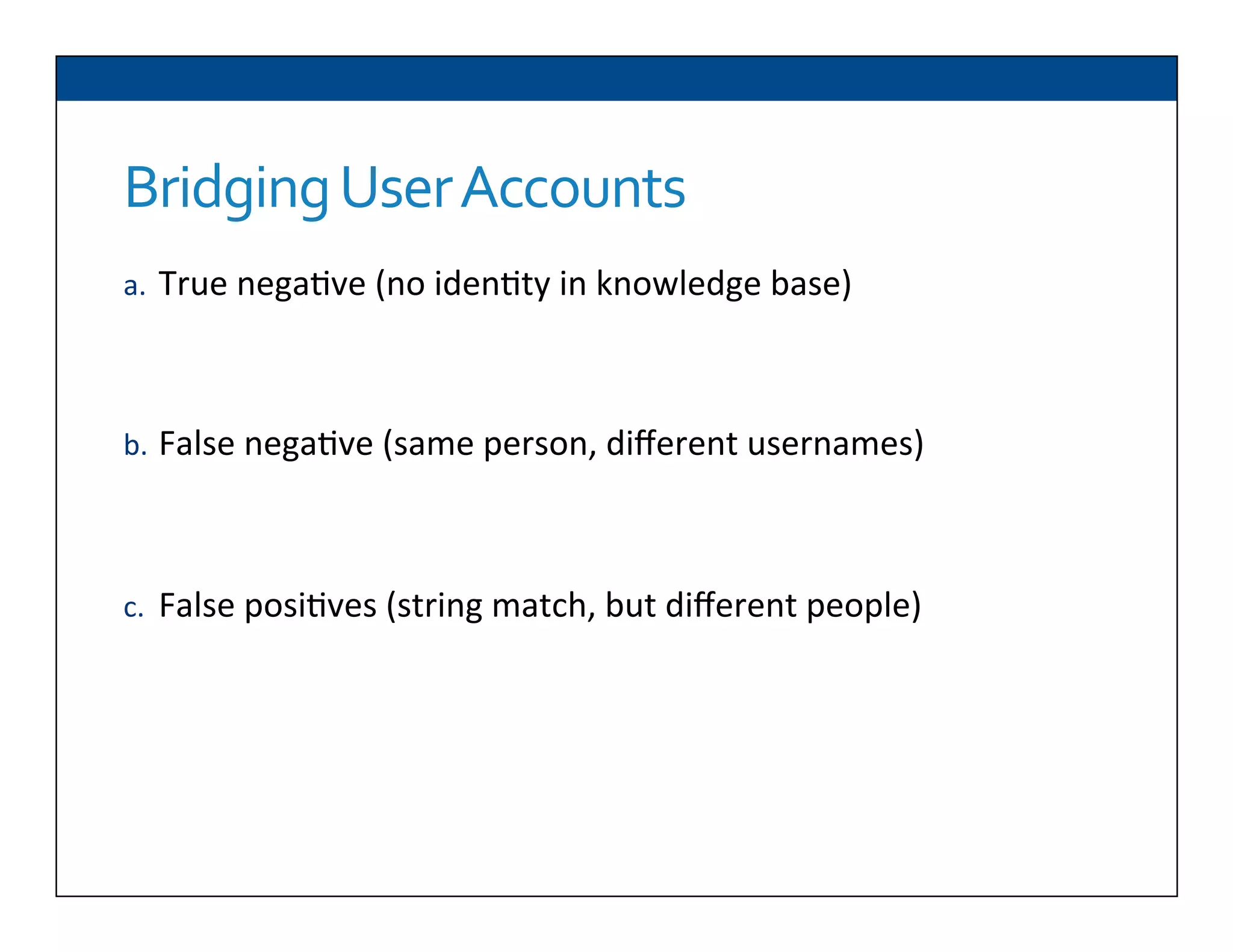
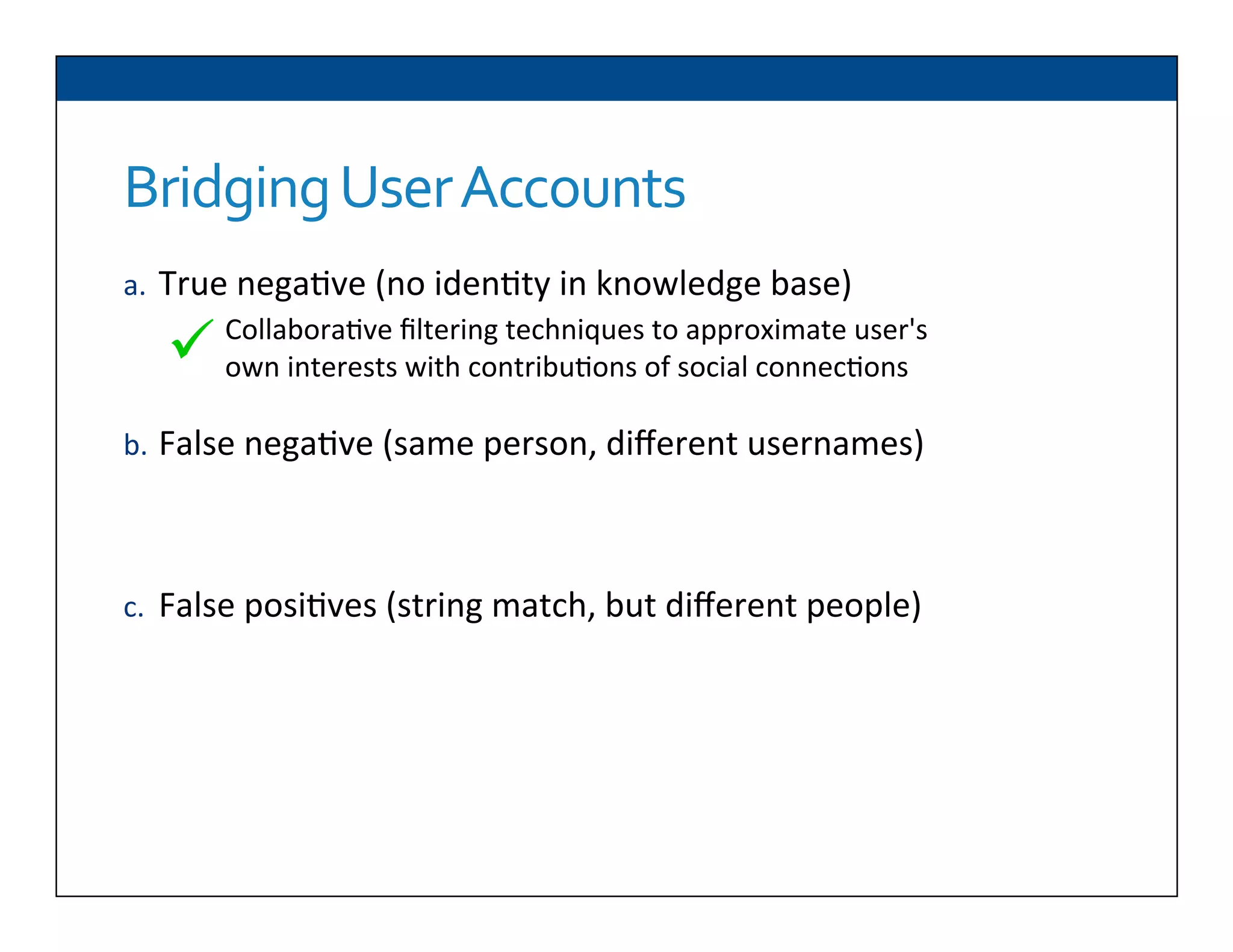
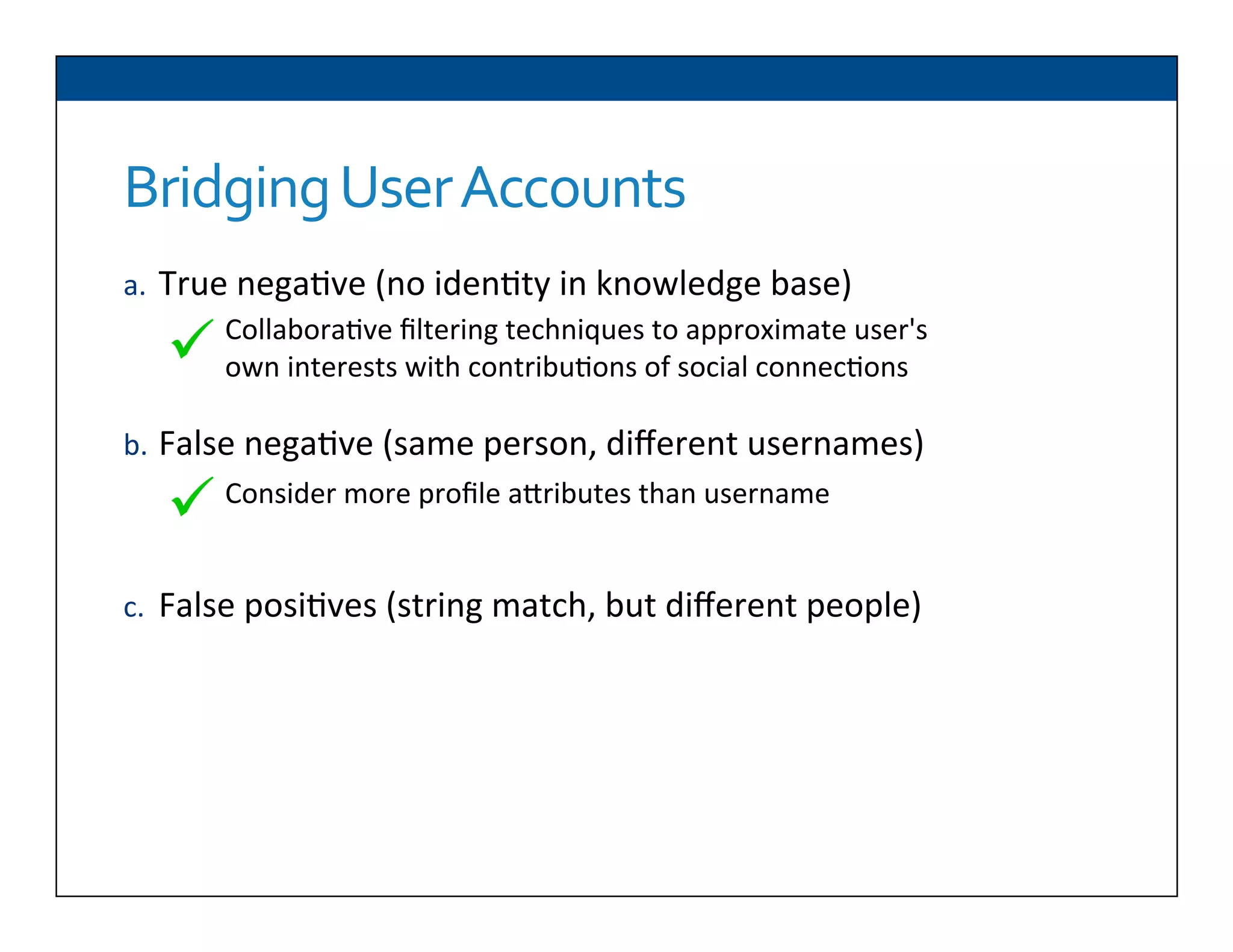
