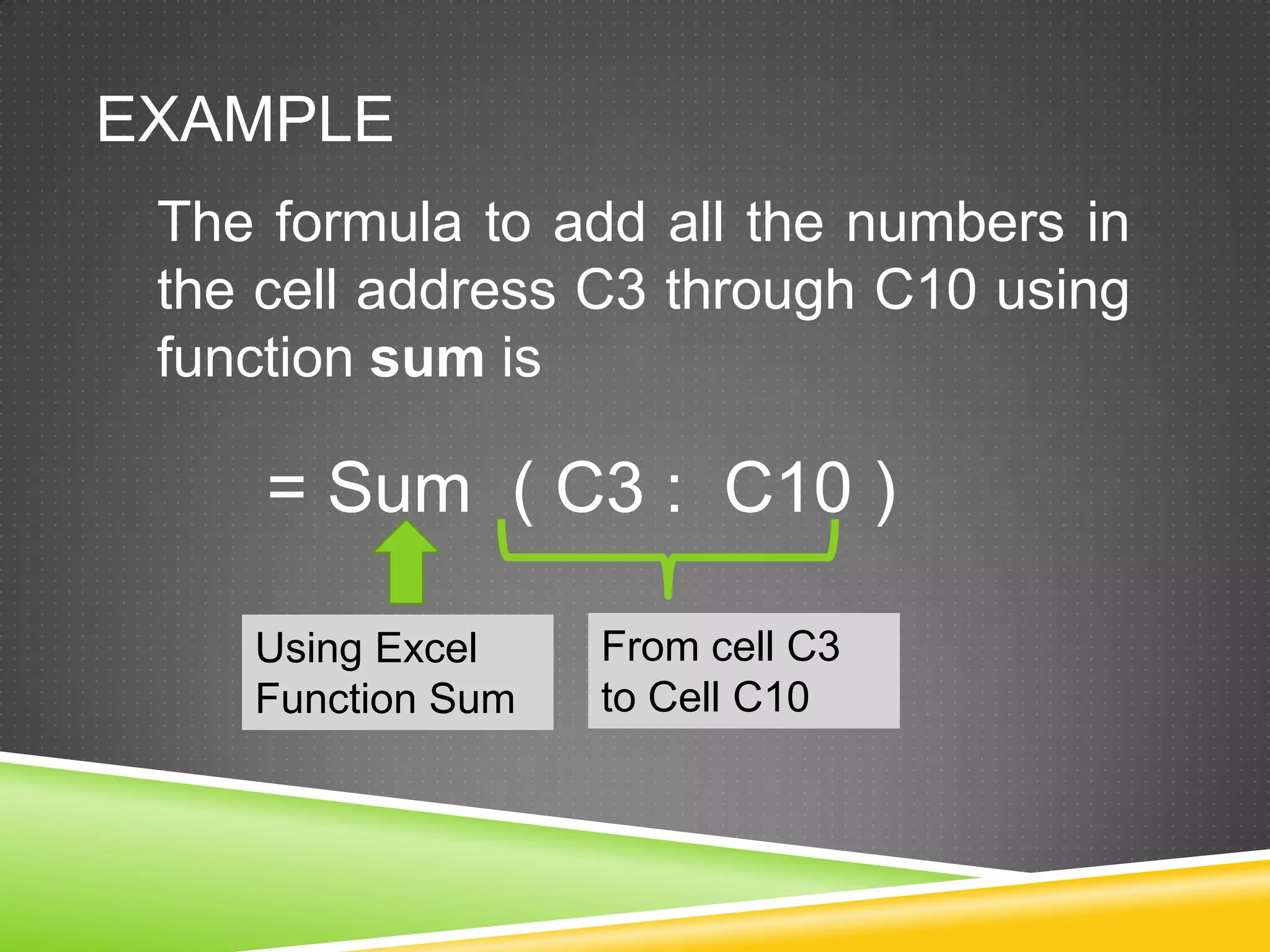
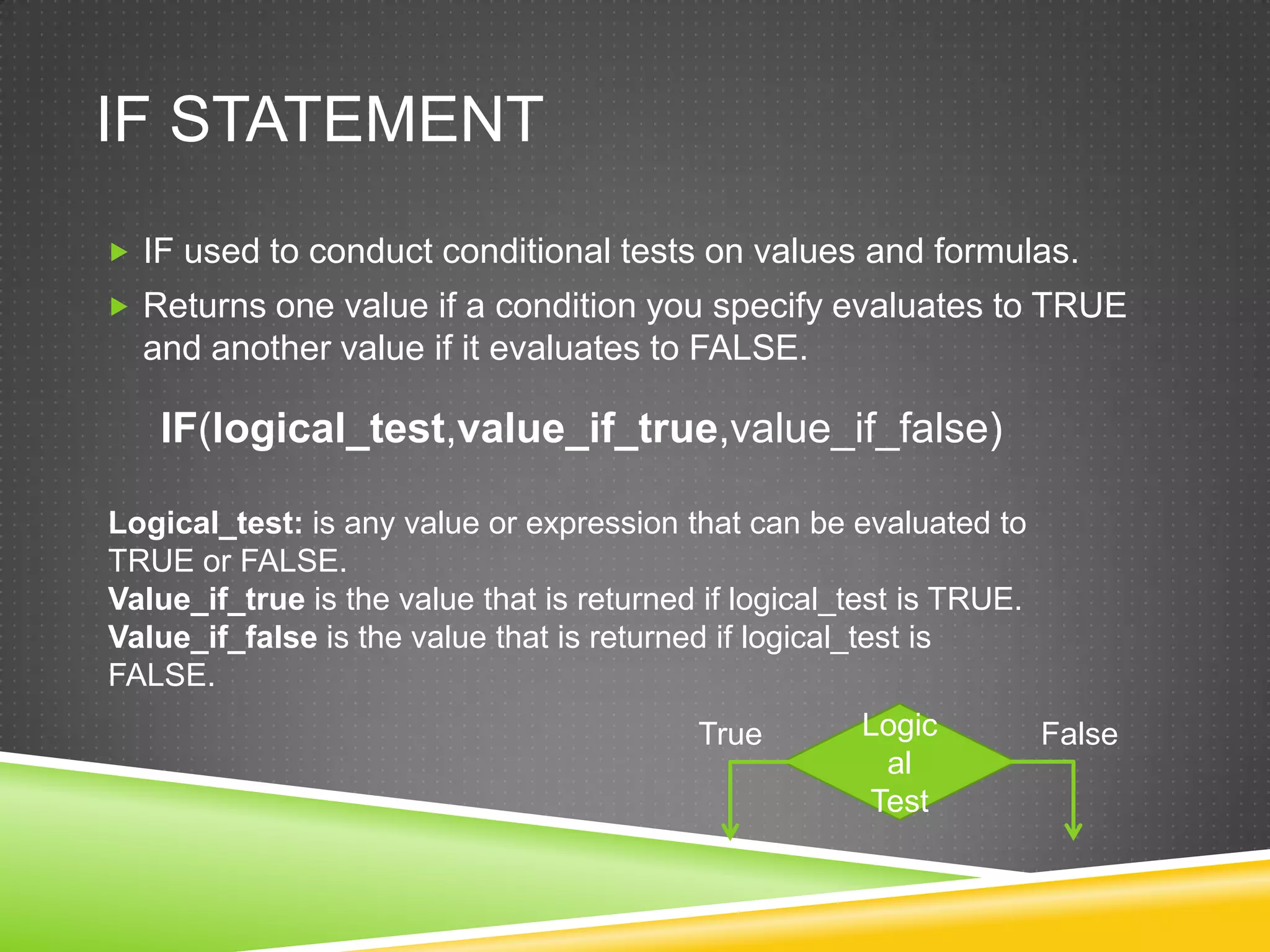
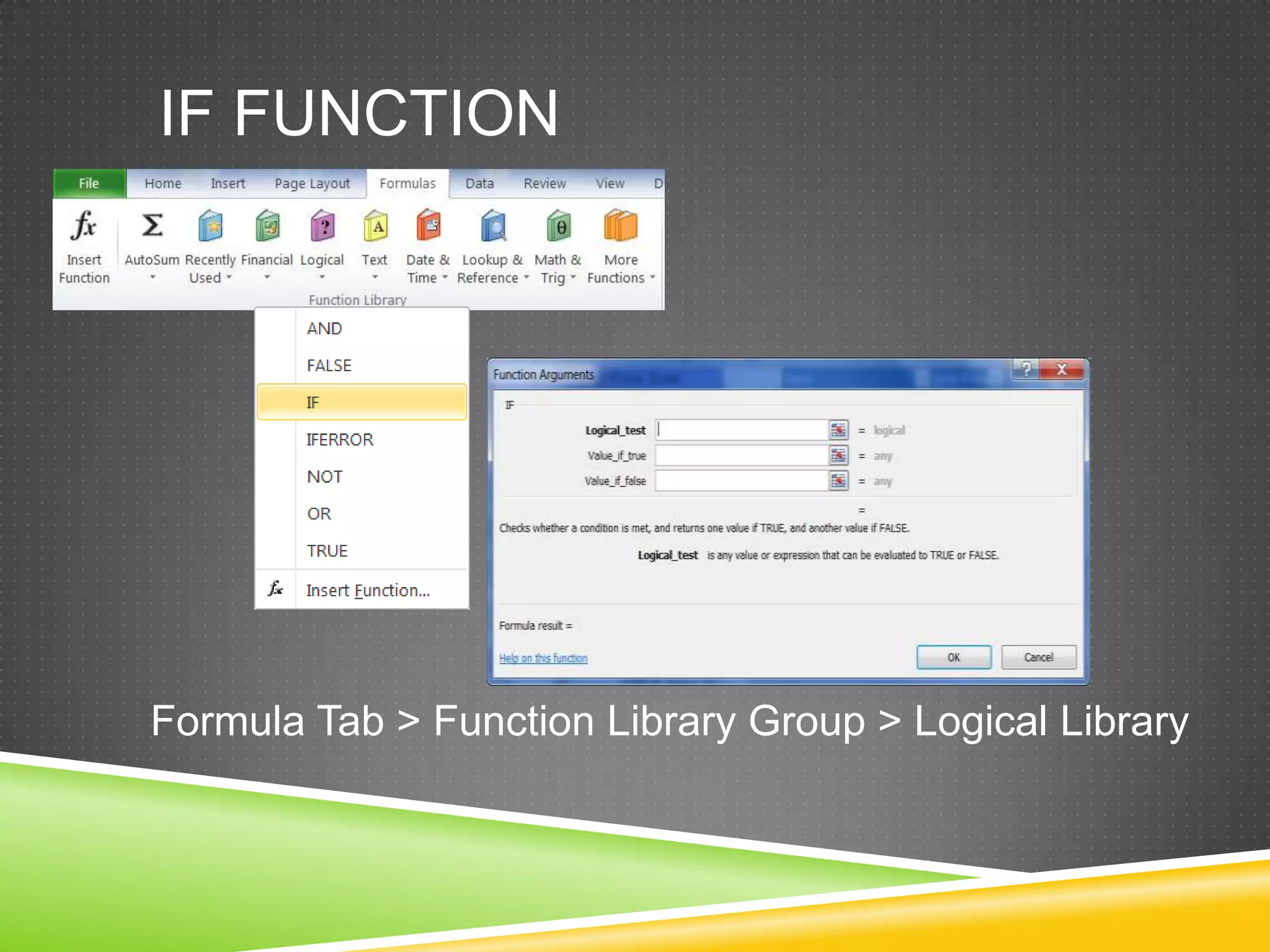
