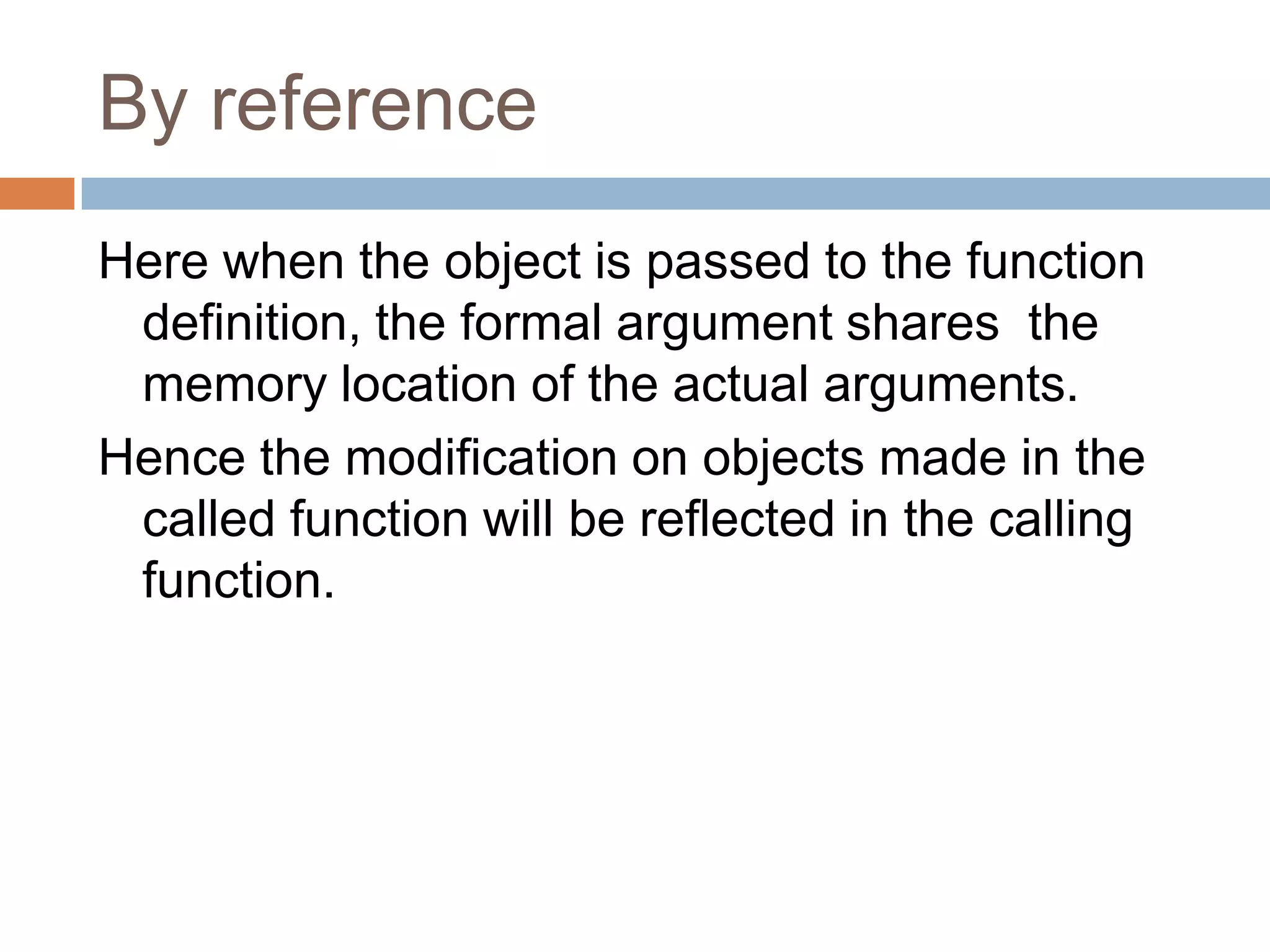
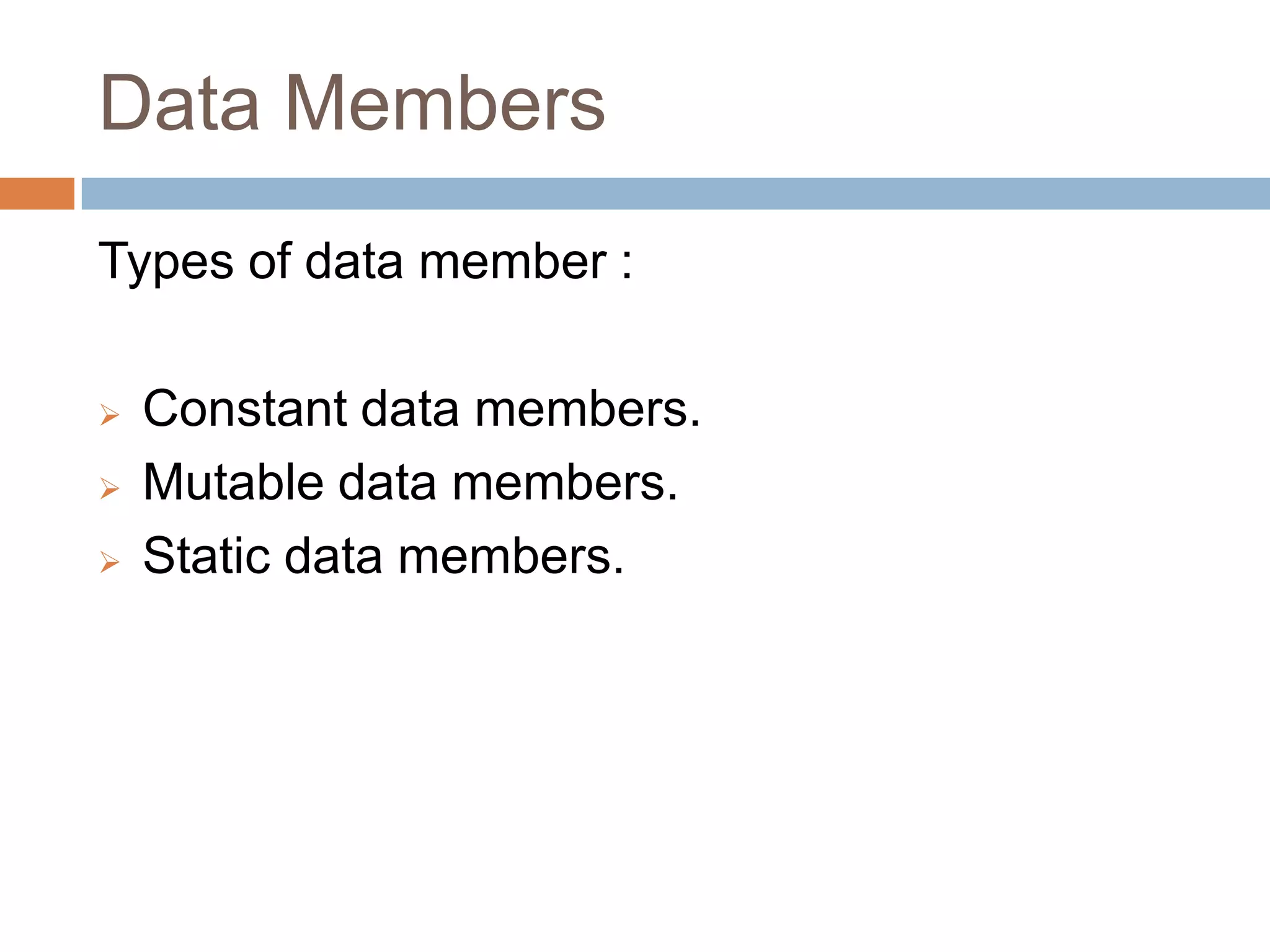
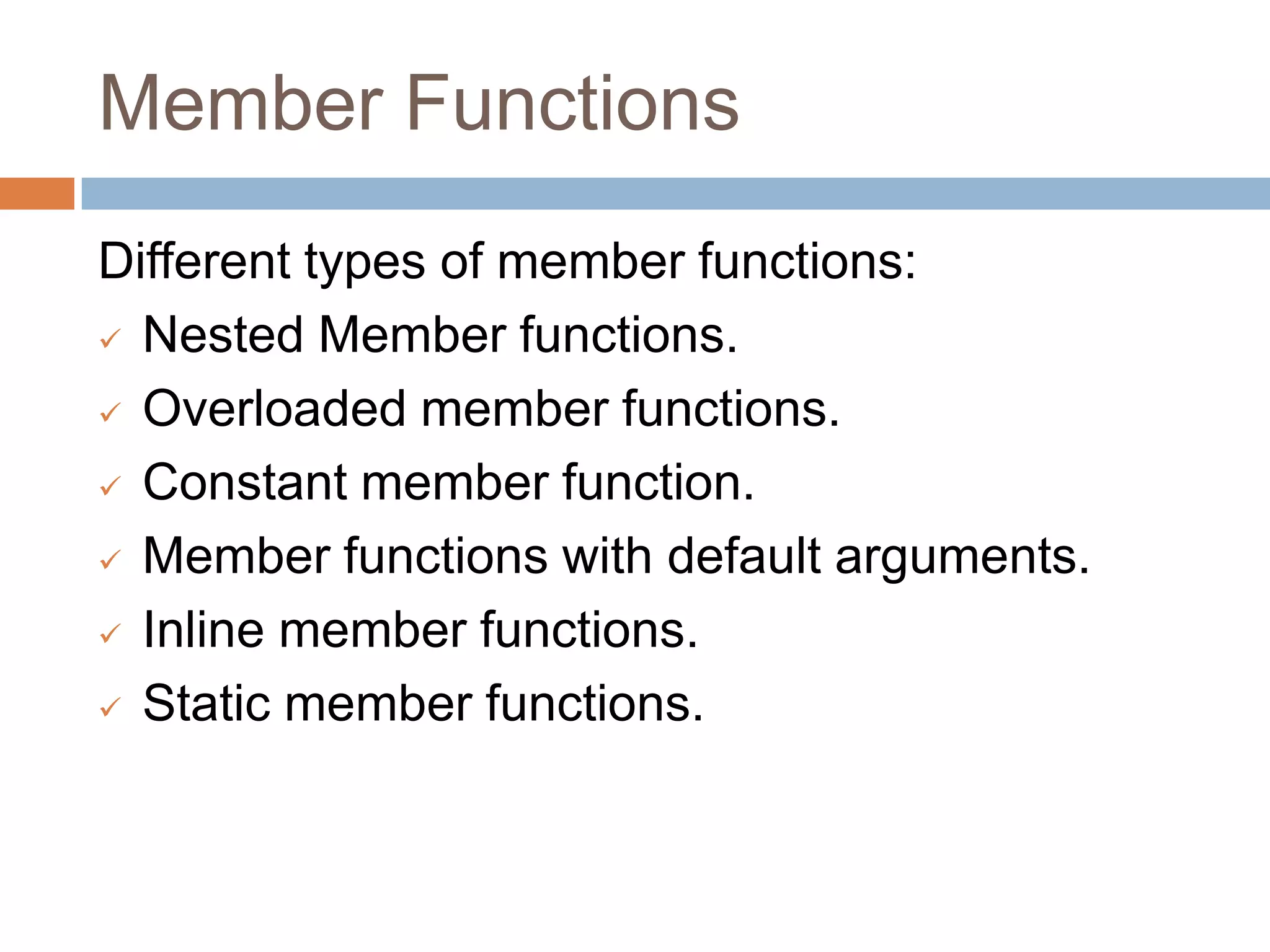
