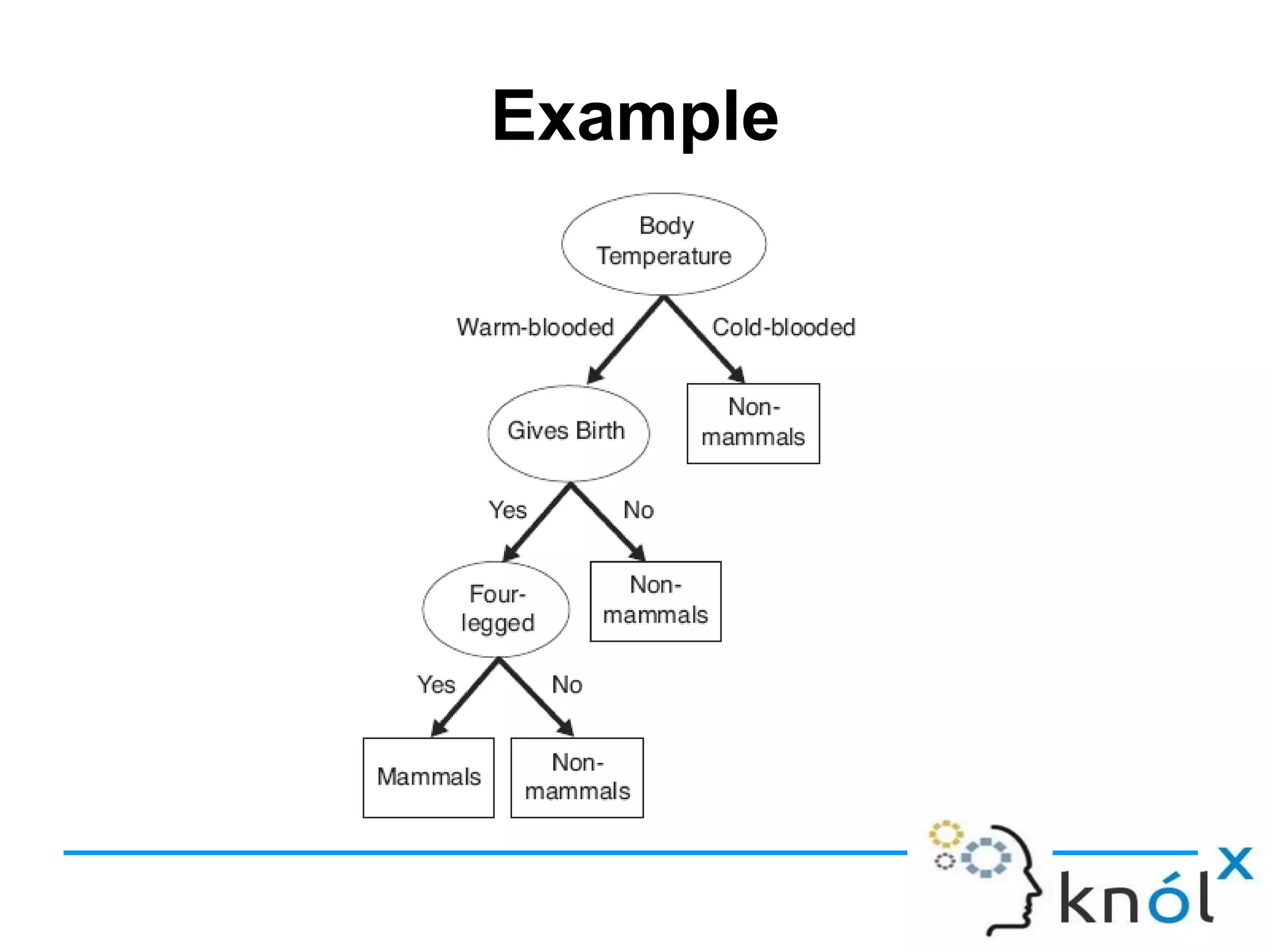
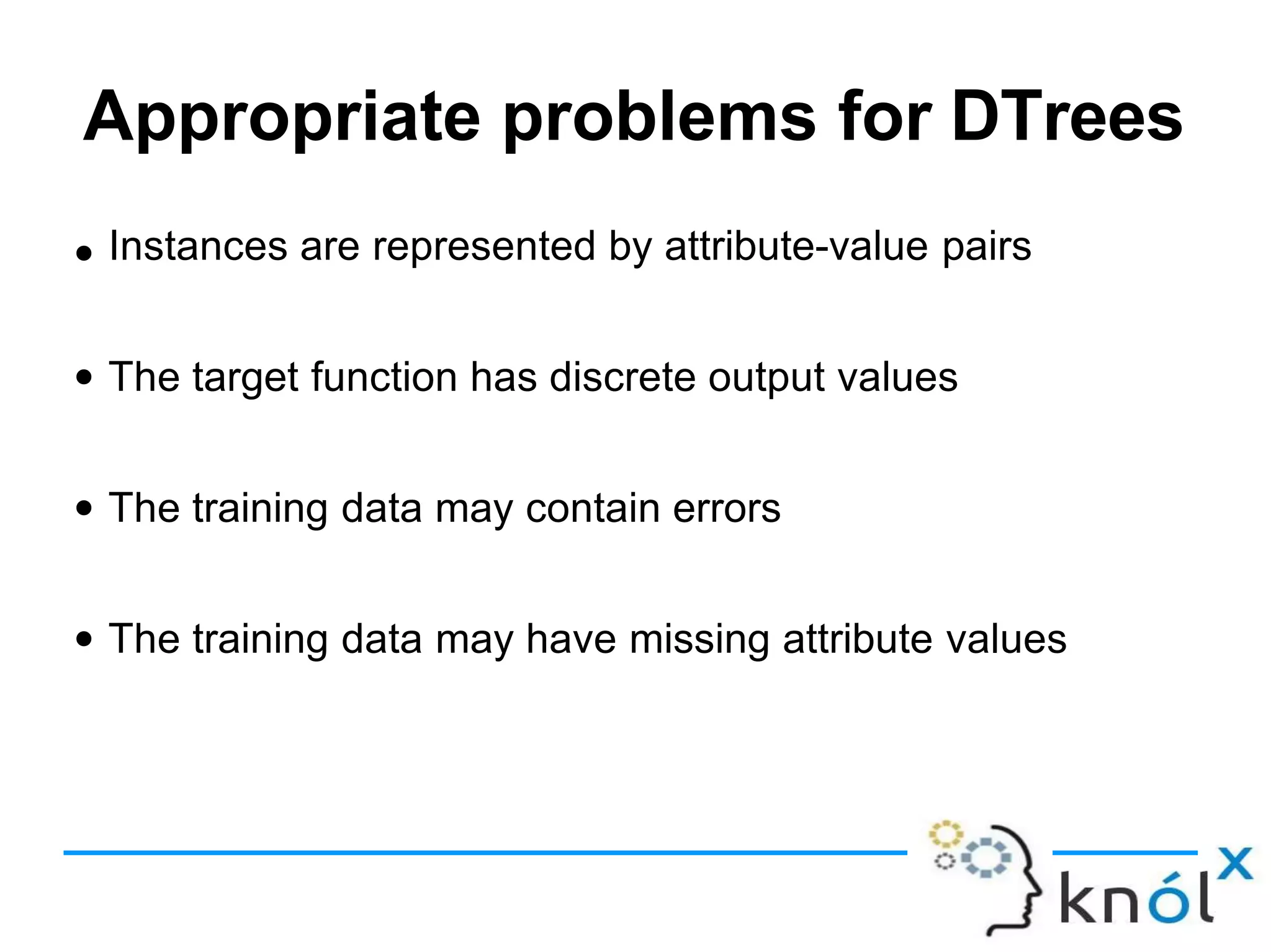
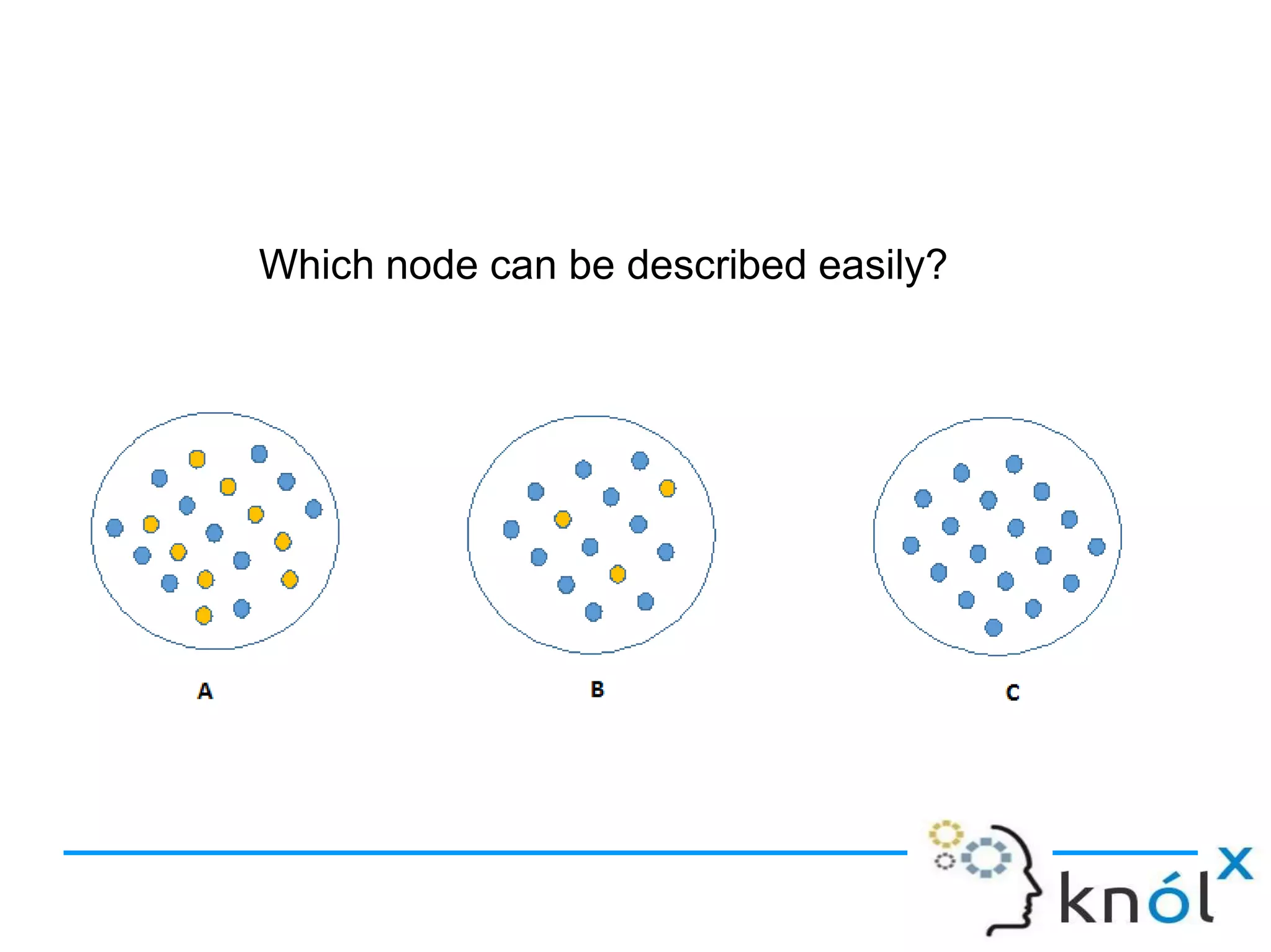
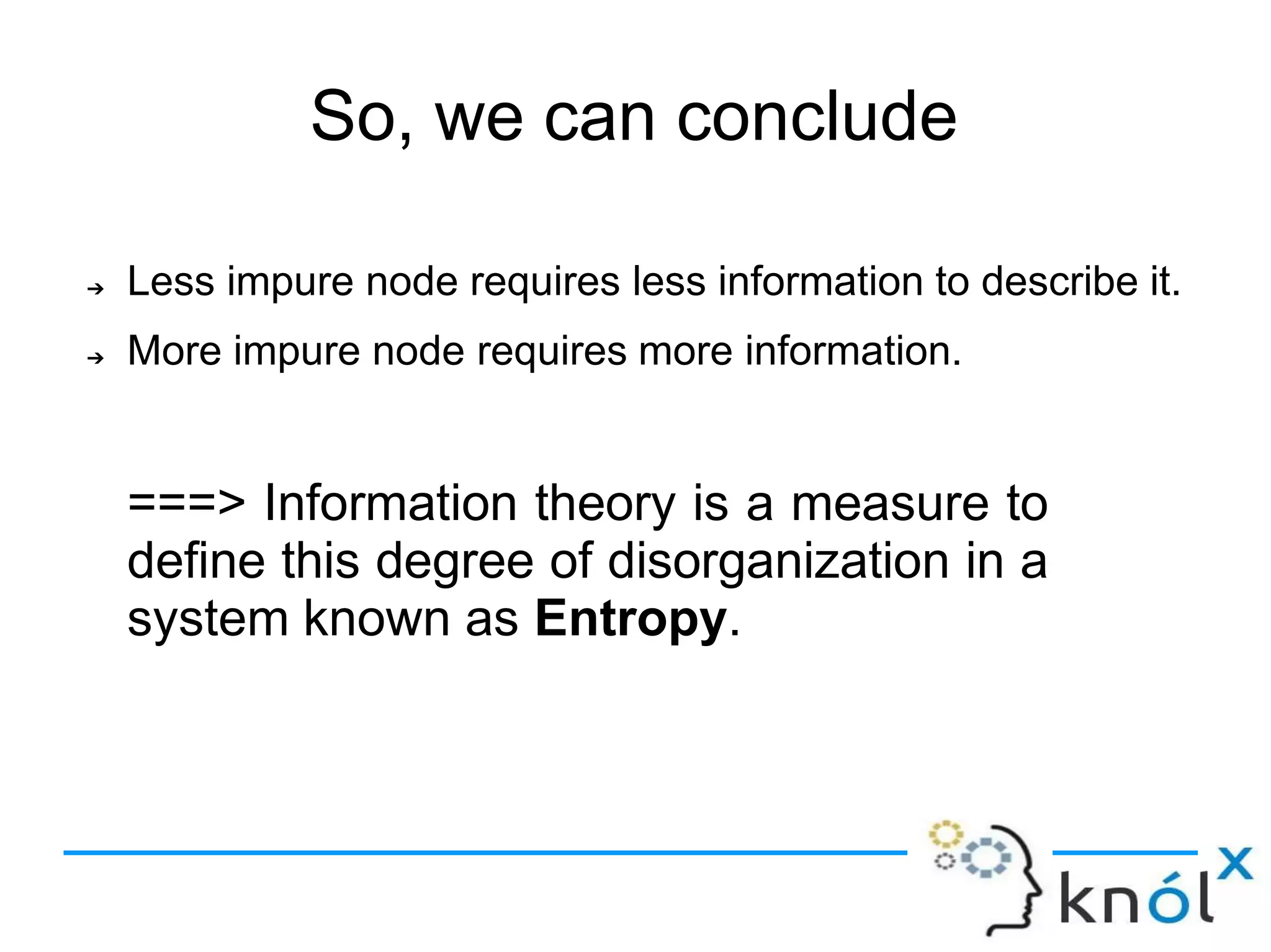
