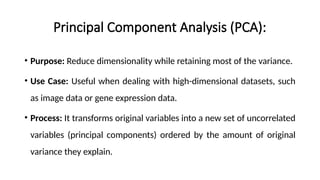
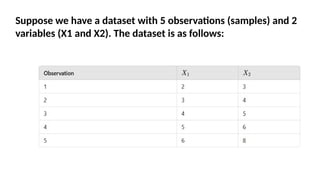
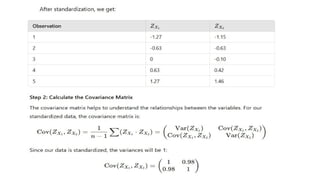
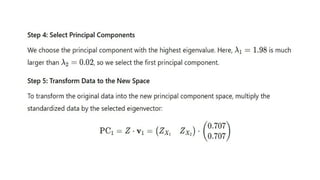
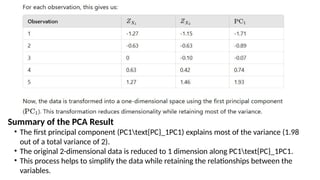
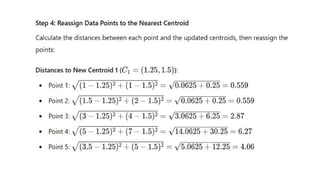
Multivariate analysis is a statistical technique for understanding relationships among multiple variables, primarily used in data analytics to extract insights and patterns. Key methods include principal component analysis (PCA) for reducing dimensionality while retaining variance, and cluster analysis for grouping similar observations. Techniques like k-means clustering are employed to segment data effectively.