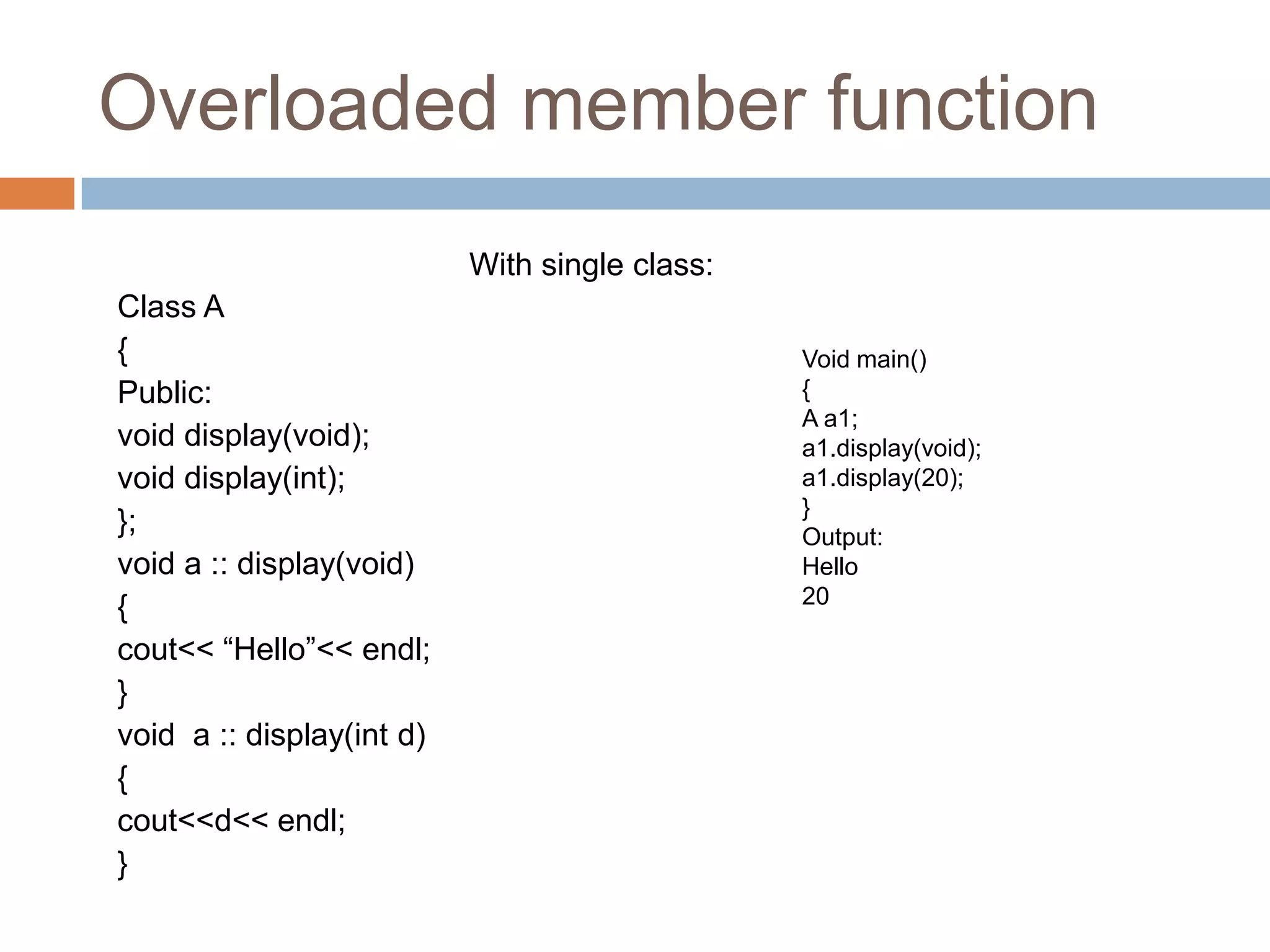
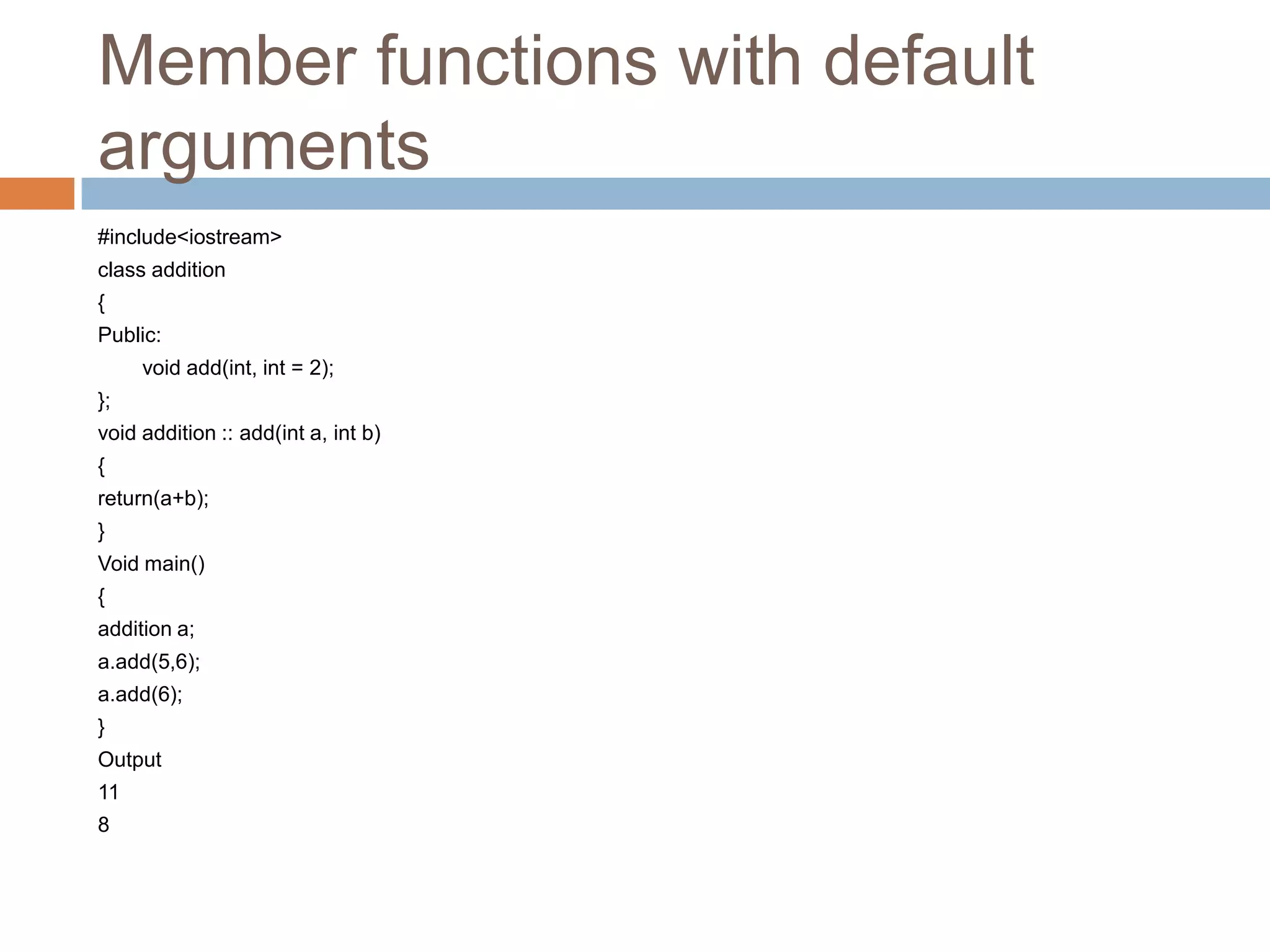
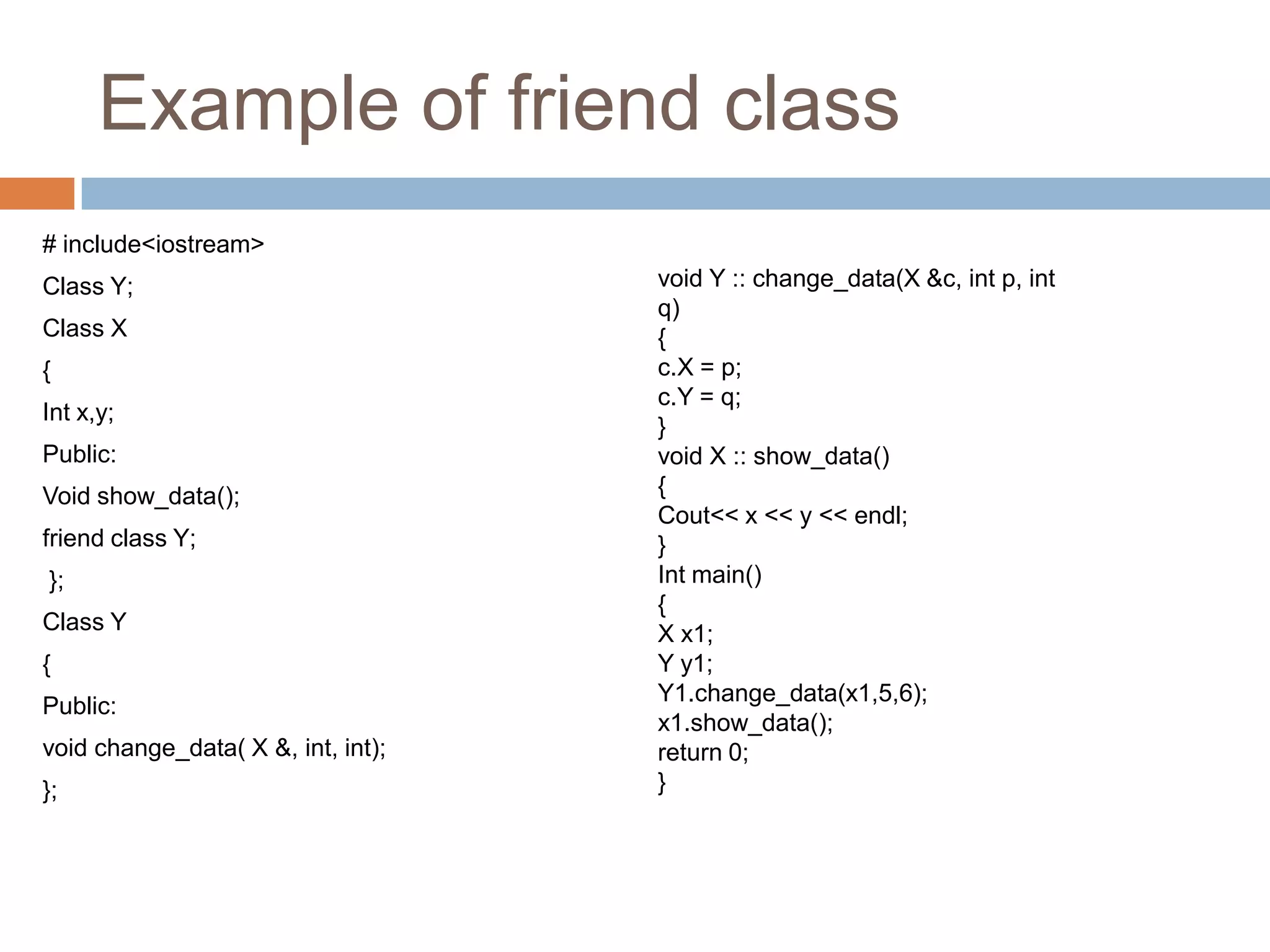
The document discusses different types of data members and member functions in classes in C++, including constant, mutable, and static data members, as well as constant, static, overloaded, and inline member functions. It provides examples of how to declare and use these various data members and member functions. It also covers topics like constant member functions, static data members, nested member functions, friend functions and classes, array of objects, and passing objects to functions by value, reference, and pointer.










