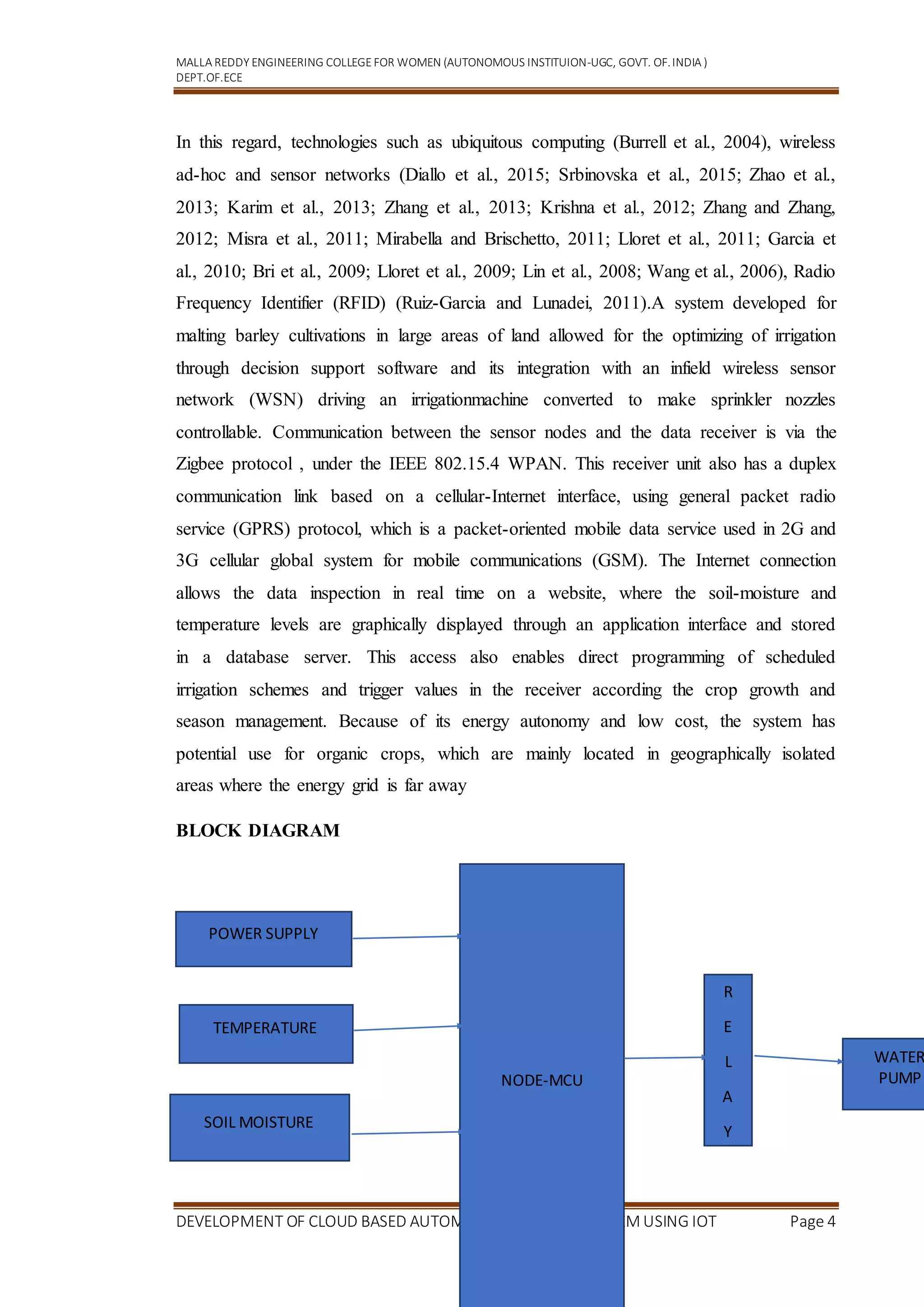
This document discusses the development of a cloud-based automatic irrigation system using IoT. It begins with an introduction explaining the need for more efficient irrigation methods due to increasing population and climate change. It then reviews existing automated irrigation systems that typically use soil moisture sensors and weather data. The proposed system would use a water level sensor in an evaporation pan to estimate soil moisture loss and trigger irrigation through solenoid valves. Sensor data and system status would be sent to the cloud for remote monitoring via an Android app. This allows irrigation to be controlled automatically based on pan water levels while avoiding manual monitoring.








