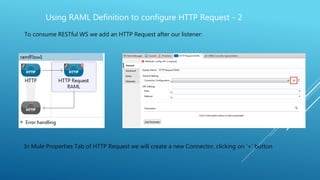
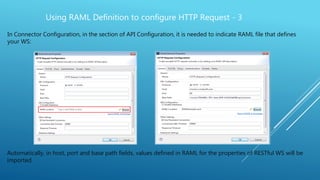
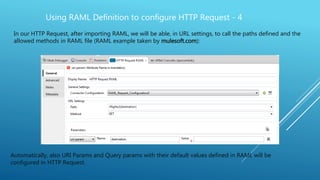
This document discusses how to use a RAML definition file to configure an HTTP request in Mule ESB. It explains that a RAML file defining a RESTful web service makes building requests easier and quicker. It provides steps to import a RAML file into an HTTP request connector in Mule, which will automatically populate fields like the host, port, base path, URI params, and query params from the RAML. This allows calling the paths and methods defined in the RAML file for the RESTful web service.