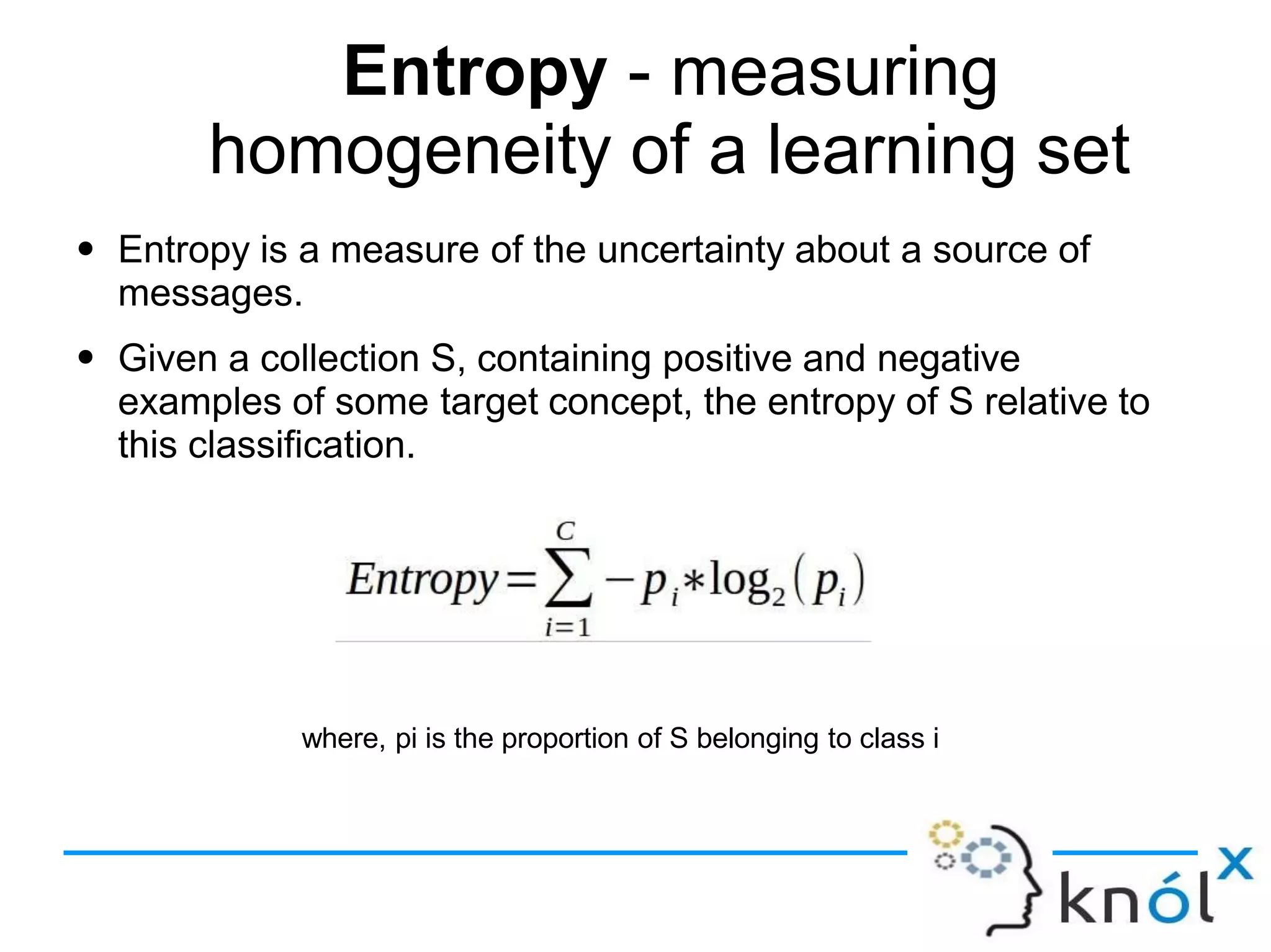
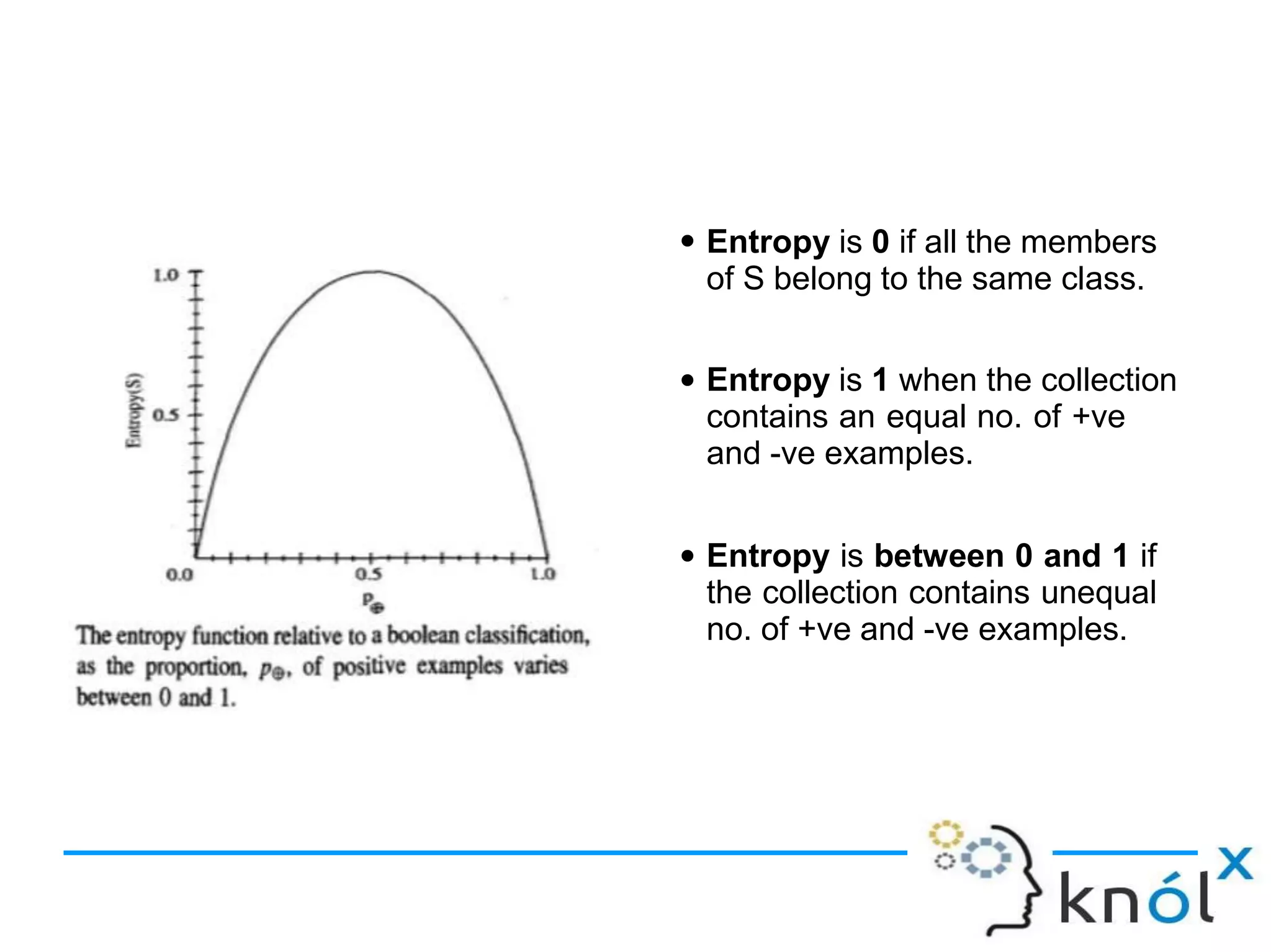
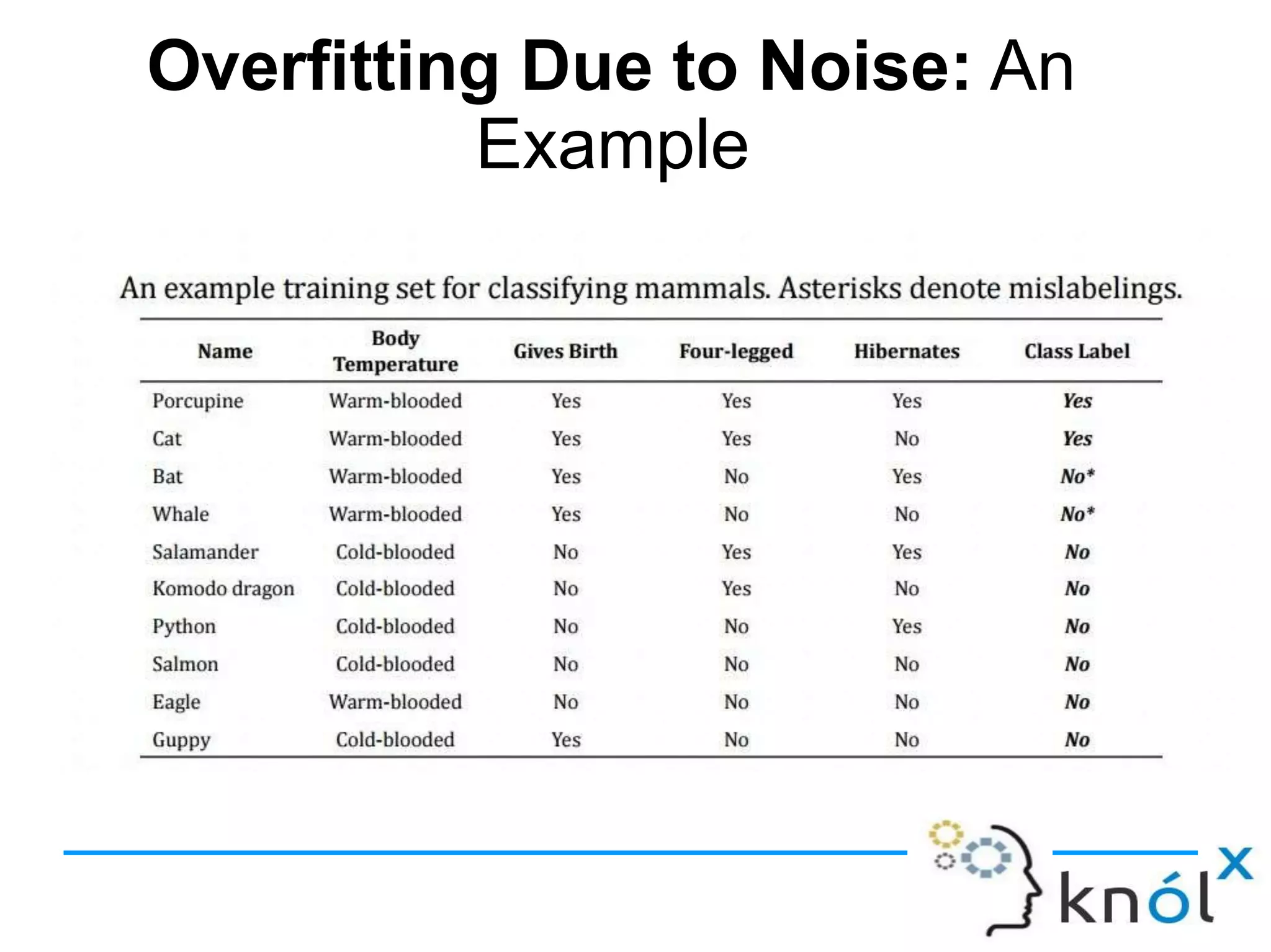