![MALLA REDDY ENGINEERING COLLEGEFOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS INSTITUION-UGC, GOVT. OF.INDIA )
DEPT.OF.ECE
DEVELOPMENT OF CLOUD BASED AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION SYSTEM USING IOT Page 11
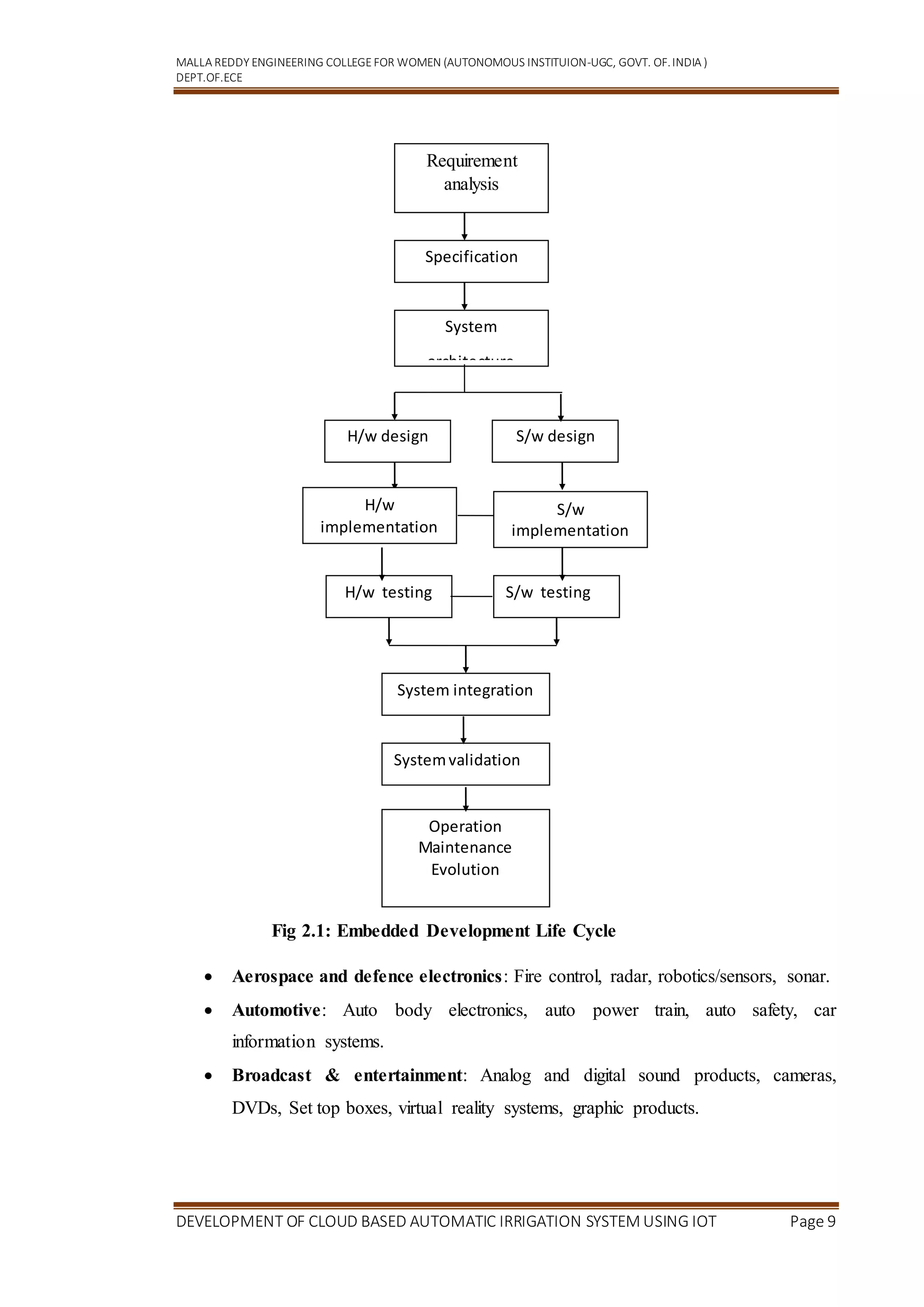
CHAPTER 3
NODE-MCU
NODE MCU:
Node-MCU is a low-cost open source IoT platform. It initially included firmware which
runs on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi SoC from Espressif Systems, and hardware which was
based on the ESP-12 module.[6][7] Later, support for the ESP32 32-bit MCU was
added
3.1 OVERVIEW:
Node MCU is an open source firmware for which open source prototyping board
designs are available. The name "Node MCU" combines "node" and "MCU" (micro-
controller unit).[8]. The term "Node MCU" strictly speaking refers to the firmware
rather than the associated development kits.[citation needed]
Both the firmware and prototyping board designs are open source.
The firmware uses the Lua scripting language. The firmware is based on the eLua
project, and built on the Espressif Non-OS SDK for ESP8266. It uses many open source
projects, such as lua-cjson[10] and SPIFFS.[11] Due to resource constraints, users need
to select the modules relevant for their project and build a firmware tailored to their
needs. Support for the 32-bit ESP32 has also been implemented.
