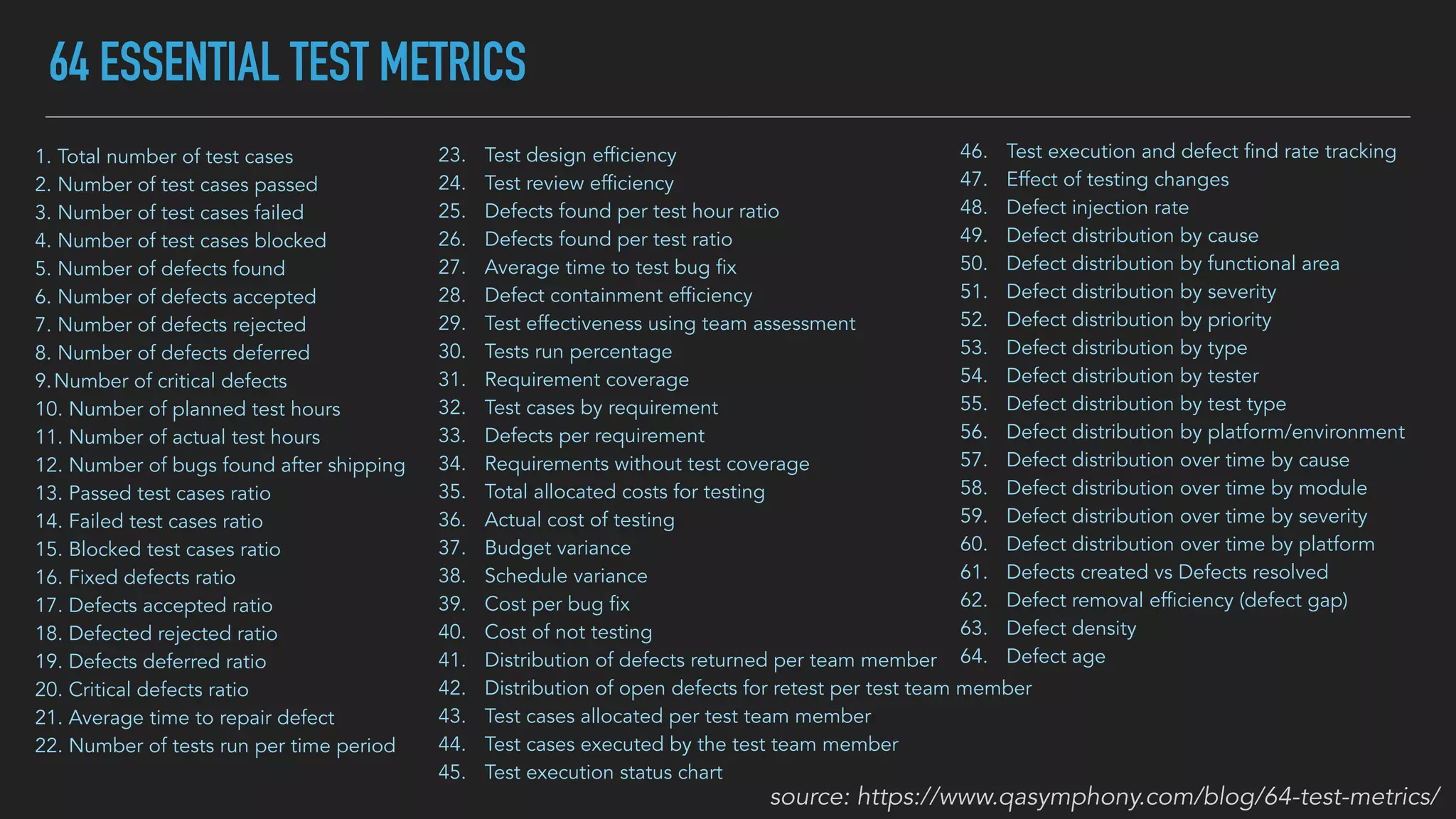
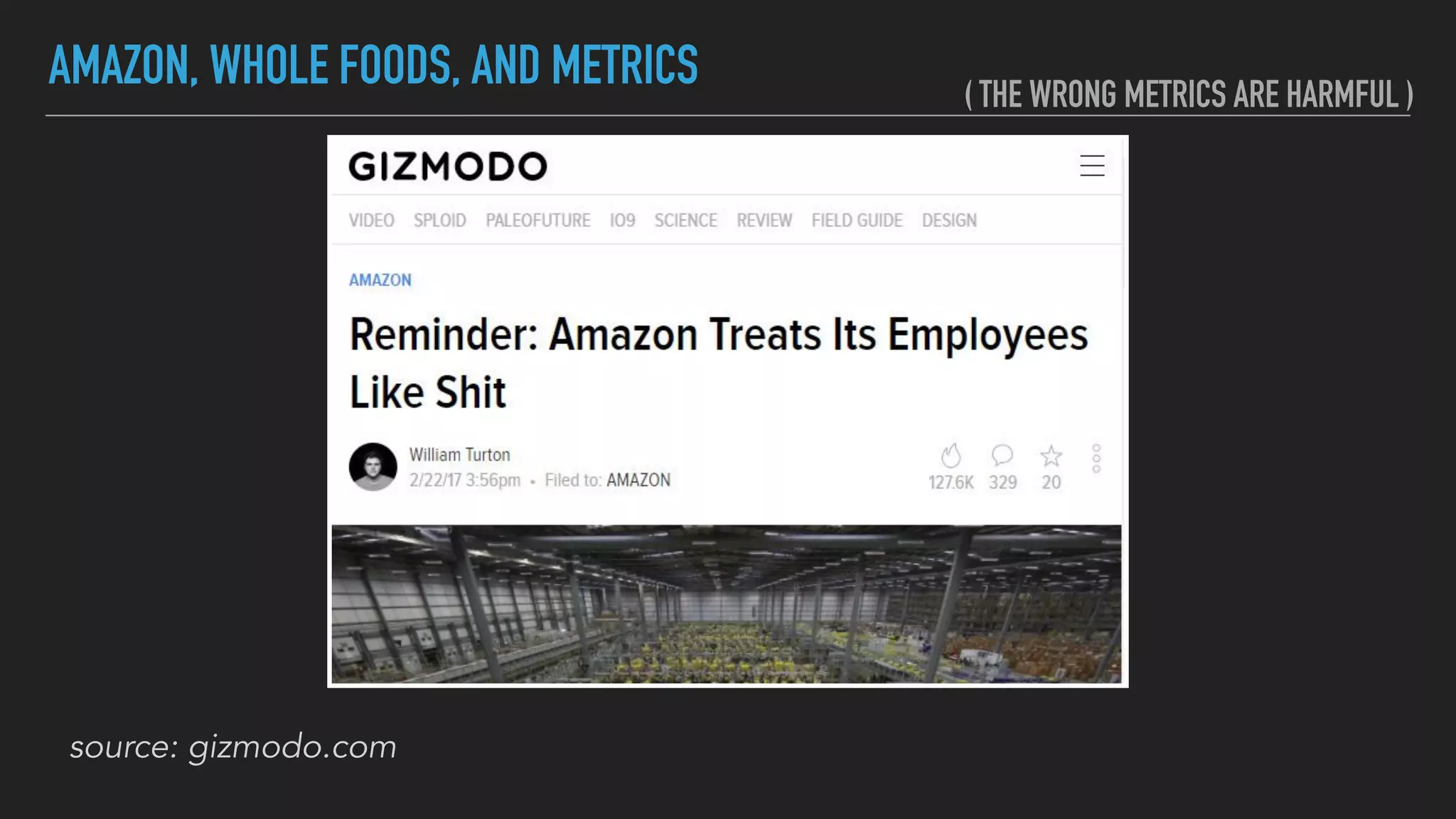
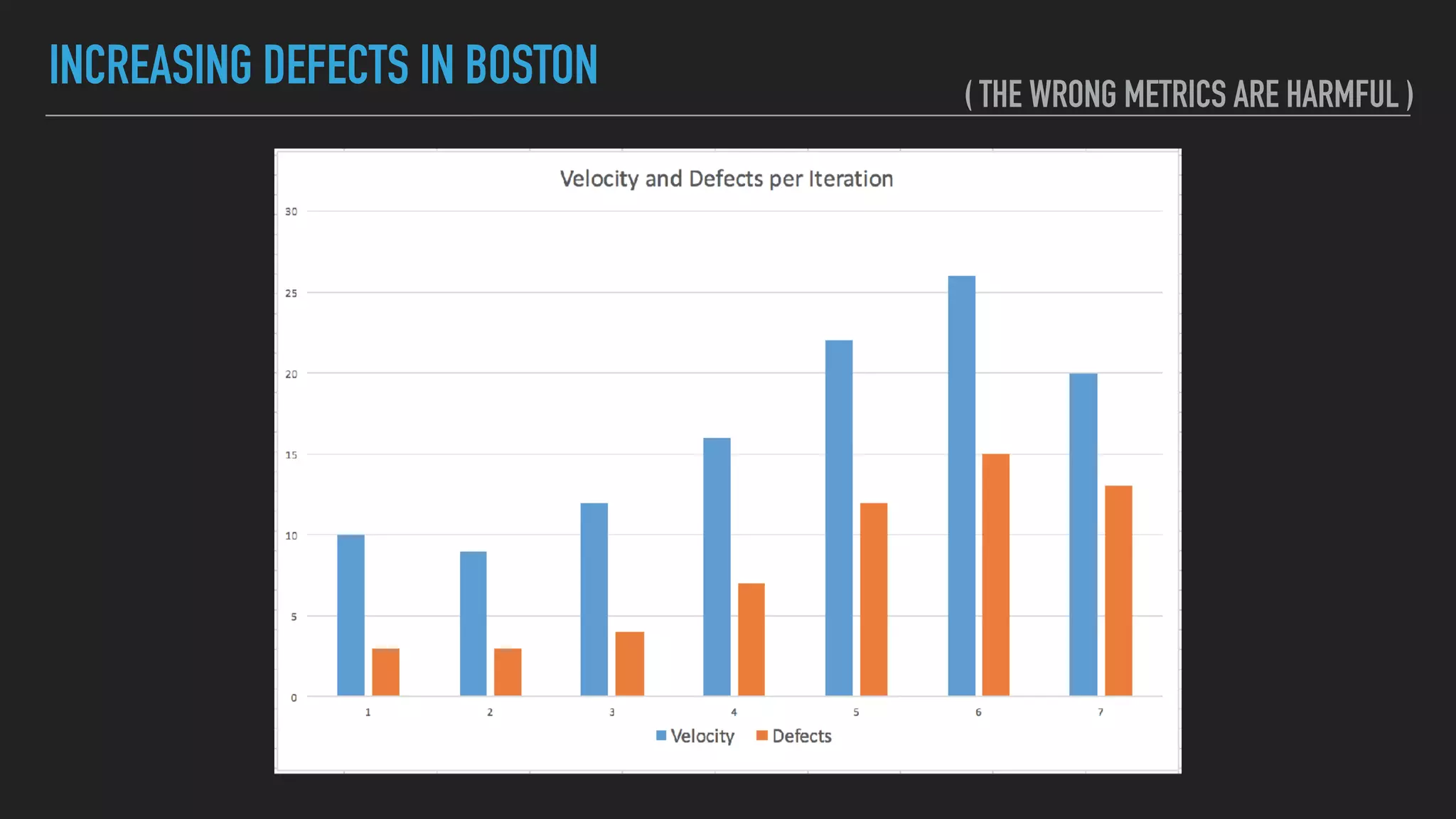