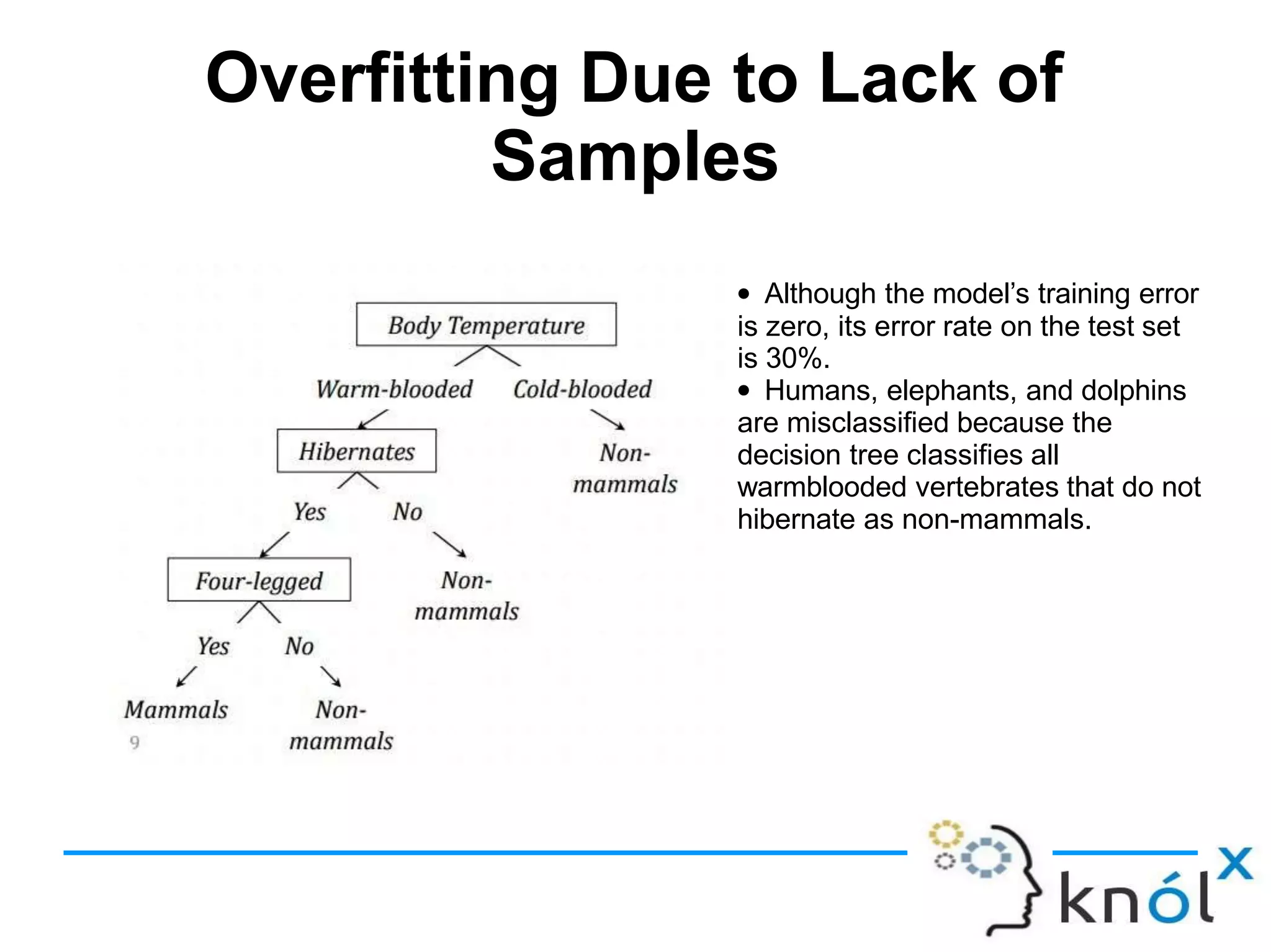
Decision trees are a type of supervised learning algorithm that can be used for classification and regression. They work by creating a tree structure where each branch represents a choice between alternatives and each leaf node represents a classification decision. Decision trees are appropriate for problems where instances are represented by attribute-value pairs and the target function has discrete output values. Information gain is used to determine which attribute to use at each decision node by selecting the attribute that reduces entropy, or uncertainty, the most. Issues with decision trees include overfitting the training data if the tree is grown too deeply, handling continuous attributes, and dealing with missing data values. Overfitting occurs when a model aligns too closely to the training data and loses its ability to generalize to new