The prototyping hardware typically used is a circuit board functioning as a dual in-line
package (DIP) which integrates a USB controller with a smaller surface-mounted board
containing the MCU and antenna. The choice of the DIP format allows for easy
prototyping on breadboards. The design was initially was based on the ESP-12 module
of the ESP8266, which is a Wi-Fi SoC integrated with a TensilicaXtensa LX106 core,
widely used in IoT applications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minidocumentation-220829135348-7871c023/75/mini_documentation-docx-11-2048.jpg)
![MALLA REDDY ENGINEERING COLLEGEFOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS INSTITUION-UGC, GOVT. OF.INDIA )
DEPT.OF.ECE
DEVELOPMENT OF CLOUD BASED AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION SYSTEM USING IOT Page 12
3.2 HISTORY:
Node MCU was created shortly after the ESP8266 came out. On December 30, 2013,
Espressif Systems[6] began production of the ESP8266.[12] Node MCU started on 13
Oct 2014, when Hong committed the first file of Node MCU-firmware to GitHub.[13]
Two months later, the project expanded to include an open-hardware platform when
developer Huang R committed the gerber file of an ESP8266 board, named devkit
v0.9.[14] Later that month, Tuan PM ported MQTT client library from Contiki to the
ESP8266 SoC platform,[15] and committed to Node MCU project, then Node MCU
was able to support the MQTT IoT protocol, using Lua to access the MQTT broker.
Another important update was made on 30 Jan 2015, when Devsaurus ported the
u8glib[16] to the Node MCU project,[17] enabling Node MCU to easily drive LCD,
Screen, OLED, even VGA displays. In the summer of 2015 the original creators
abandoned the firmware project and a group of independent contributors took over. By