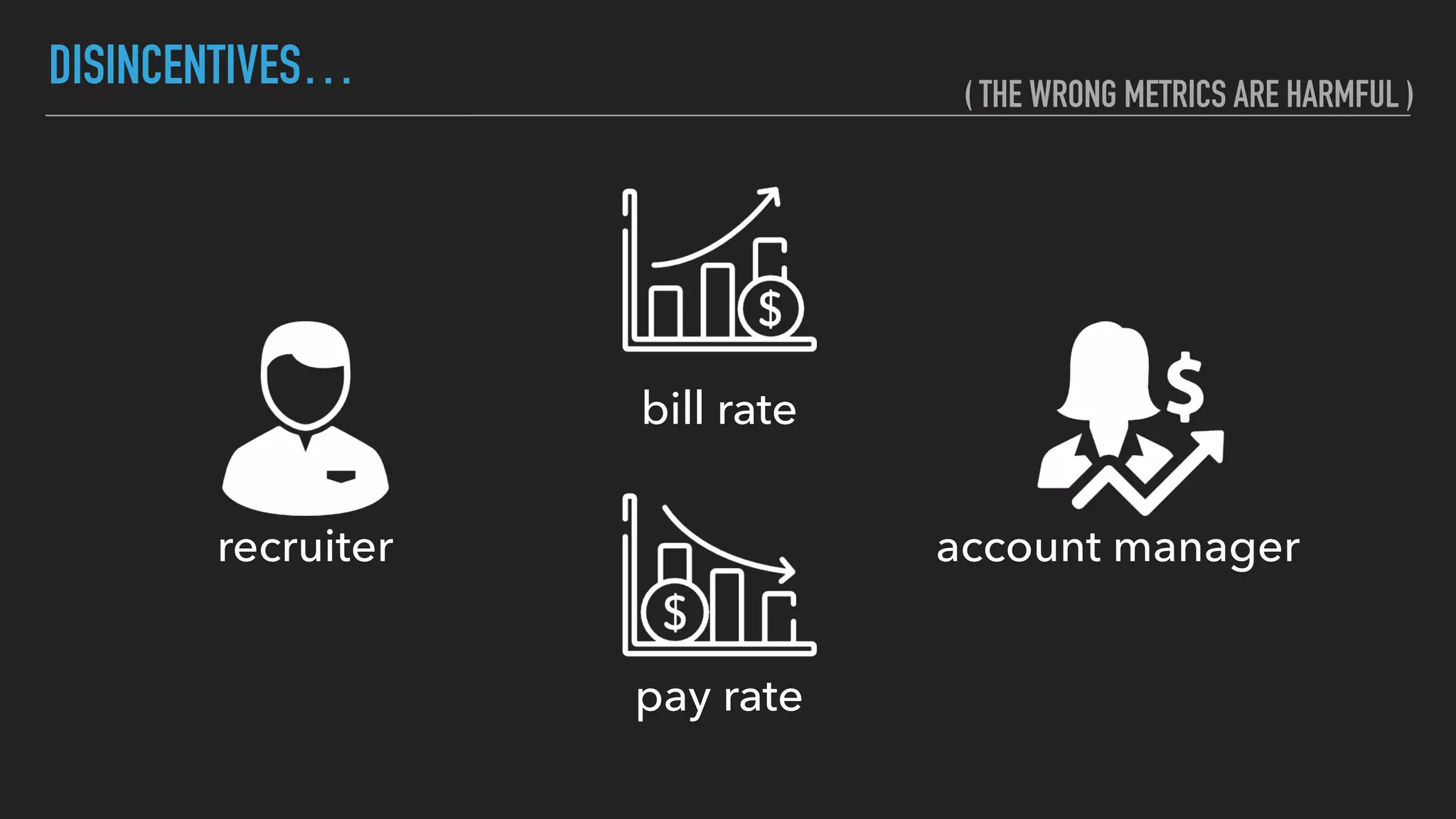
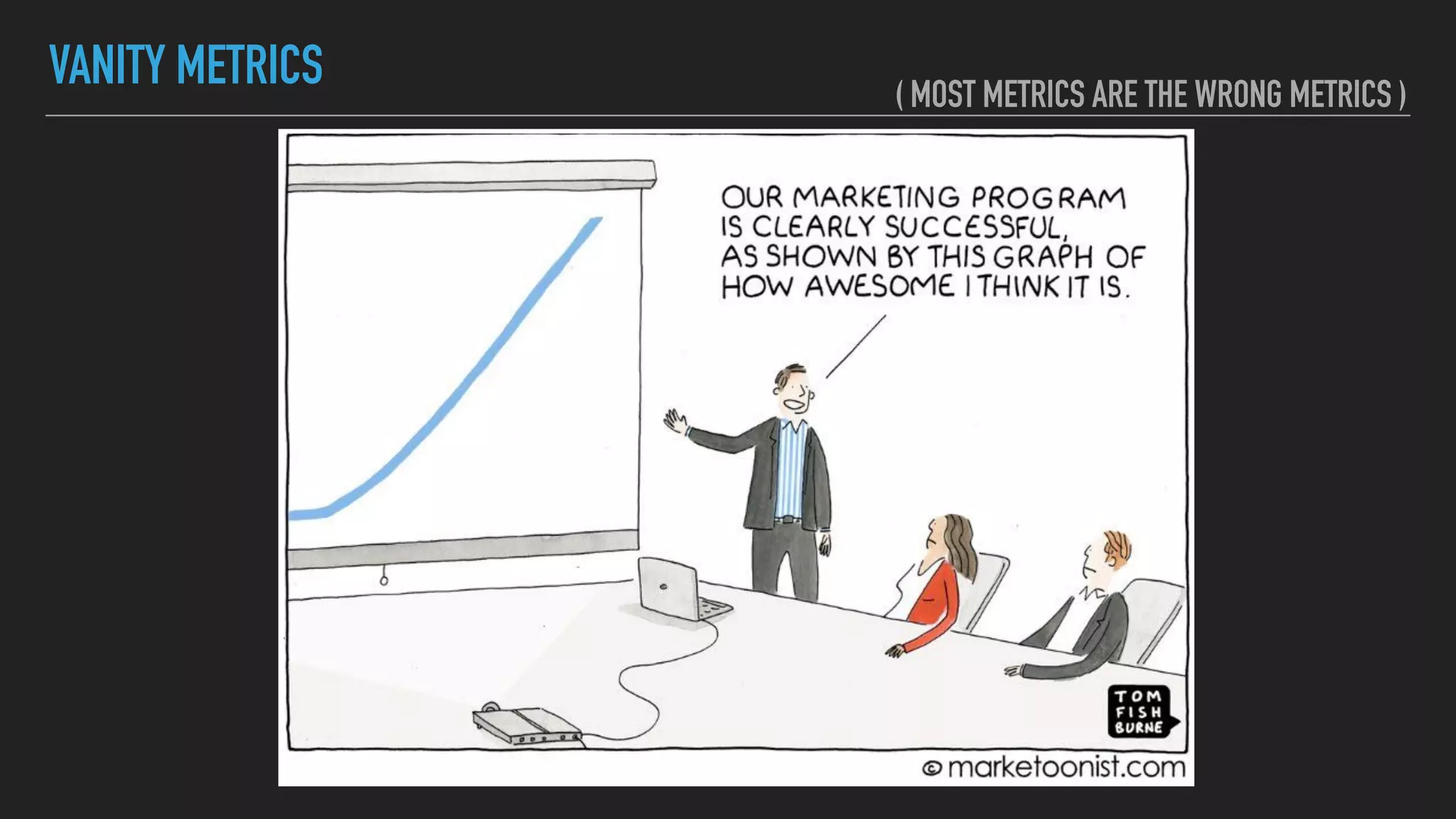
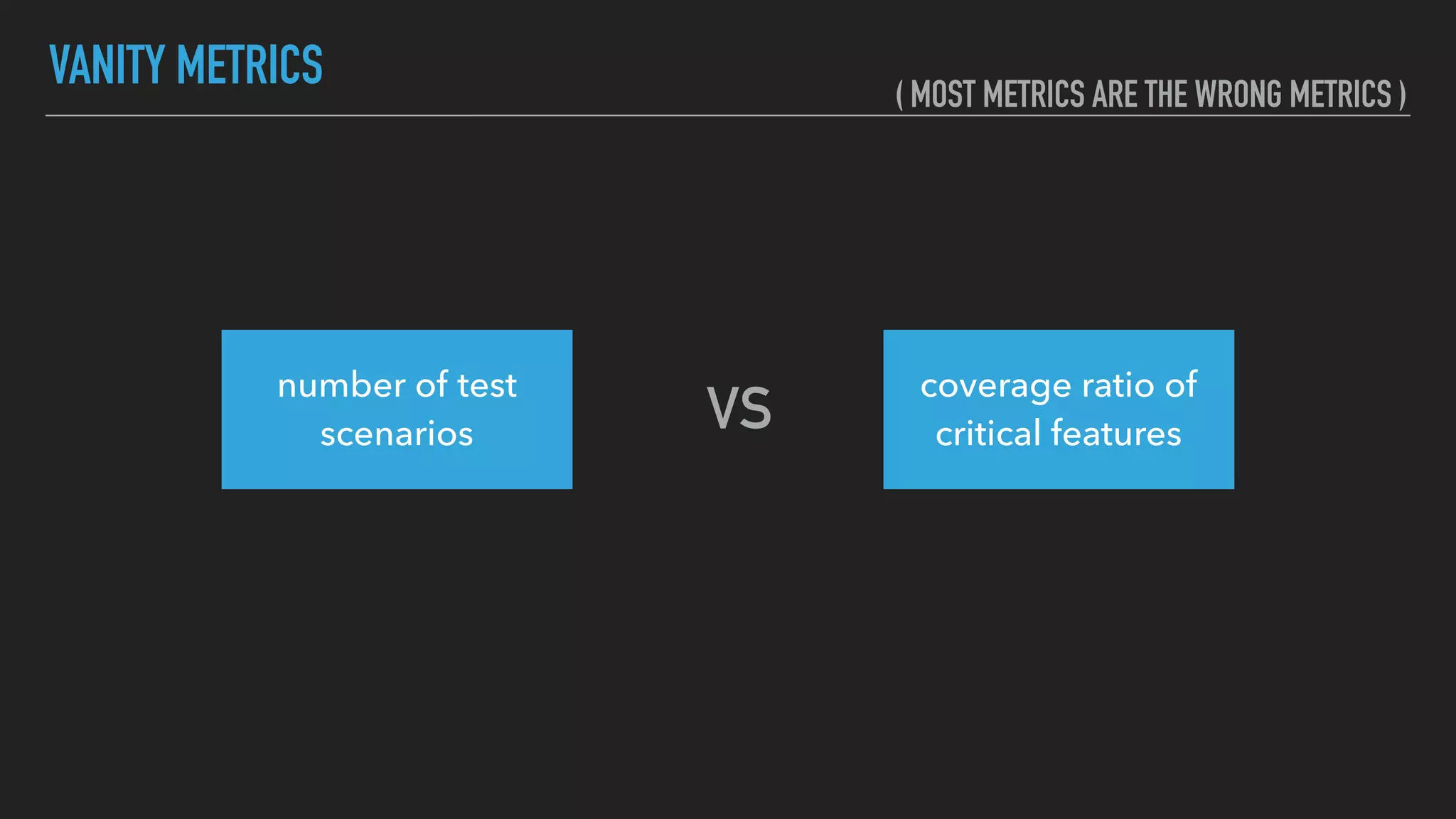
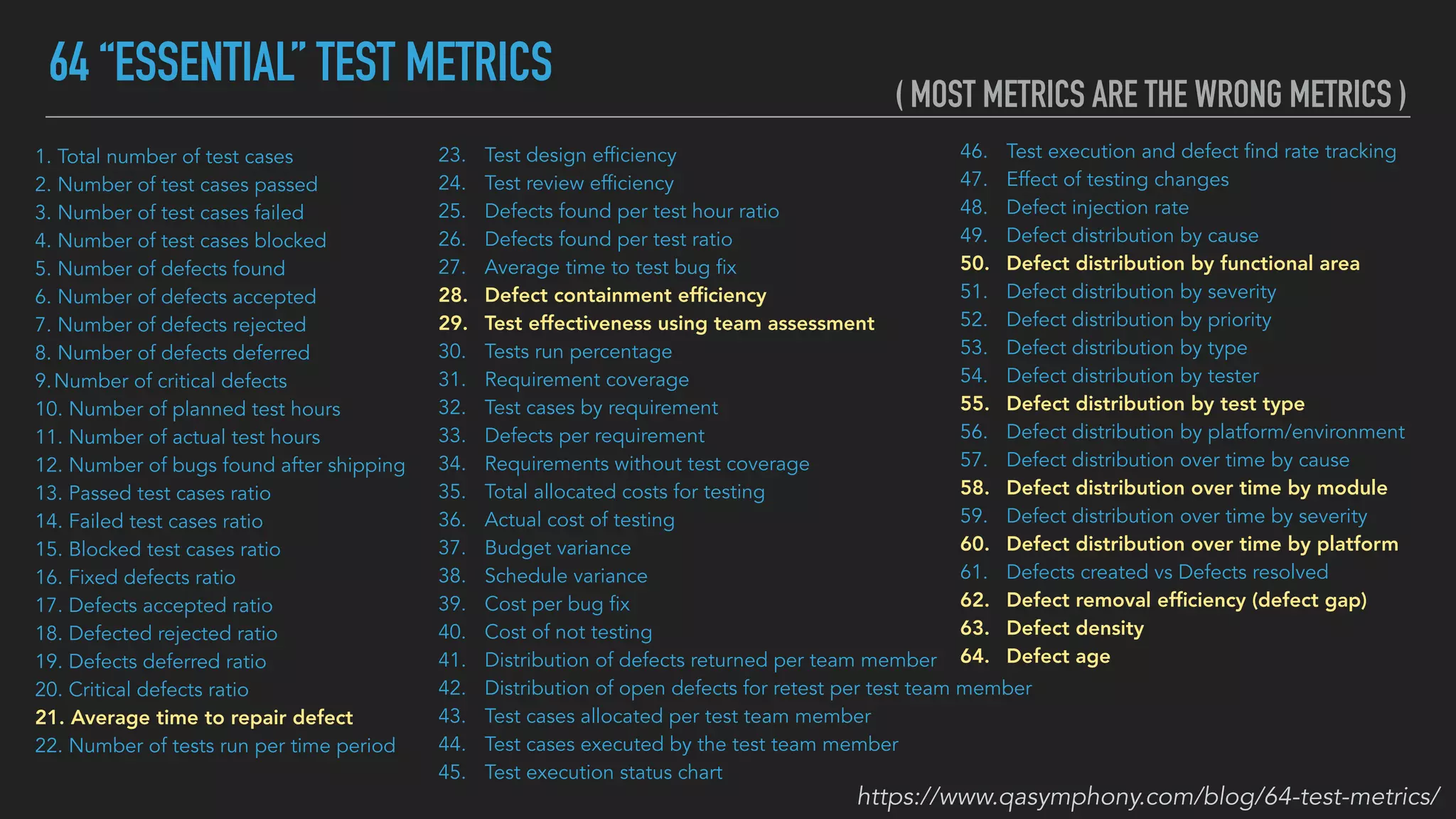
