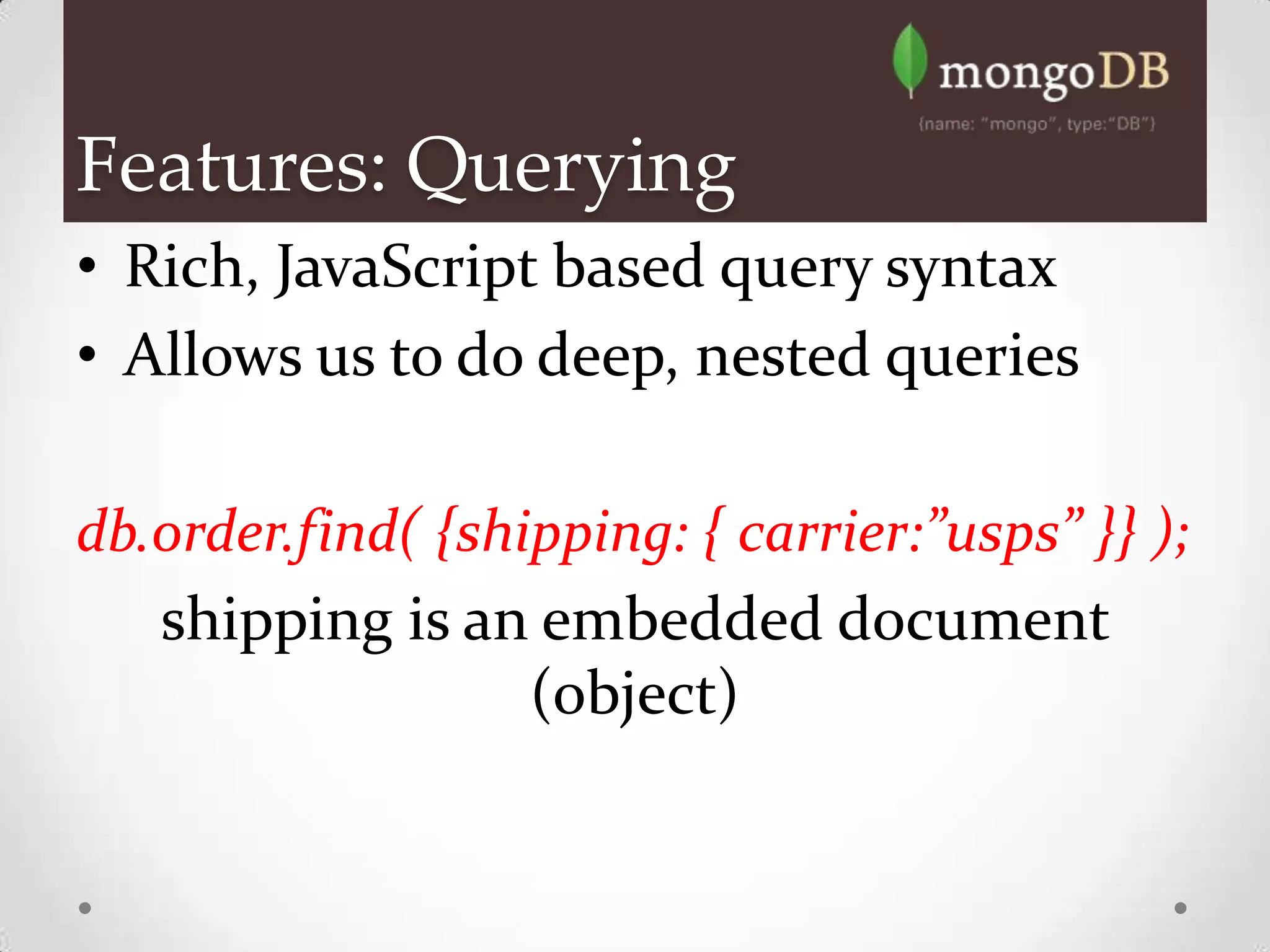
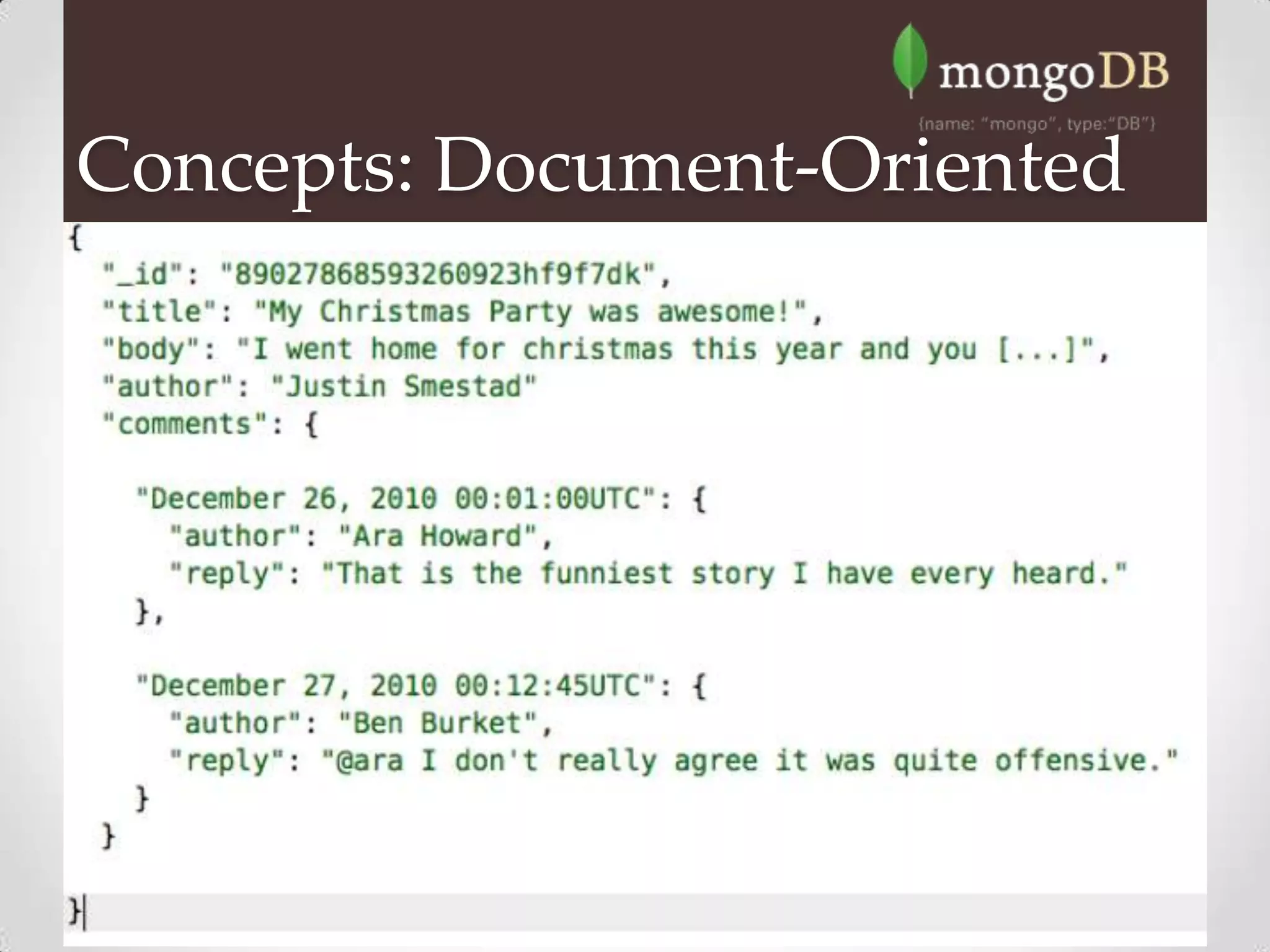
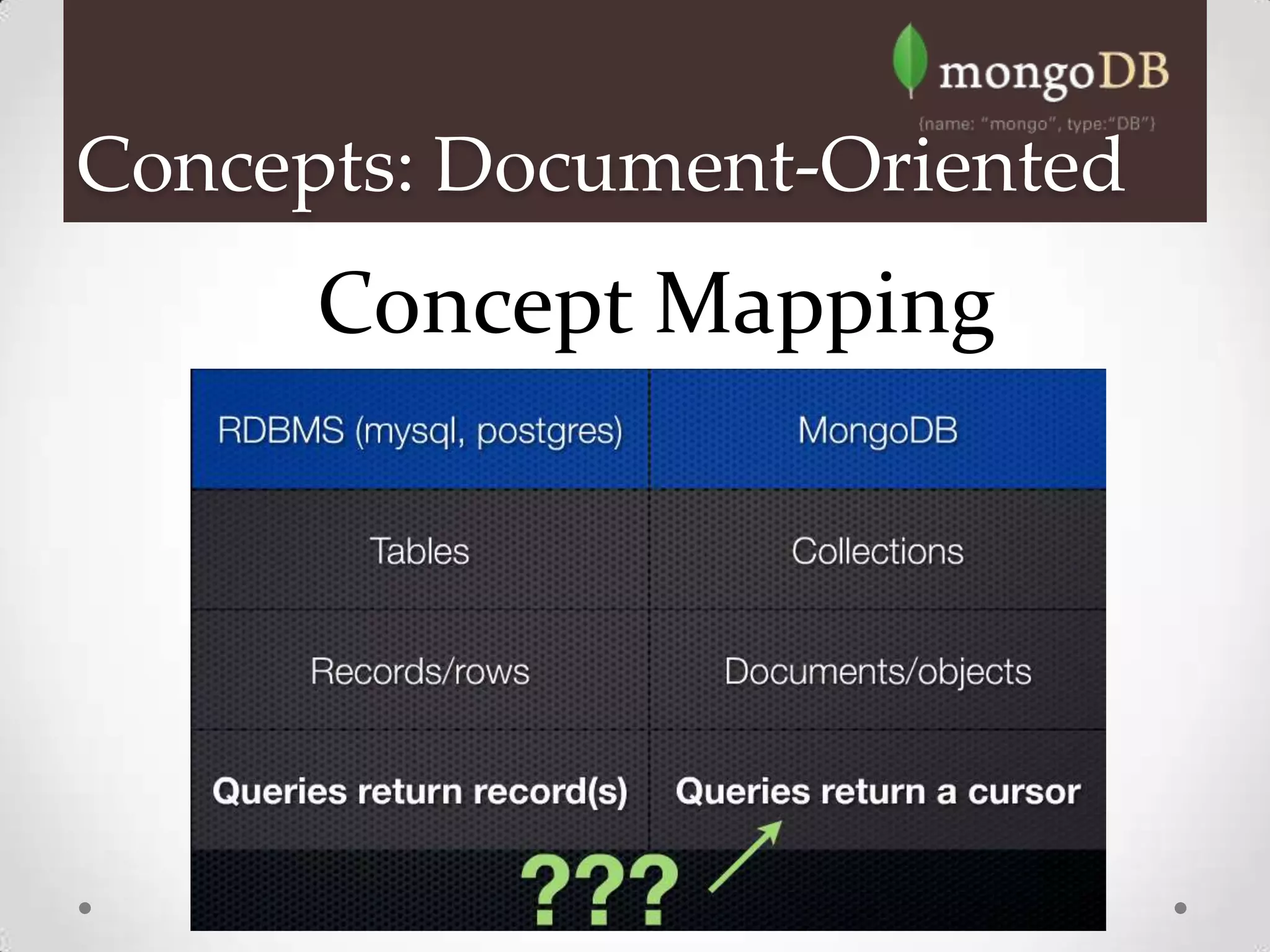
MongoDB is a document database that stores data in BSON format, which is similar to JSON. It is a non-relational, schema-free database that scales easily and supports massive amounts of data and high availability. MongoDB can replace traditional relational databases for certain applications, as it offers dynamic schemas, horizontal scaling, and high performance. Key features include indexing, replication, MapReduce and rich querying of embedded documents.