the summer of 2016 the Node MCU included more than 40 different modules.
3.3 INTRODUCTION TO NODE MCU:
Node MCU is an open source LUA based firmware developed for ESP8266 wifi chip.
Node MCU Development Kit/Board consist of ESP8266 wifi chip. ESP8266 chip has
GPIO pins, serial communication protocol, etc. features on it.ESP8266 is a low-
cost Wi-Fi chip developed by Espressif Systems with TCP/IP protocol. For more
information about ESP8266, you can refer ESP8266 WiFi Module.The features of
ESP8266 are extracted on Node MCU Development board. Node MCU (LUA based
firmware) with Development board/kit that consist of ESP8266 (wifi enabled chip) chip
combines Node MCU Development board which make it stand-alone device in IoT
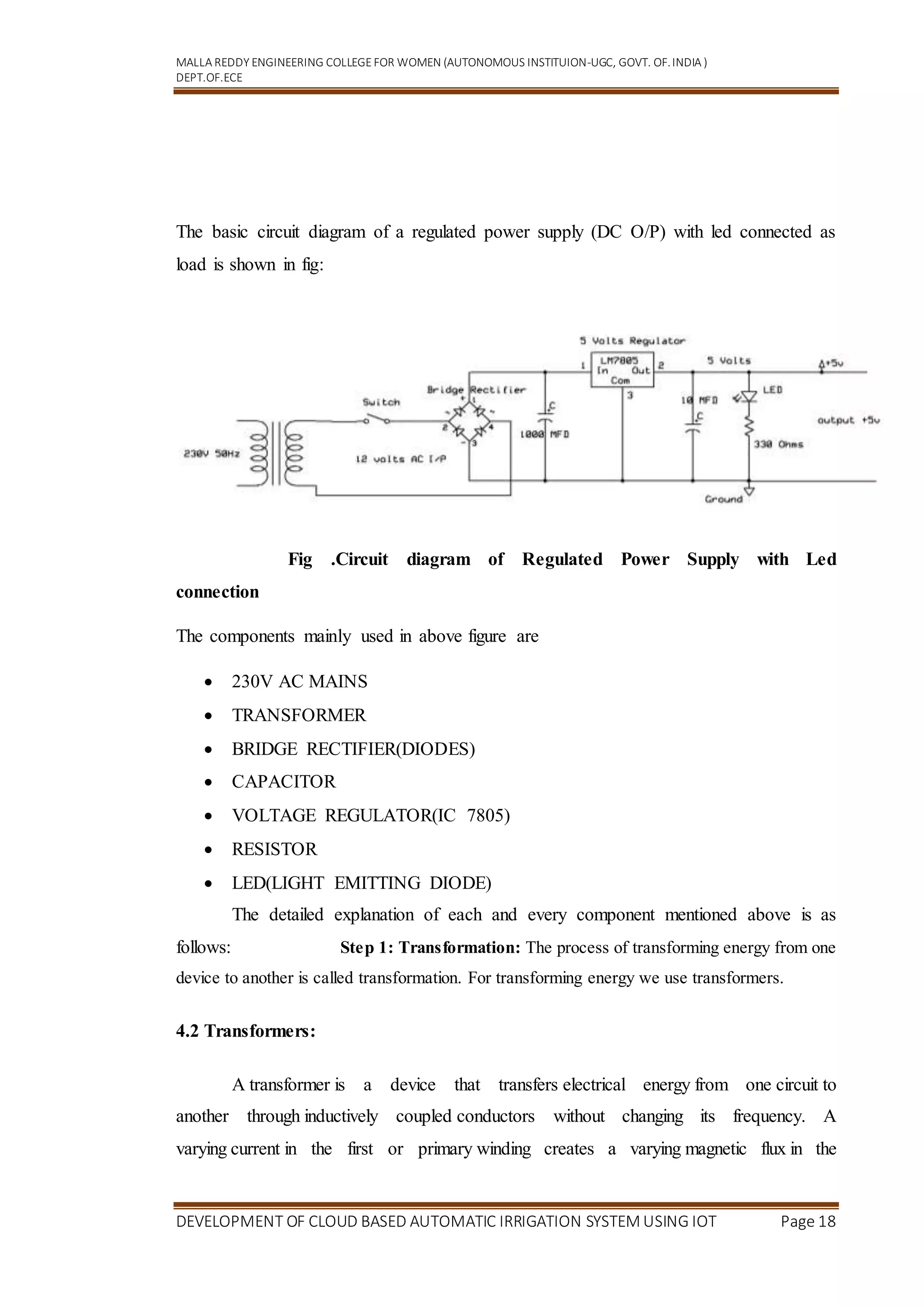
applications.Let’s see 1st version of Node MCU Dev Kit and its pinout as shown in
below images.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minidocumentation-220829135348-7871c023/75/mini_documentation-docx-12-2048.jpg)







![MALLA REDDY ENGINEERING COLLEGEFOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS INSTITUION-UGC, GOVT. OF.INDIA )
DEPT.OF.ECE
DEVELOPMENT OF CLOUD BASED AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION SYSTEM USING IOT Page 25
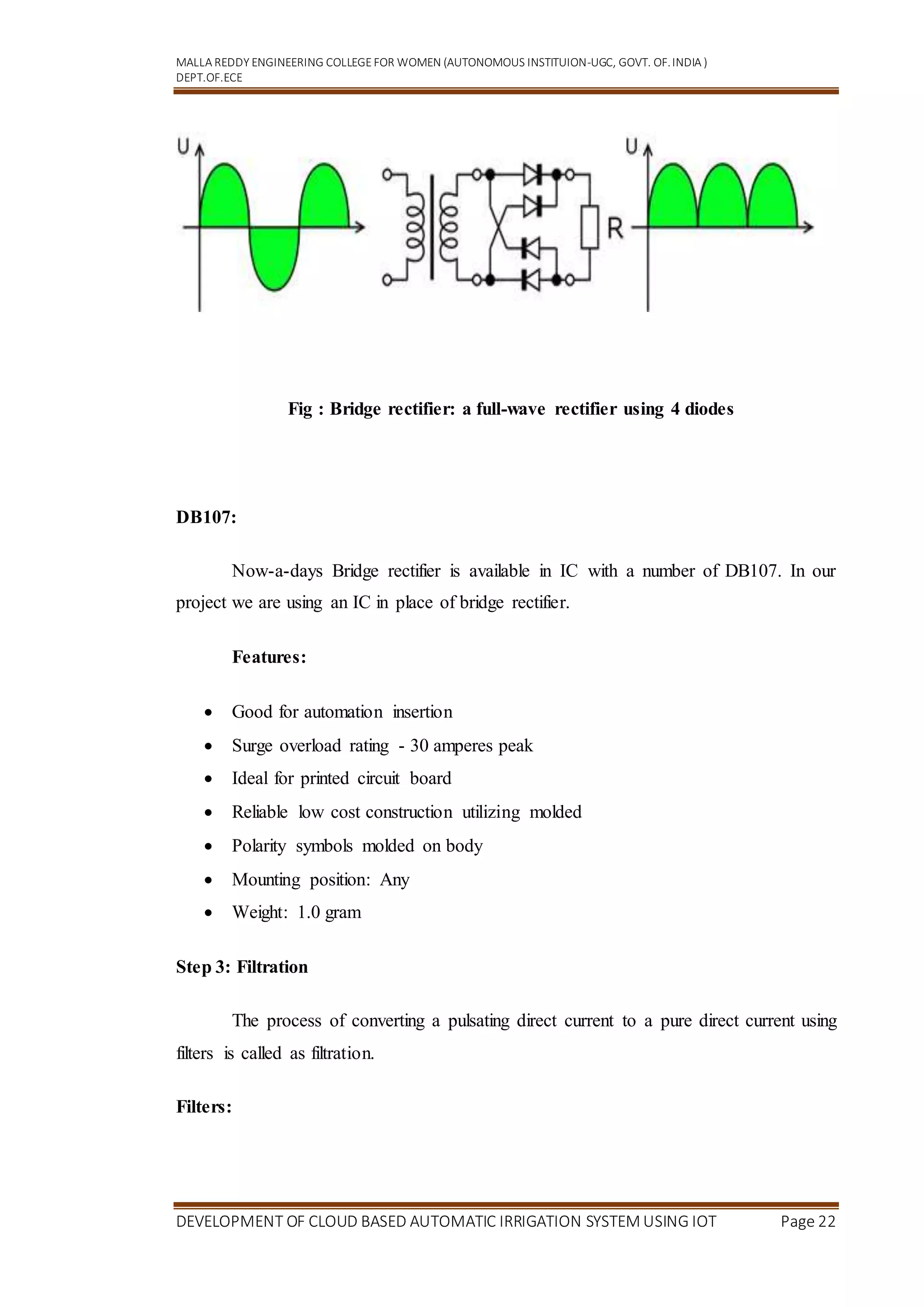
It is not possible to obtain a voltage lower than the stated rating. You cannot use
a 12V regulator to make a 5V power supply. Voltage regulators are very robust. These
can withstand over-current draw due to short circuits and also over-heating. In both
cases, the regulator will cut off before any damage occurs. The only way to destroy a
regulator is to apply reverse voltage to its input. Reverse polarity destroys the regulator
almost instantly. Fig: 3.3.10 shows voltage regulator.
