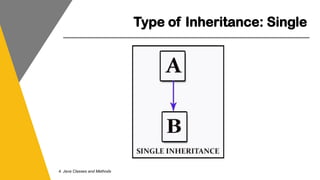
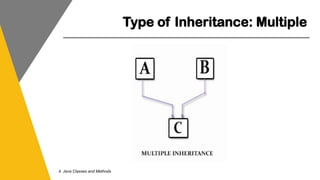
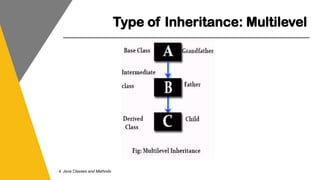
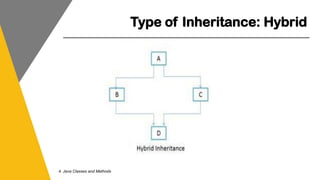
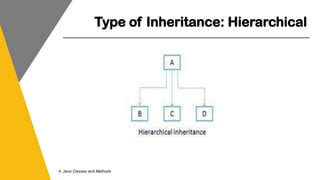
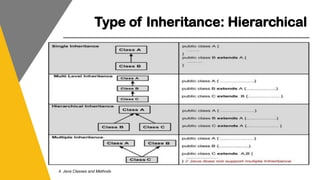
This document covers key concepts of inheritance and polymorphism in Java, explaining different types of inheritance including single, multiple, multilevel, hierarchical, and hybrid. It outlines the use of the 'extends' keyword for subclassing, the 'super' keyword for referencing superclass members, and the 'instanceof' operator for type comparison. Additionally, it introduces the concept of polymorphism, showcasing how a child class can be treated as an instance of its parent class.