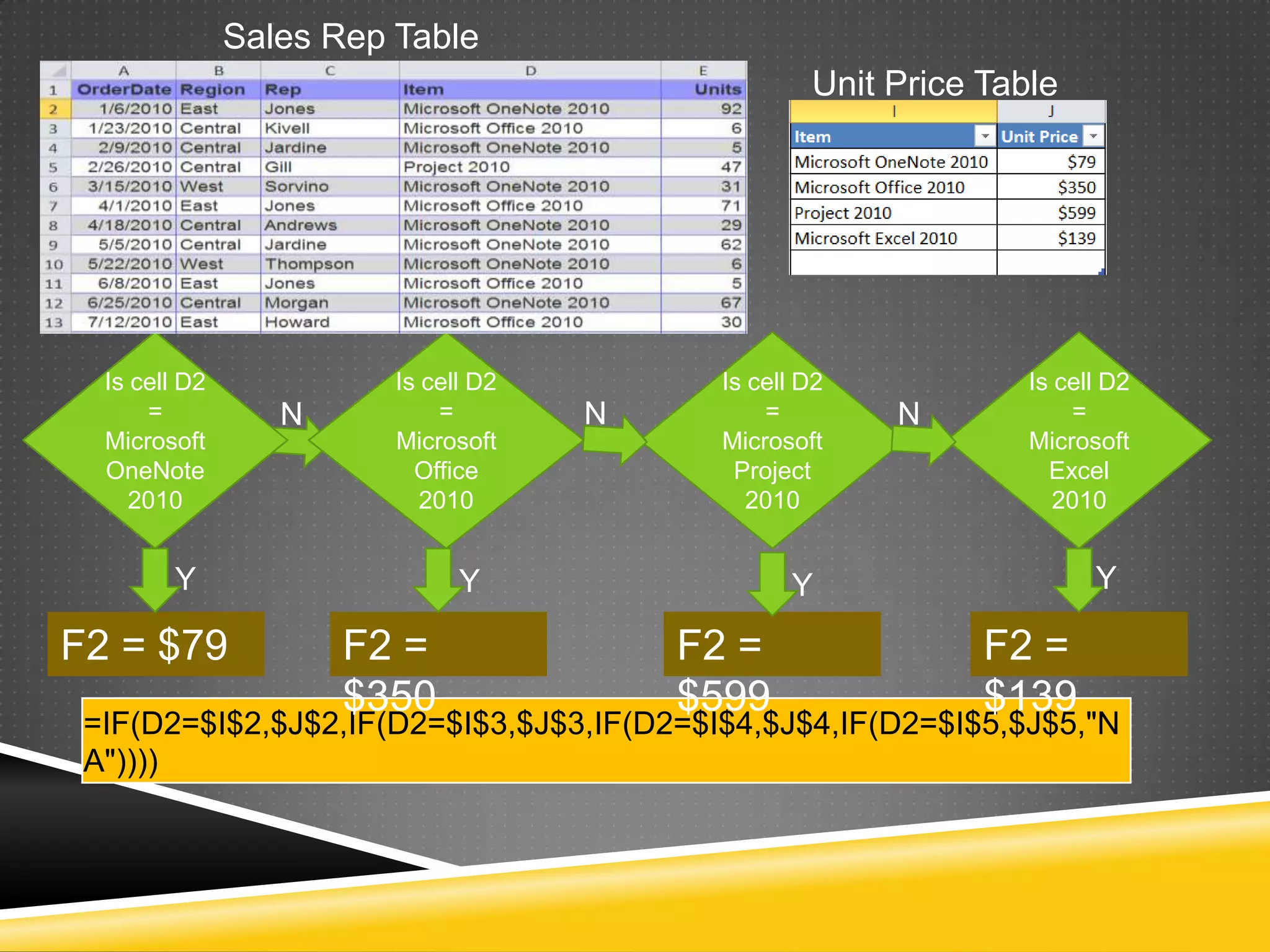
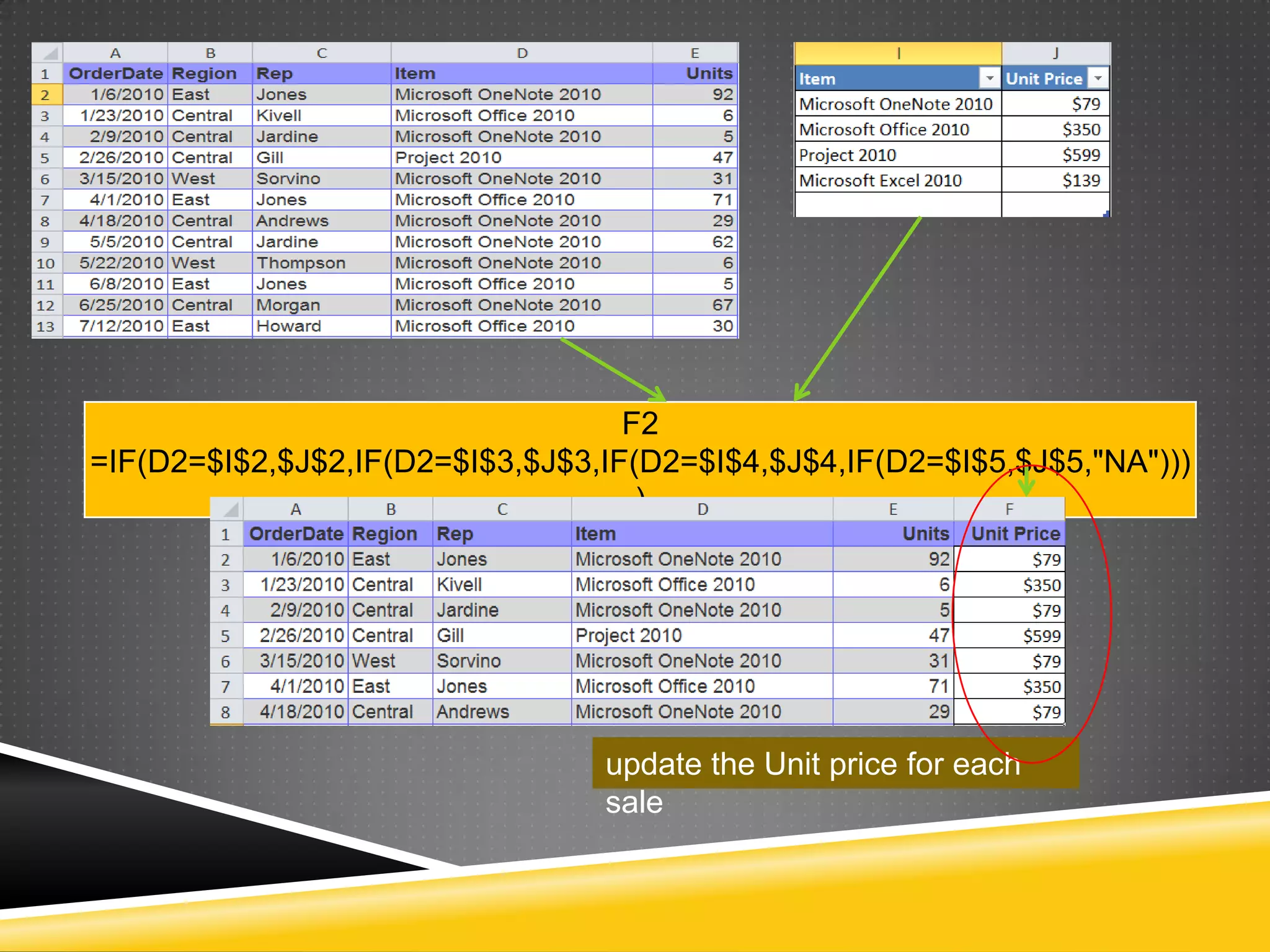