Fig : Voltage Regulator
Resistors:
A resistor is a two-terminal electronic component that produces a voltage across
its terminals that is proportional to the electric current passing through it in accordance
with Ohm's law: [ V = IR ]
Resistors are elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are
ubiquitous in most electronic equipment. Practical resistors can be made of various
compounds and films, as well as resistance wire (wire made of a high-resistivity alloy,
such as nickel/chrome).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minidocumentation-220829135348-7871c023/75/mini_documentation-docx-25-2048.jpg)
![MALLA REDDY ENGINEERING COLLEGEFOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS INSTITUION-UGC, GOVT. OF.INDIA )
DEPT.OF.ECE
DEVELOPMENT OF CLOUD BASED AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION SYSTEM USING IOT Page 26
The primary characteristics of a resistor are the resistance, the tolerance,
maximum working voltage and the power rating. Other characteristics include
temperature coefficient, noise, and inductance. Less well-known is critical resistance,
the value below which power dissipation limits the maximum permitted current flow,
and above which the limit is applied voltage. Critical resistance is determined by the
design, materials and dimensions of the resistor.
Theory of operation:
Ohm's law:
The behaviour of an ideal resistor is dictated by the relationship specified in
Ohm's law: [ V = IR ]
Ohm's law states that the voltage (V) across a resistor is proportional to
the current (I) through it where the constant of proportionality is the resistance (R).
Power dissipation:
The power dissipated by a resistor (or the equivalent resistance of a resistor
network) is calculated using the following:
