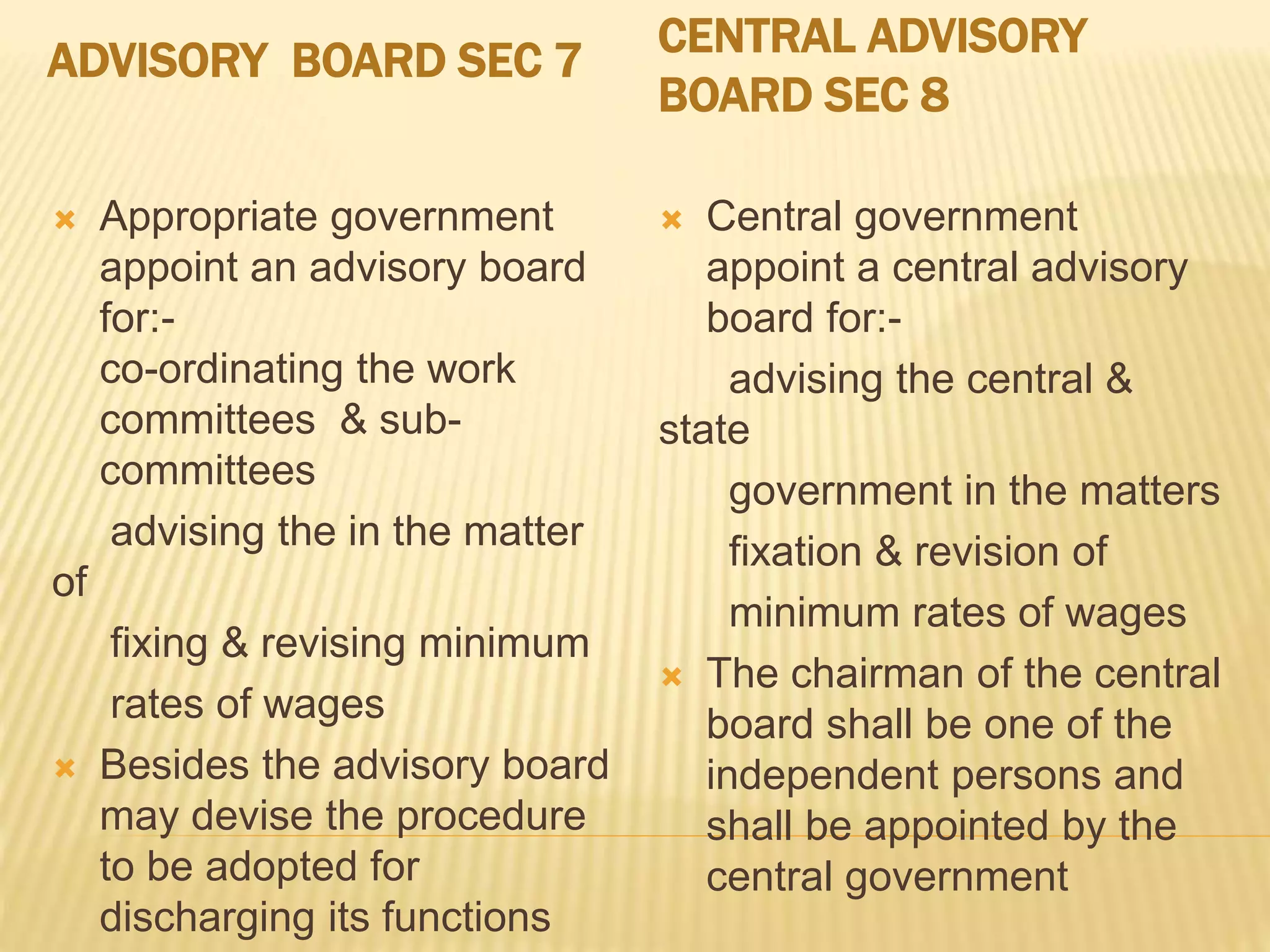
The Minimum Wages Act 1948 empowers the appropriate government to fix minimum wages in scheduled employments to prevent exploitation of workers. It applies across India and allows state governments to add employments or issue directions. The Act requires wages be paid in cash and sets minimum time rates, piece rates and overtime rates. It enables fixing working hours and weekly holidays. Records must be maintained and penalties imposed for violations. Its objectives are to provide minimum wages, prevent exploitation and empower governments to set and revise wages regularly in organized sectors.