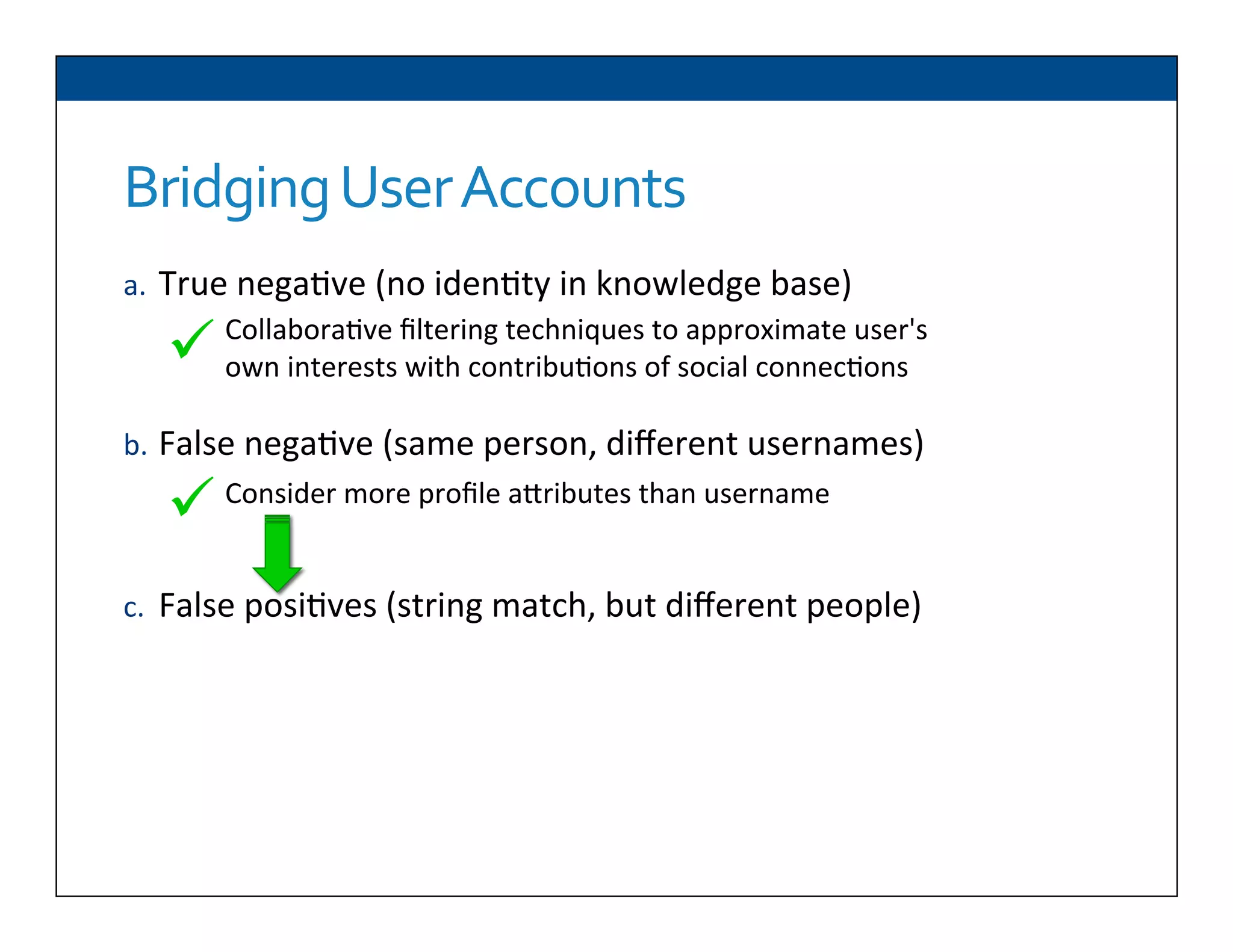
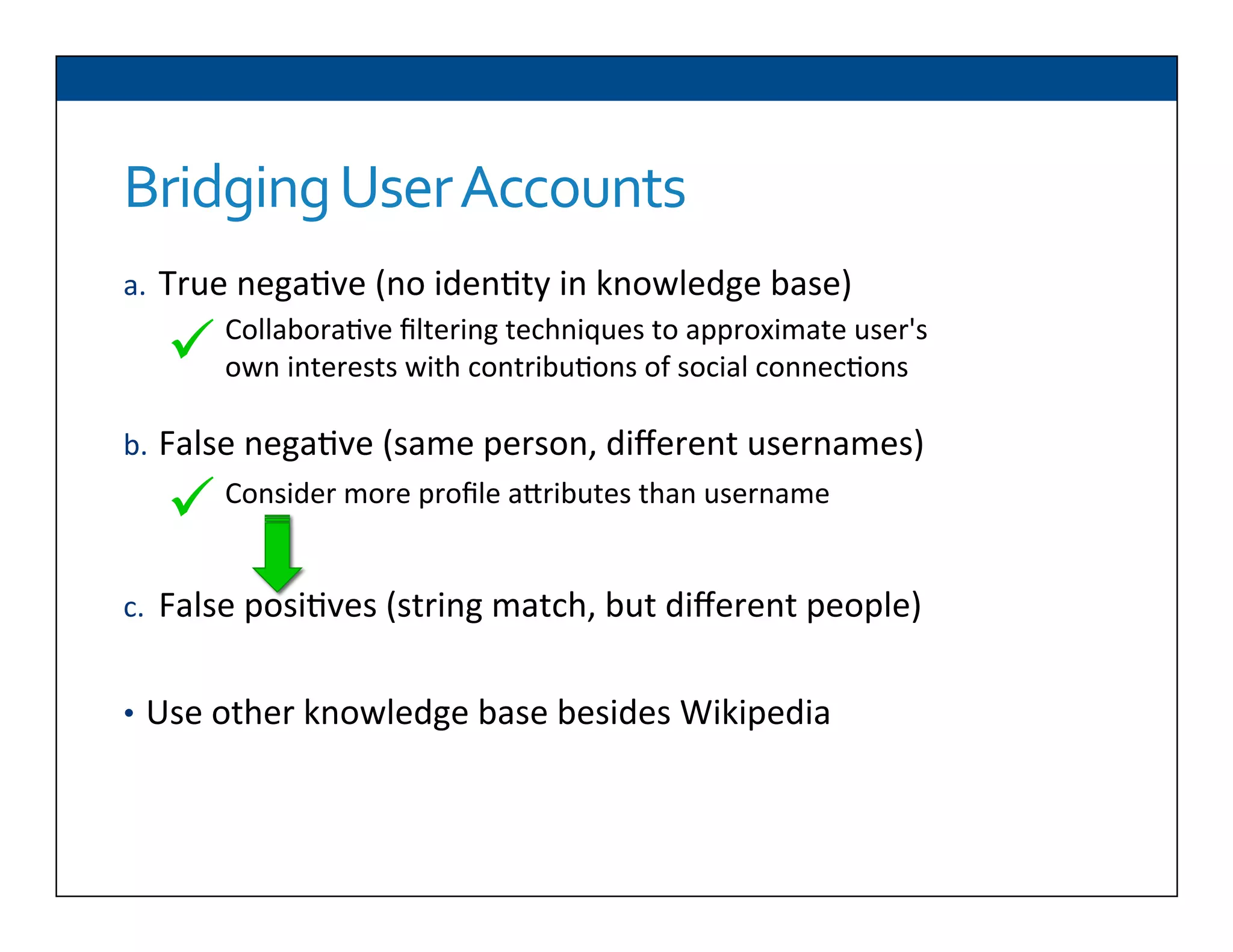
