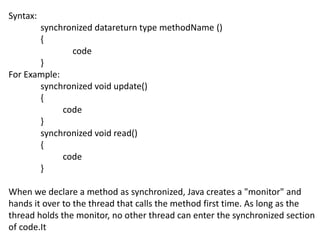
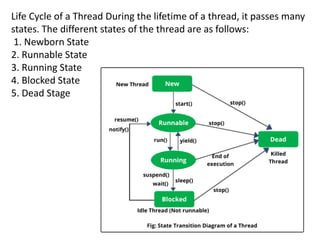
This document provides an introduction to multithreading in Java. It discusses that a thread is similar to a program with a single flow of control and Java supports executing multiple threads concurrently through multithreading. It describes the different states a thread passes through during its lifetime, including newborn, runnable, running, blocked, and dead. It also explains how to create threads in Java by extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface and calling the start() method. Finally, it discusses synchronization which is used to prevent threads from concurrently accessing shared resources and introduces race conditions.






![import java.lang.Thread;
class thread1 extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for(int i =1;i<=10;i++)
{
System.out.println("thread1: "+i);
}
}
}
class thread2 extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
System.out.println("thread2: "+i);
}
}
}
class thread3 extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
System.out.println("thread3 :"+i);
}
}
}
public class multithread1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
thread1 t1=new thread1();
thread2 t2=new thread2();
thread3 t3=new thread3();
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-221225131720-9a450cc5/85/Multithreading-pptx-8-320.jpg)

![class ADC extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for(int j=1;j<=5;j++)
{
System.out.println("Thread ADC"+j);
}
}
}
public class threadtest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new ADA().start();
new ADB().start();
new ADC().start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-221225131720-9a450cc5/85/Multithreading-pptx-10-320.jpg)

![import java.lang.Runnable;
class ADA implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
System.out.println("Thread ADA"+i);
}
}
}
public class threadtest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ADA A=new ADA();
Thread tt=new Thread(A);
tt.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-221225131720-9a450cc5/85/Multithreading-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![import java.lang.Runnable;
class test11 implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
for(int i=1;i<=50;i++)
{
System.out.println("test11 thread : "+i);
}
}
}
class test12 implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
for(int i=1;i<=50;i++)
{
System.out.println("test12 thread : "+i);
}
}
}
class test13 implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
for(int i=1;i<=50;i++)
{
System.out.println("test13 thread : "+i);
}
}
}
public class threadtest12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test11 t=new test11();
test12 t1=new test12();
test13 t2=new test13();
Thread tt=new Thread(t);
Thread tt1=new Thread(t1);
Thread tt2=new Thread(t2);
tt.start();
tt1.start();
tt2.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-221225131720-9a450cc5/85/Multithreading-pptx-13-320.jpg)




![// Java program to demonstrate the usage of
// setDaemon() and isDaemon() method.
public class DaemonThread extends Thread
{
public DaemonThread(String name){
super(name);
}
public void run()
{
// Checking whether the thread is Daemon or not
if(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon())
{
System.out.println(getName() + " is Daemon thread");
}
else
{
System.out.println(getName() + " is User thread");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DaemonThread t1 = new DaemonThread("t1");
DaemonThread t2 = new DaemonThread("t2");
DaemonThread t3 = new DaemonThread("t3");
// Setting user thread t1 to Daemon
t1.setDaemon(true);
// starting first 2 threads
t1.start();
t2.start();
// Setting user thread t3 to Daemon
t3.setDaemon(true);
t3.start();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-221225131720-9a450cc5/85/Multithreading-pptx-18-320.jpg)