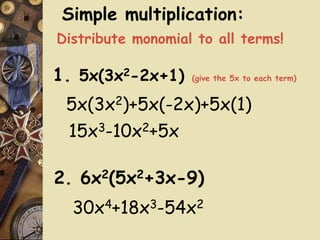
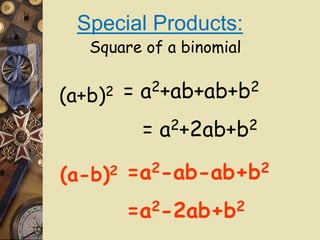
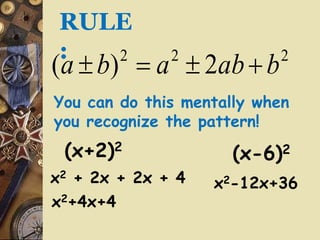
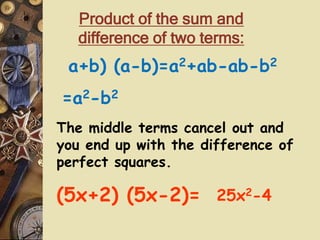
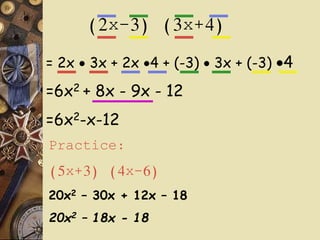The document discusses factoring polynomials and operations on polynomials. It explains that students will learn to factor polynomials using various methods, add, subtract, and multiply polynomials, and sketch rough graphs using key features like zeros. The document provides examples of factoring polynomials using the distributive property, FOIL method, and special products like the square of a binomial and difference of squares. It also gives rules and examples for performing operations on polynomials.