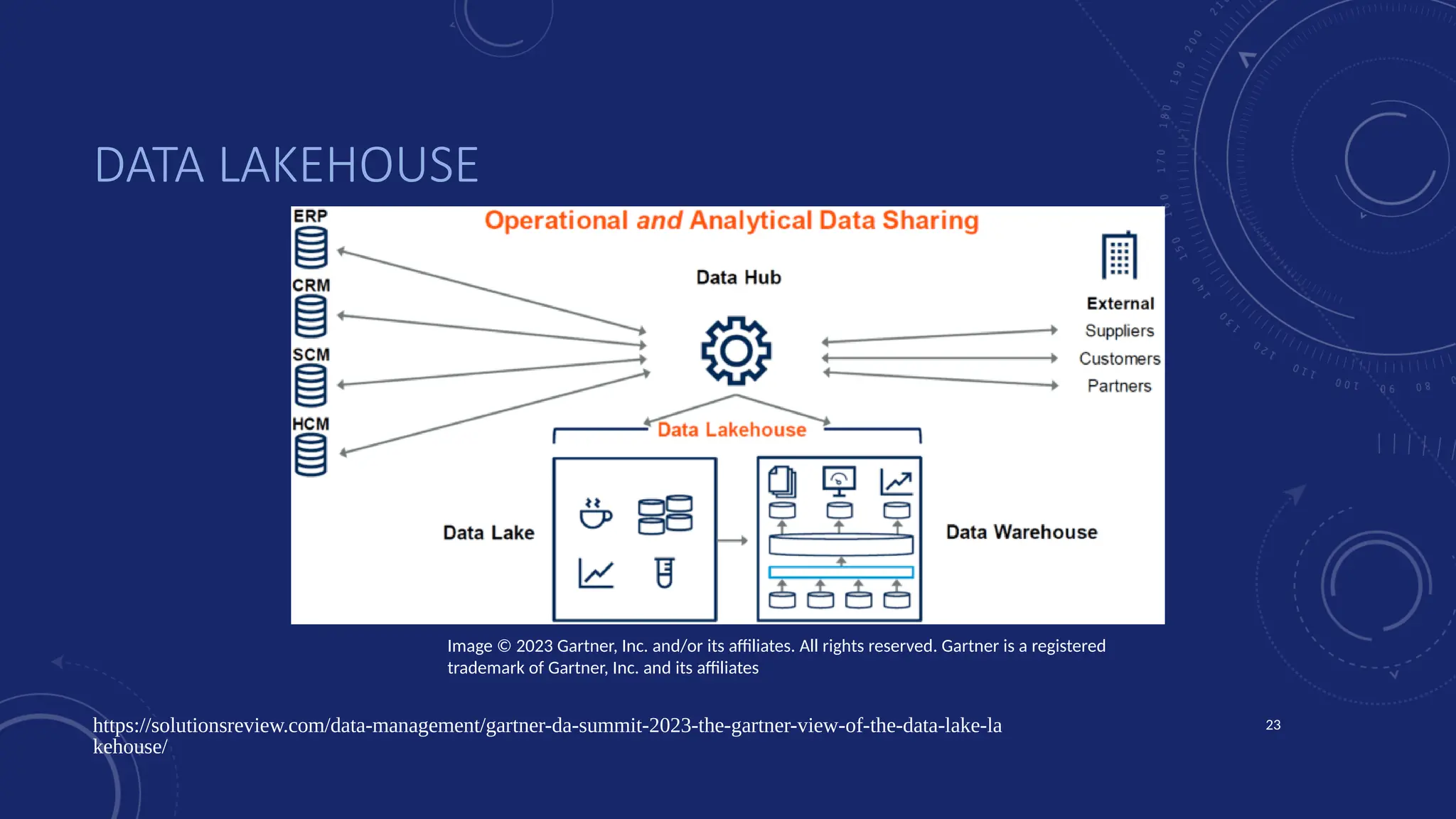
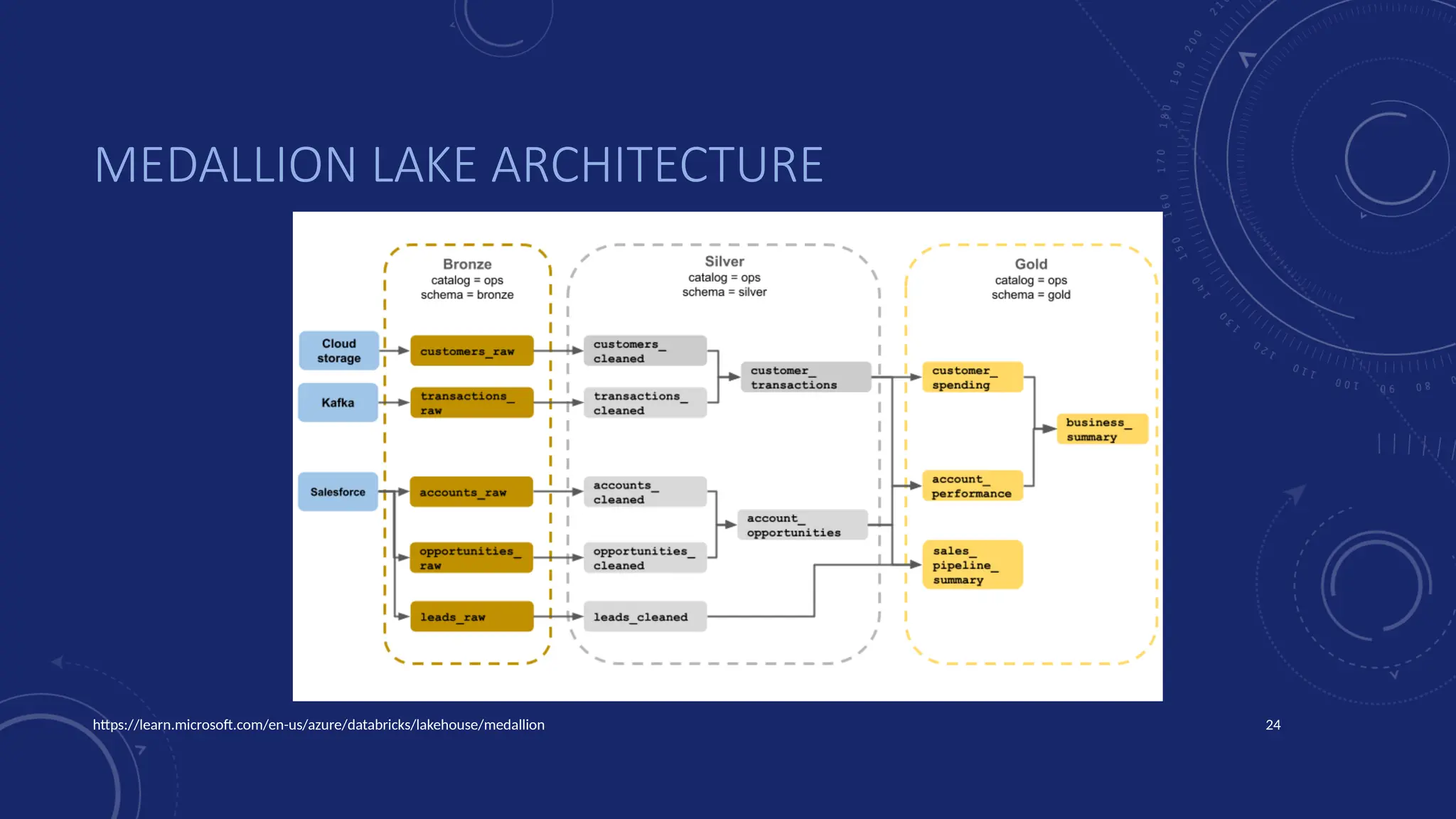
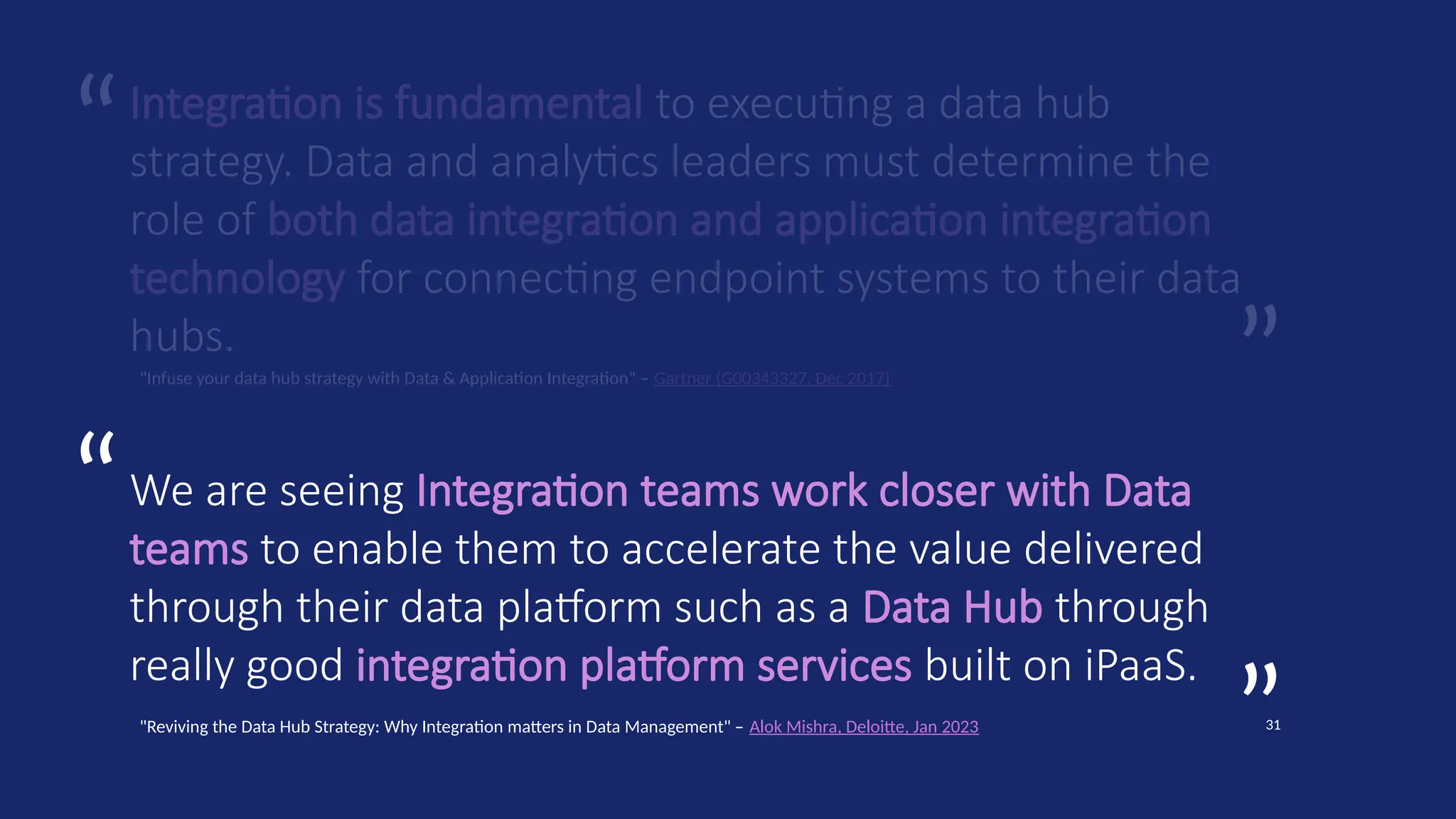
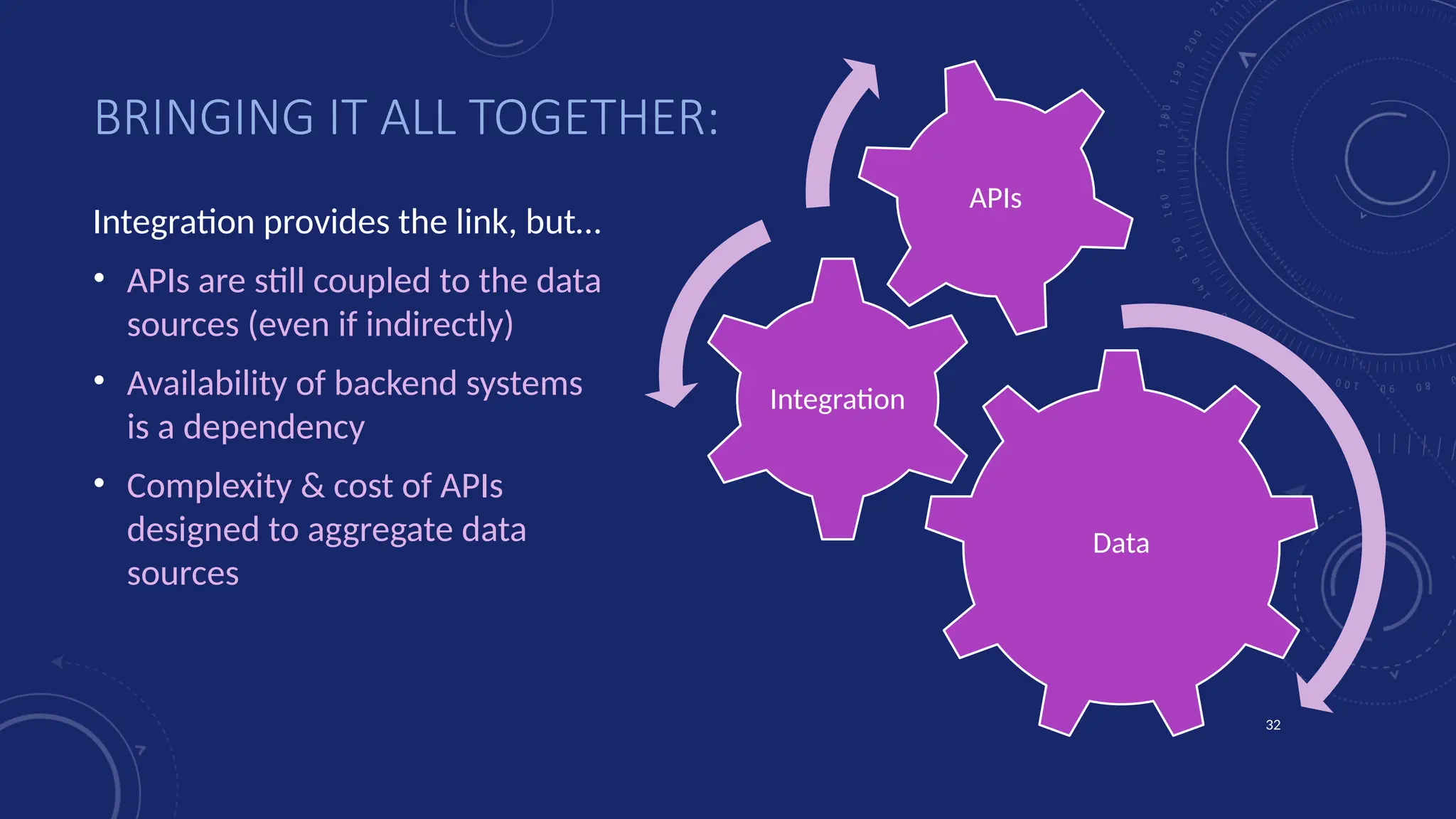
