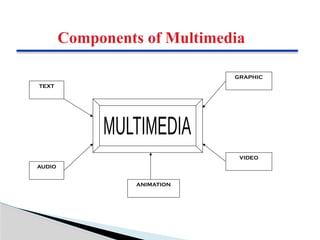
Multimedia is defined as a combination of text, graphics, sound, animation, and video delivered interactively through electronic means. It can be classified into linear and non-linear categories, with applications across various fields such as business, education, entertainment, and public spaces. The document emphasizes the significance of multimedia in enhancing communication and engagement by utilizing multiple senses.