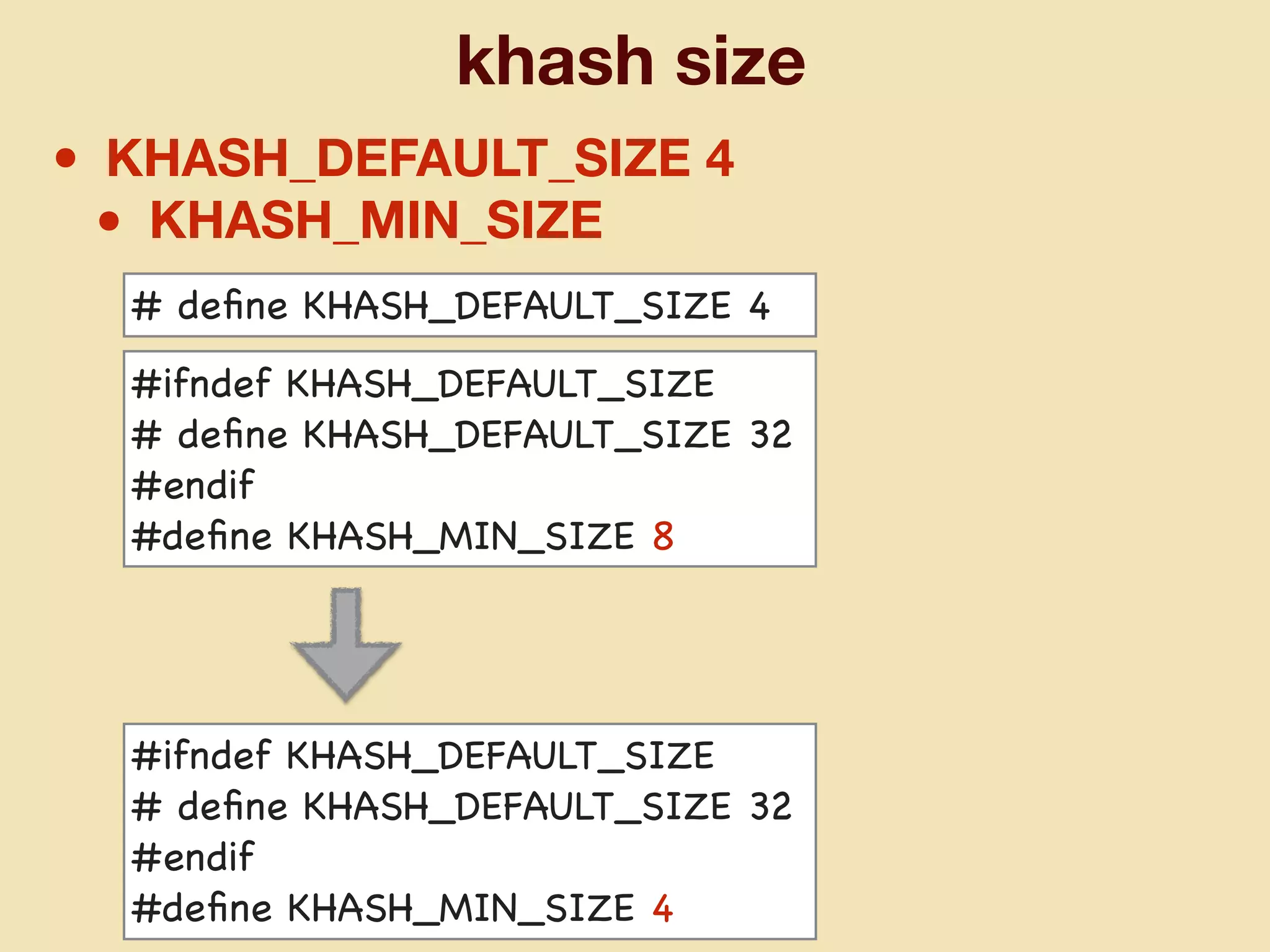
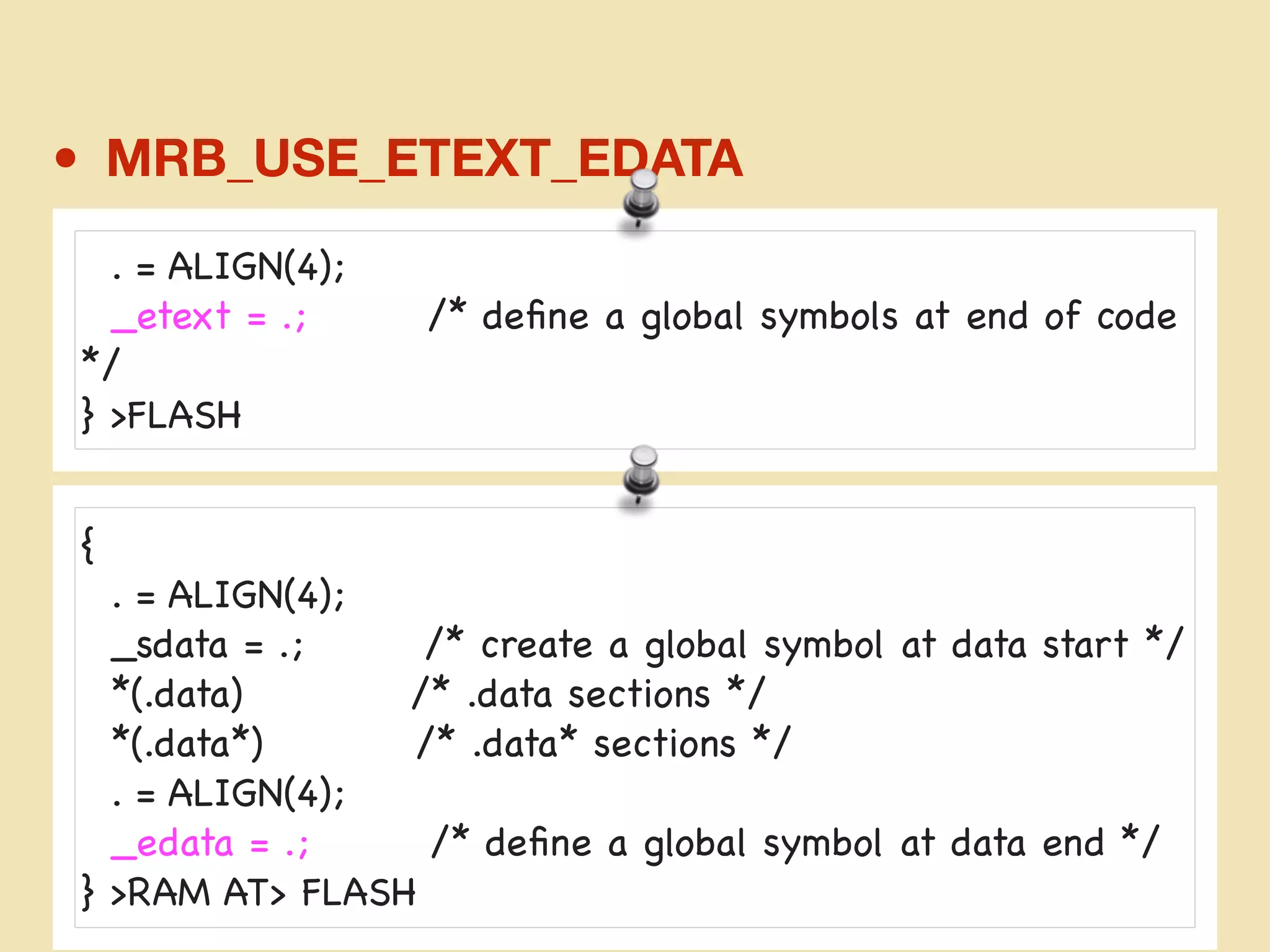
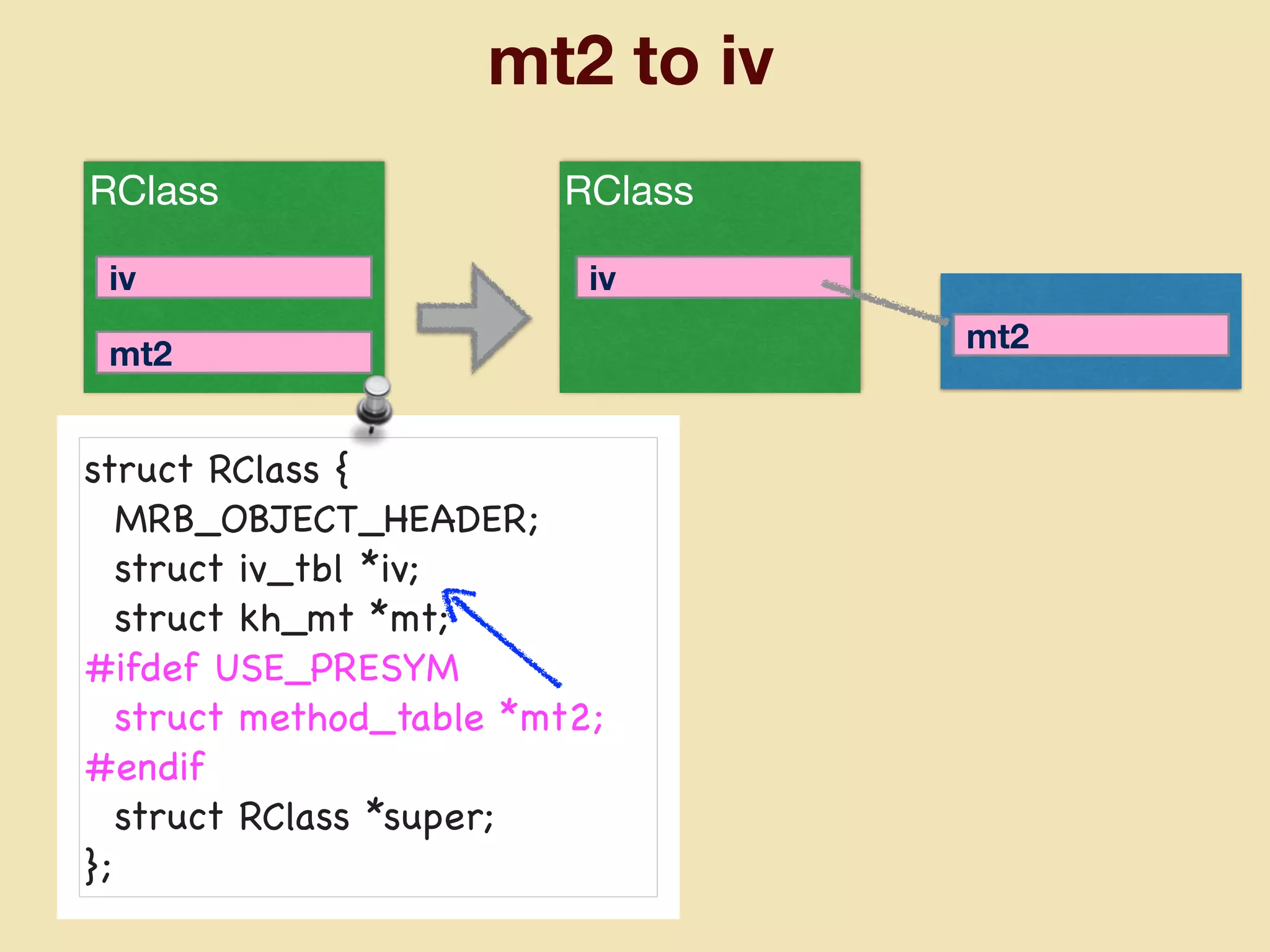
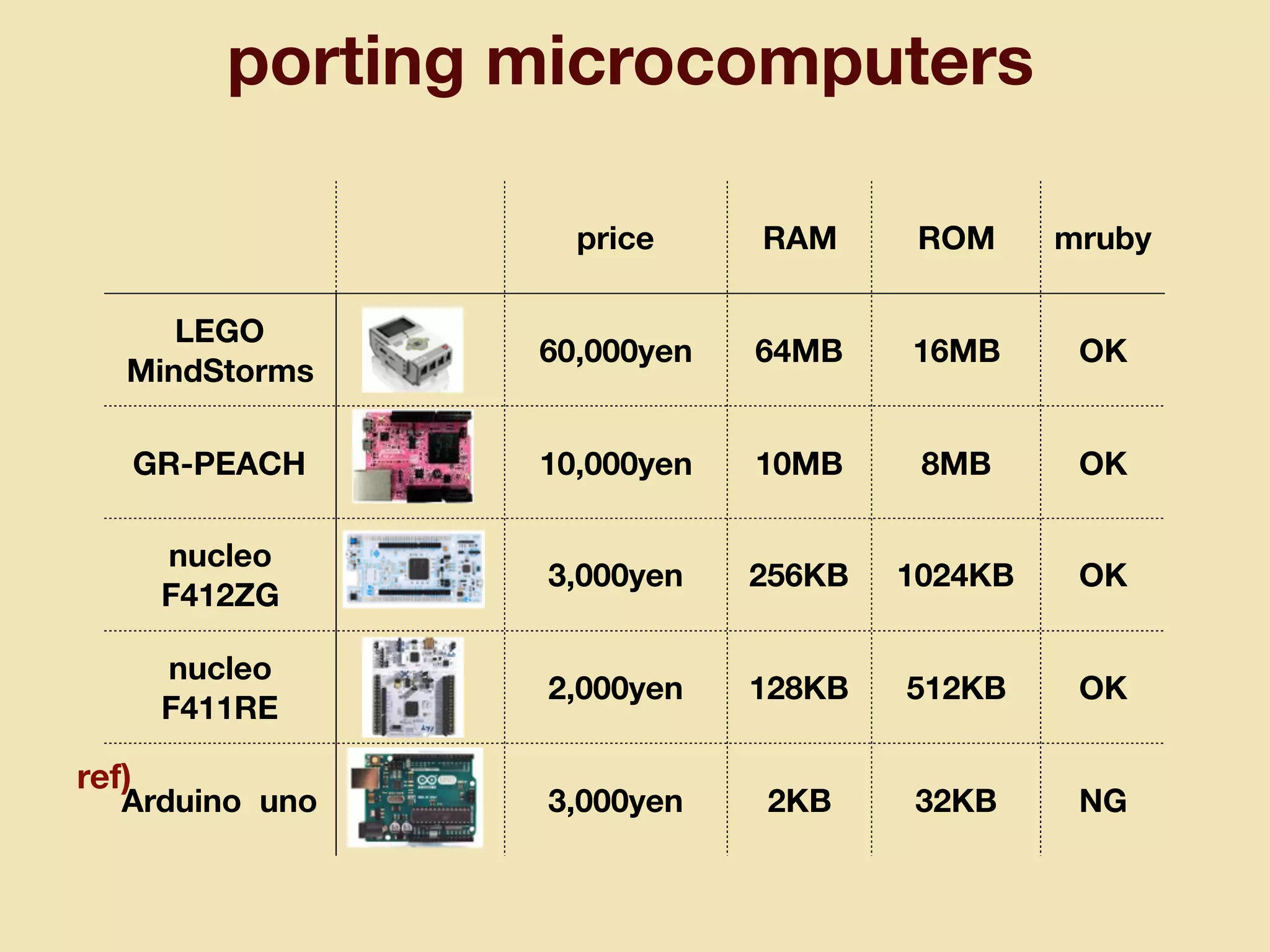
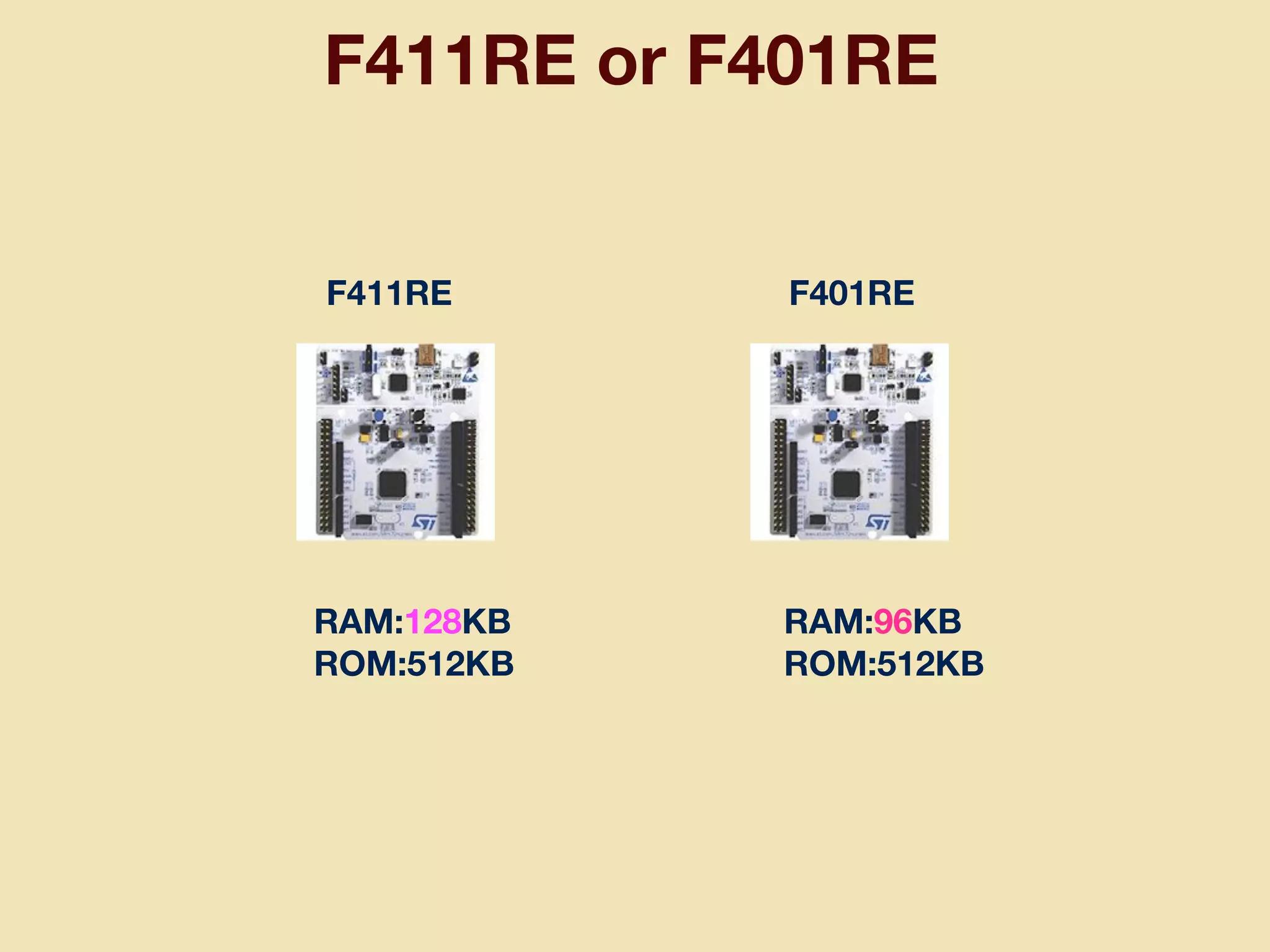
