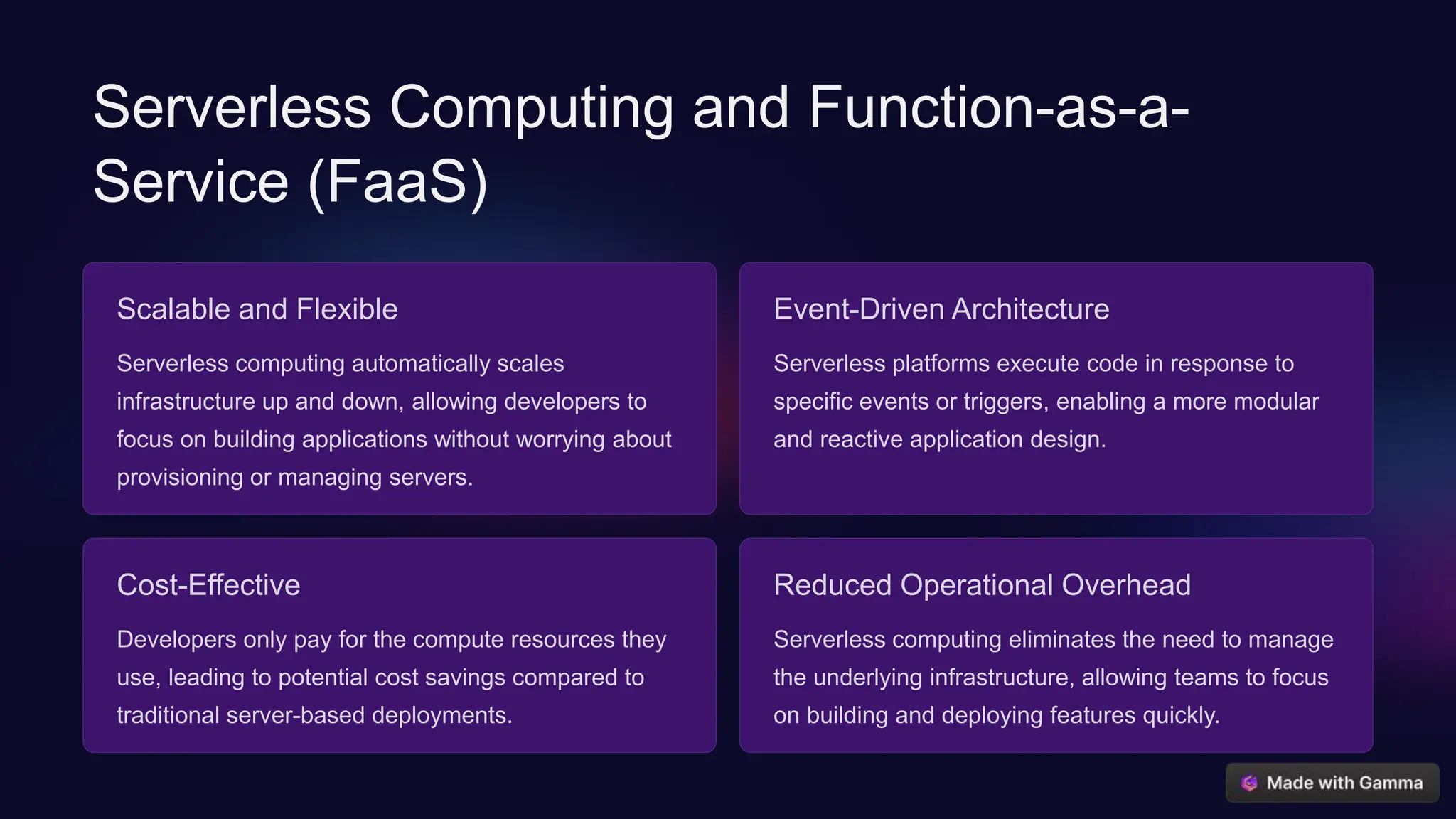
The document explores modern web and mobile application architectures, emphasizing advancements like microservices, serverless computing, and containerization for building scalable and efficient applications. It contrasts traditional monolithic architecture with microservices, highlighting their benefits in flexibility and scalability. Additionally, it covers serverless computing and container orchestration using Docker and Kubernetes, as well as the advantages of Single Page Applications (SPAs) in enhancing user experience.