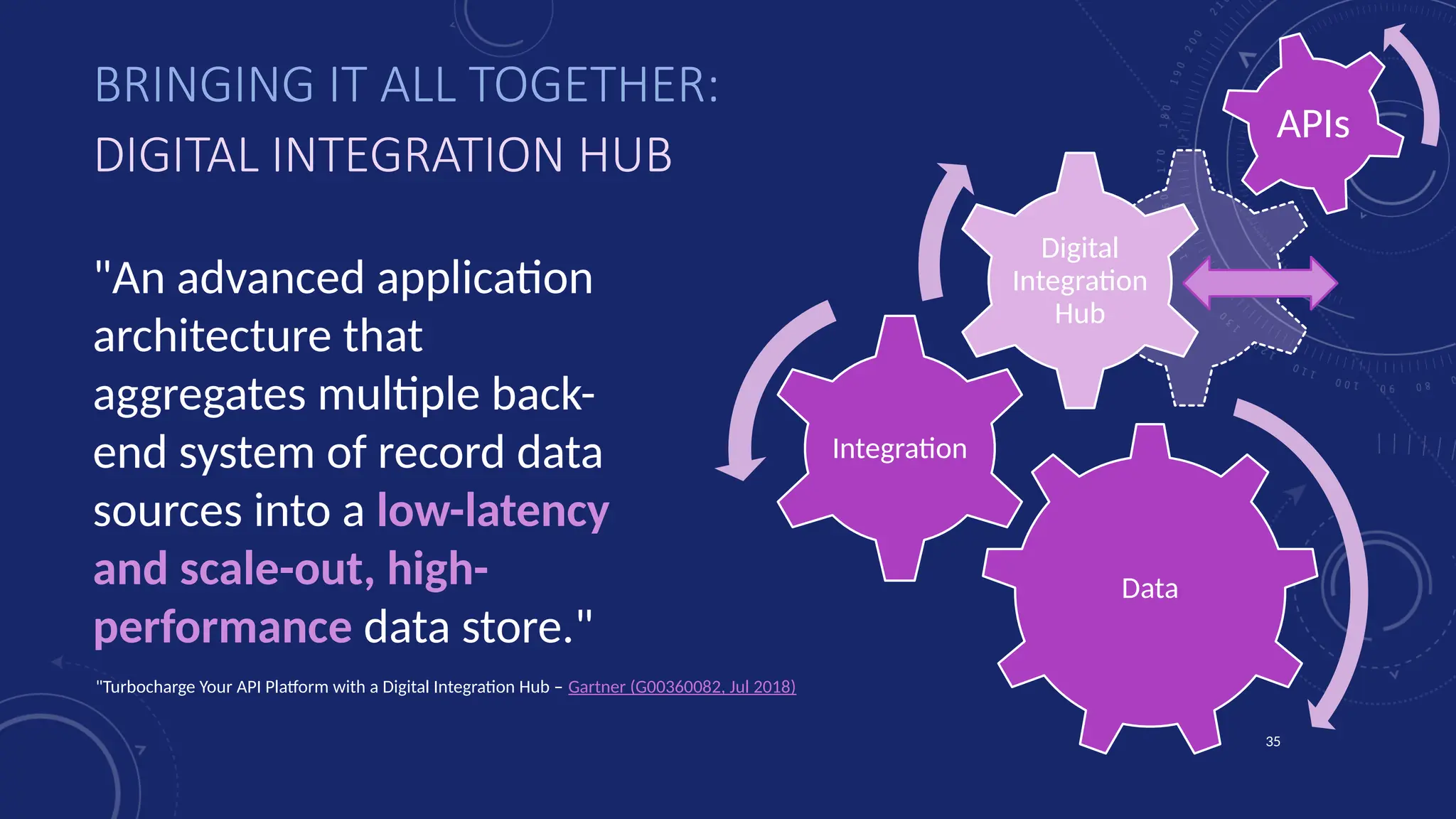
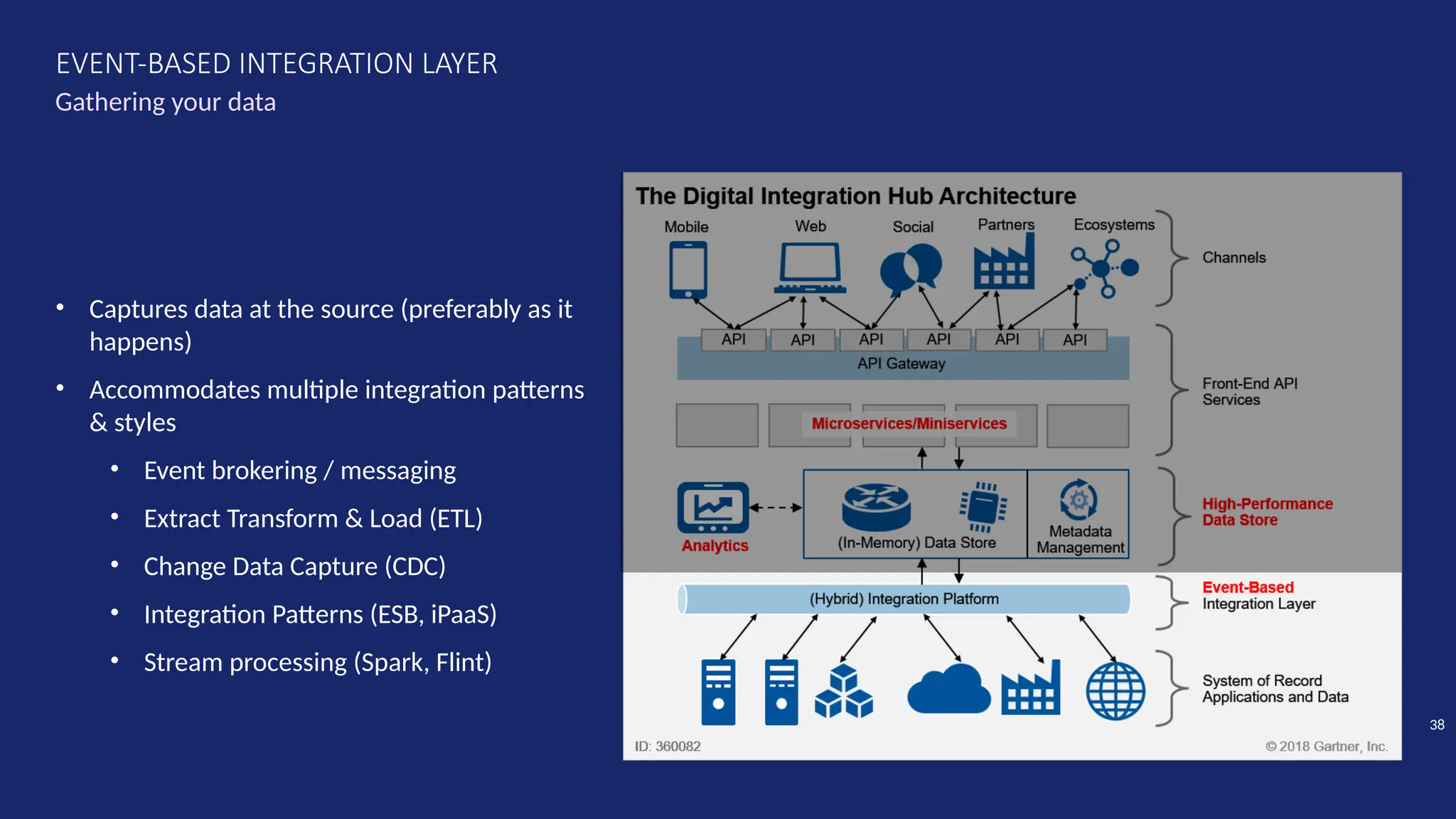
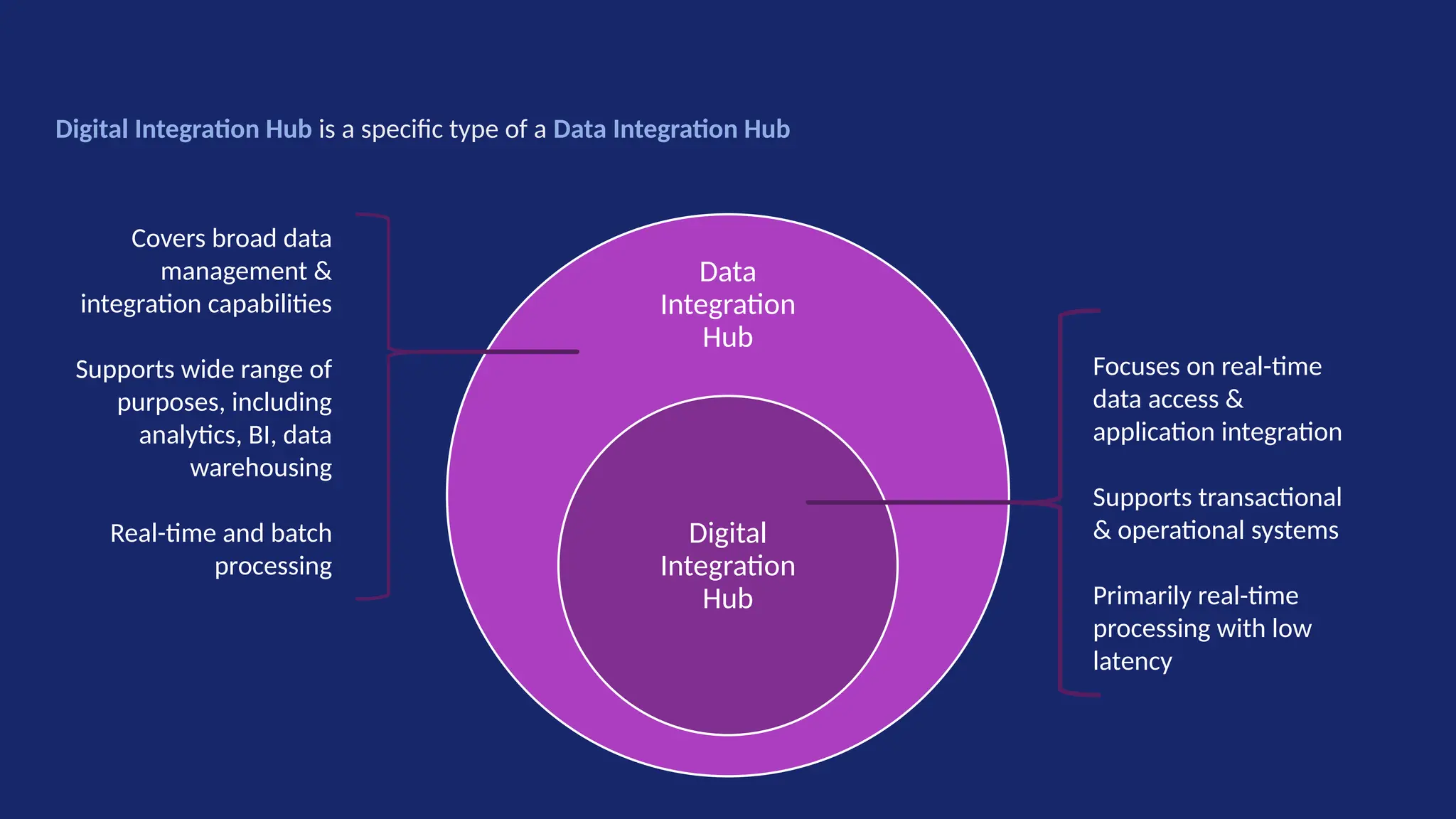