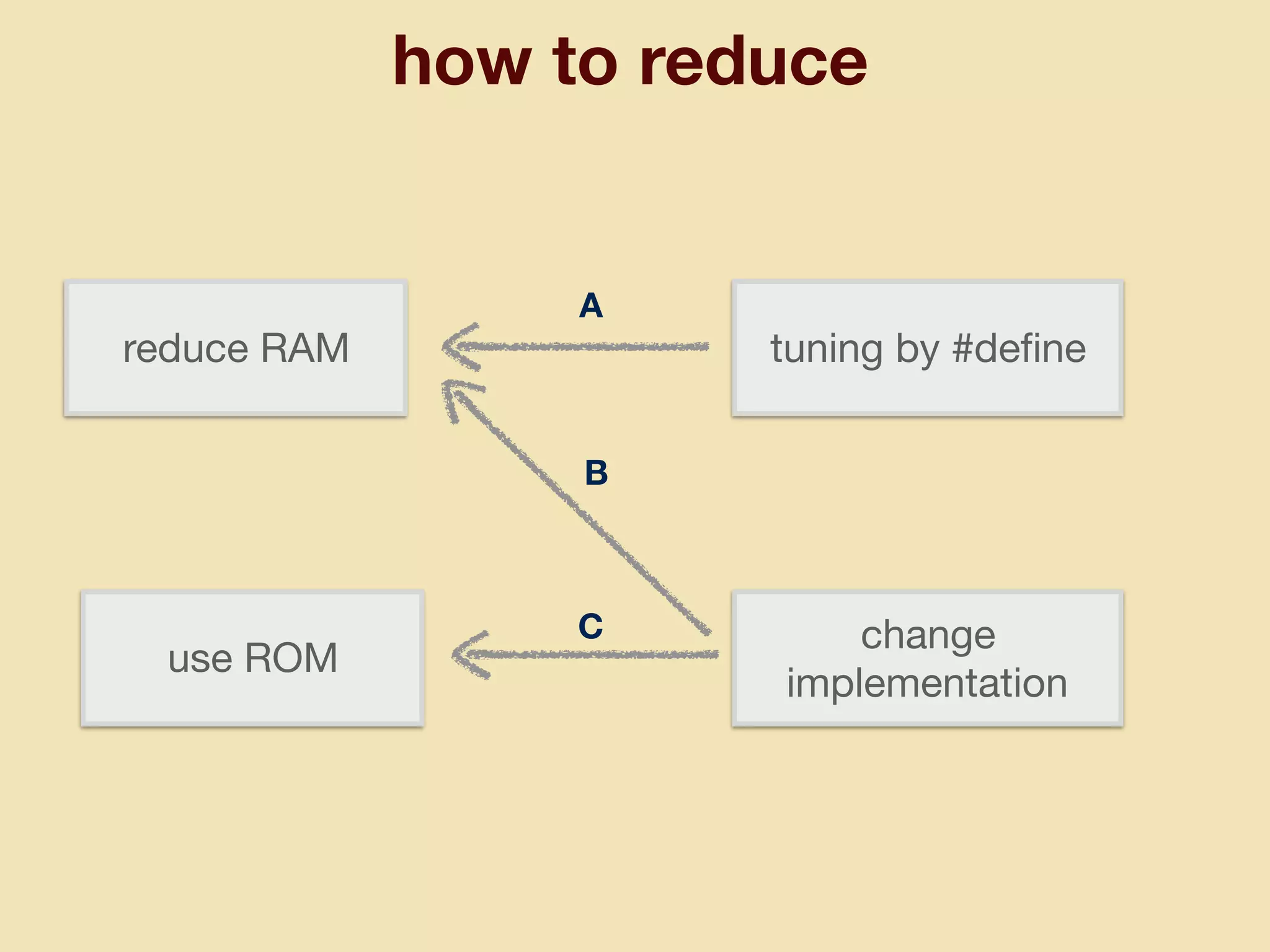
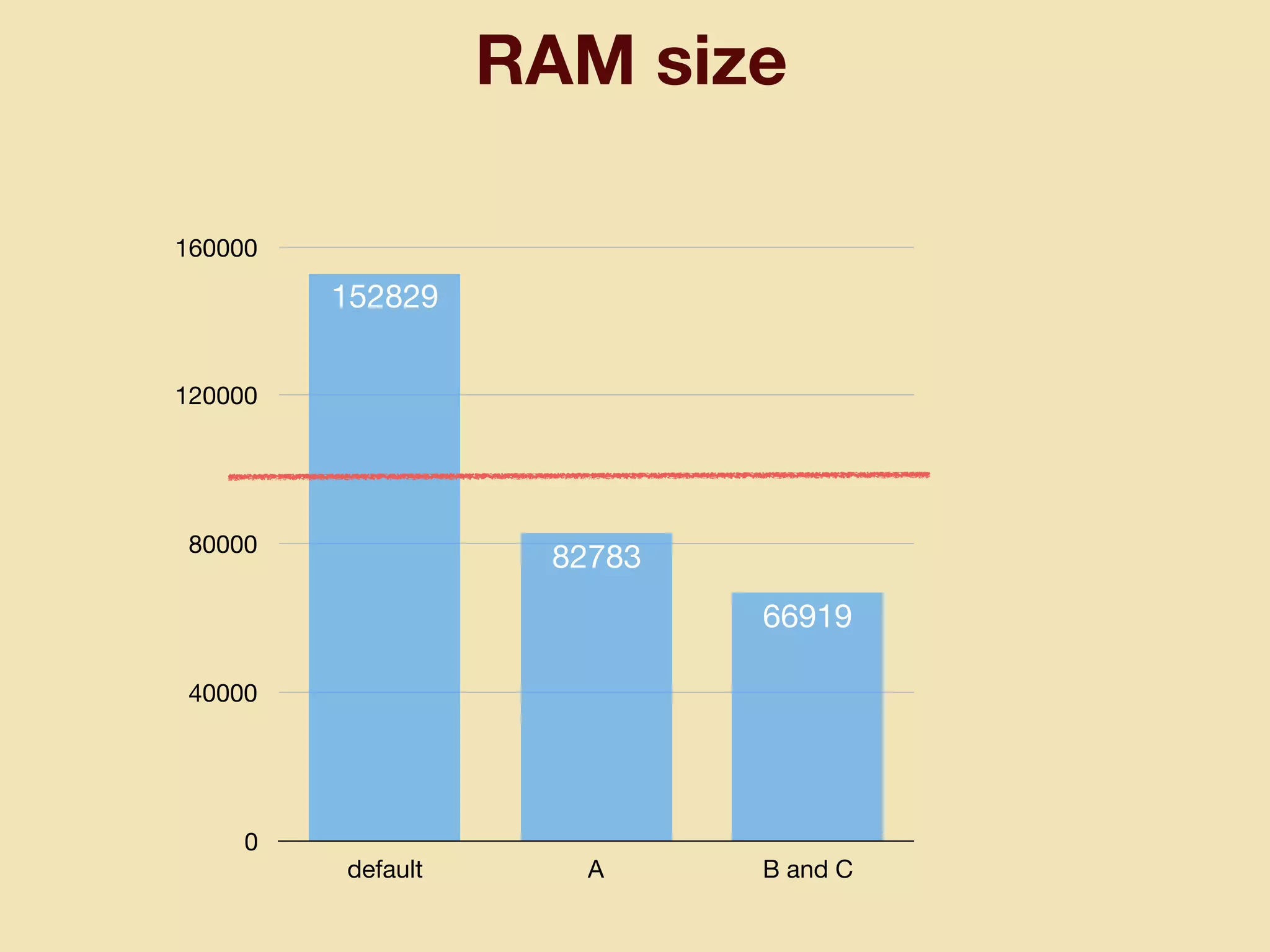
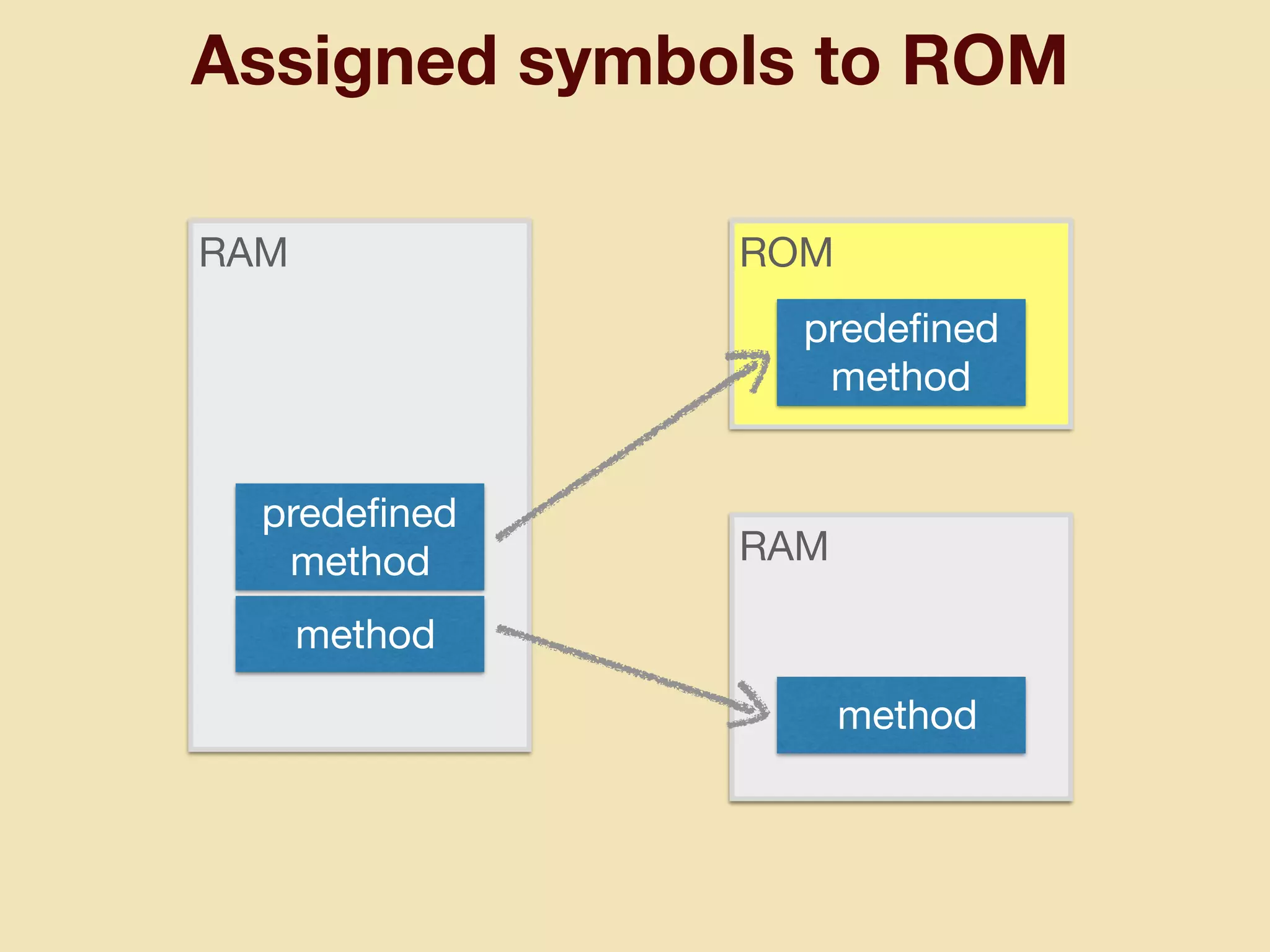
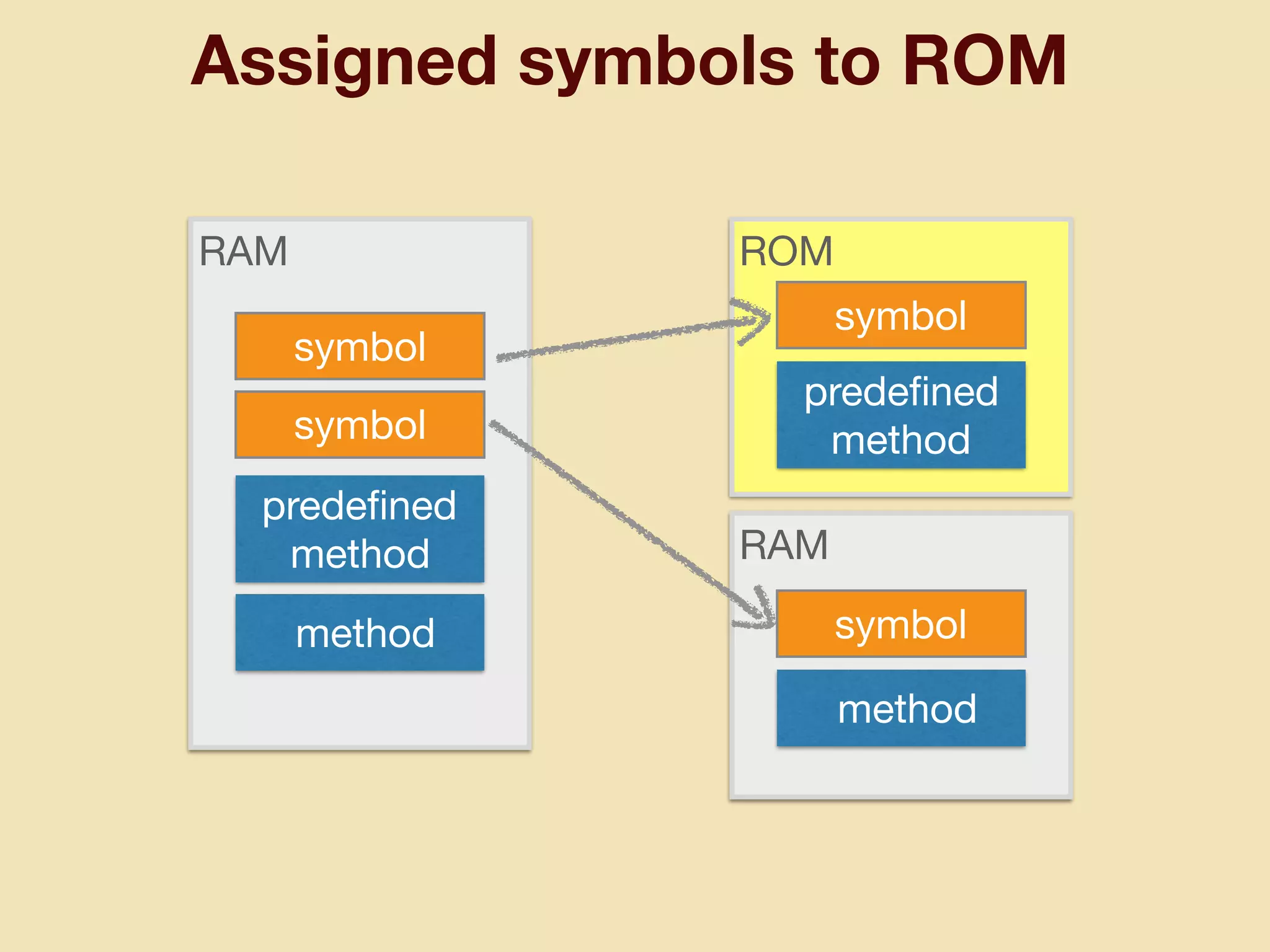
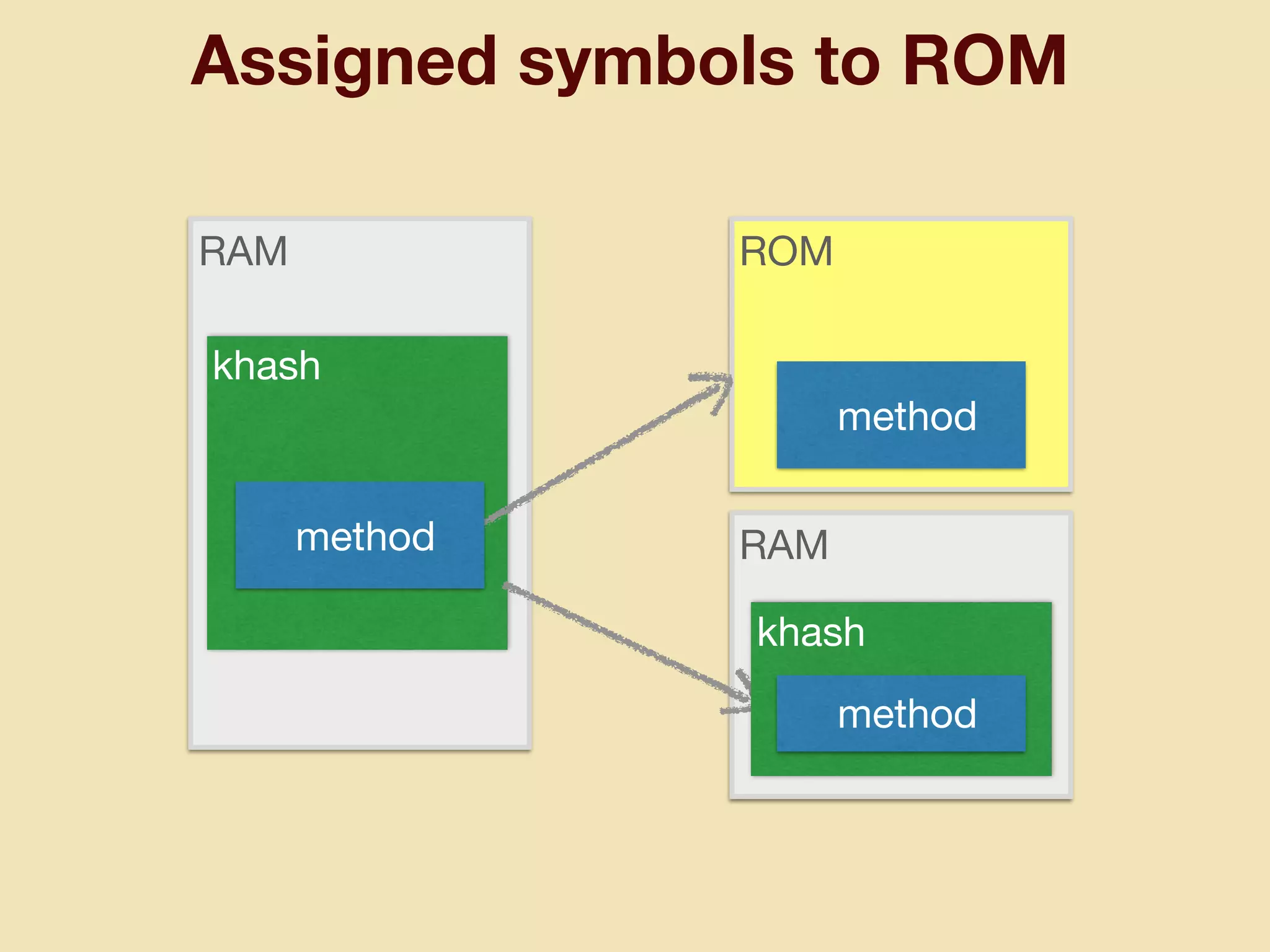
