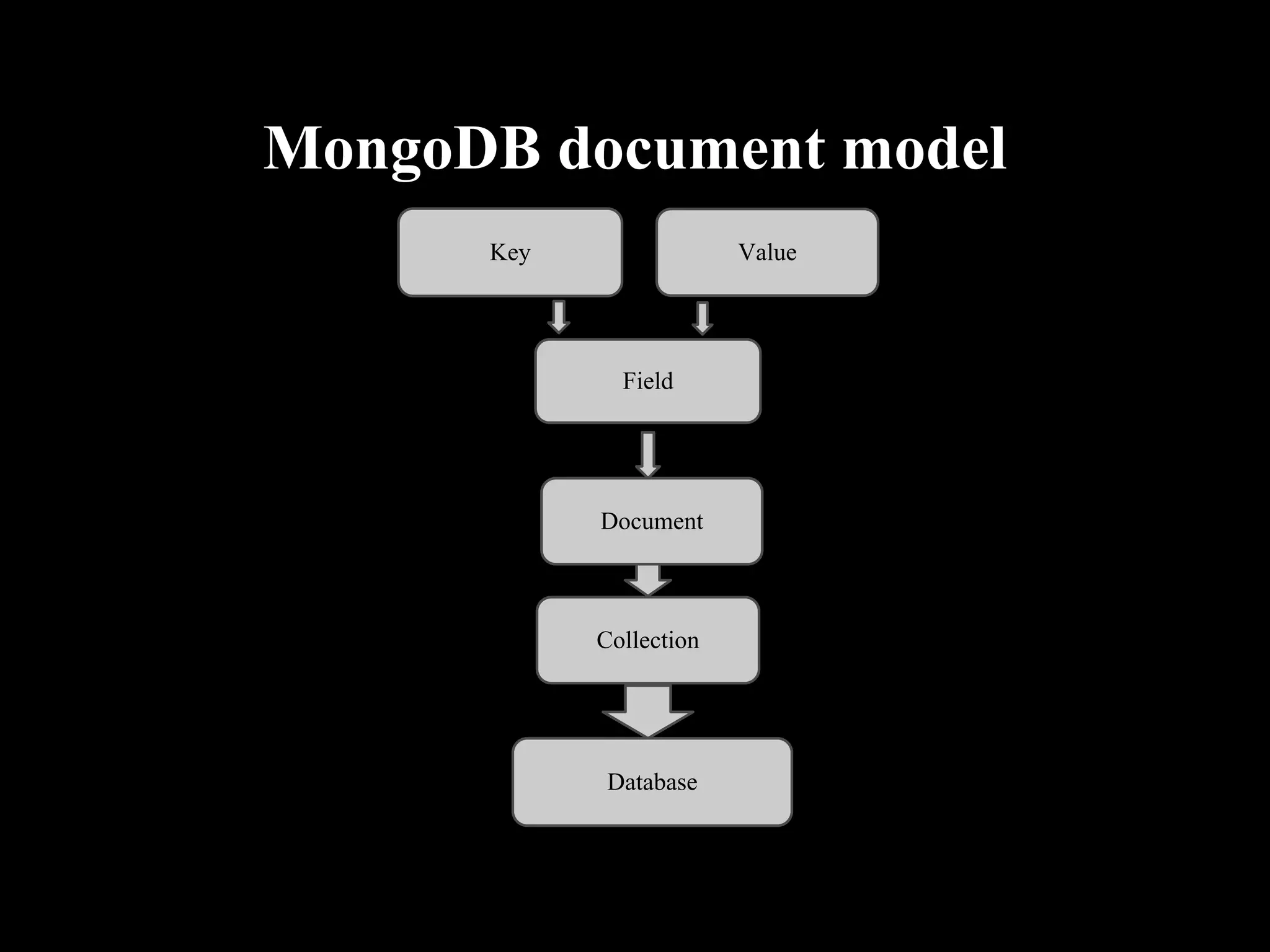
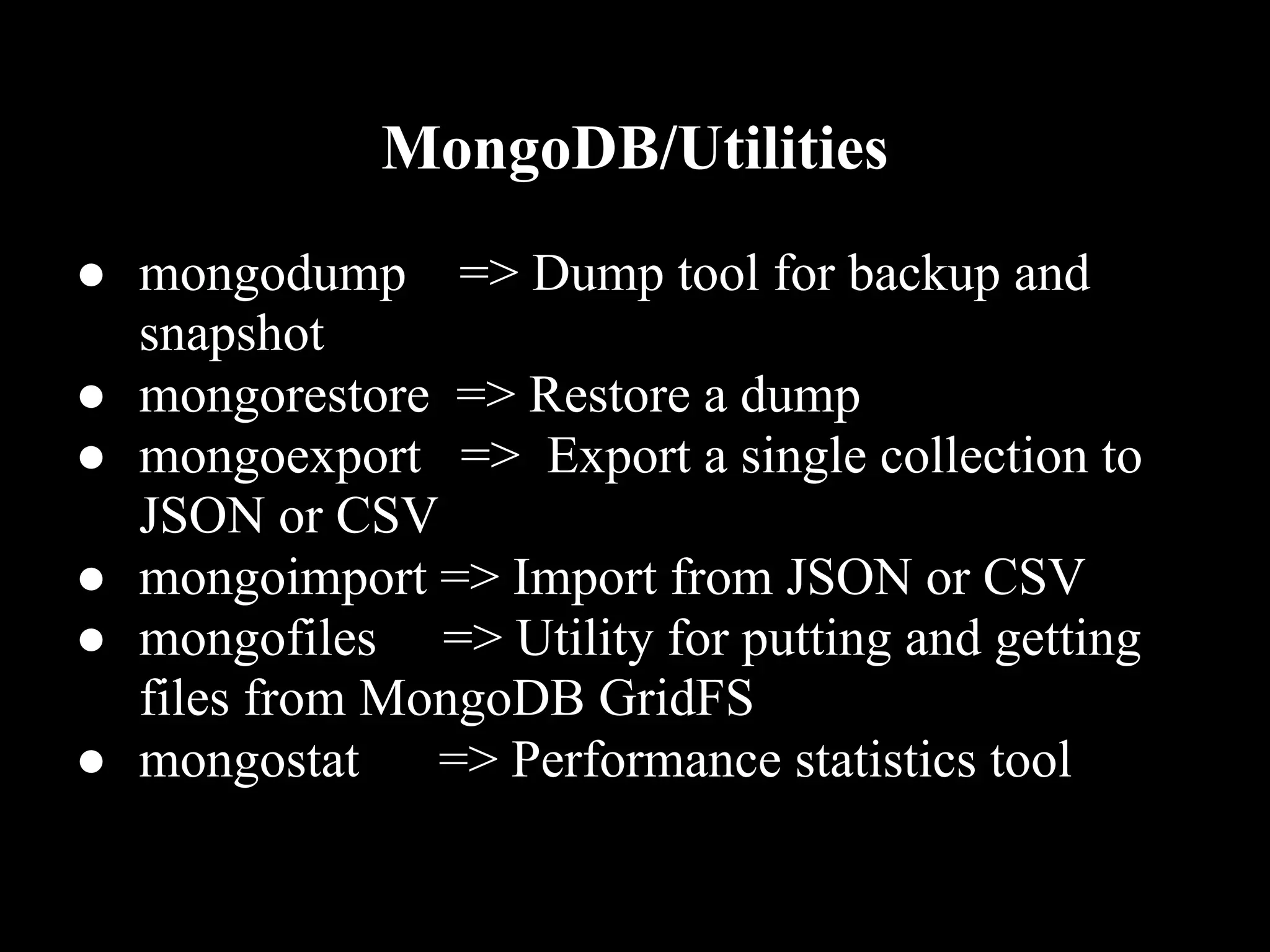
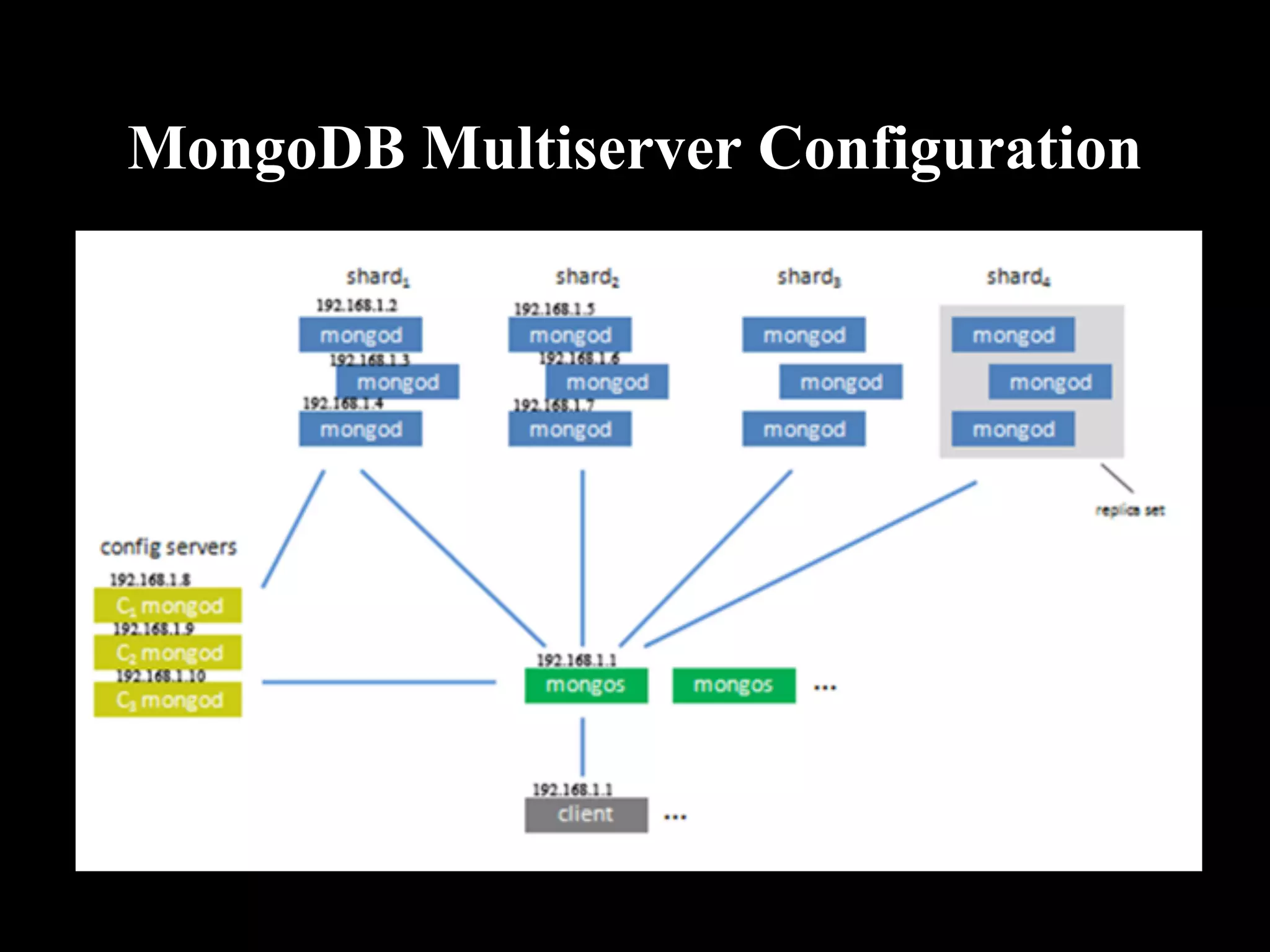
MongoDB is a document-oriented database that stores data in JSON-like documents. It does not use a schema and allows dynamic typing. Documents can be embedded within other documents to create complex data structures. MongoDB provides high availability through replication and automatic failover. It scales easily through auto-sharding which partitions data across servers. MongoDB supports many programming languages and frameworks and can handle over a million operations per second. It is a good choice for applications that need to scale easily and work with dynamic or complex data structures.