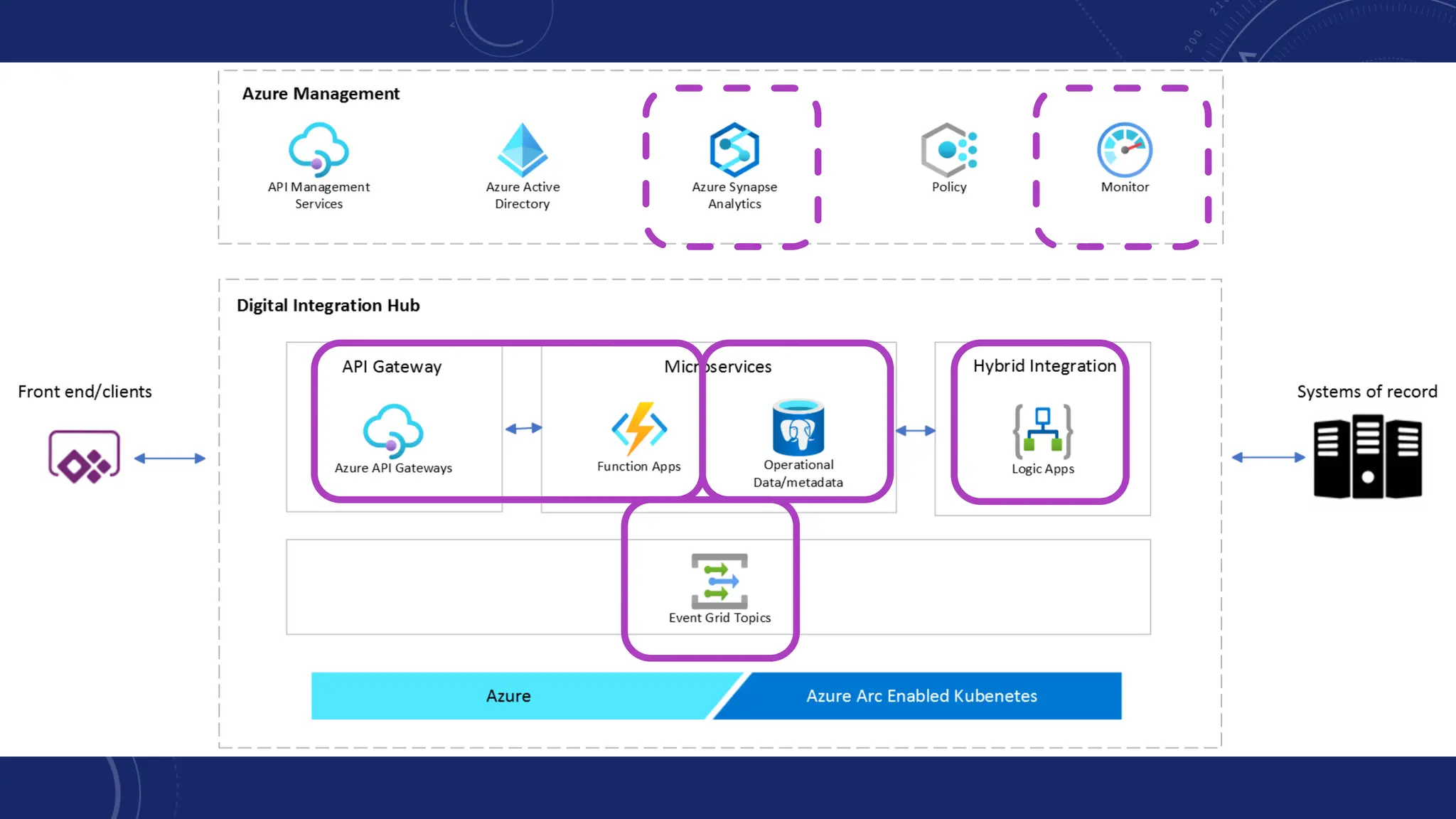
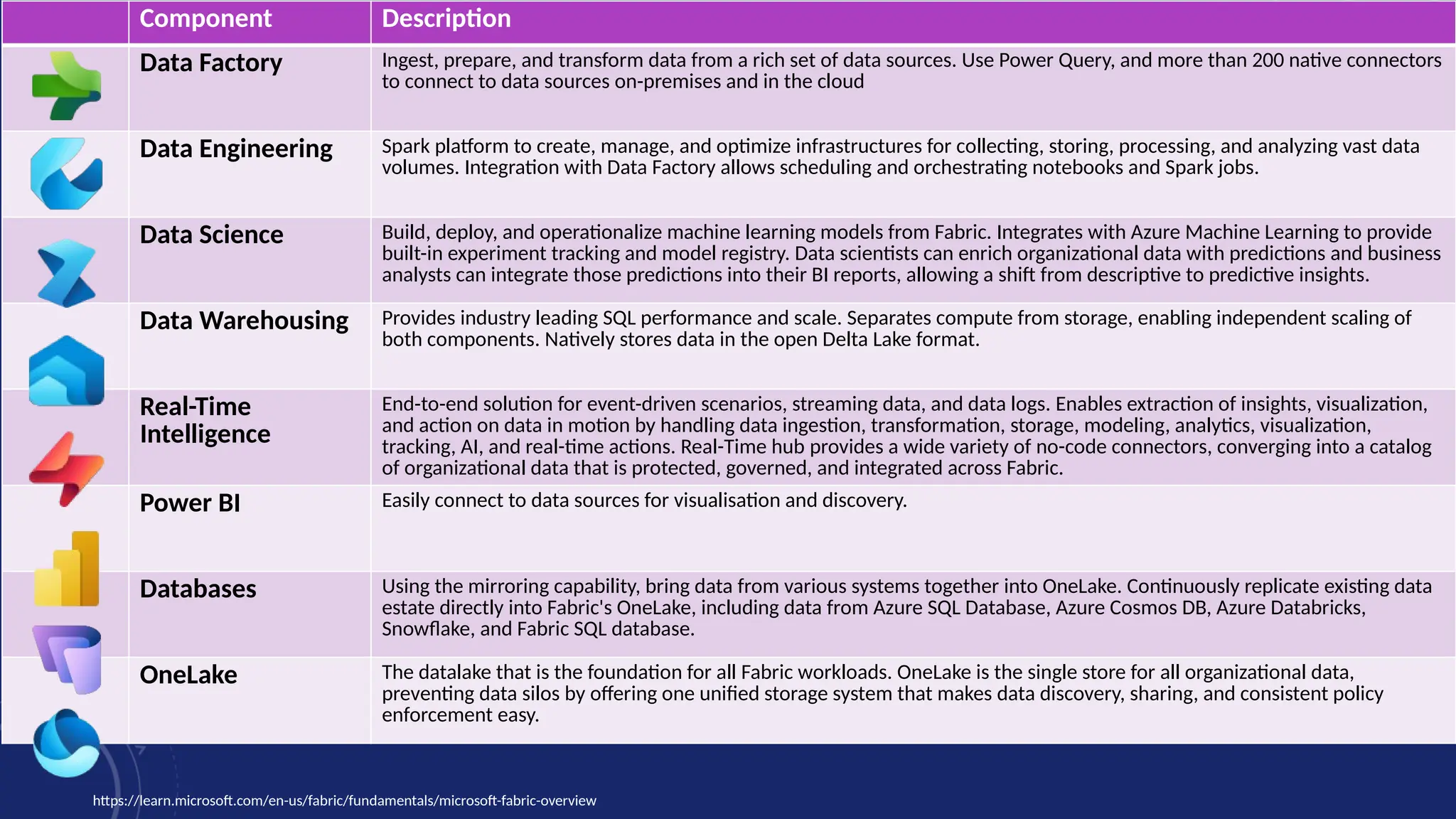
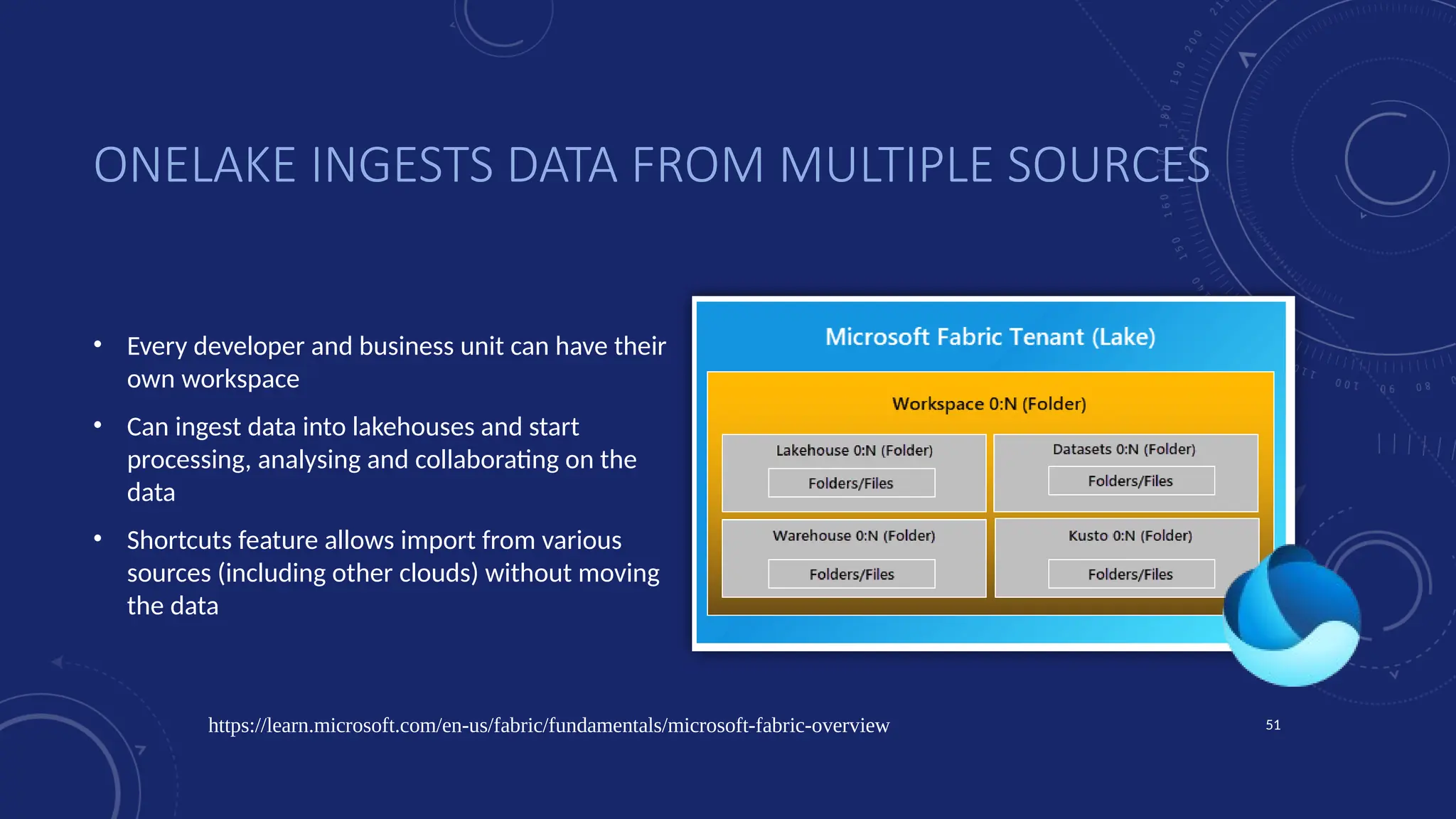
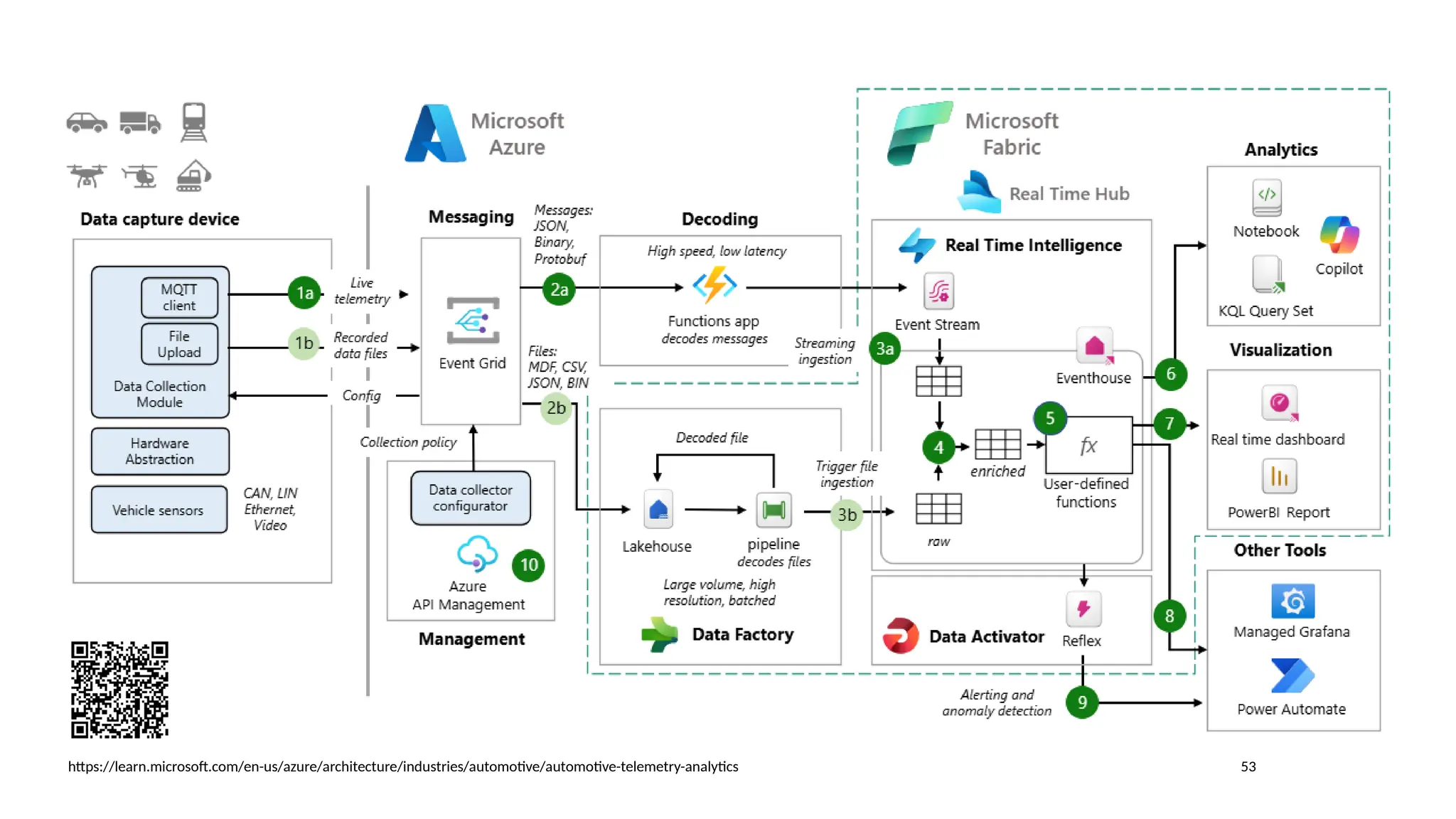