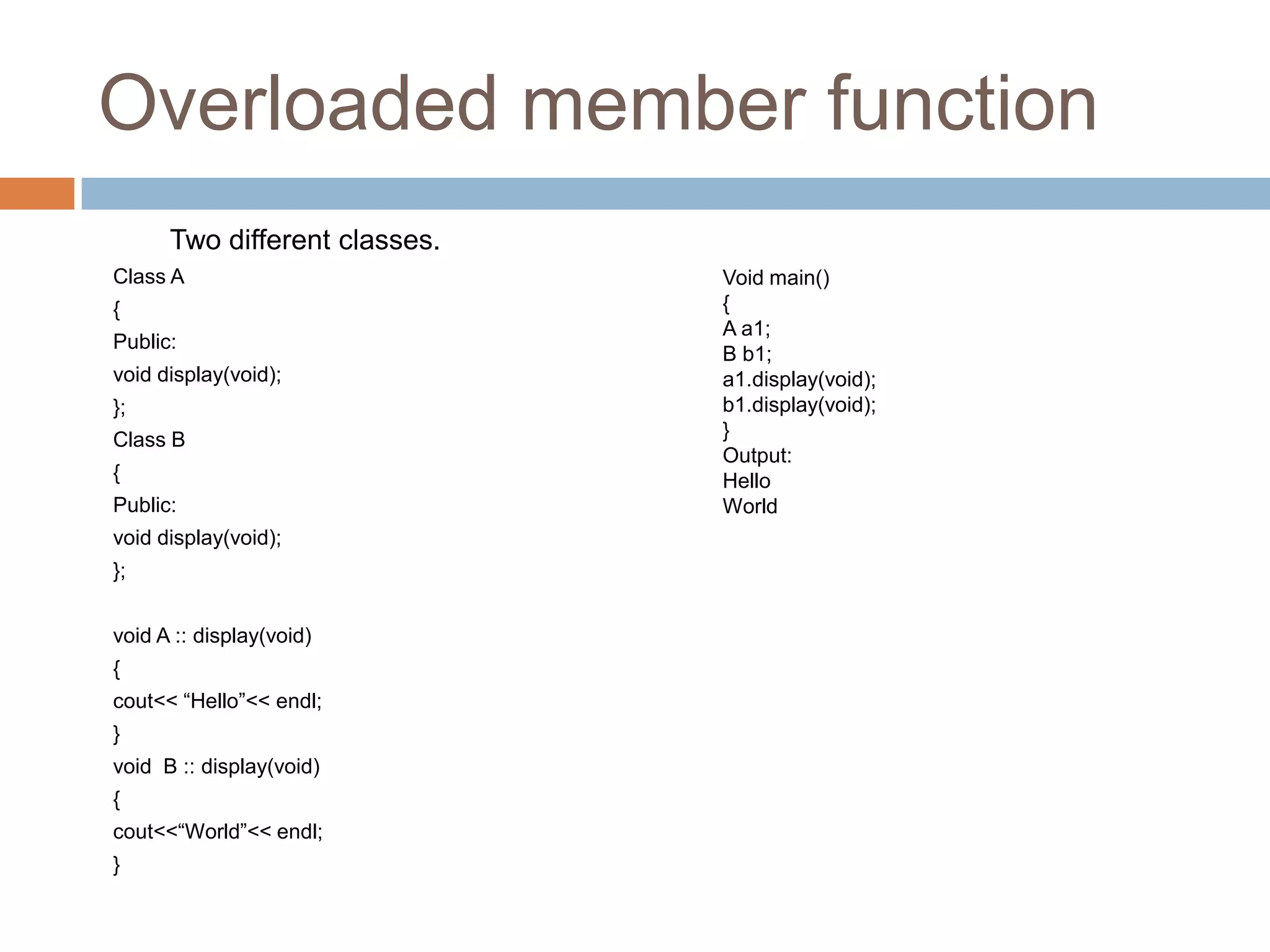





![Array of class objects
Array of class objects is similar to the array of
structures.
Syntax:
Class <class_name>
{
// class body
};
<class_name><object_name[size]>;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap4-121118092325-phpapp02/75/More-on-Classes-and-Objects-22-2048.jpg)
![Example:
Class Employee
{
Char name[20];
Float salary;
Public:
Void getdata();
Void display();
};
Employee e[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap4-121118092325-phpapp02/75/More-on-Classes-and-Objects-23-2048.jpg)