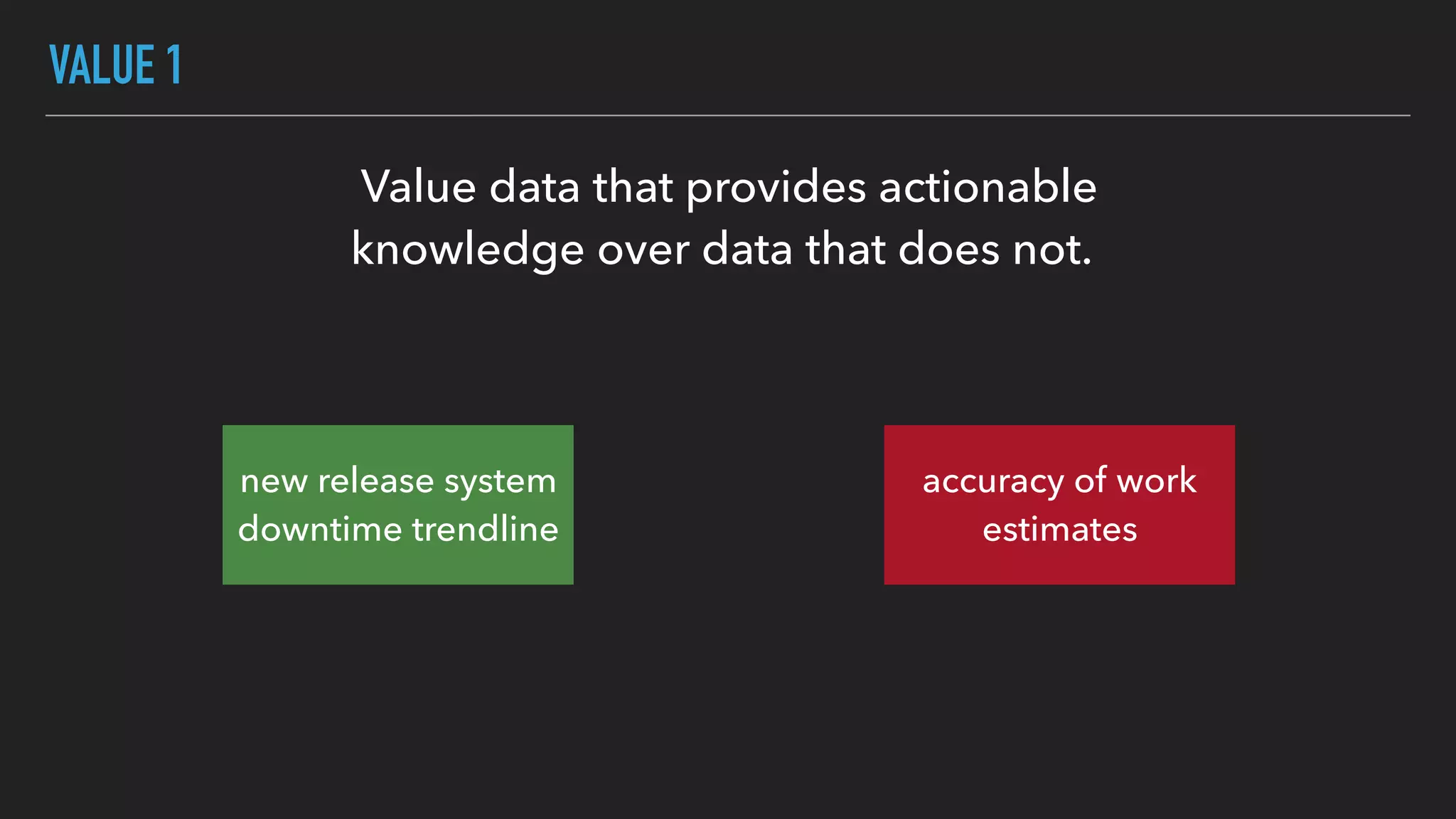
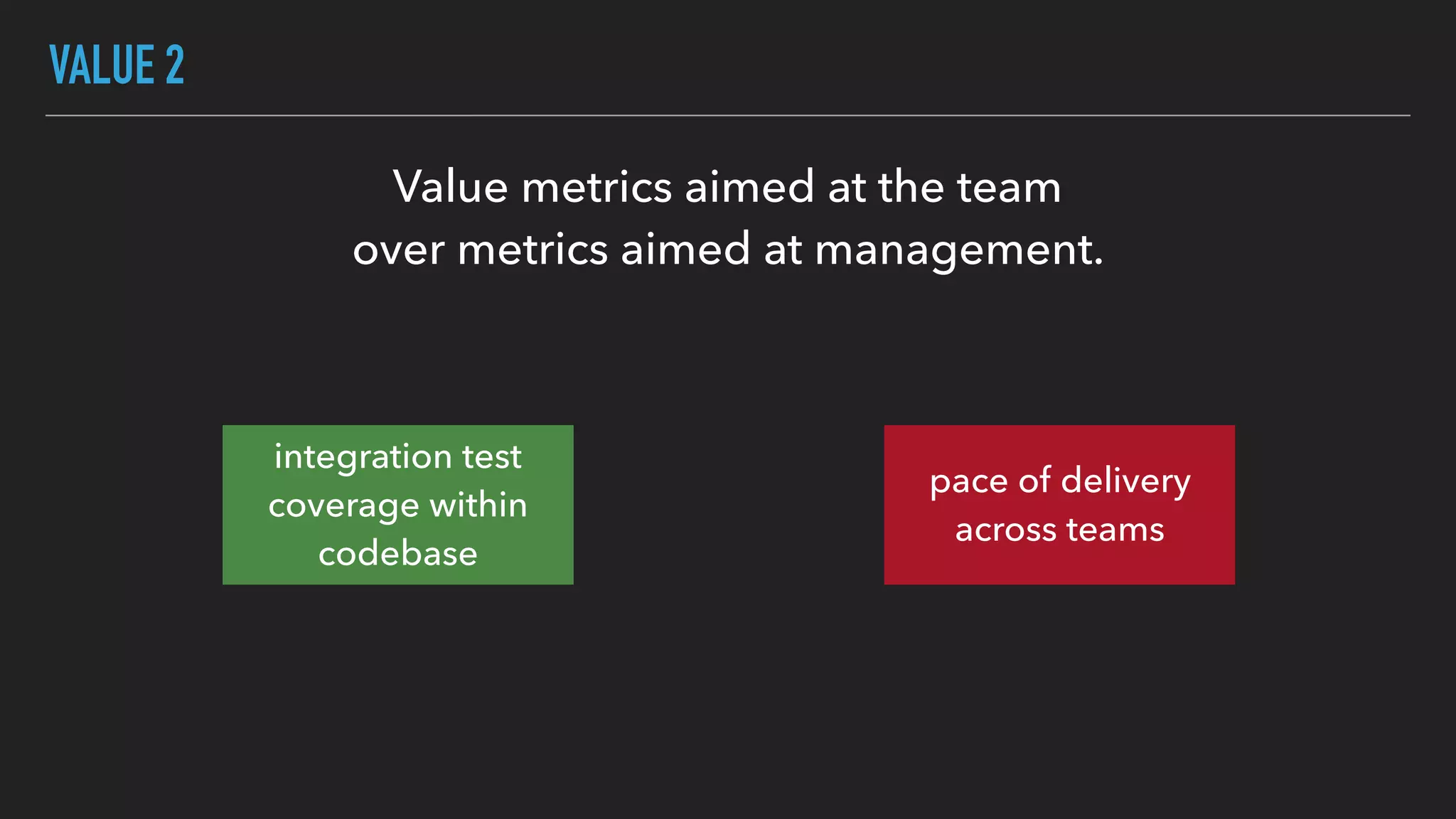
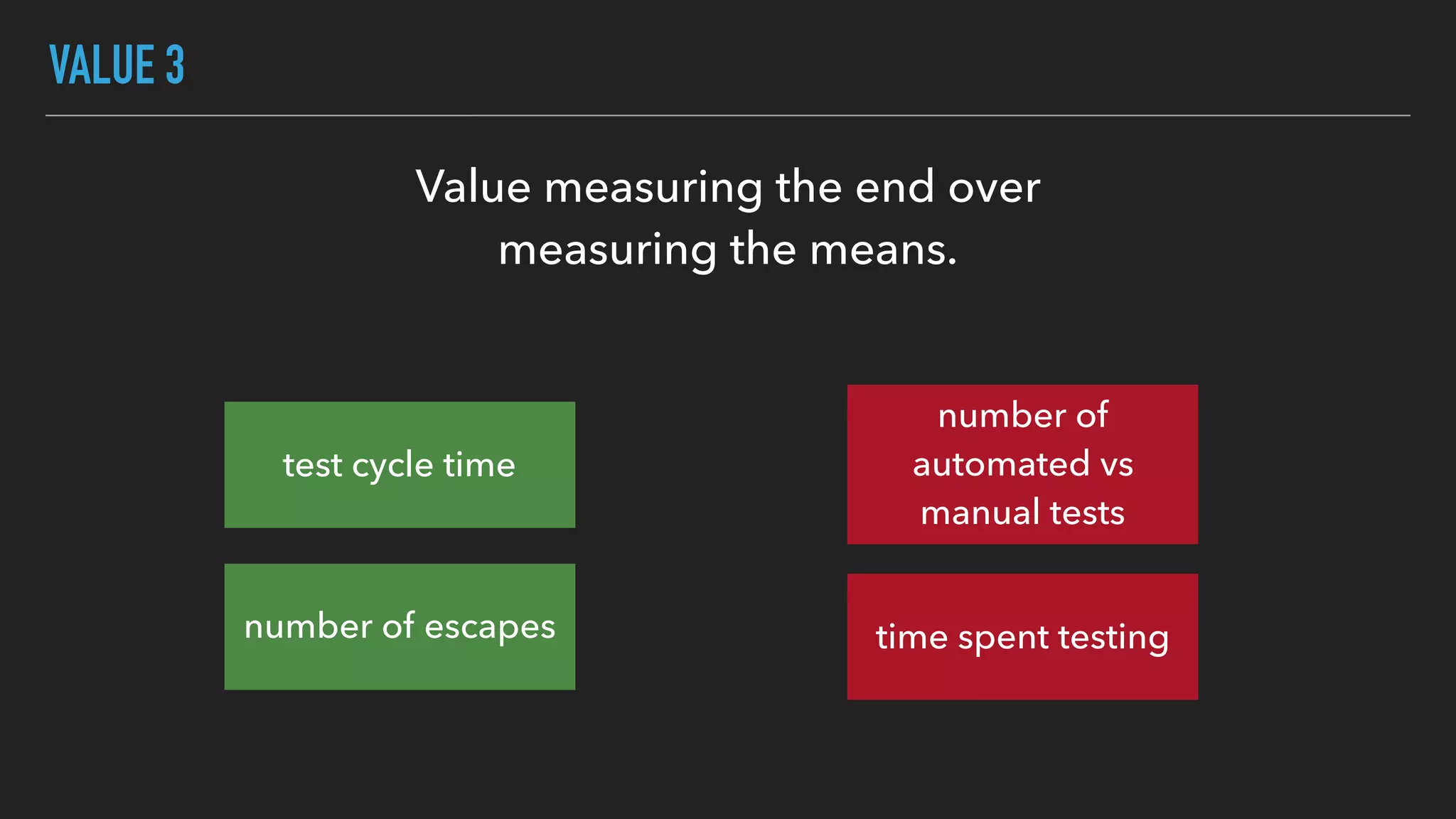