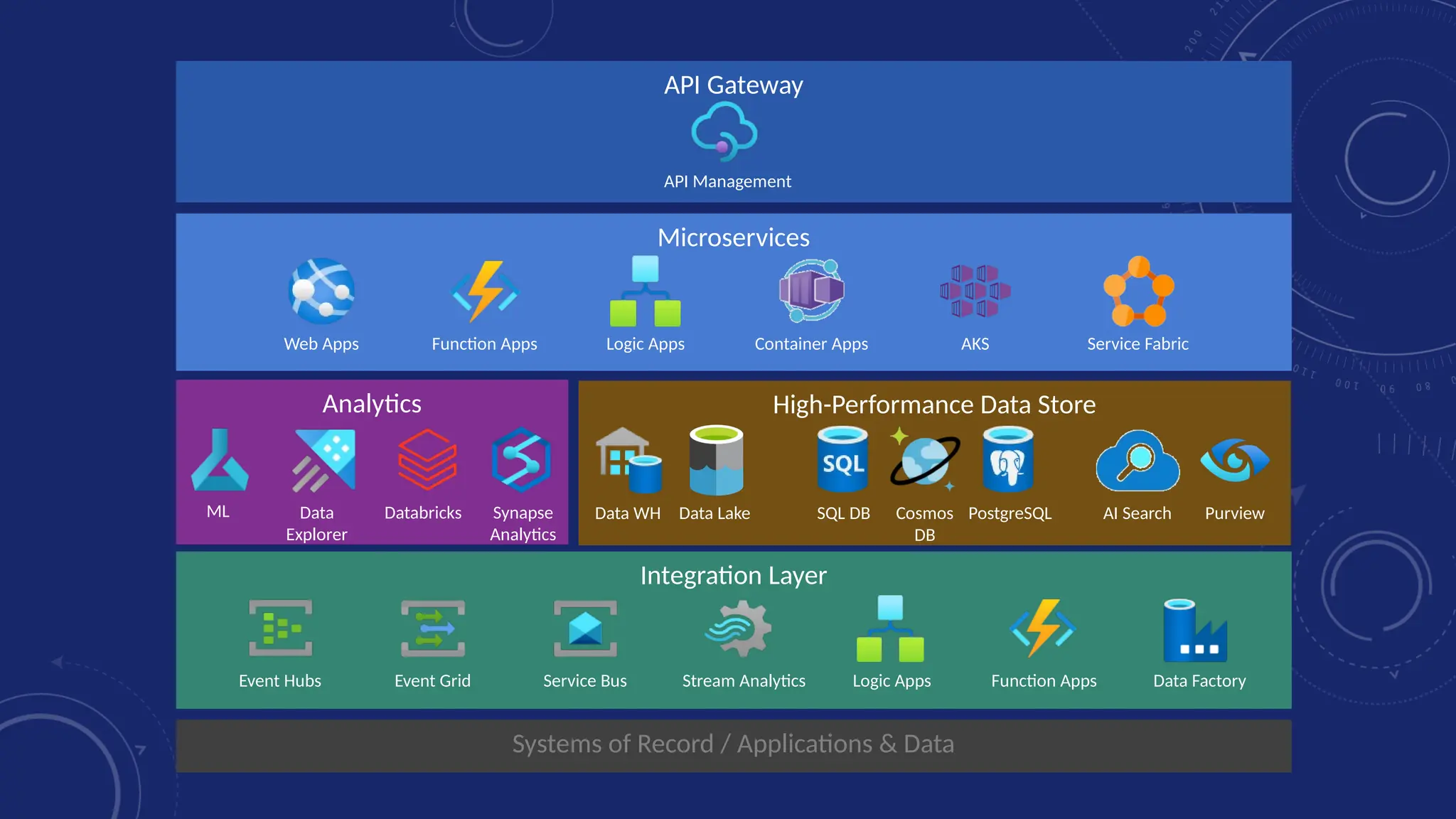
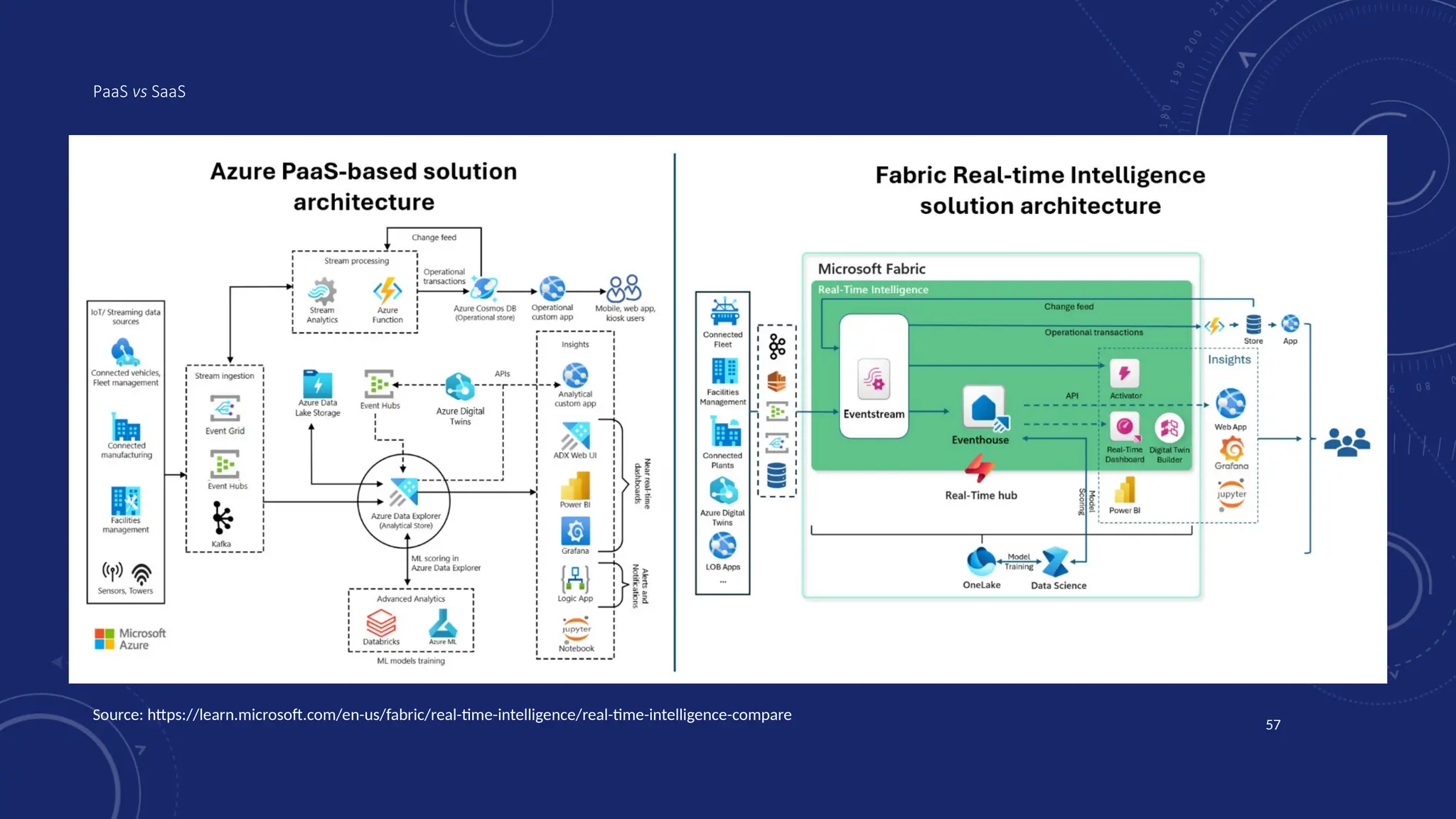
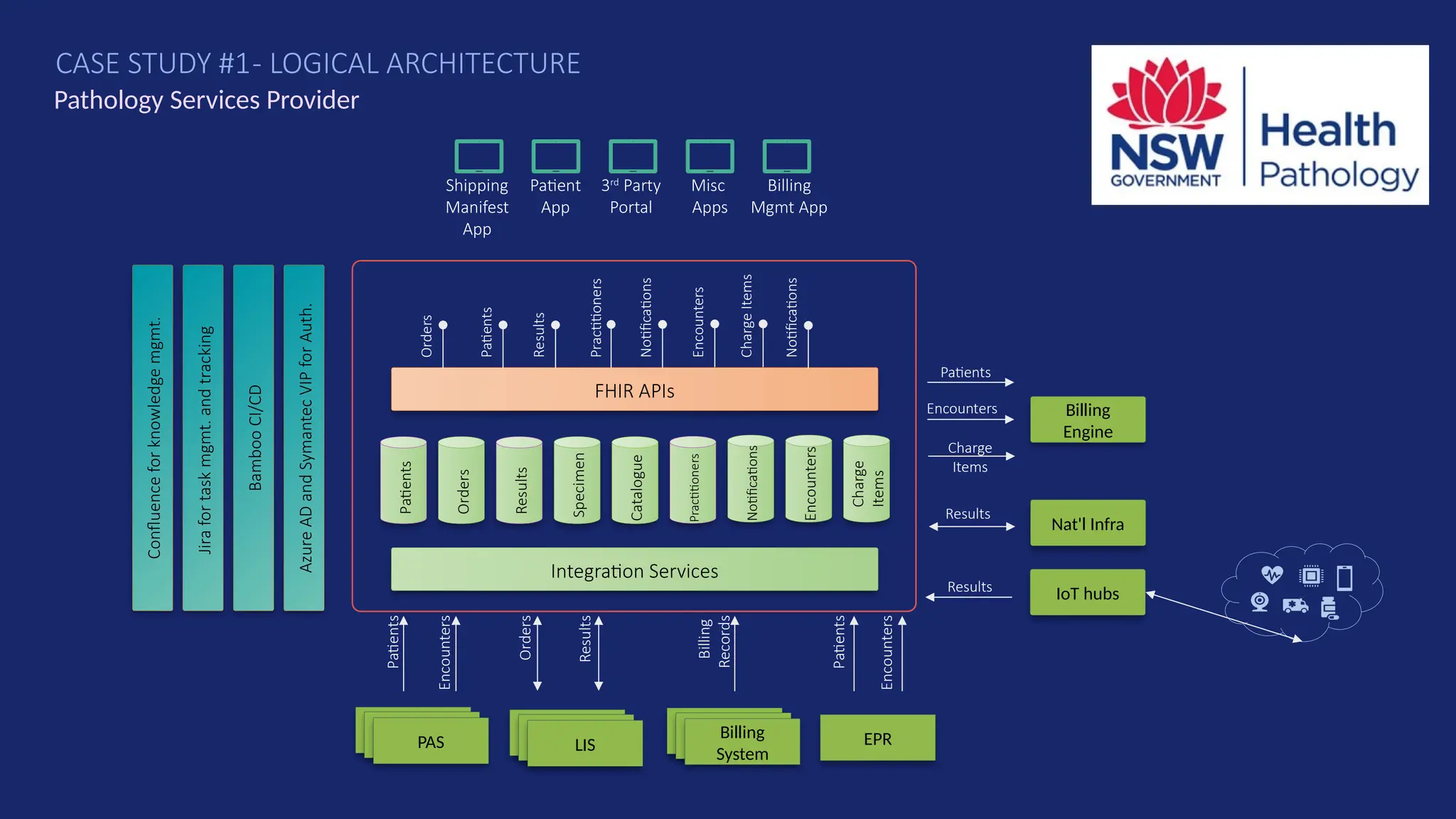
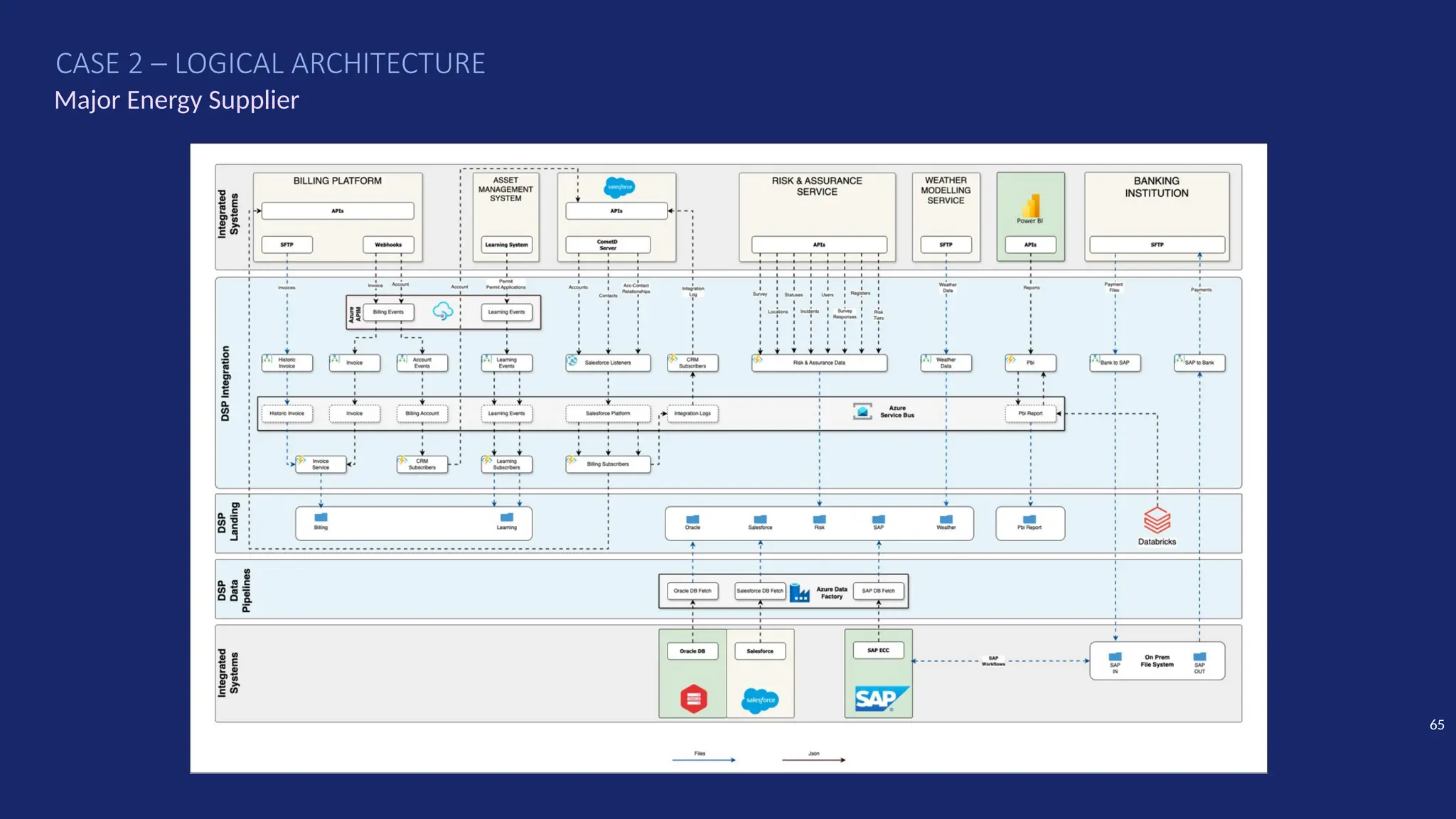
