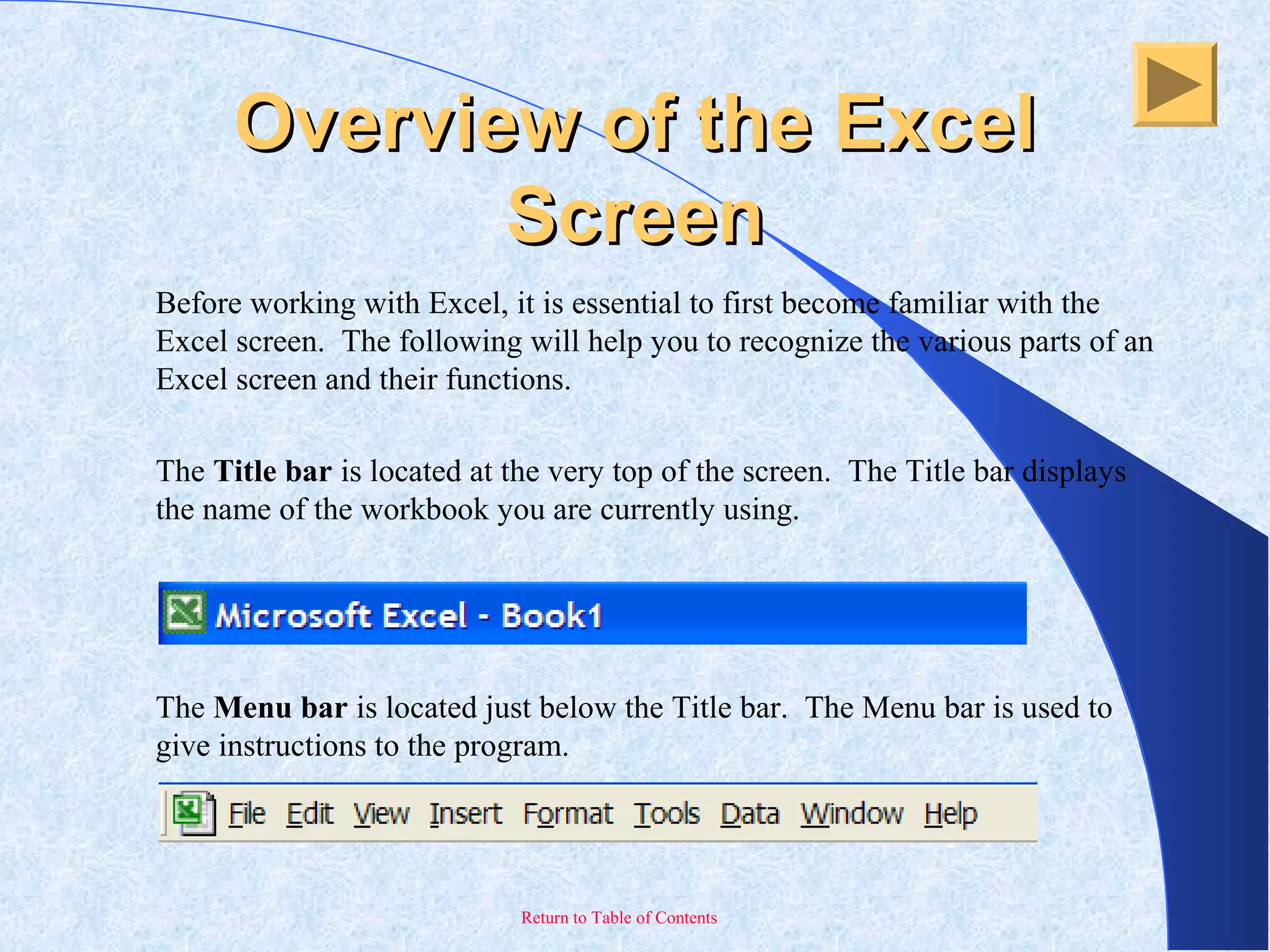
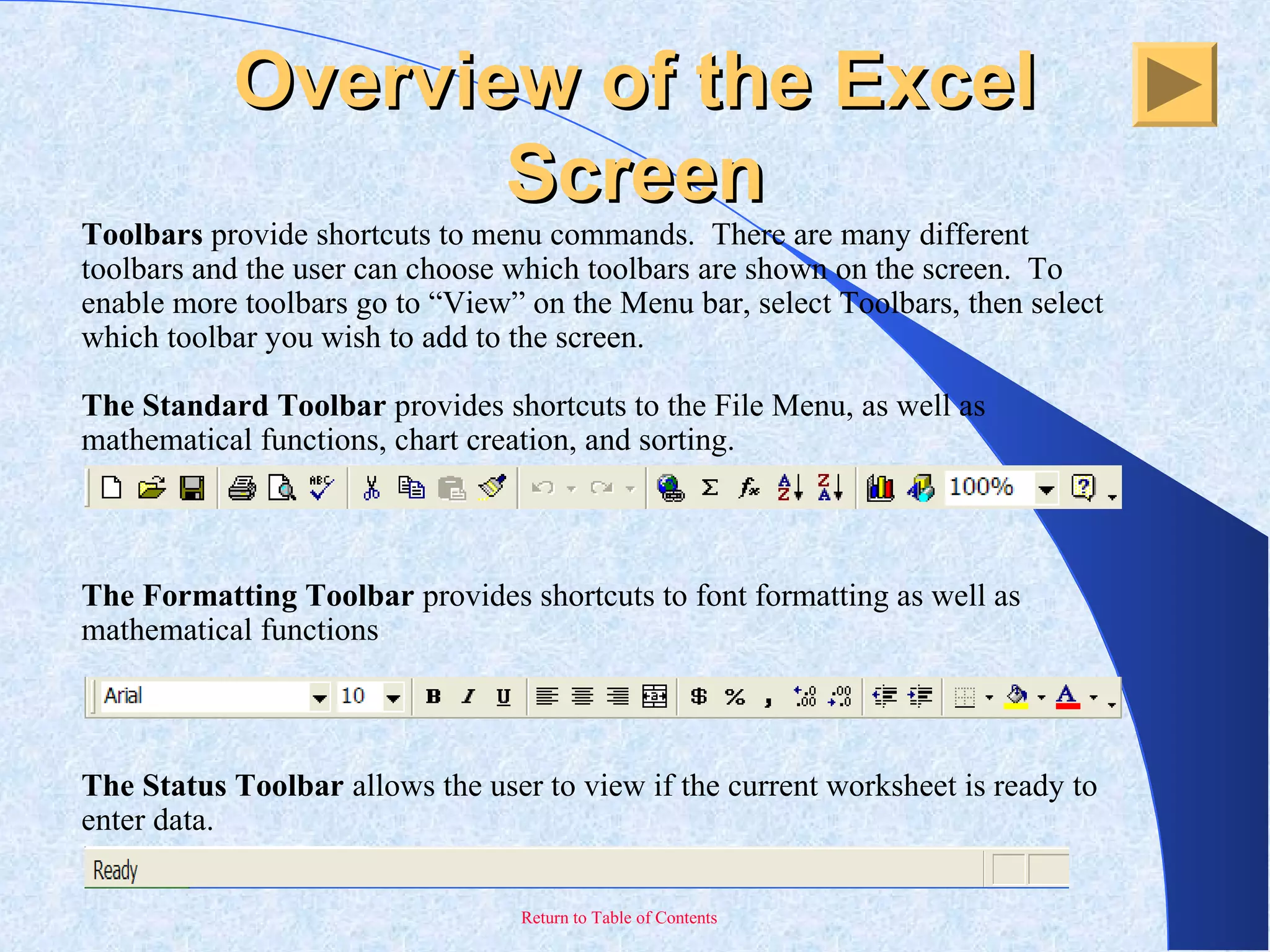
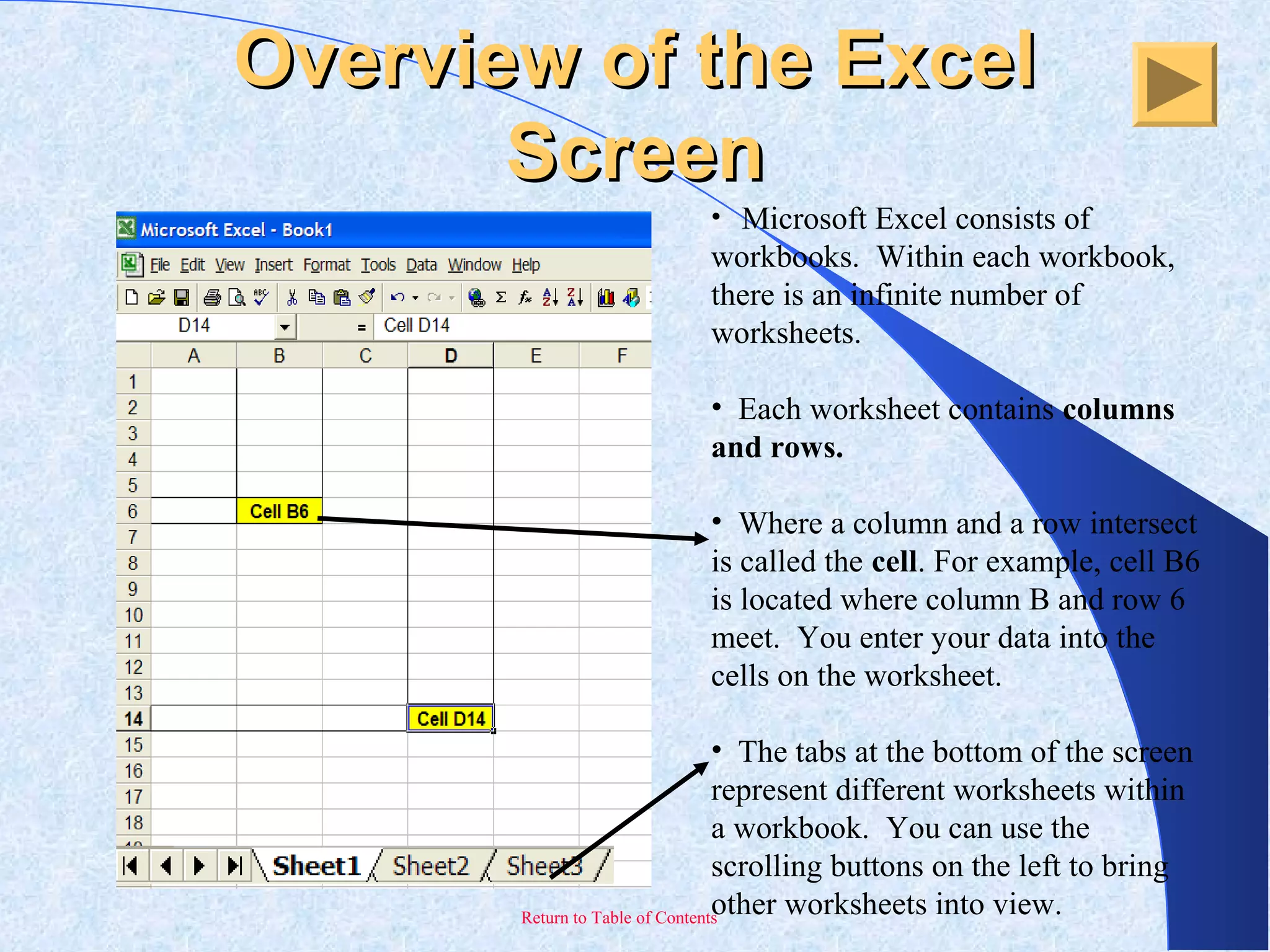
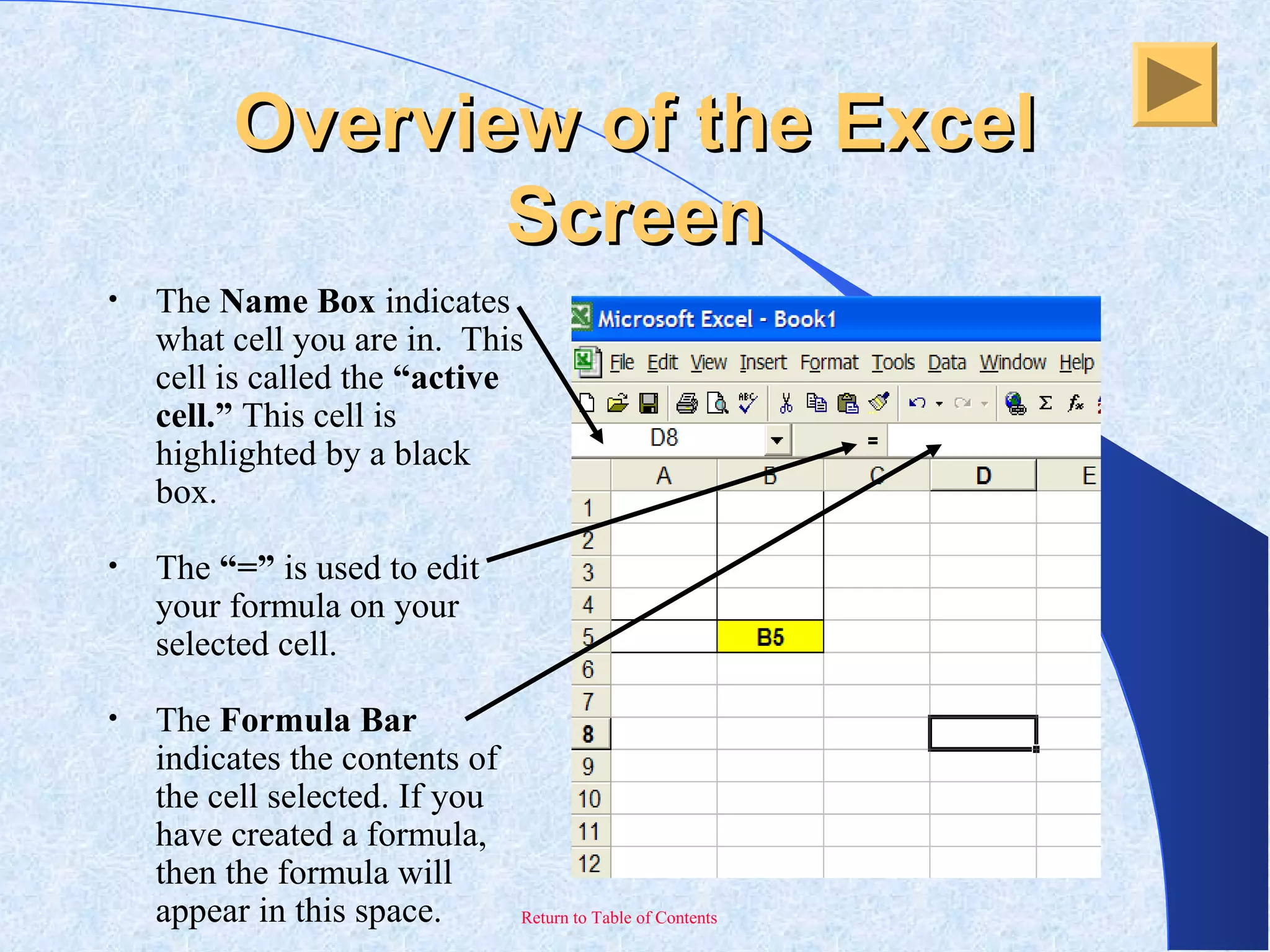