Fig : Resistor Fig : Colour Bands In Resistor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minidocumentation-220829135348-7871c023/75/mini_documentation-docx-26-2048.jpg)



![MALLA REDDY ENGINEERING COLLEGEFOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS INSTITUION-UGC, GOVT. OF.INDIA )
DEPT.OF.ECE
DEVELOPMENT OF CLOUD BASED AUTOMATIC IRRIGATION SYSTEM USING IOT Page 33
CHAPTER-5
SOFTWARE DESCRIPTION
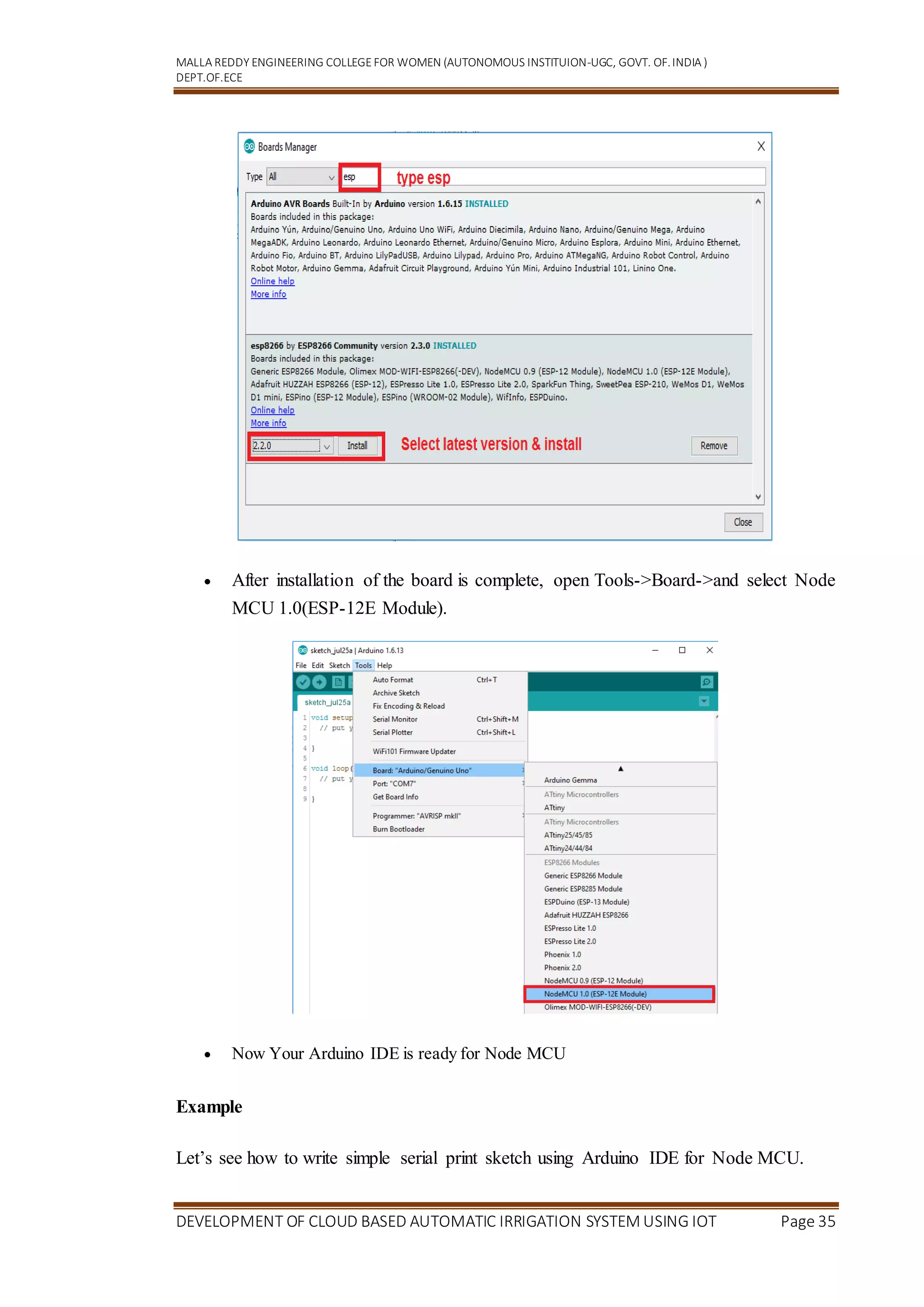
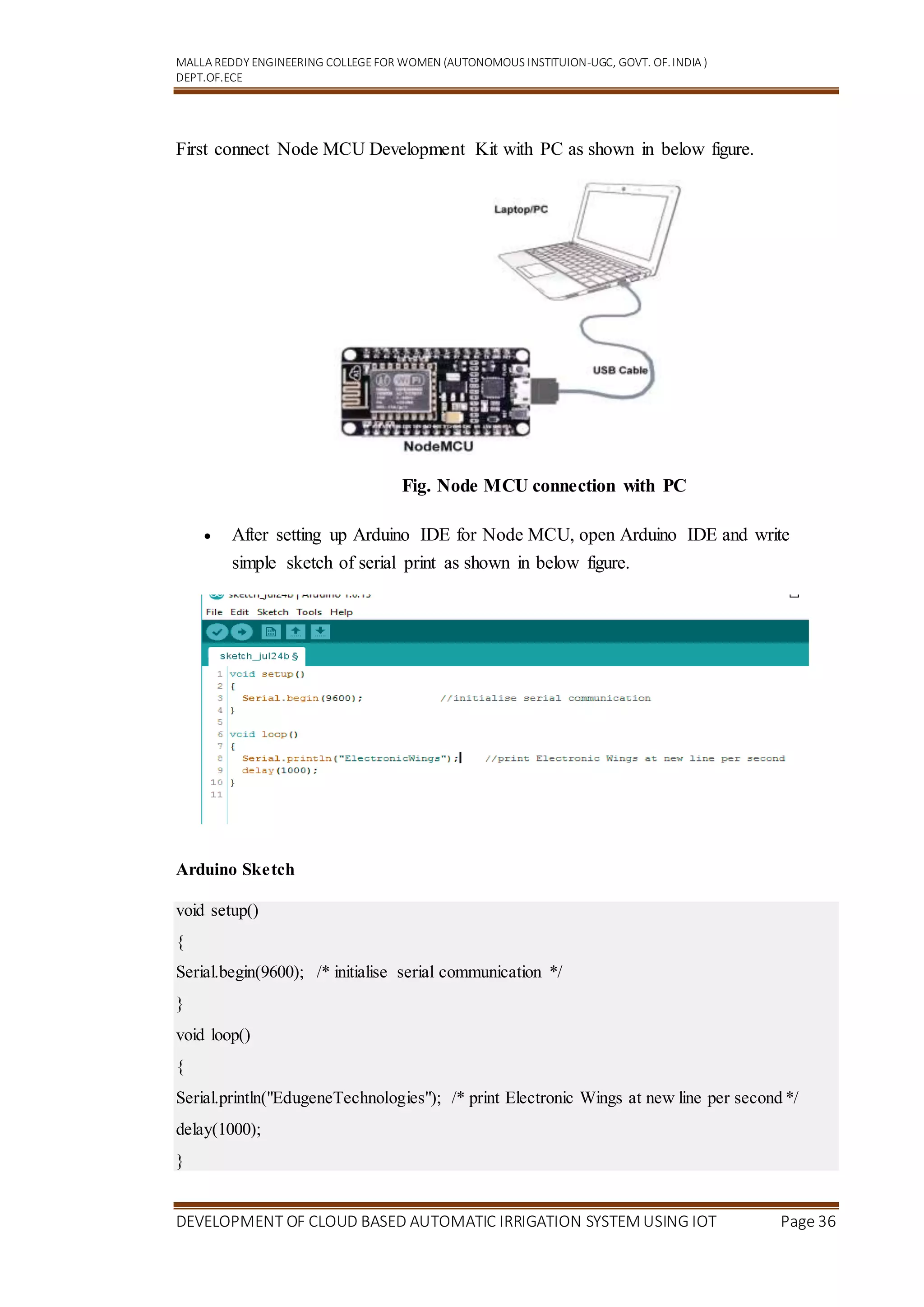
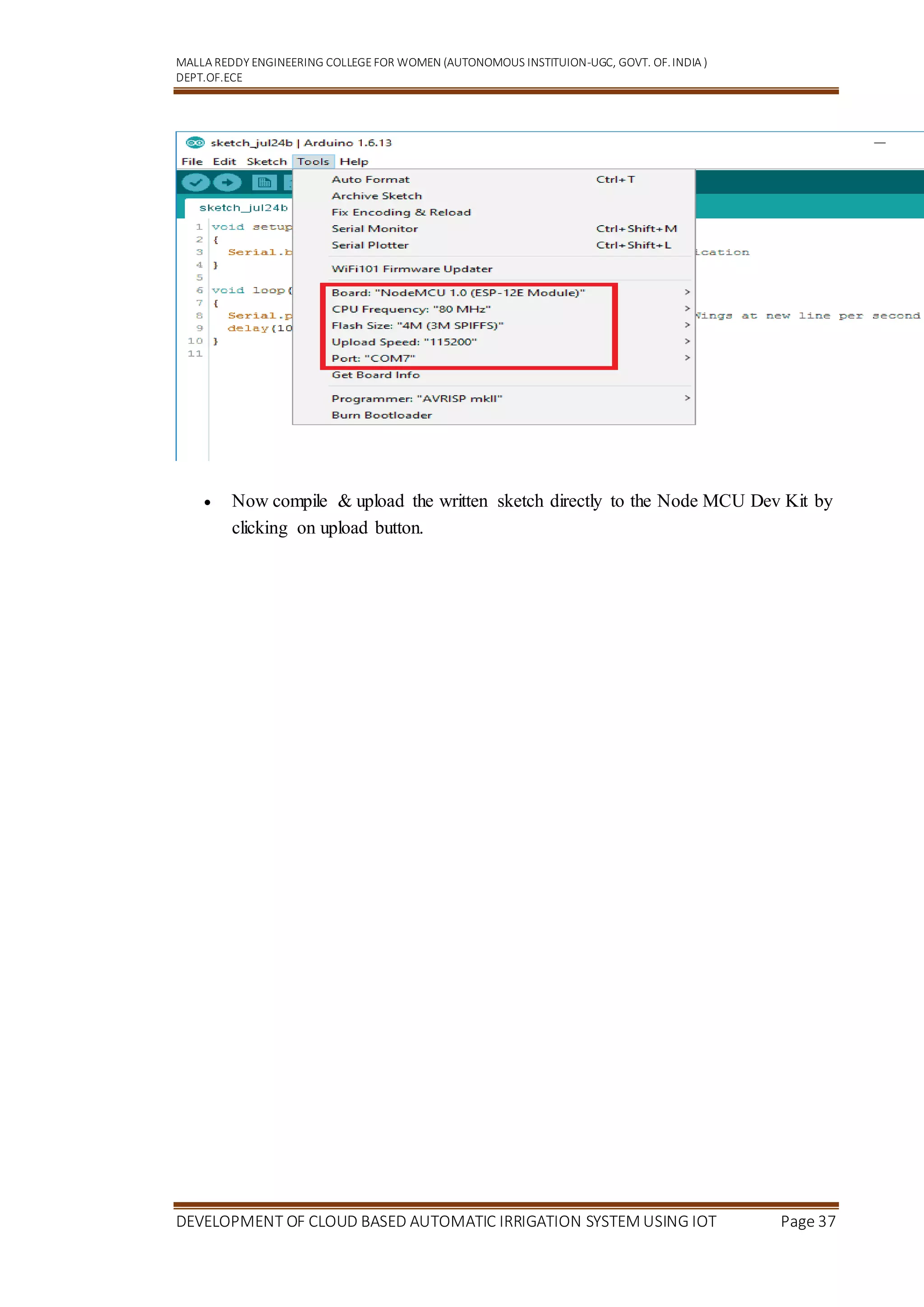
Getting Started with Node MCU using Arduino IDE
5.1 Introduction
Node MCU is Lua based firmware of ESP8266. Generally, ESPlorer IDE is referred for
writing Lua scripts for Node MCU. It requires to get familiar with ESPlorer IDE and
Lua scripting language. There is another way of developing Node MCU with a well-
known IDE . First download Arduino IDE(version1.6+) .