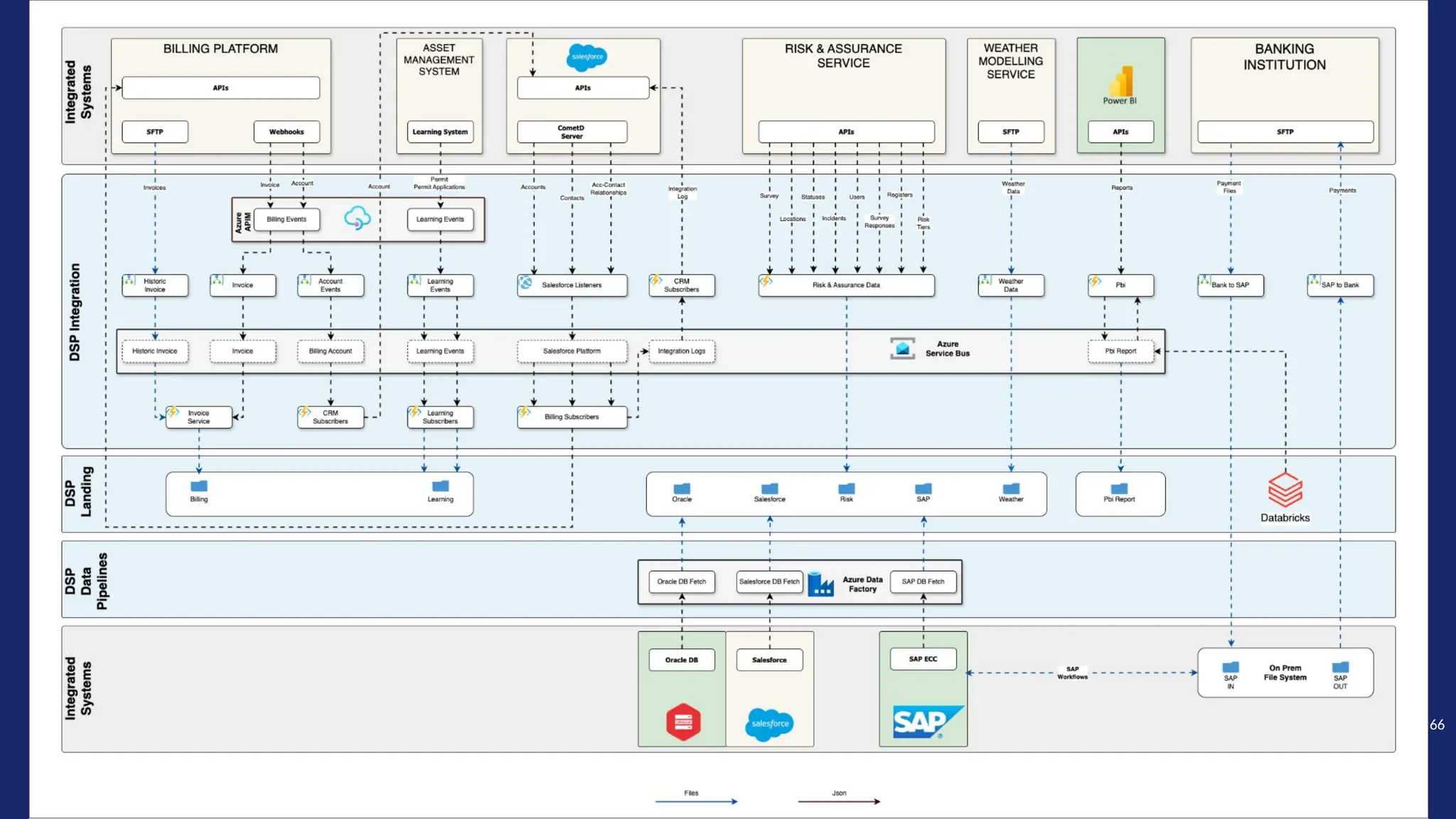
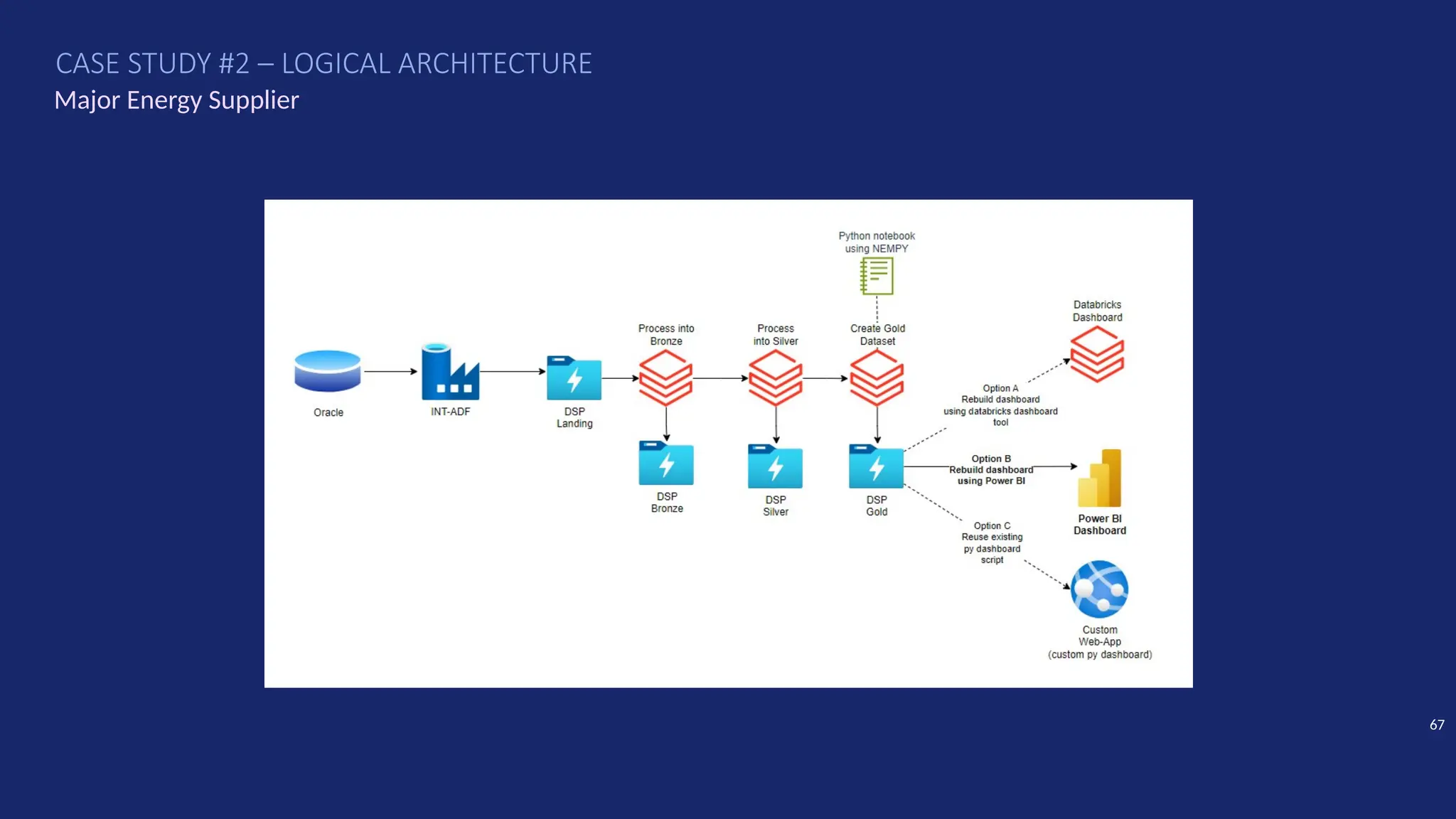
Gartner introduced the Digital Integration Hub