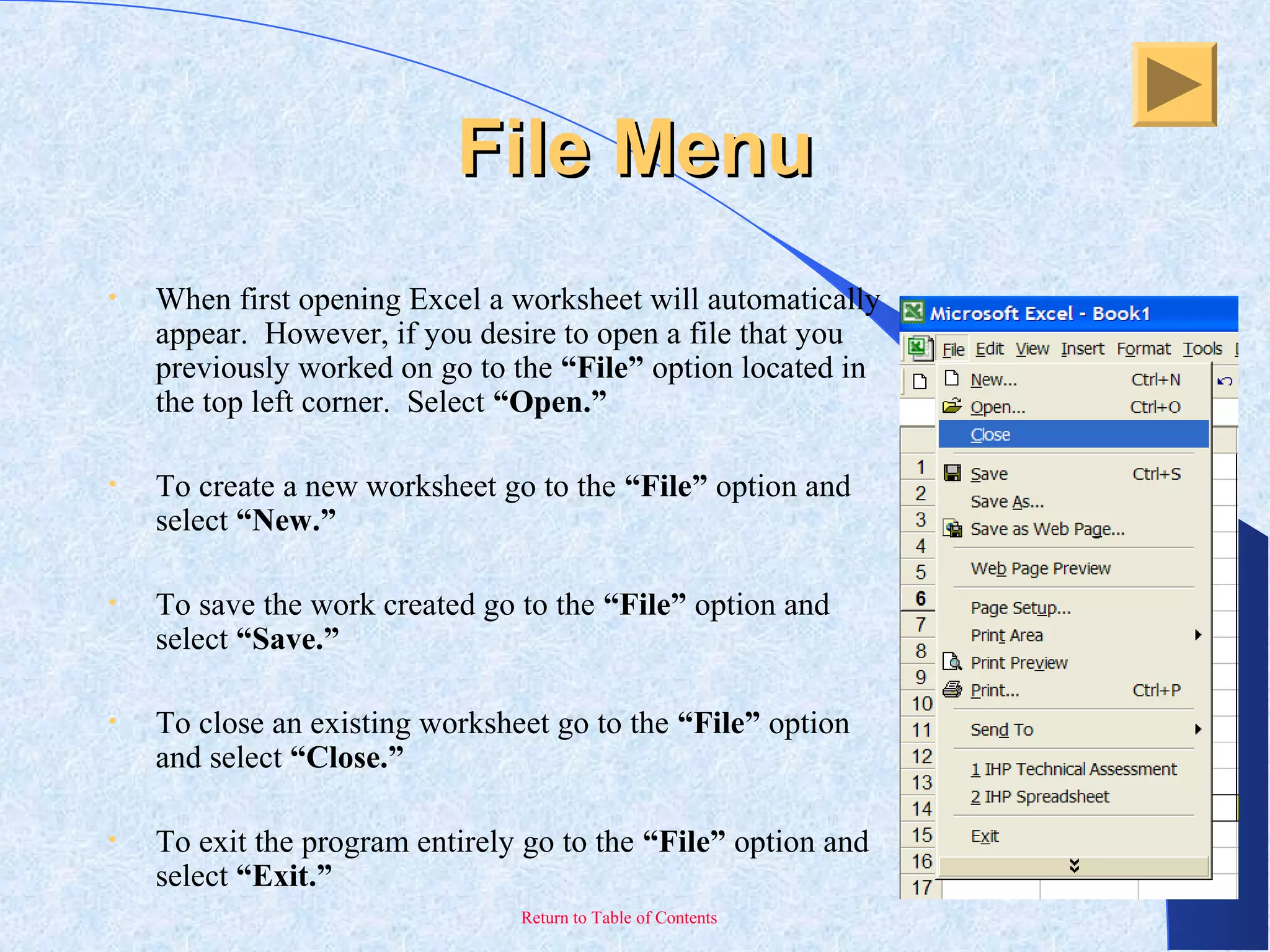
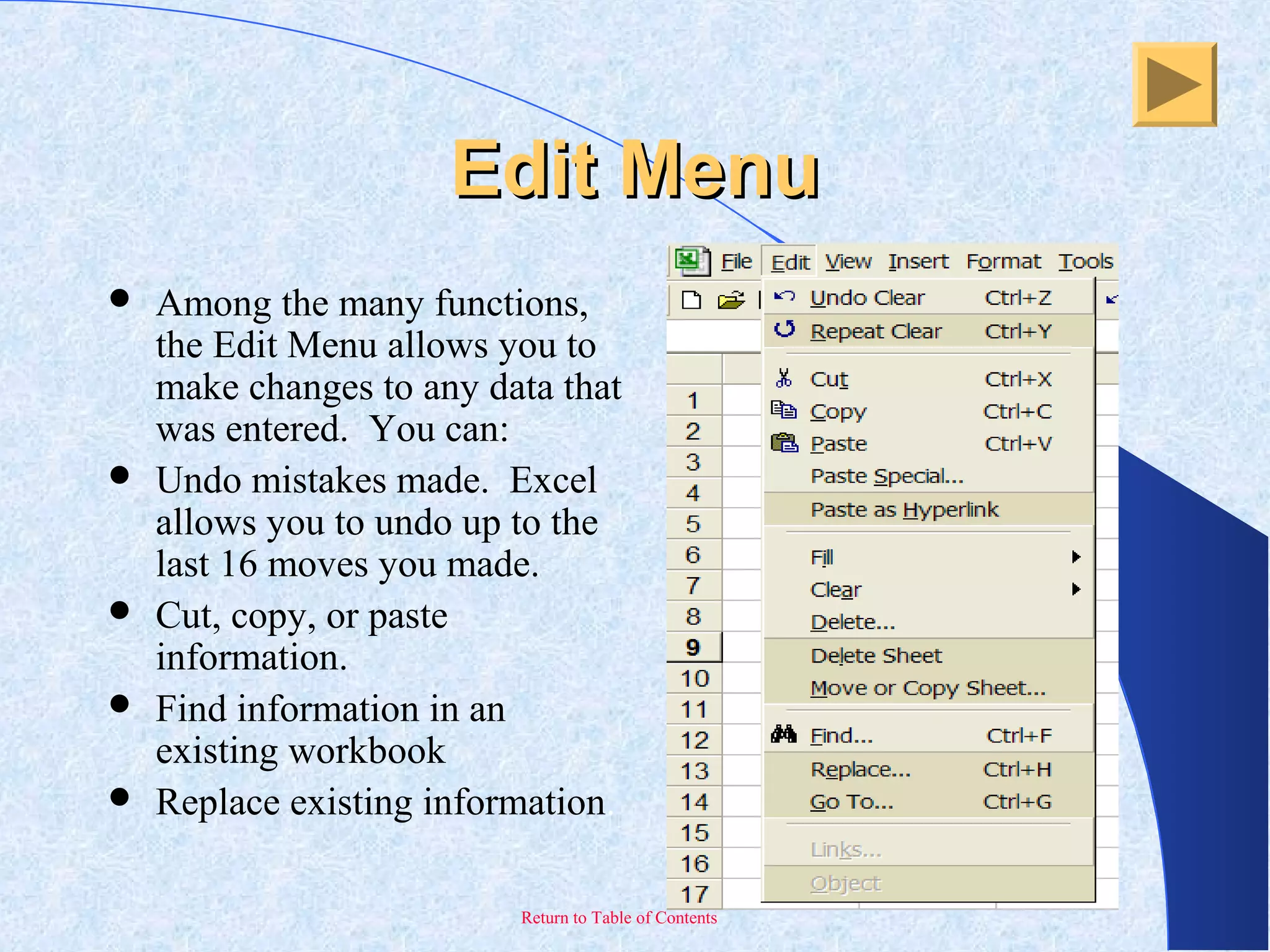
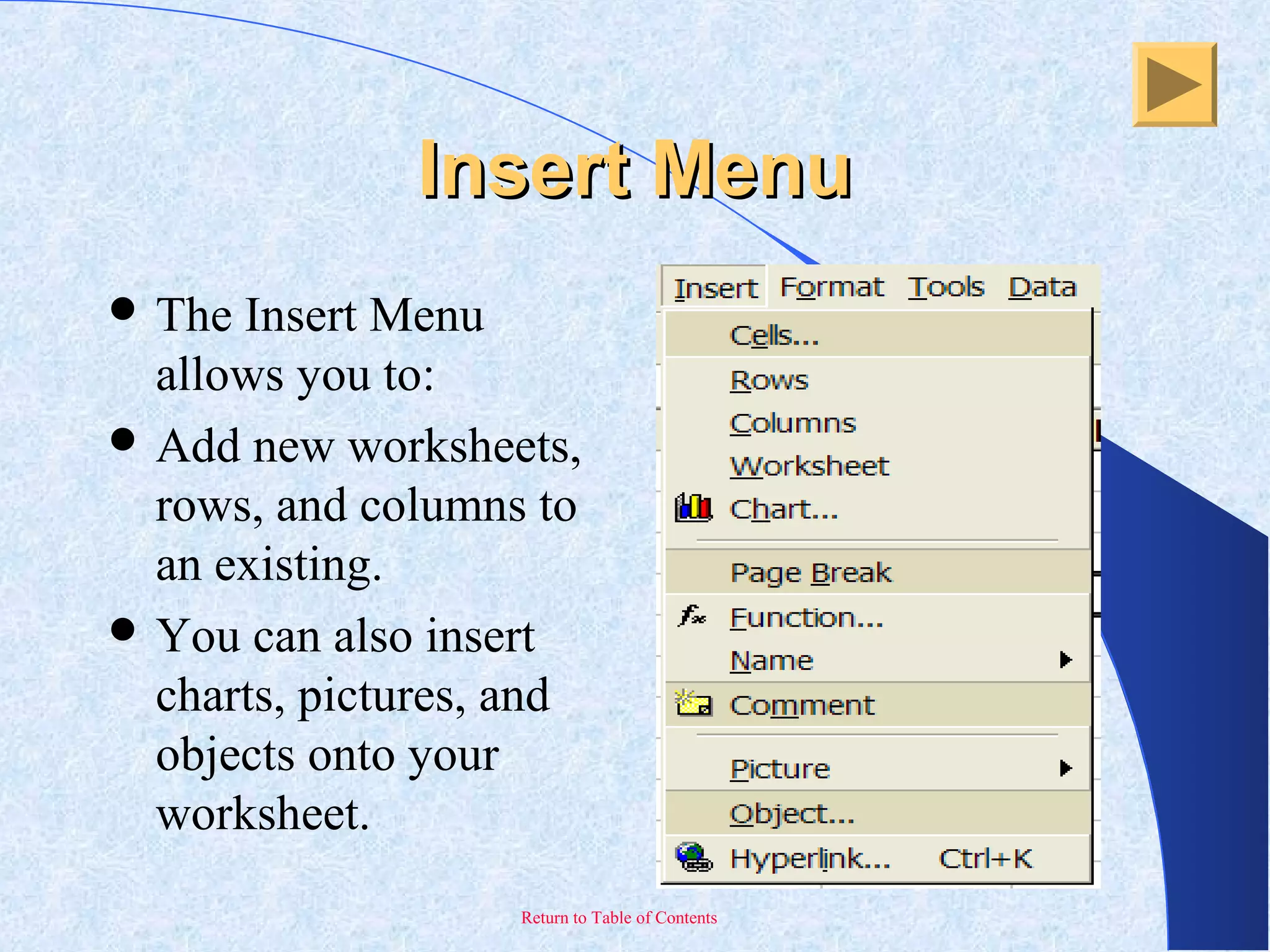