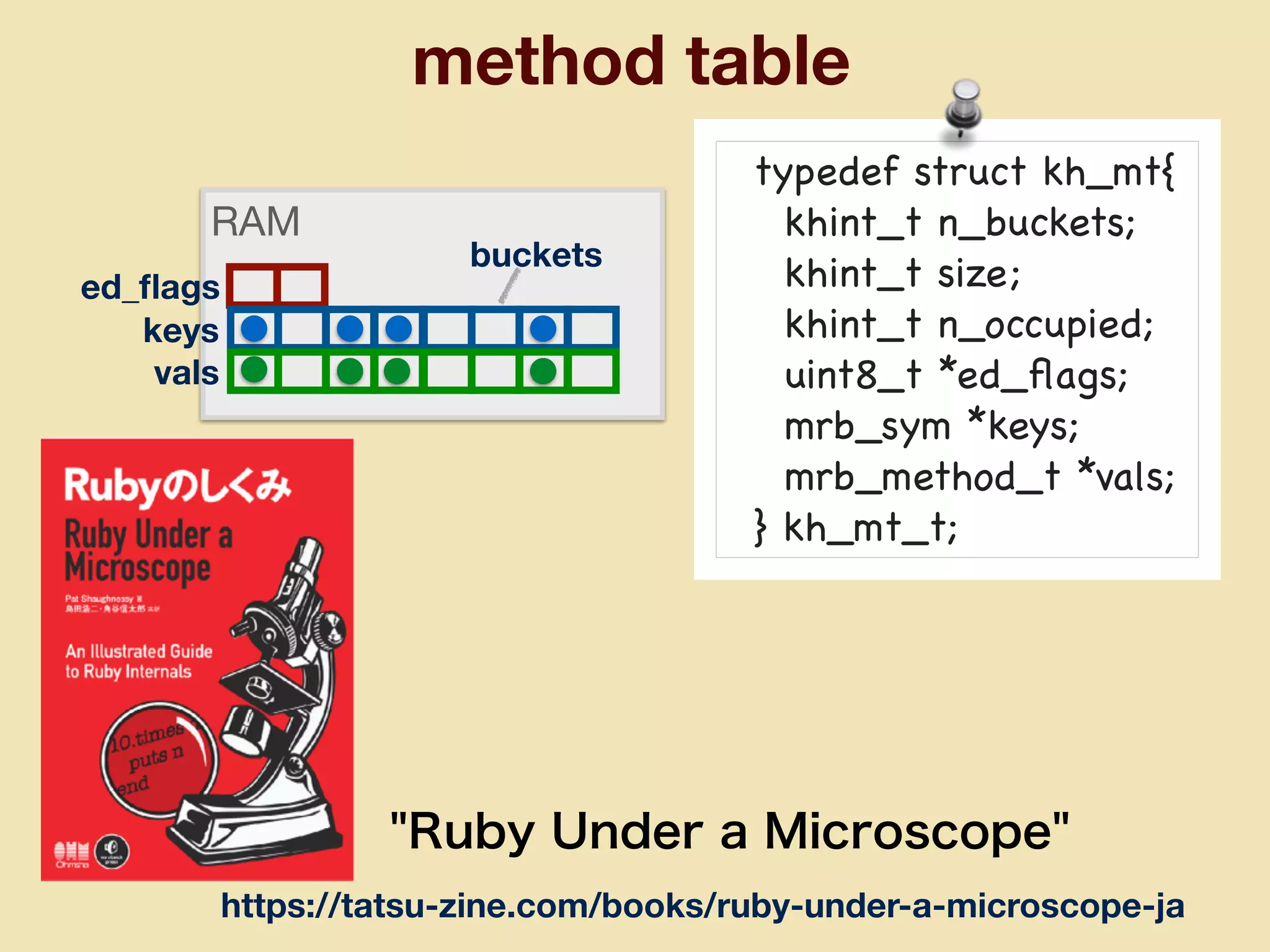
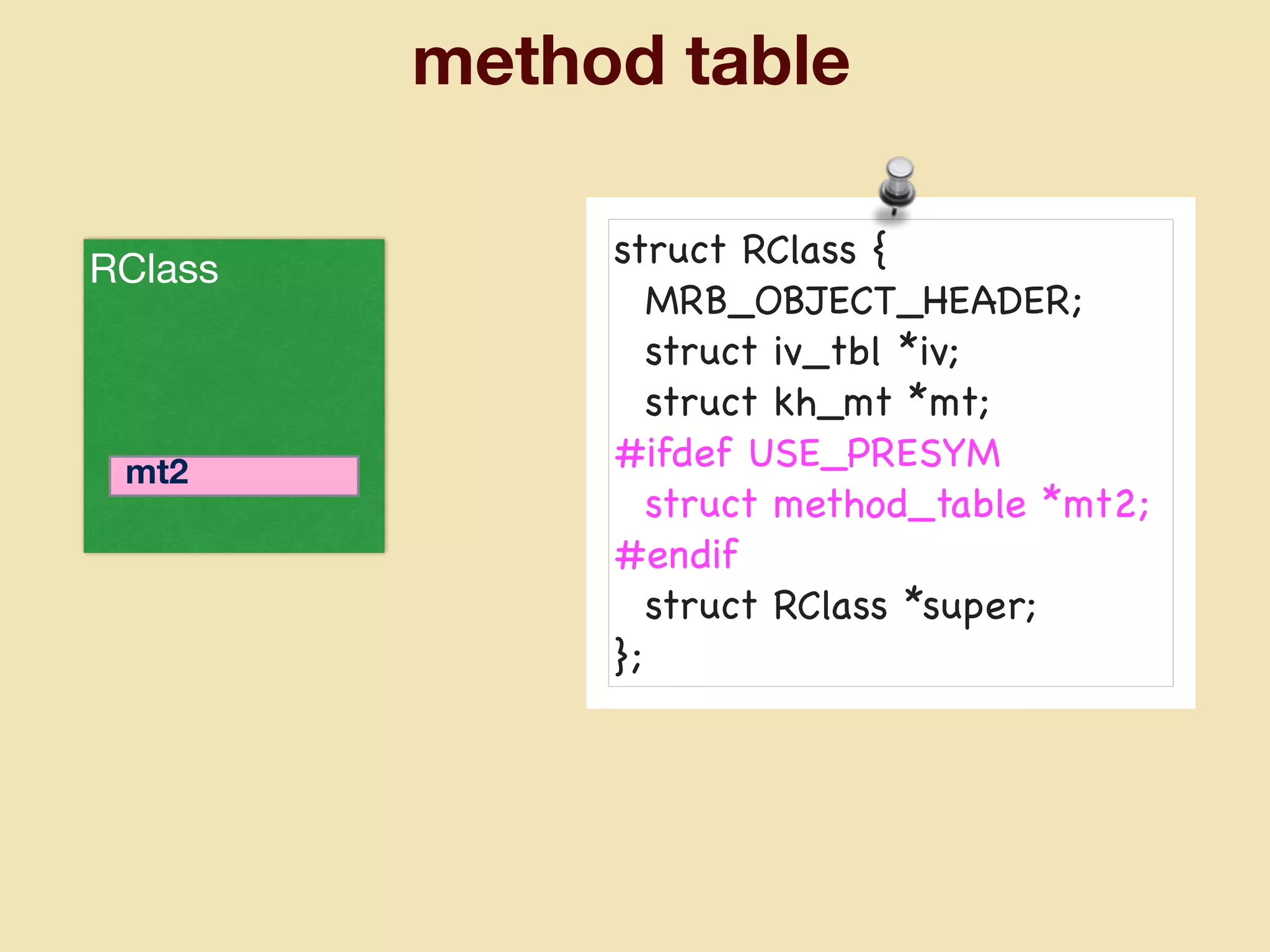
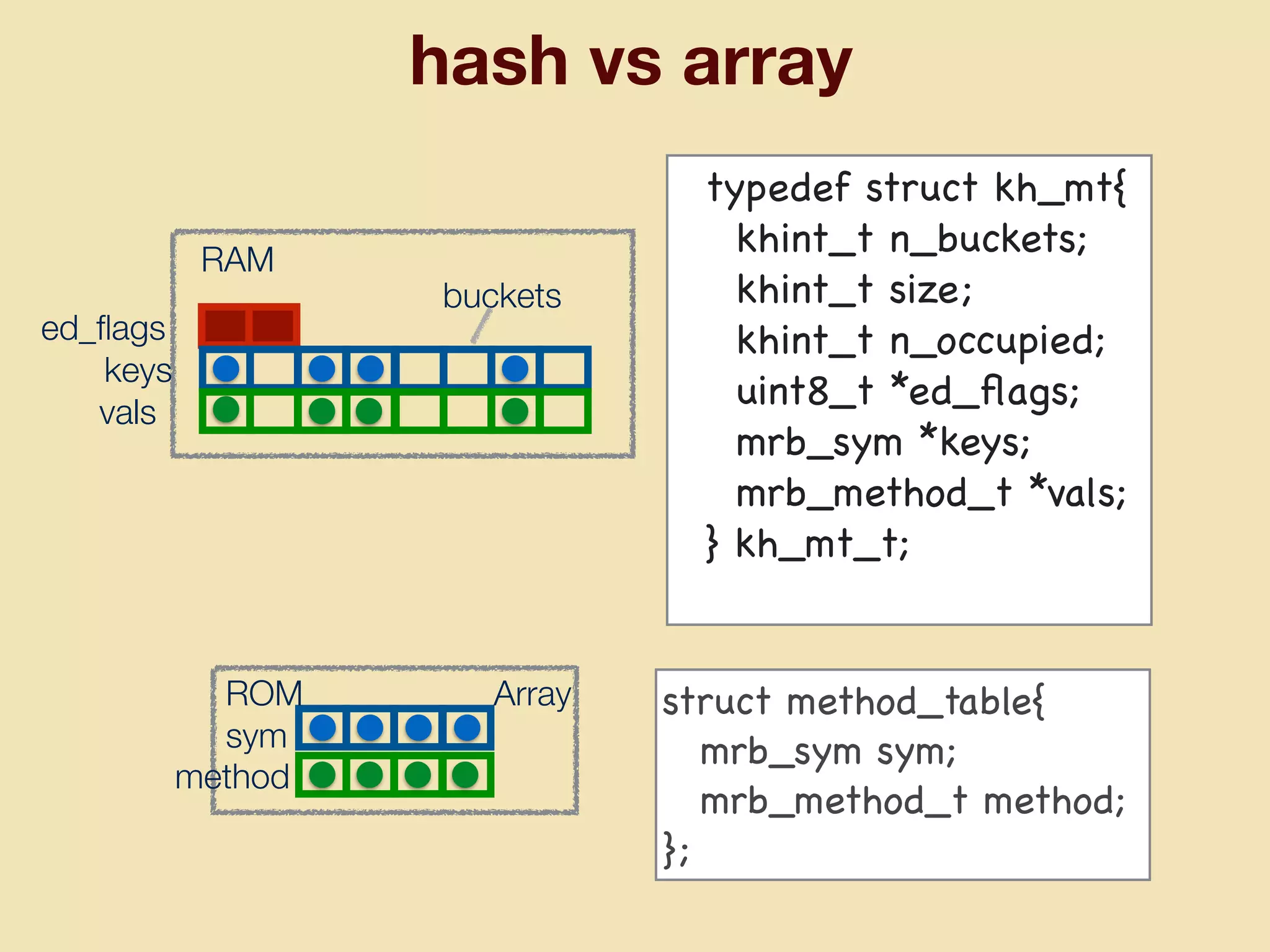
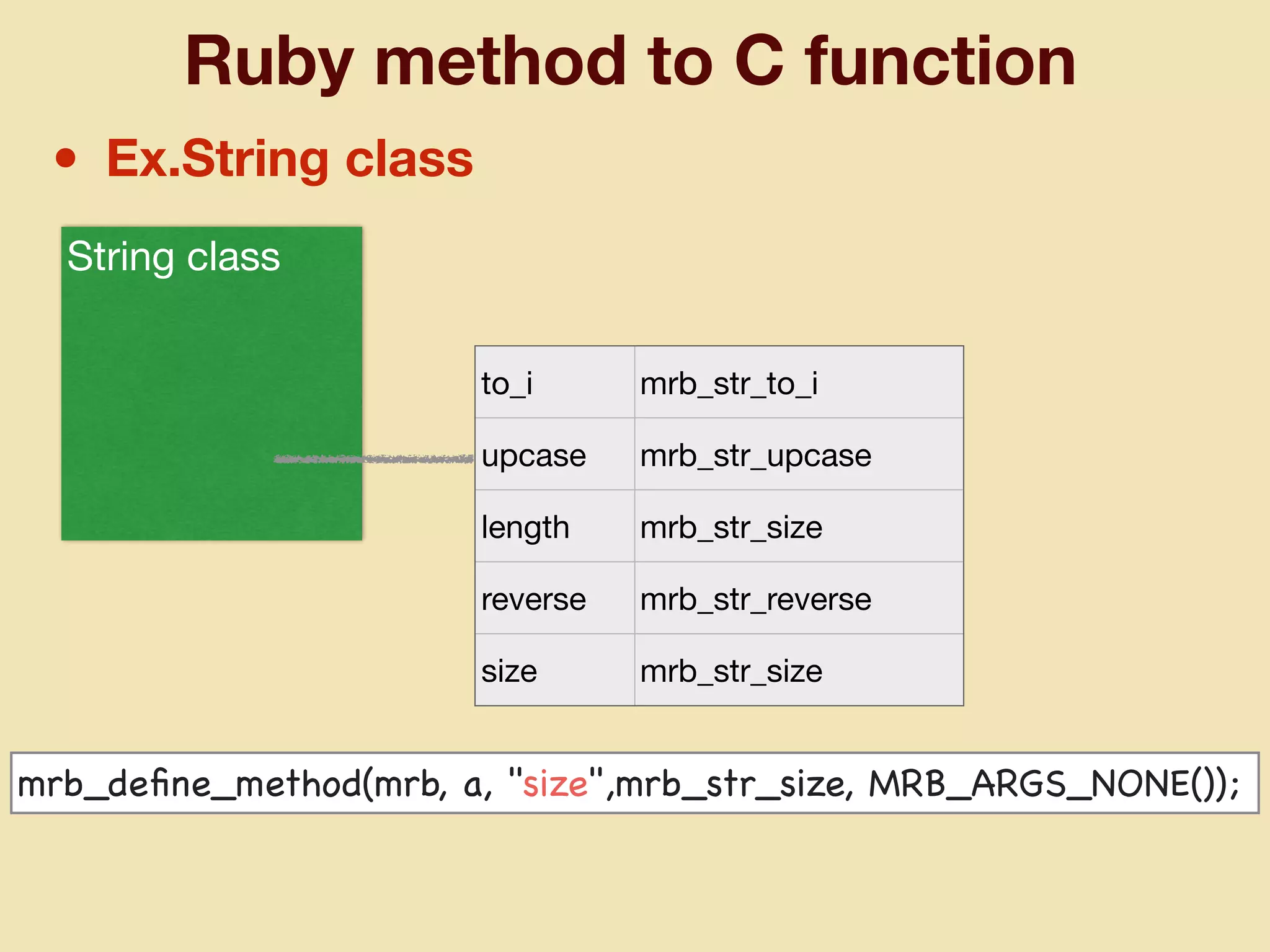
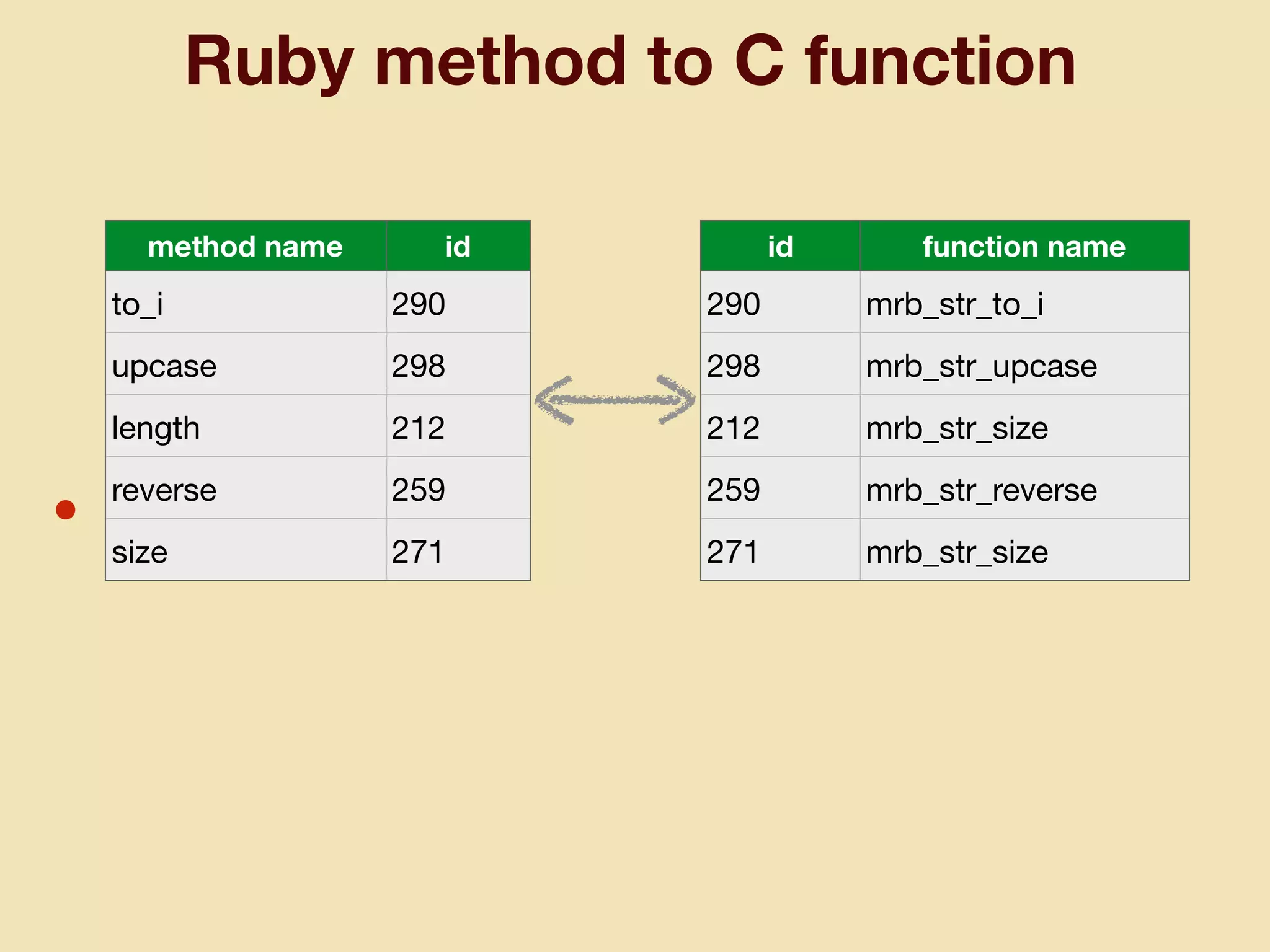