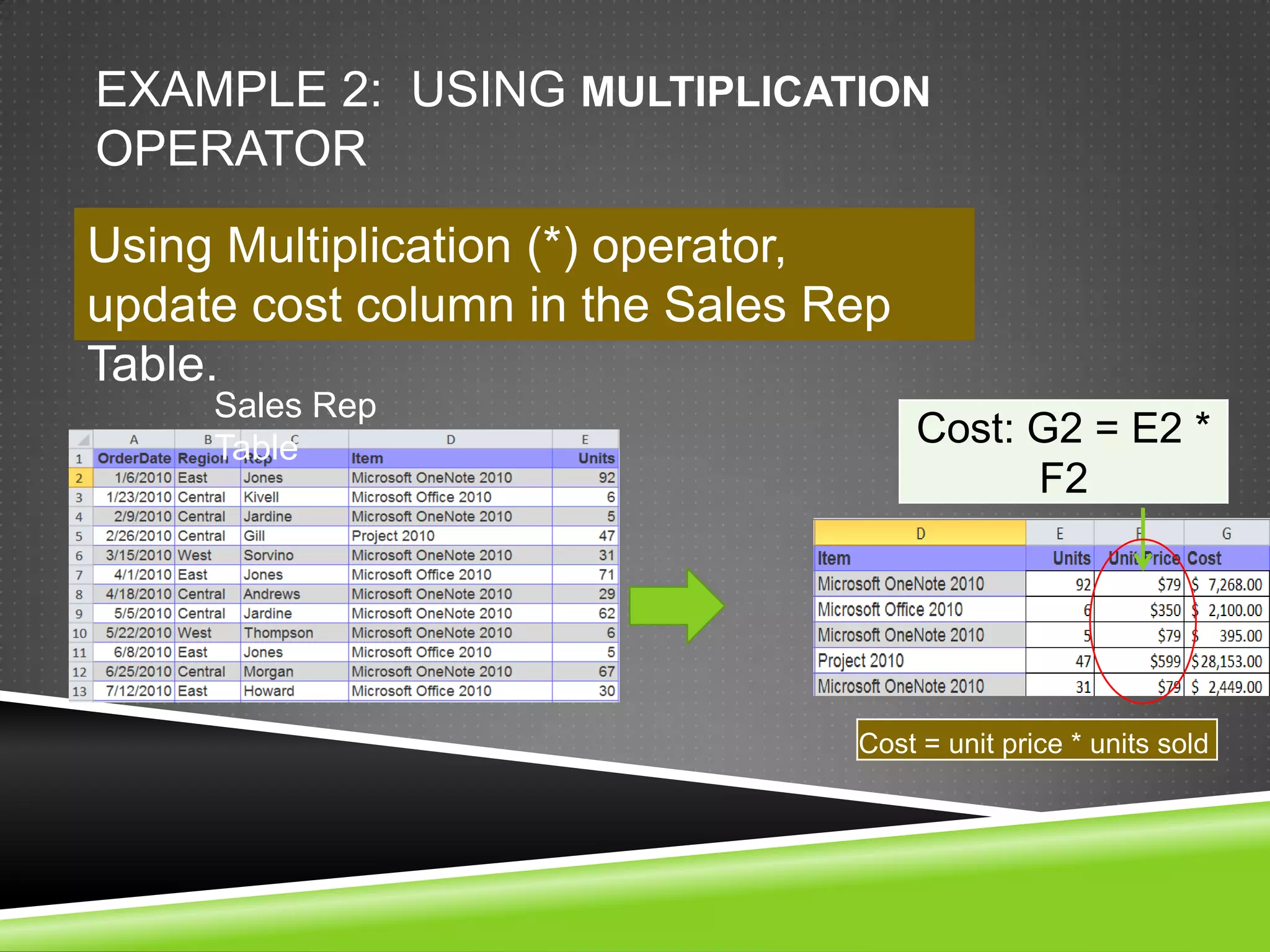
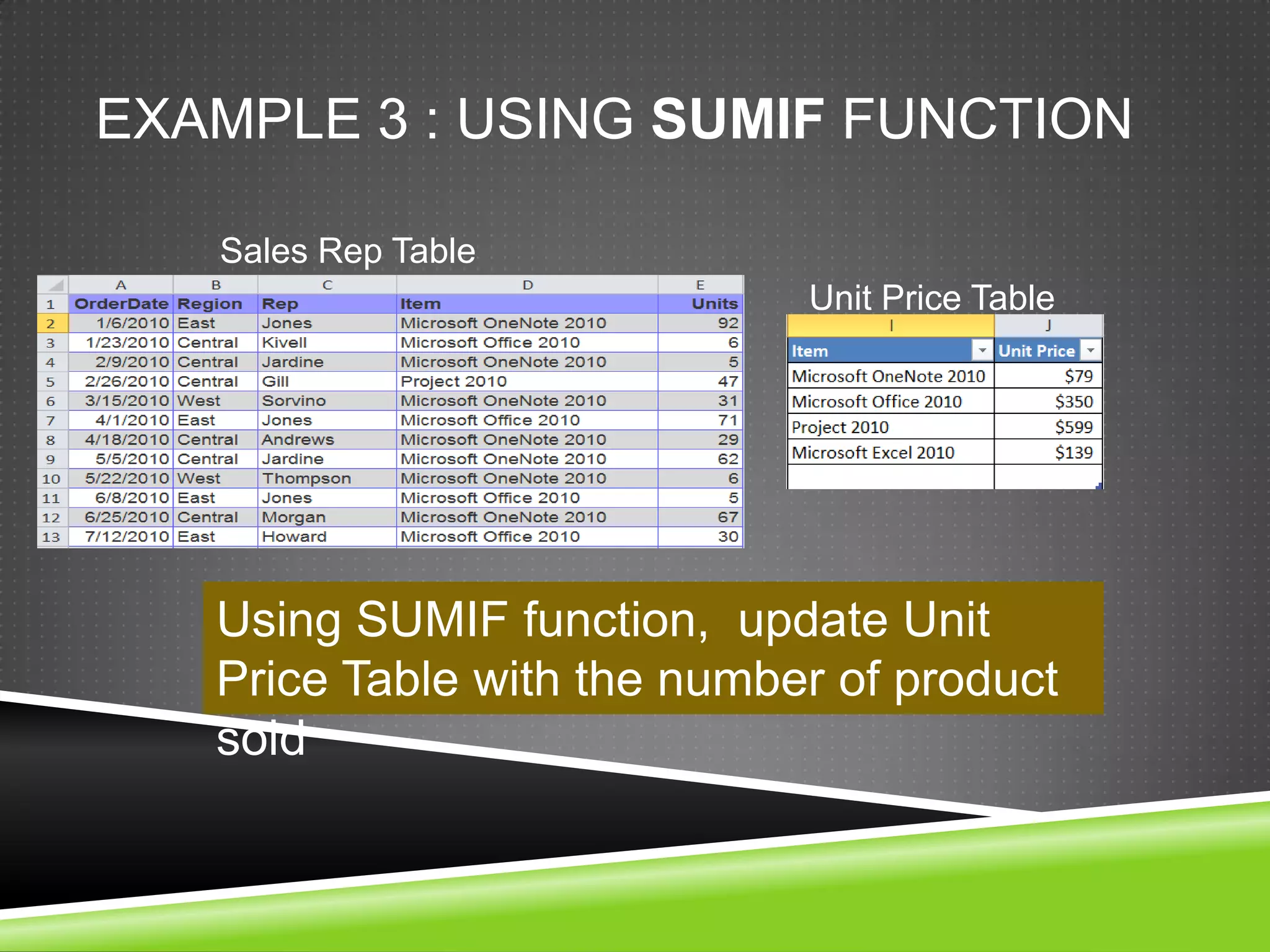
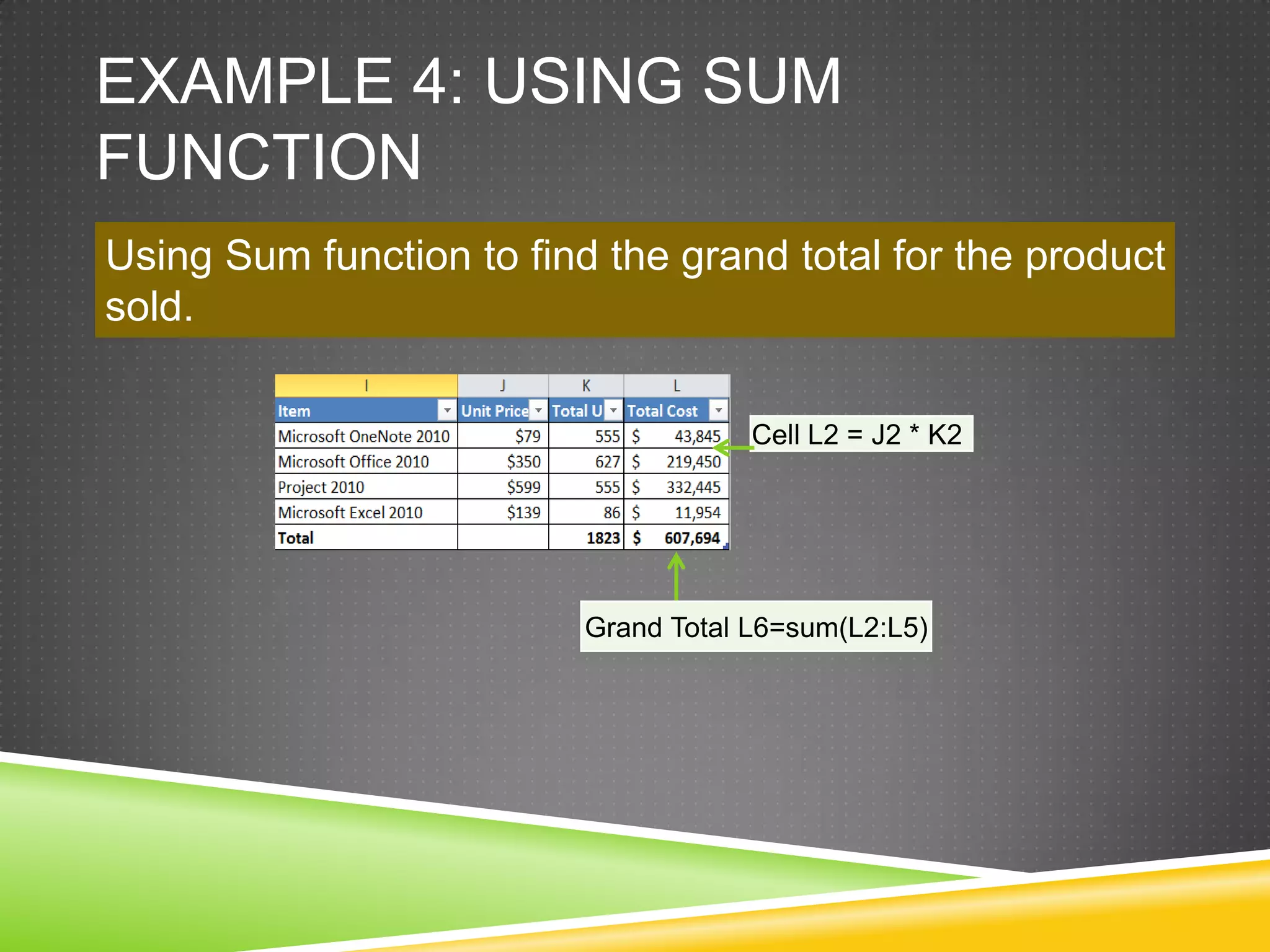