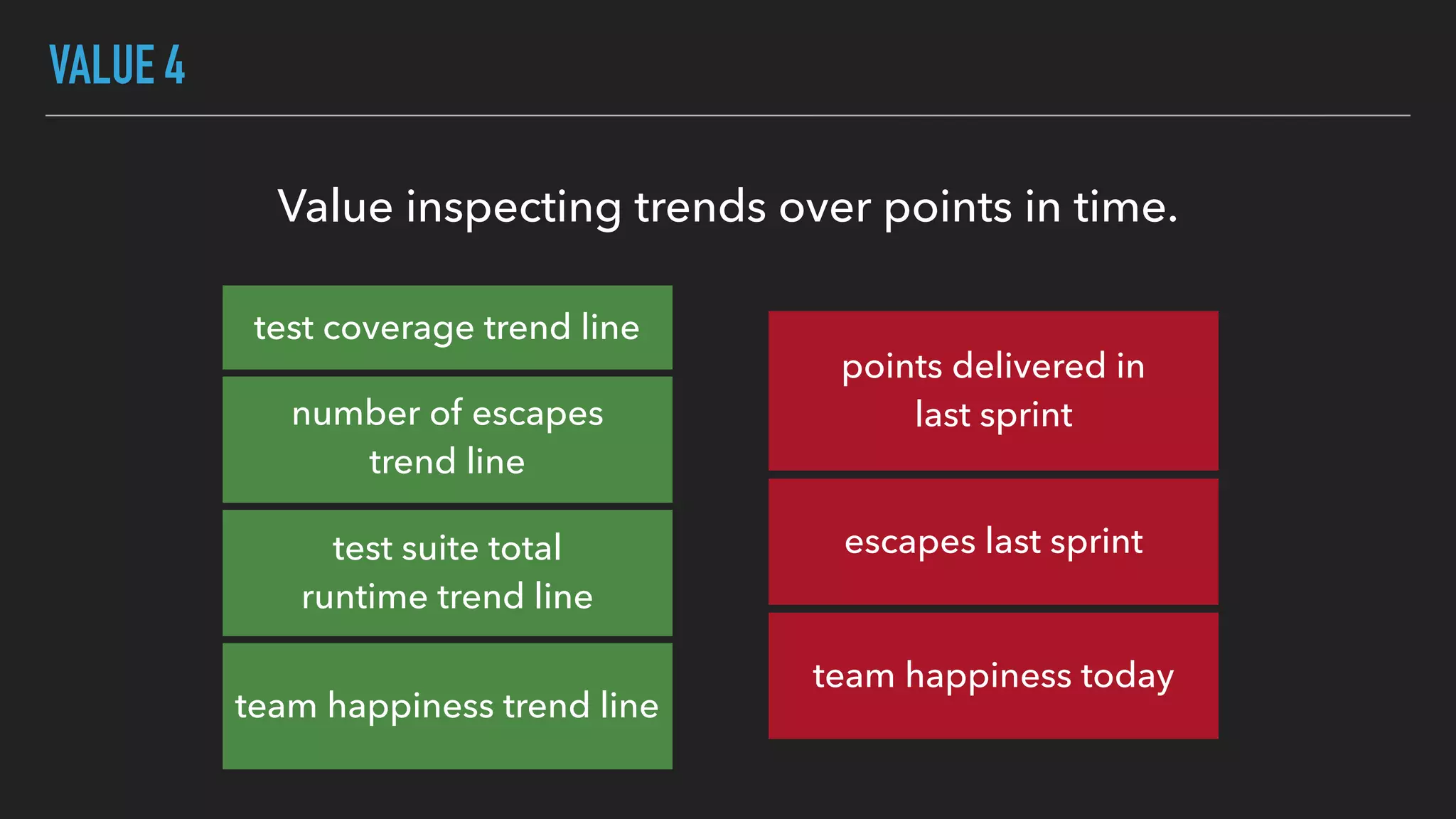
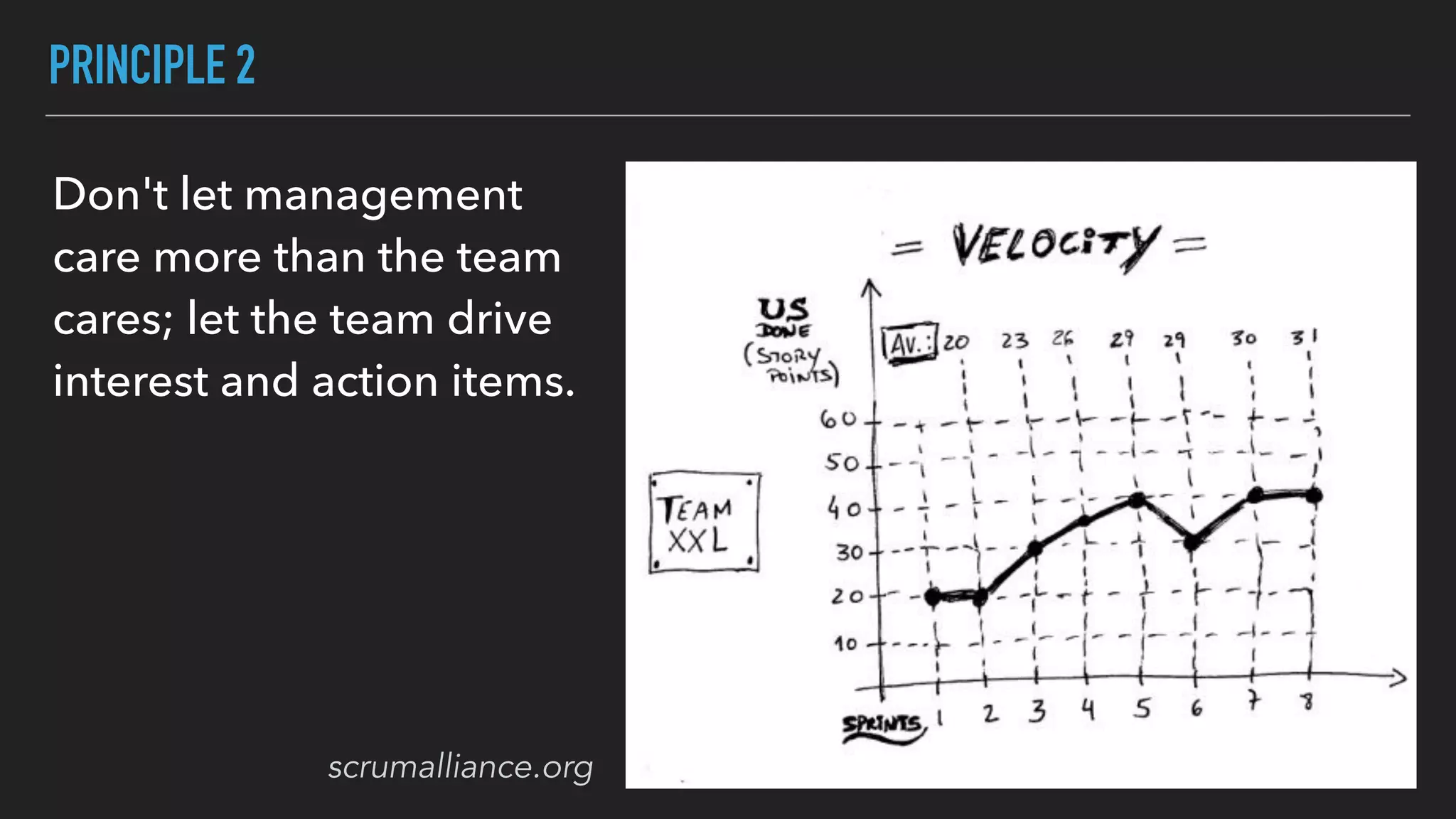
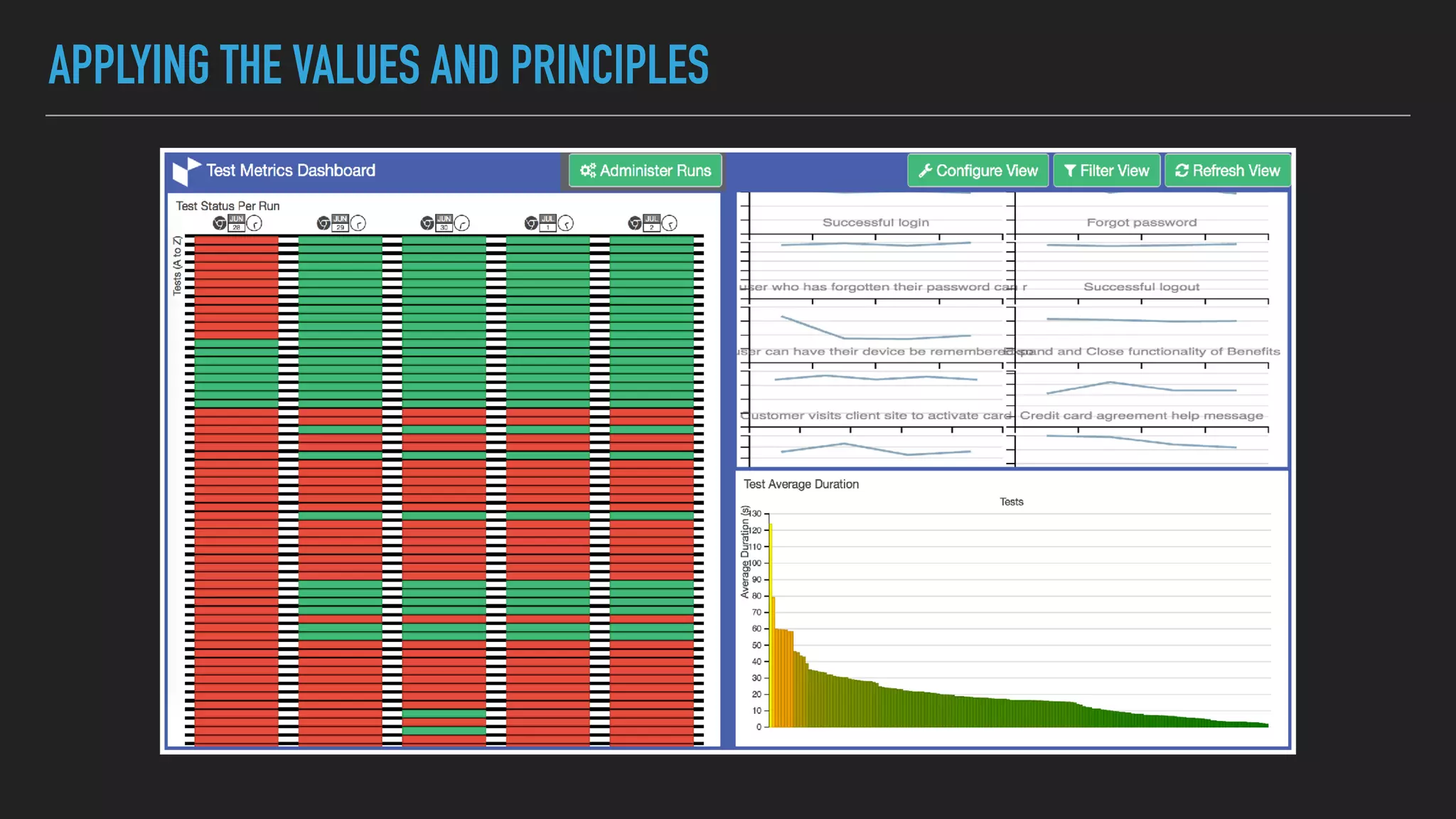
The document discusses the complexities and potential harms of using metrics in organizations, particularly emphasizing that many commonly used metrics can be harmful if they are the wrong ones. It outlines various types of metrics and essential test metrics while proposing rules for identifying good metrics that promote positive behavior without creating undue pressure. The importance of thoughtful metric application is highlighted, along with principles to ensure metrics serve their intended purpose without leading to negative consequences.