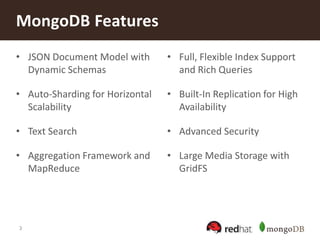
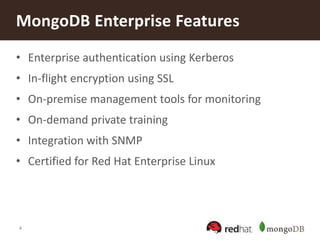
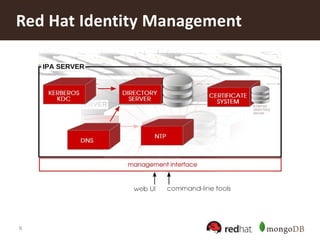
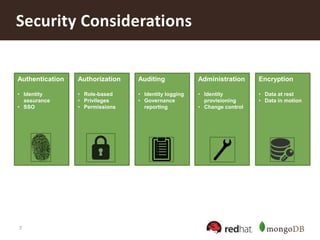
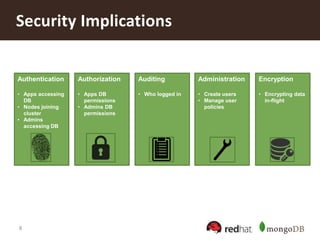
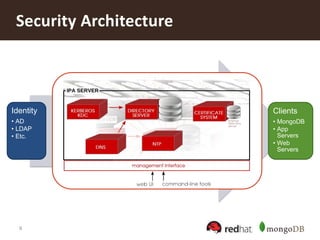
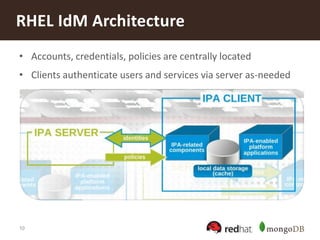
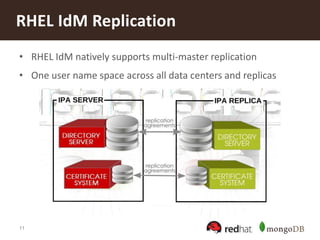
The document discusses securing MongoDB using Red Hat Enterprise Linux Identity Management, detailing key features of MongoDB including dynamic schema support, high availability, and advanced security measures. It outlines the integration of identity management, authentication, and encryption through Kerberos and SSL, and provides instructions for setting up both the IDM server and client. Additionally, it highlights the importance of centralized identity management for improved security and compliance, along with proper configurations for MongoDB deployment.




![14
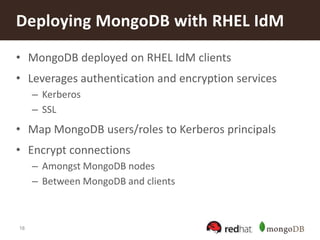
IdM Server Setup
# run IdM installation
$ ipa-server-install --setup-dns
# add IdM server DNS
$ nano /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver [IdM server IP address]
# authenticate as admin via Kerberos
$ kinit admin
# list active authentications
$ klist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbandrhelidm20131002-131002123709-phpapp01/85/Securing-Your-Deployment-with-MongoDB-and-Red-Hat-s-Identity-Management-in-Red-Hat-Enterprise-Linux-14-320.jpg)

![16
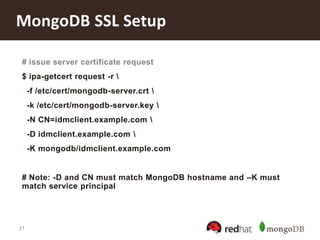
IdM Client Setup
# point DNS to IdM server
$ nano /etc/resolv.conf
search example.com
nameserver [IdM server IP address]
# automatically enroll this machine into IdM
$ ipa-client-install --enable-dns-updates
Discovery was successful!
Hostname: idmclient.example.com
Realm: EXAMPLE.COM
DNS Domain: example.com
IPA Server: idmhost.example.com
BaseDN: dc=example,dc=com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbandrhelidm20131002-131002123709-phpapp01/85/Securing-Your-Deployment-with-MongoDB-and-Red-Hat-s-Identity-Management-in-Red-Hat-Enterprise-Linux-16-320.jpg)
![17
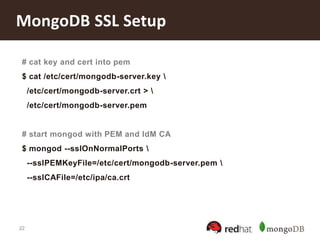
IdM Client Setup
# ex. reverse addr: 243-16-164-10.in-addr.arpa.
# add a reverse-DNS zone
$ ipa dnszone-add [idmclient-reverse-addr]
--name-server idmserver.example.com. --force
# add a reverse-DNS record
$ ipa dnsrecord-add [idmclient-reverse-addr]
[record-name] --ptr-hostname idmclient.example.com.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbandrhelidm20131002-131002123709-phpapp01/85/Securing-Your-Deployment-with-MongoDB-and-Red-Hat-s-Identity-Management-in-Red-Hat-Enterprise-Linux-17-320.jpg)