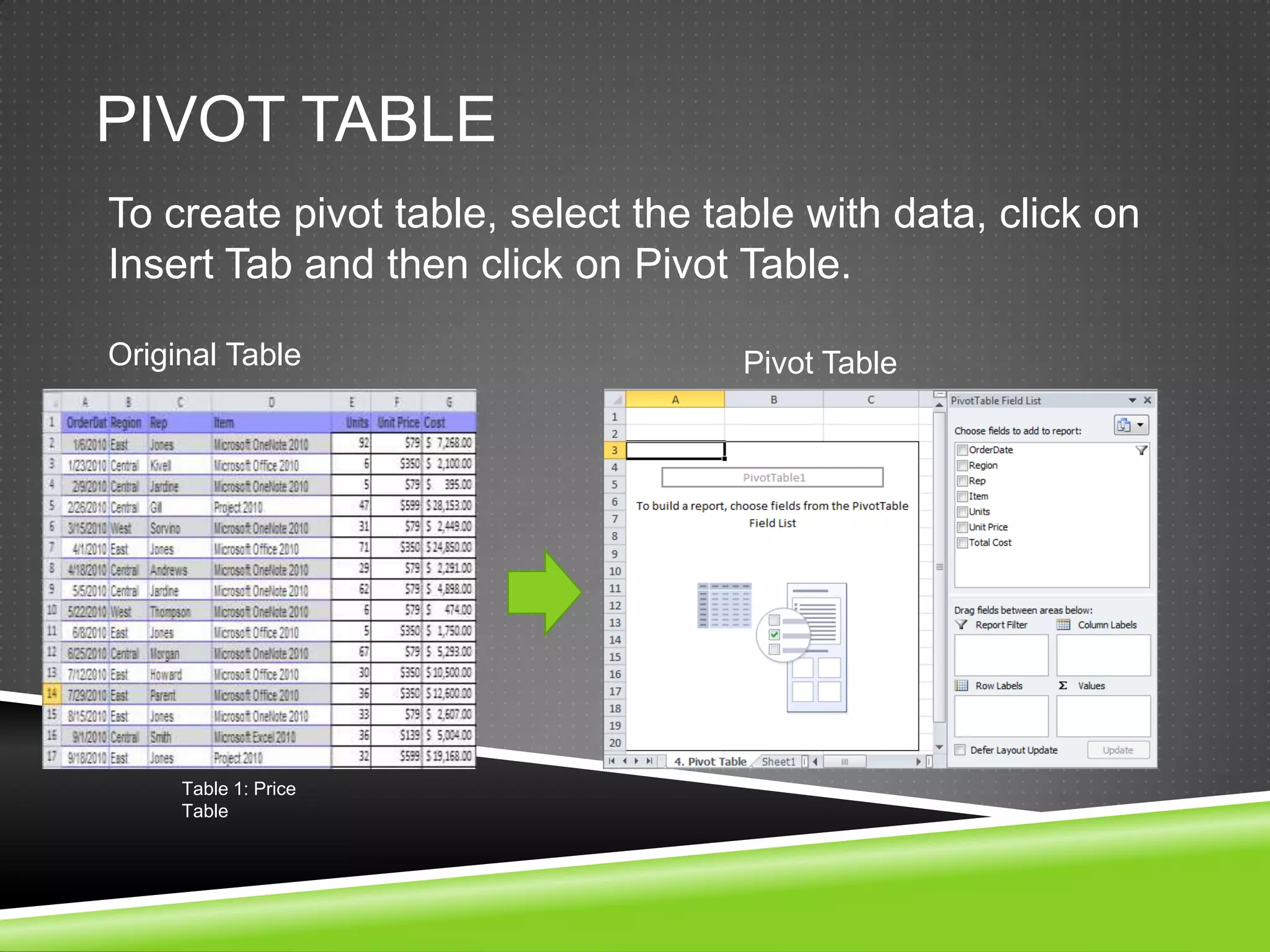
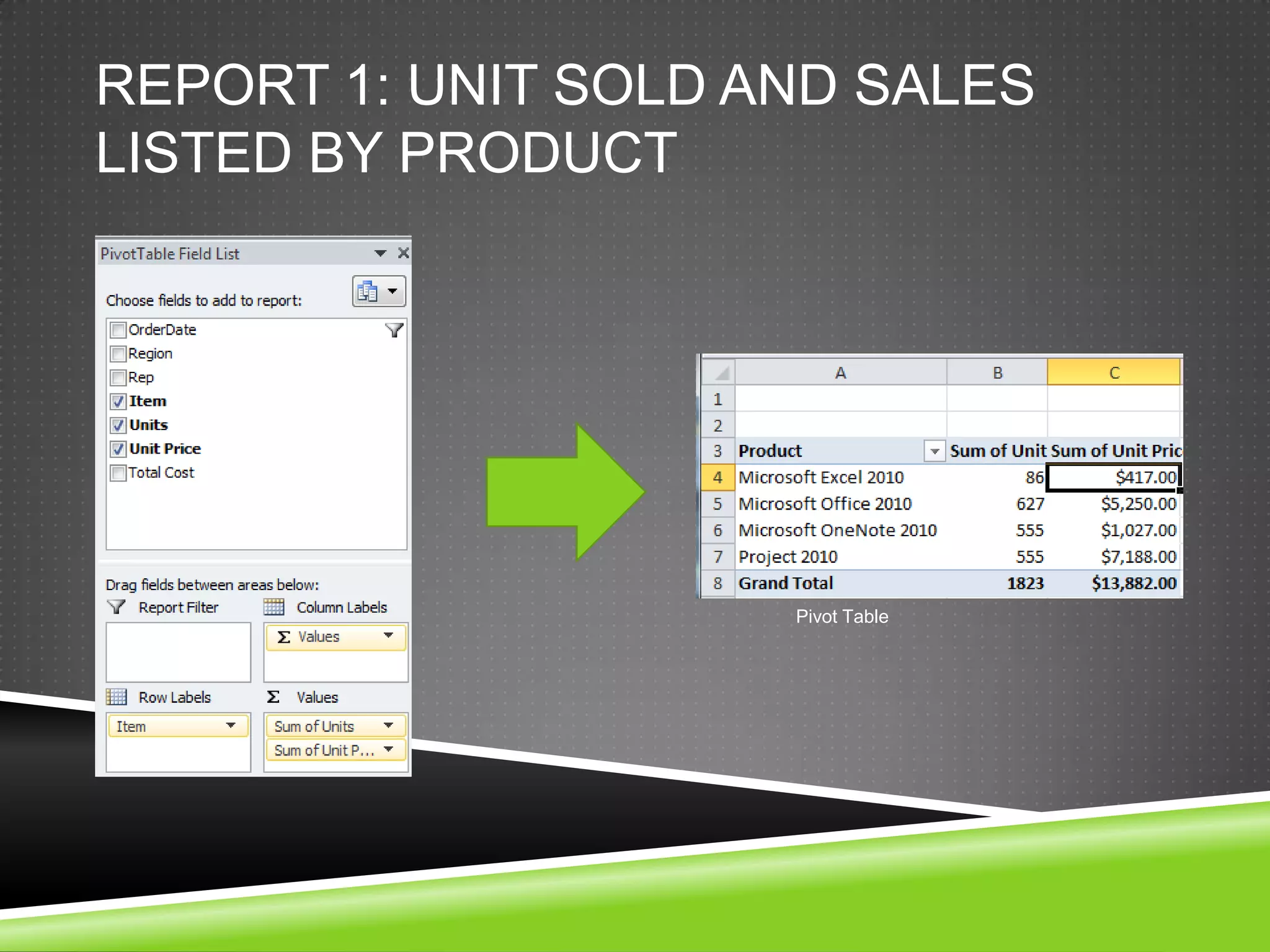
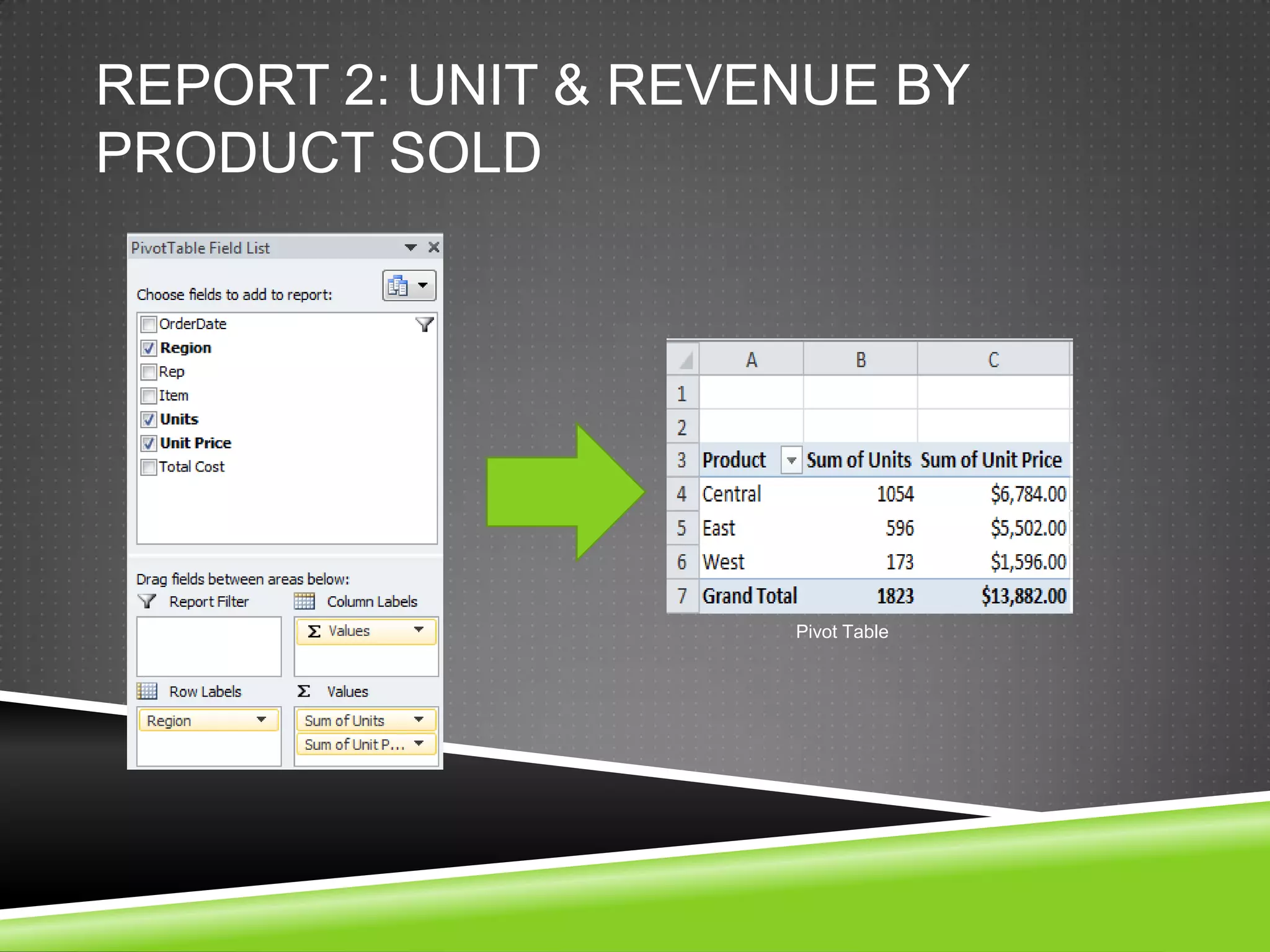