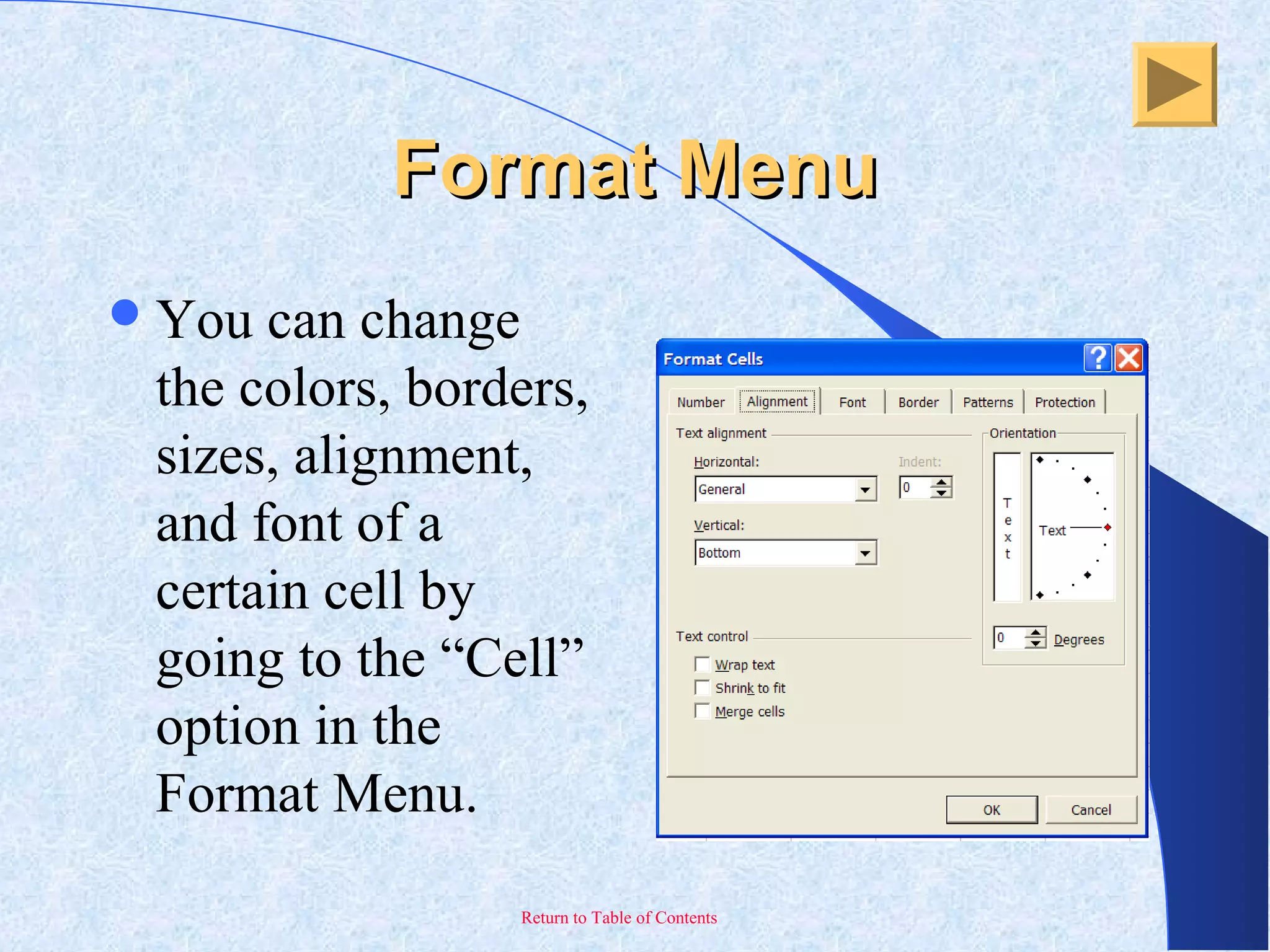
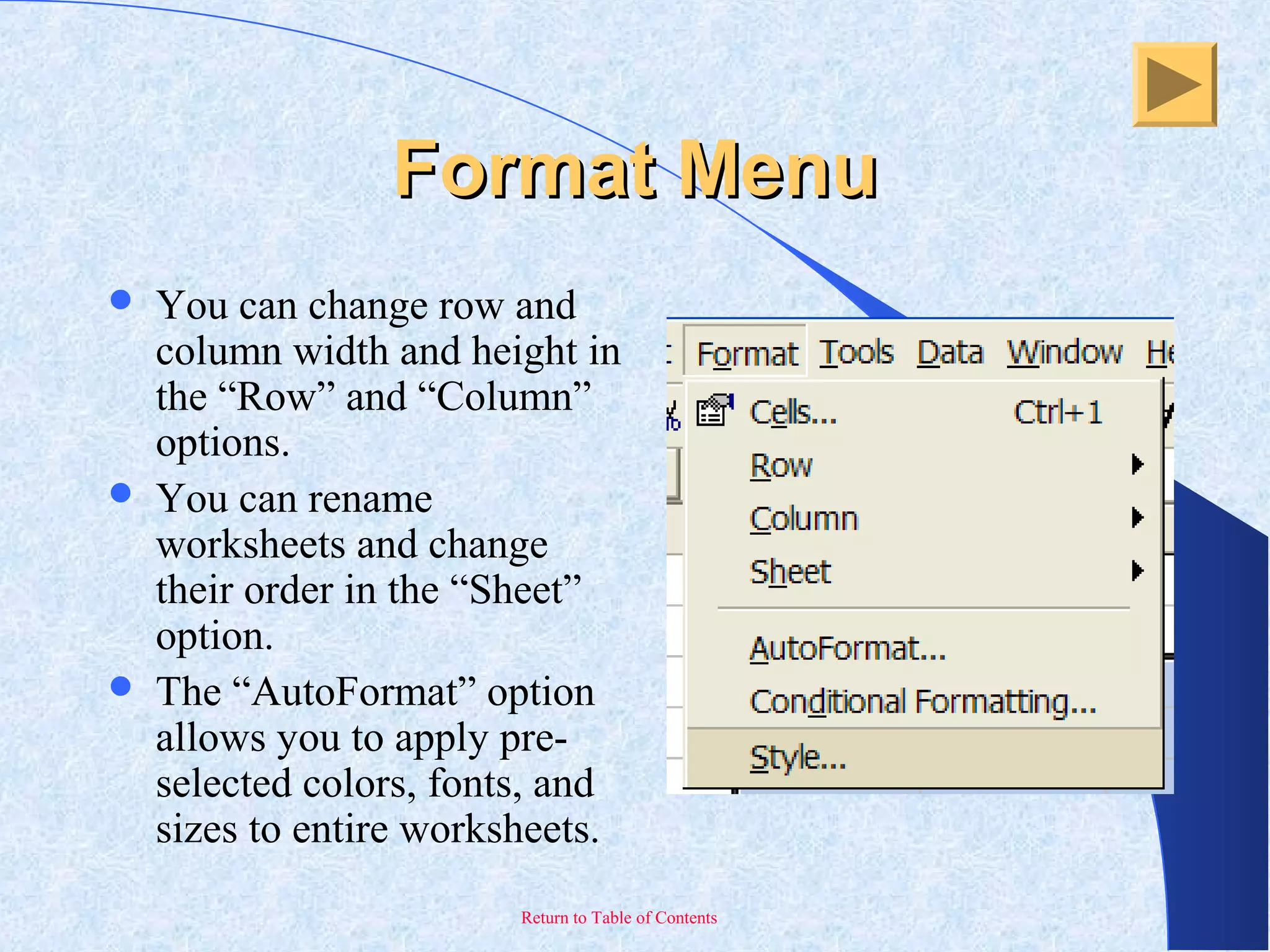
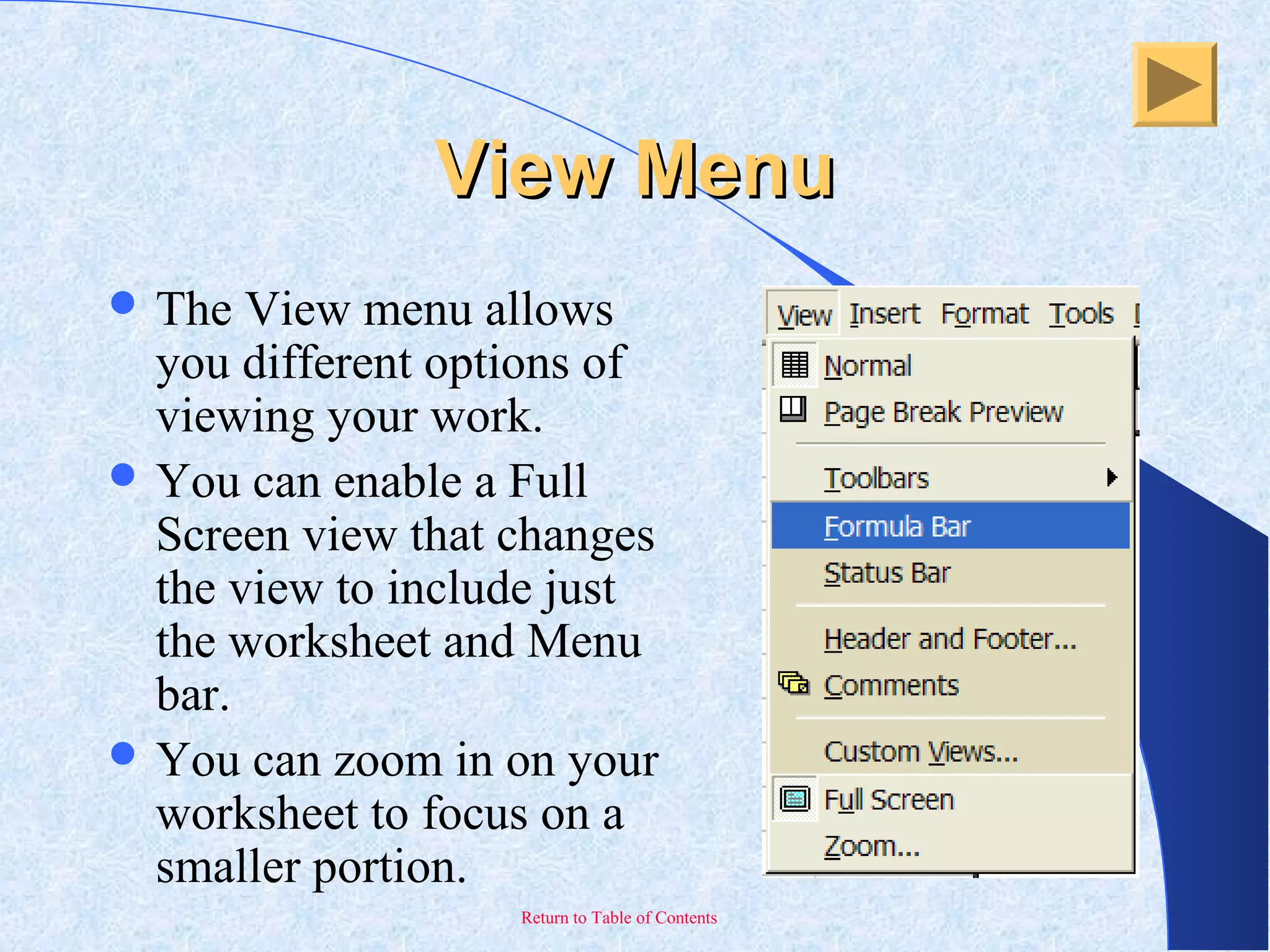
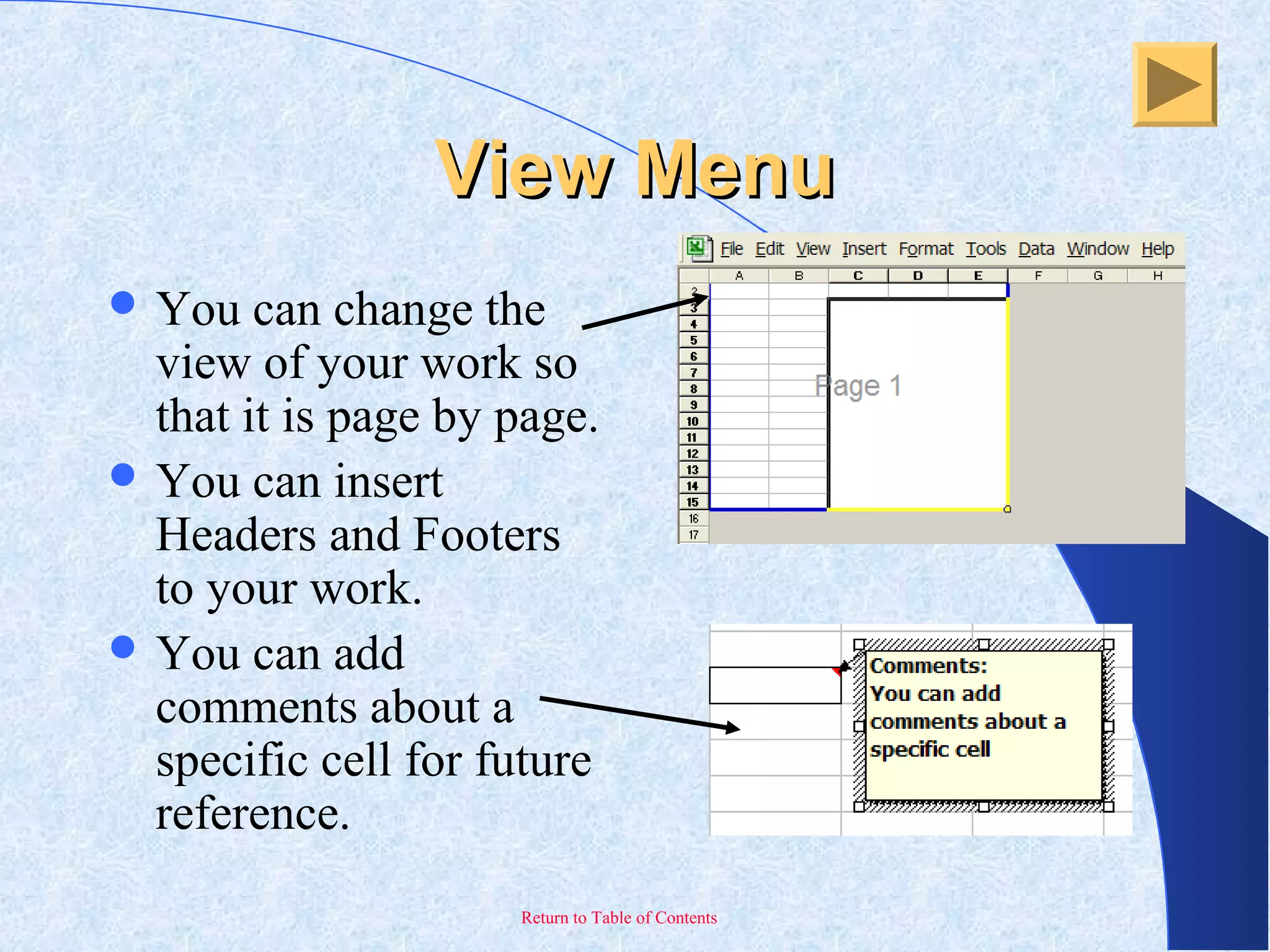