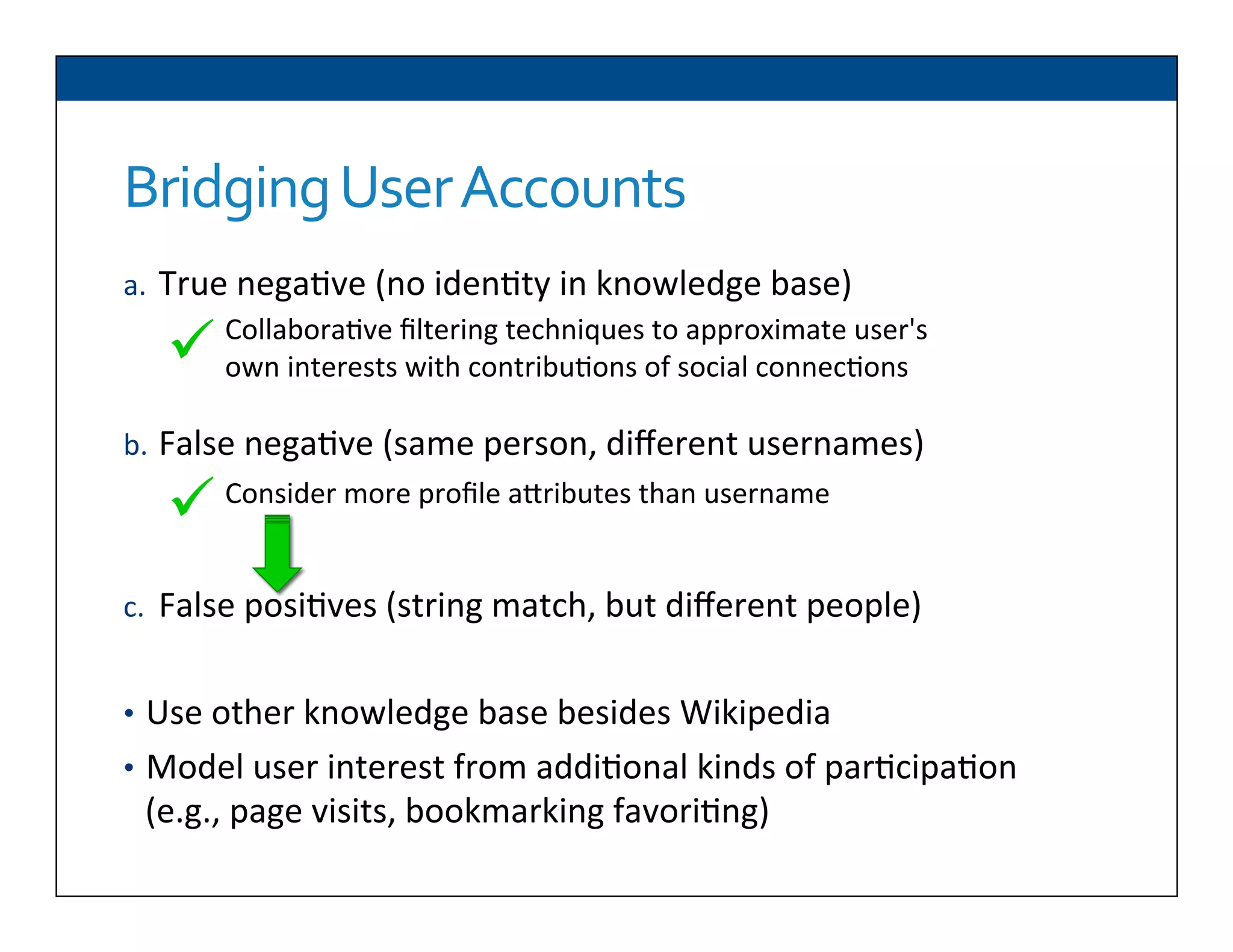
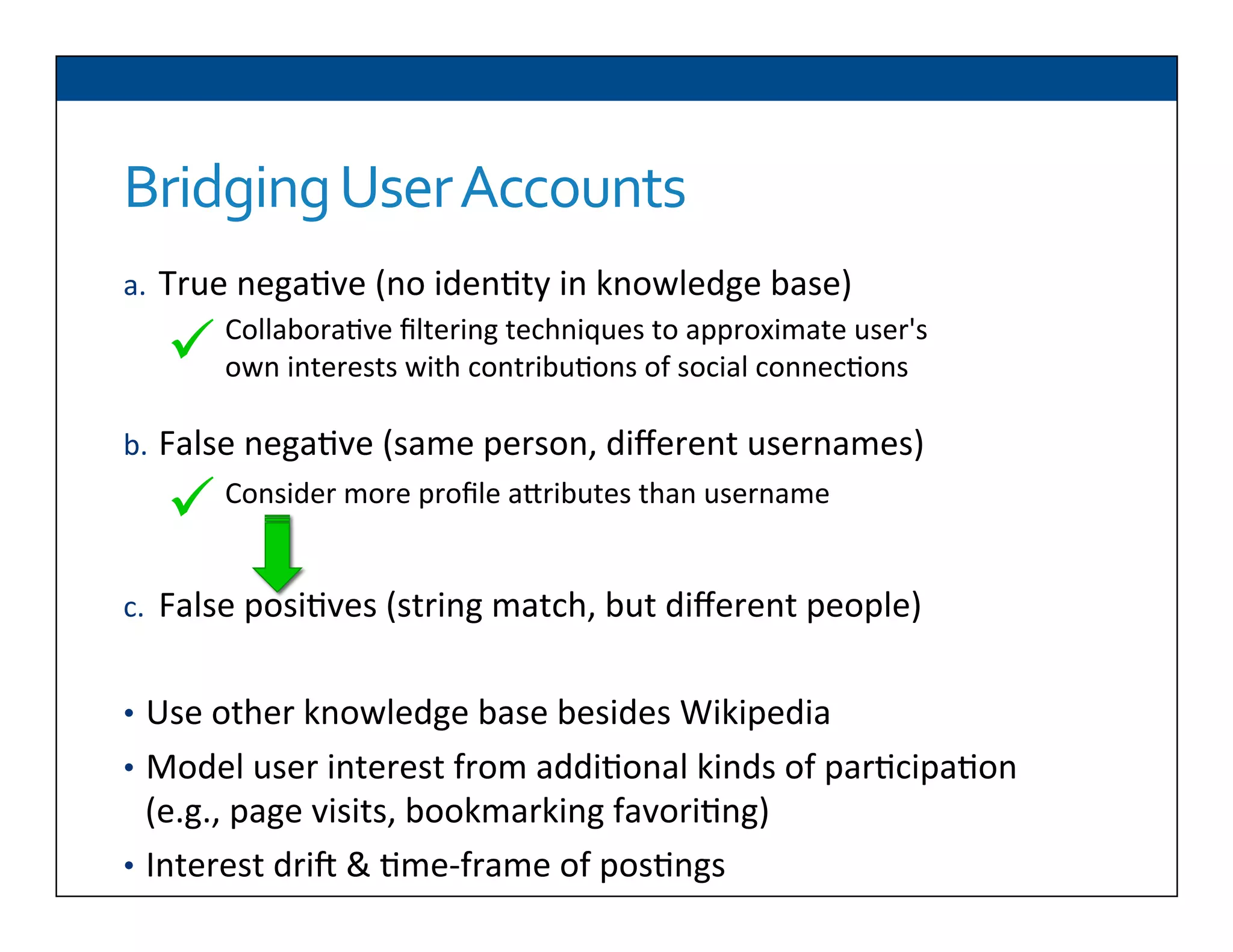
The document presents RESLVE, a personalized approach to entity disambiguation focused on enhancing the recognition of ambiguous entities in short texts, particularly in social media. It discusses challenges such as the shortness and noise of tweets and limitations of traditional techniques that fail in such contexts, while proposing a model that utilizes user-specific semantic data to improve accuracy. Experiments and future work are also outlined to evaluate and refine the RESLVE system.