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
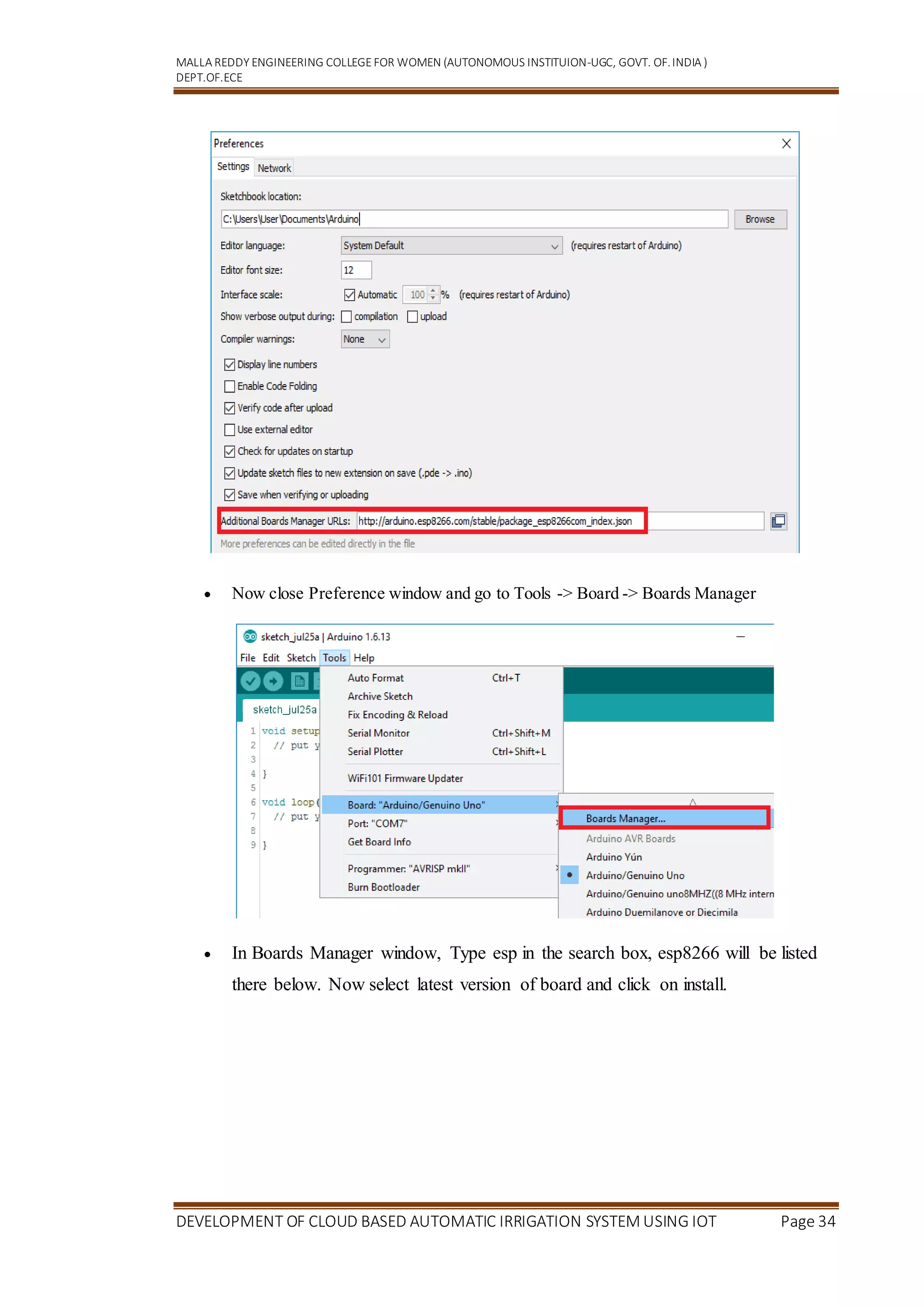
Open Arduino IDE and Go to File -> Preference.
Now on Preference window, Enter below link in Additional Boards Manager
URLs[ http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minidocumentation-220829135348-7871c023/75/mini_documentation-docx-33-2048.jpg)