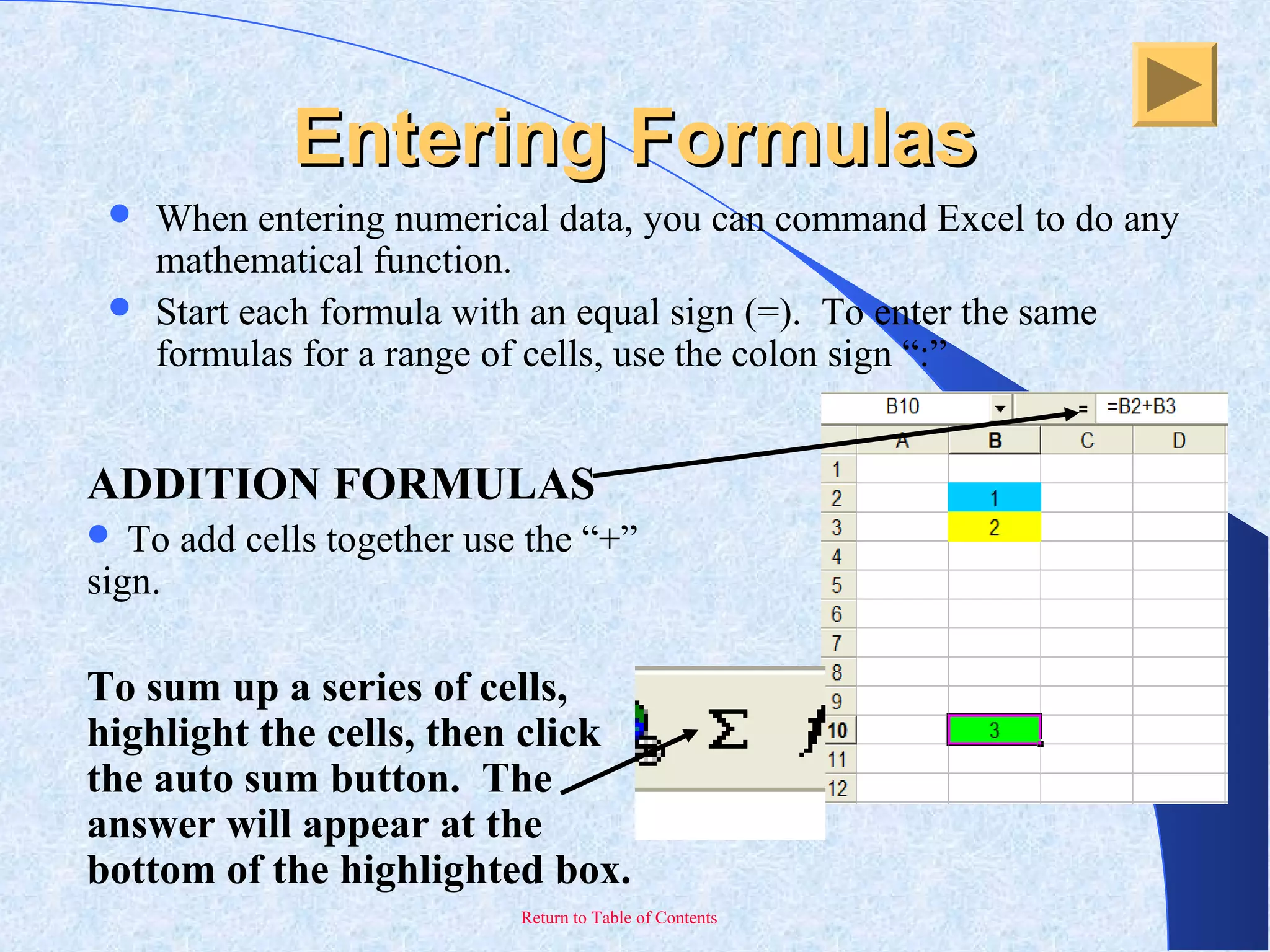
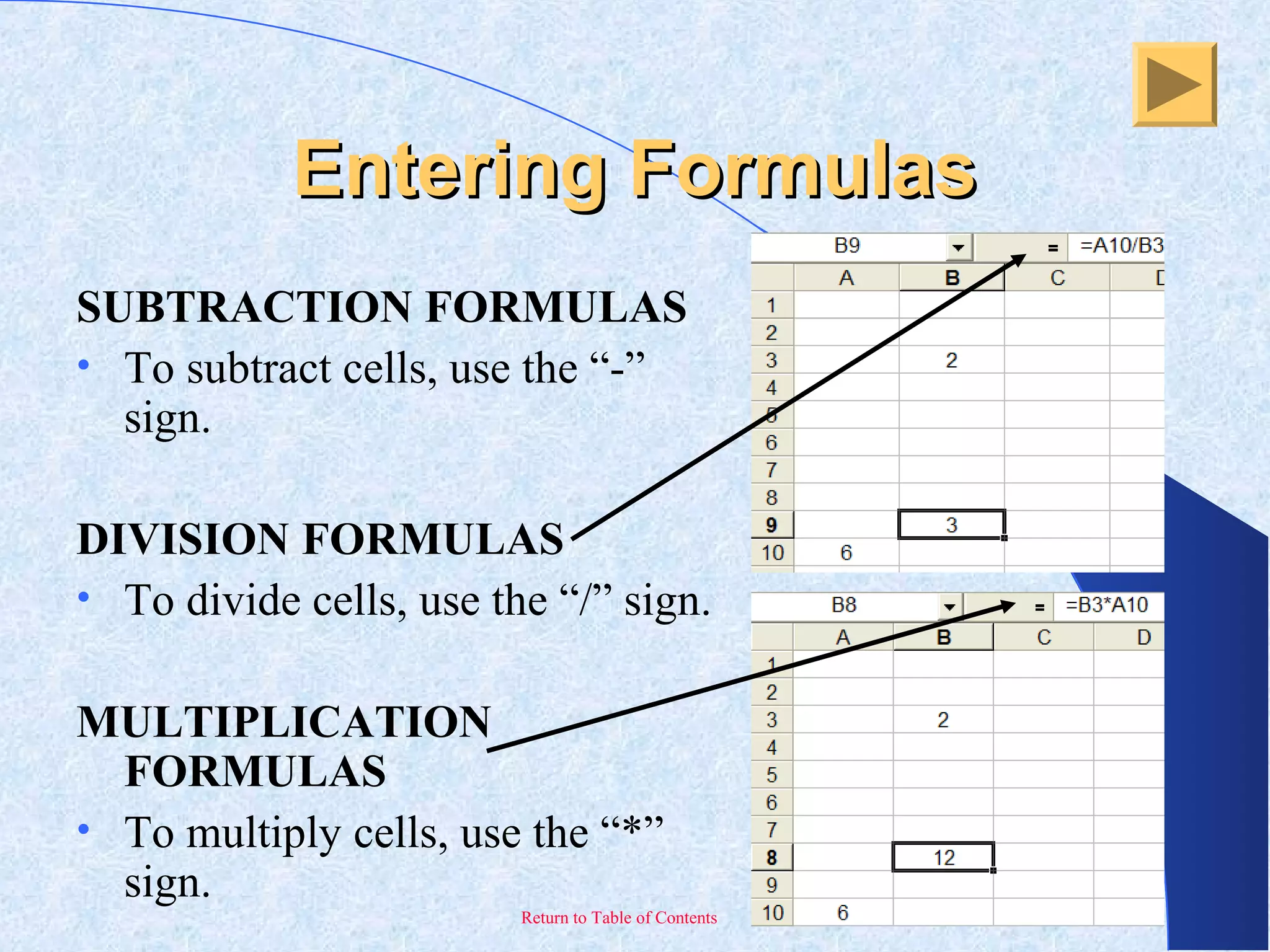
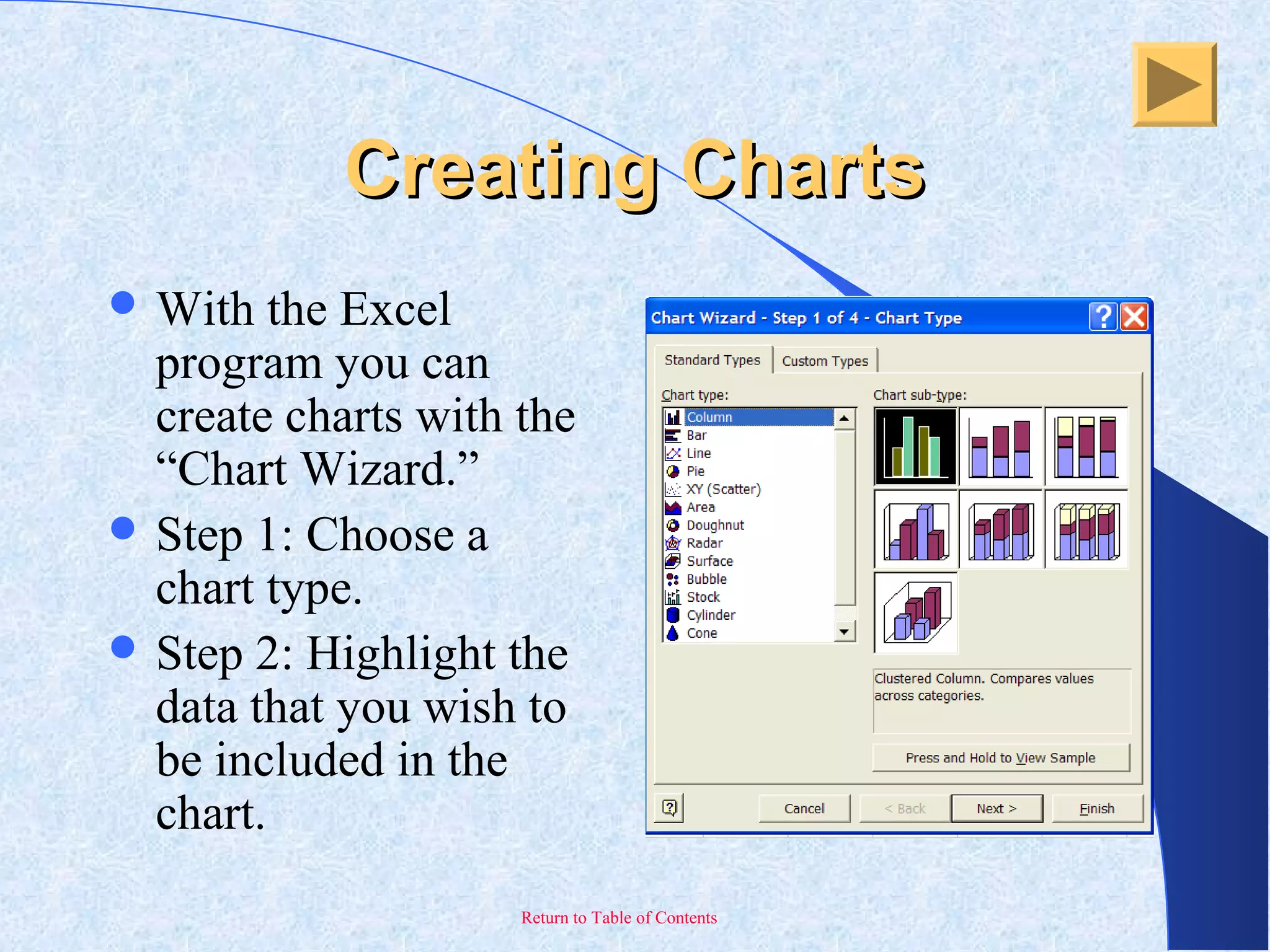
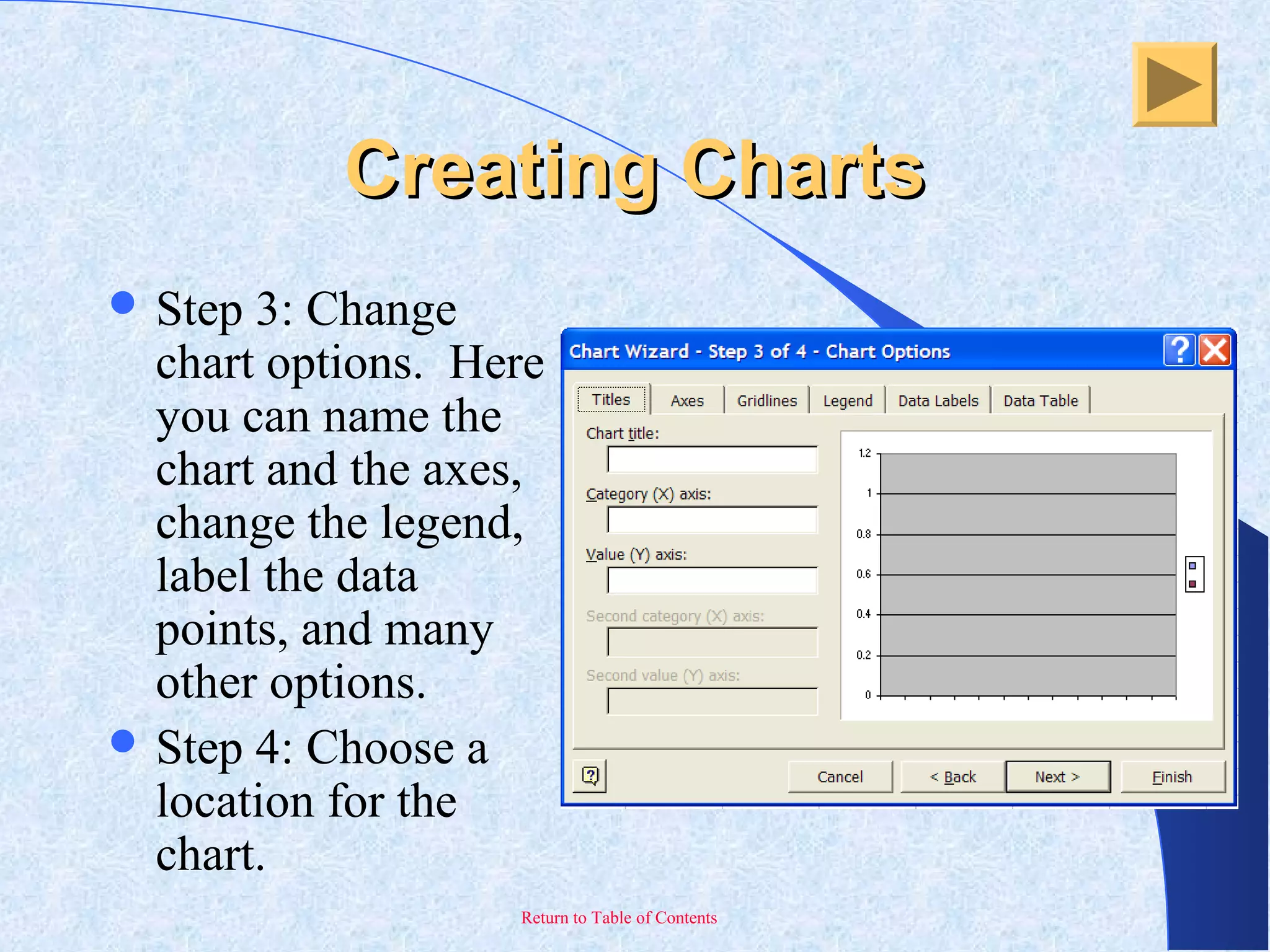