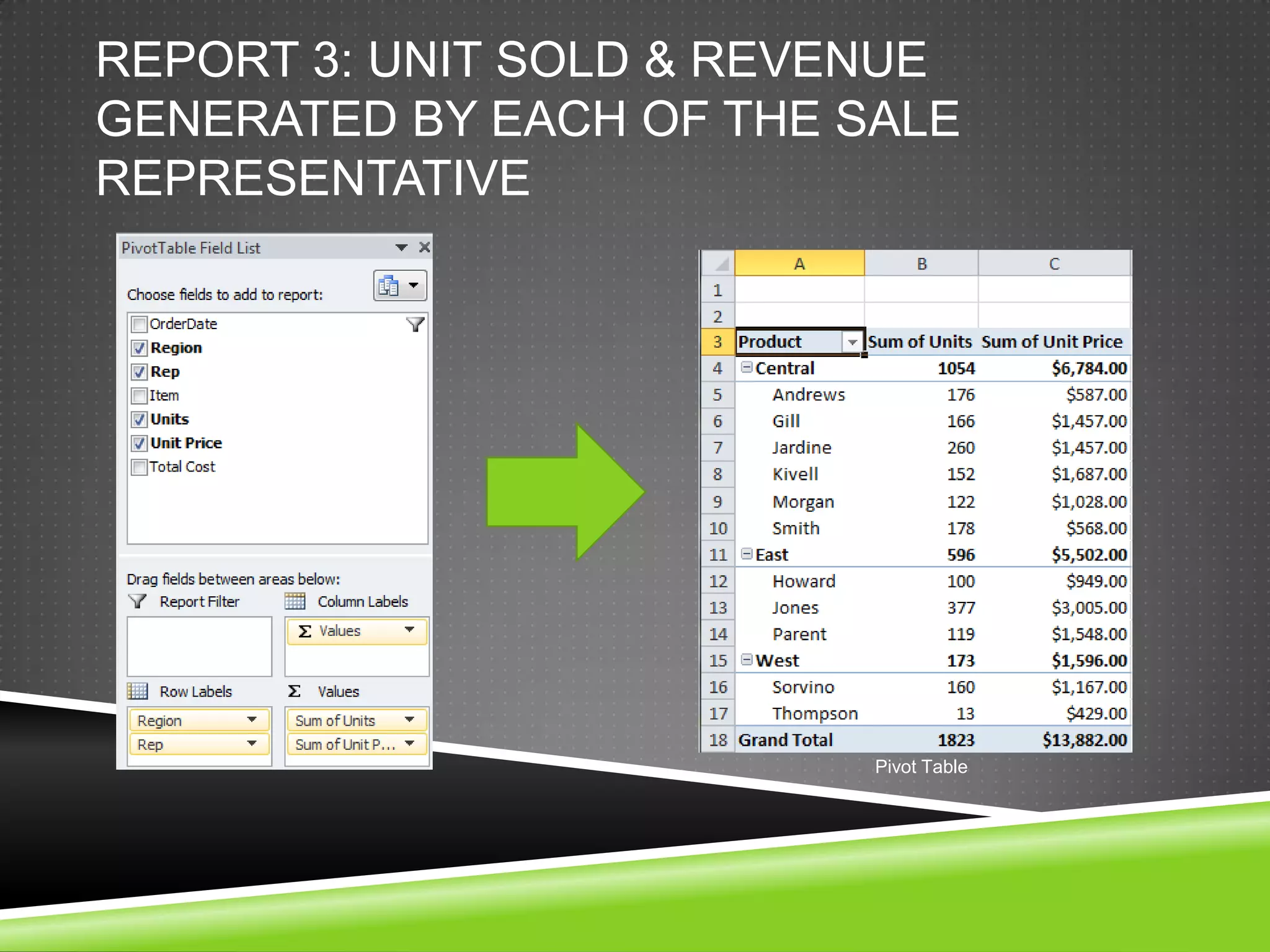
NR Computer Learning Center (NRCLC), located in Orange, CA, specializes in Microsoft product training with a focus on improving business productivity. The document details the features of Microsoft Excel 2010, including formulas, cell references, and functions like IF and SUMIF, alongside its hands-on training offerings. Additional training options and contact information for NRCLC are also provided.