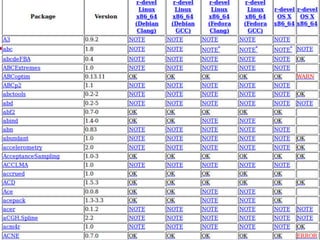
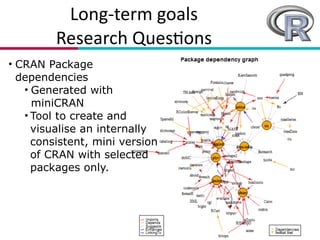
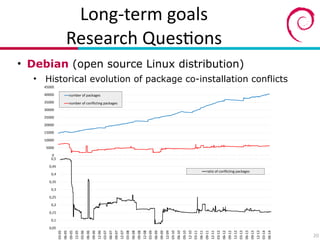
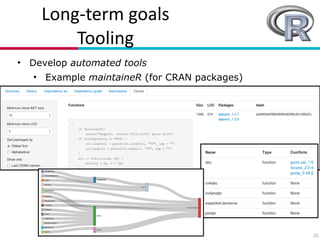
The document presents an overview of research related to software ecosystems, focusing on software evolution, quality, and model-driven engineering conducted at the University of Mons. It outlines ongoing projects that explore community aspects, evolutionary dynamics, and empirical studies on software systems like open source and data-intensive systems. Key goals include understanding factors influencing success or failure in open source software (OSS) projects and developing automated tools to support practitioners in software development.