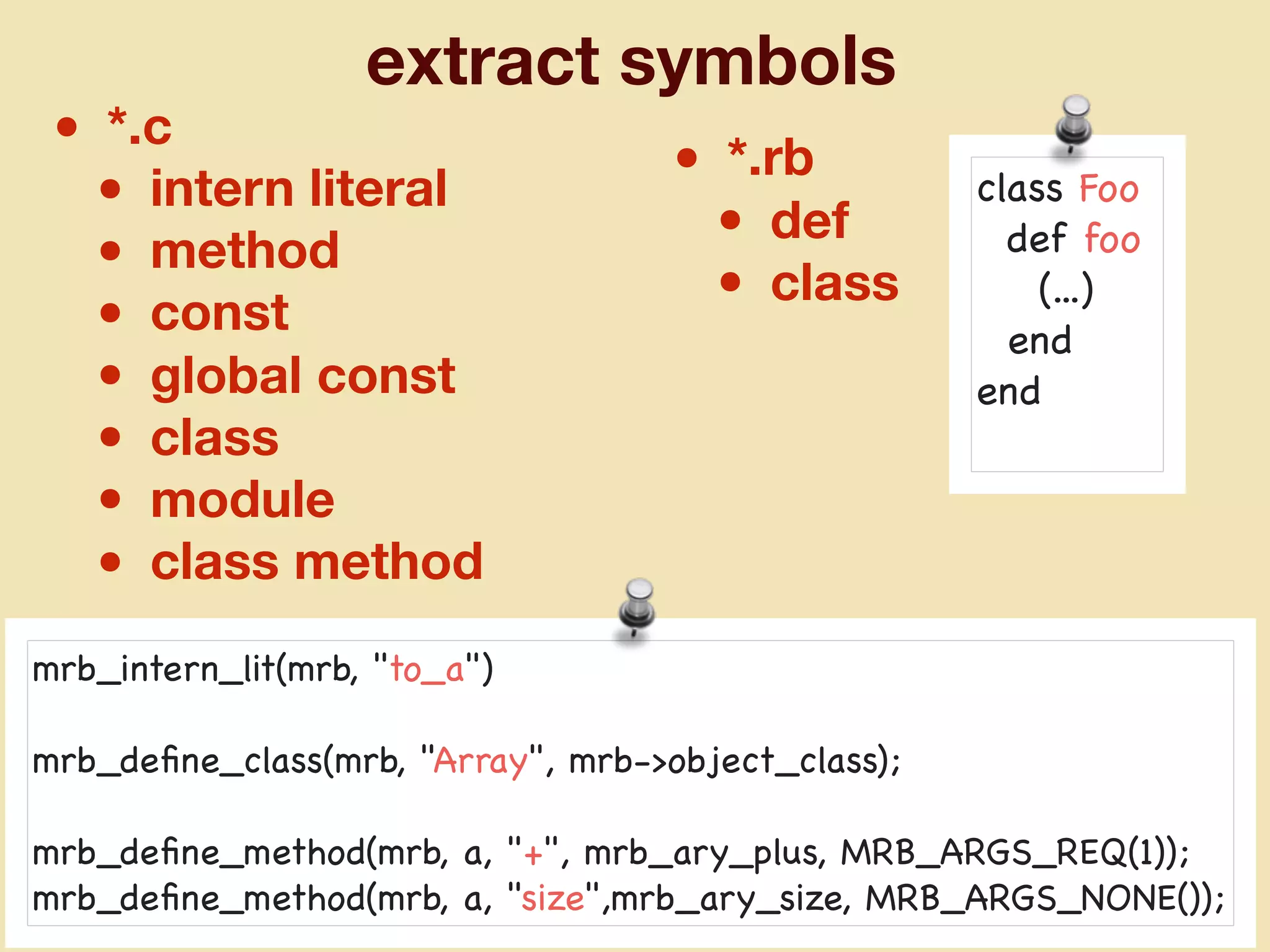
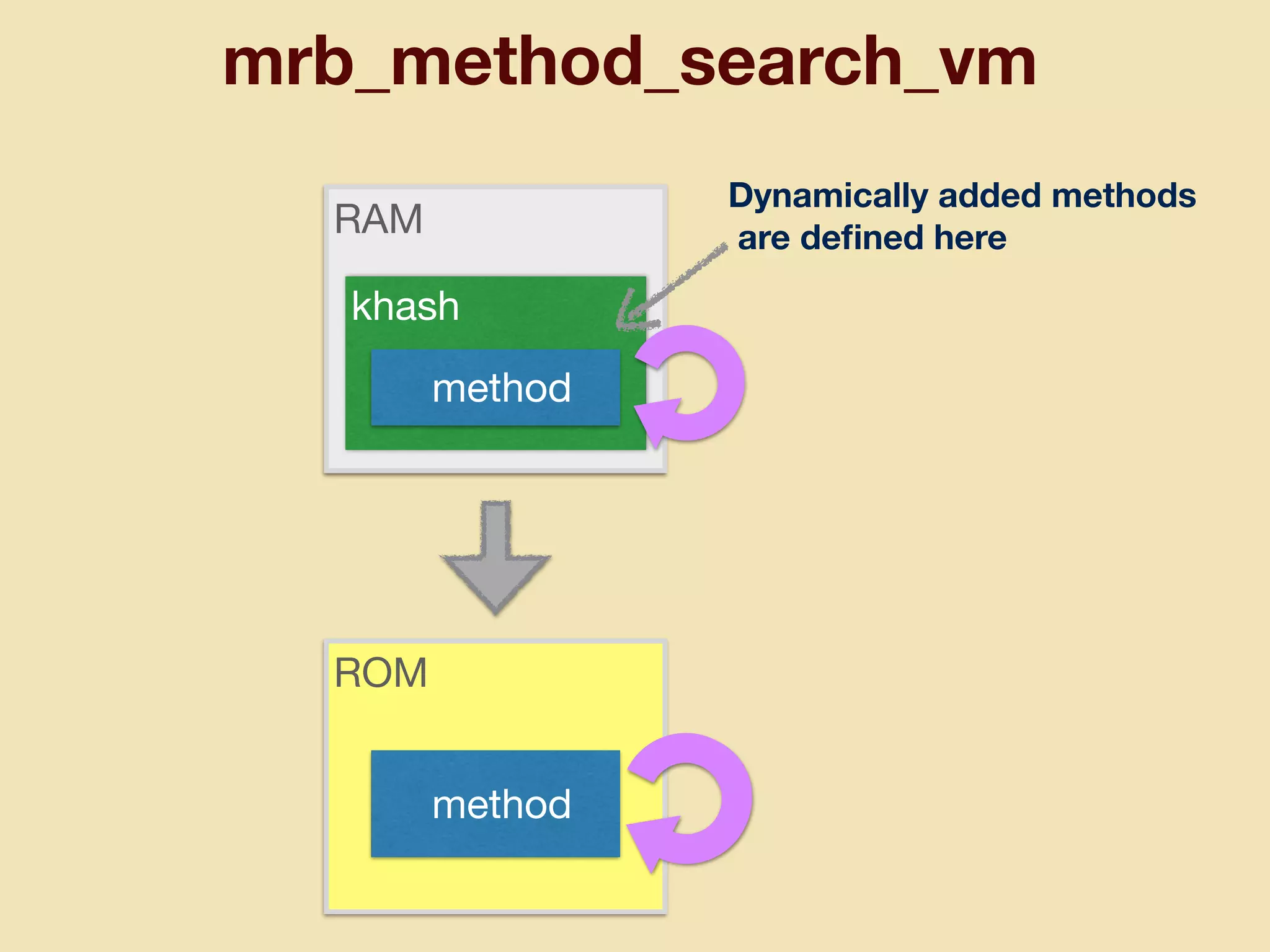
mruby can be made more lightweight by reducing its memory usage. Techniques include assigning symbols and method definitions to read-only memory (ROM) instead of random-access memory (RAM), using arrays instead of hash tables to store method lookup data, removing local variable name metadata from bytecode, and tuning configuration options like hash table size. This allows mruby to run on microcontrollers with very limited RAM and ROM, expanding its usage in small low-cost embedded devices.











![remove local variable's names
• make bytecode without irep->lv
static void
irep_remove_lv(mrb_state *mrb, mrb_irep *irep)
{
int i;
if (irep->lv) {
mrb_free(mrb, irep->lv);
irep->lv = NULL;
}
for (i = 0; i < irep->rlen; ++i) {
irep_remove_lv(mrb, irep->reps[i]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rubykaigi2018-yamanekko-180618145908/75/mruby-can-be-more-lightweight-26-2048.jpg)