architecture years ago... but with new data platforms, AI and advanced analytics, things have evolved.
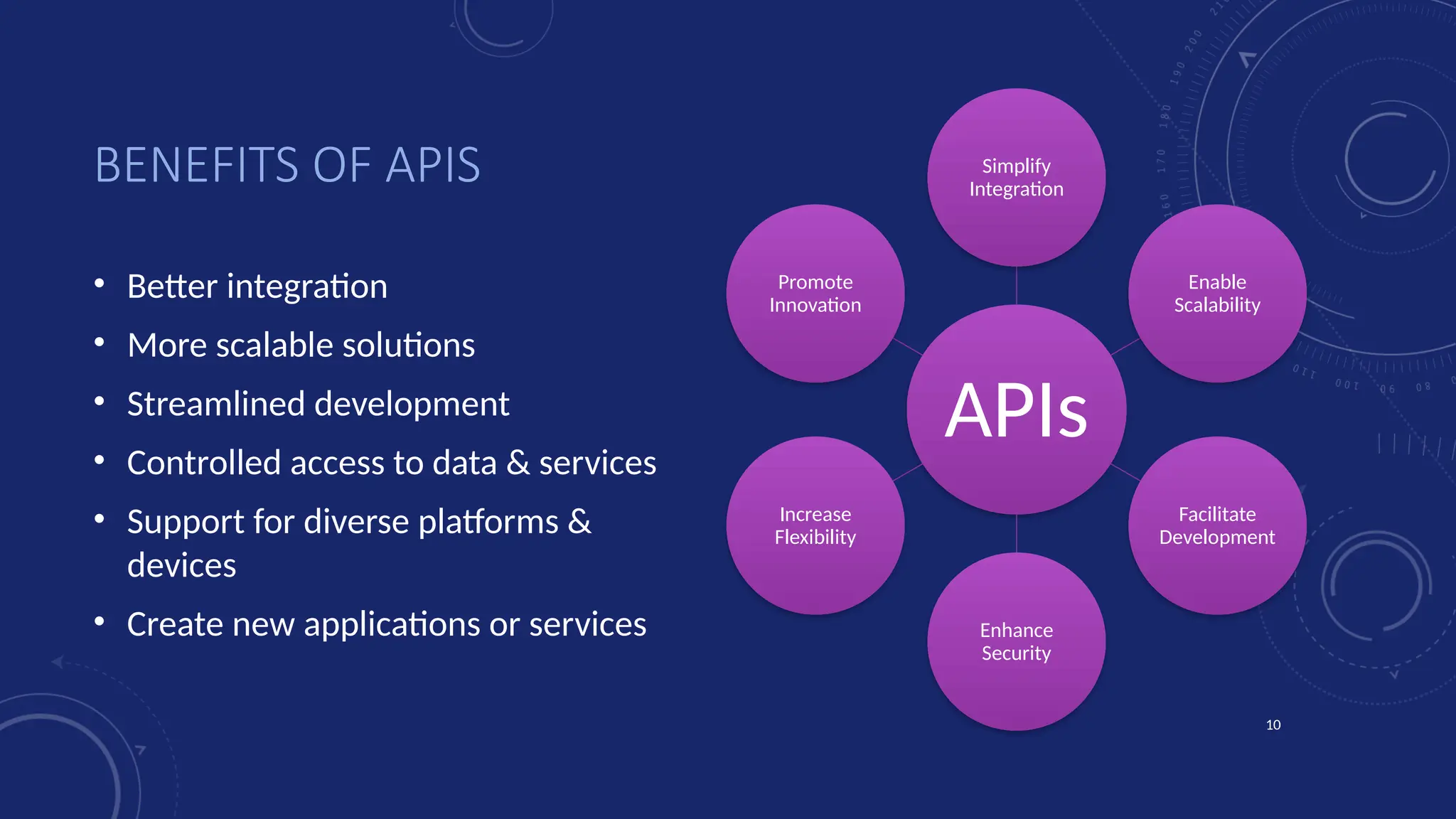
Data is at the heart of every organisation, and the ability to share that data reliably and efficiently in a controlled manner with internal and external consumers is critical to business operations. Let Dan show you how a modernised Digital Integration Hub built in the Microsoft cloud can be the answer!