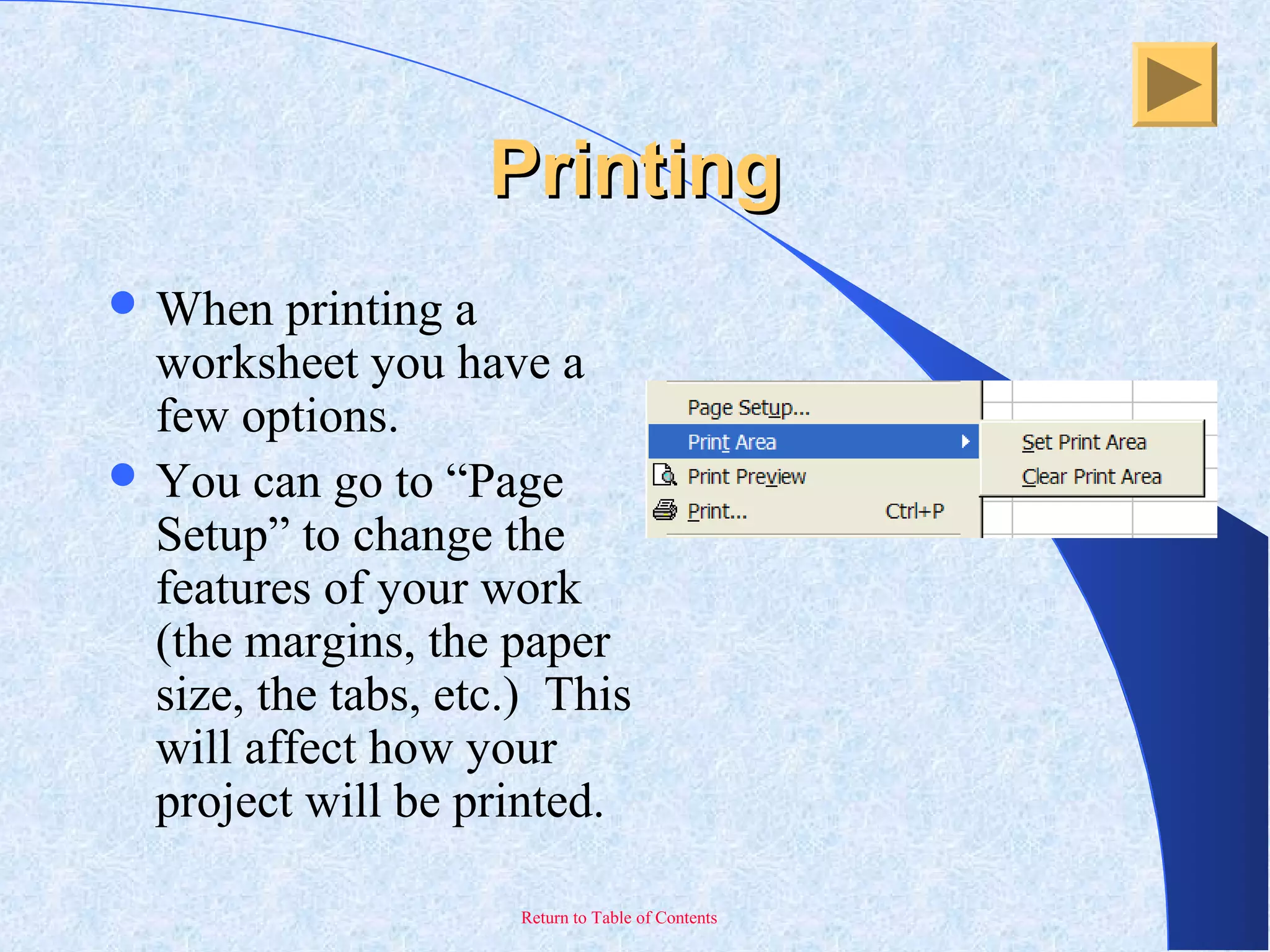
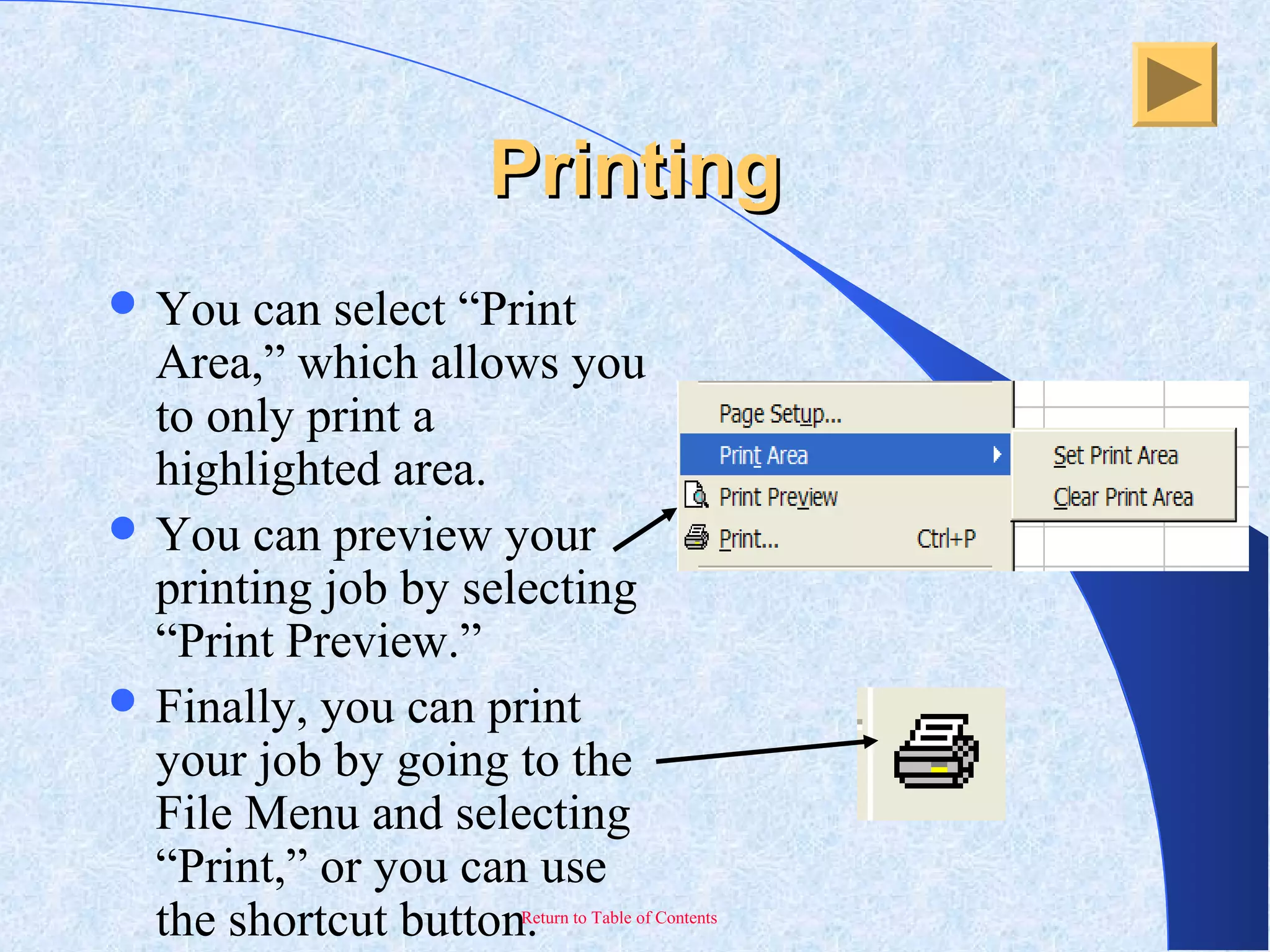
This document provides an overview and introduction to Microsoft Excel. It discusses the Excel screen layout including titles bars, menus, toolbars, and worksheets. It describes how to navigate and enter data into cells. Various Excel functions are also outlined such as formulas for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Other topics covered include formatting worksheets, creating charts, printing, and keyboard shortcuts. The document serves as a basic guide for getting started using Excel.