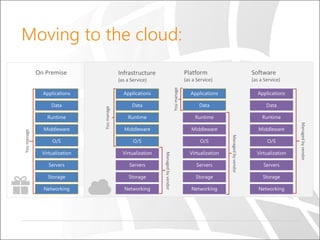
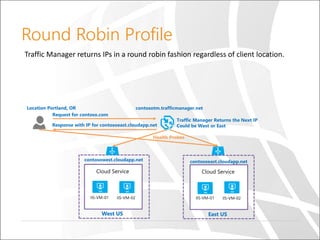
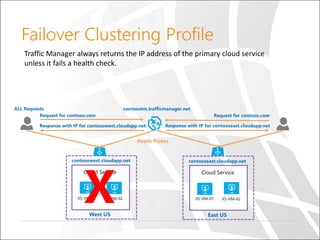
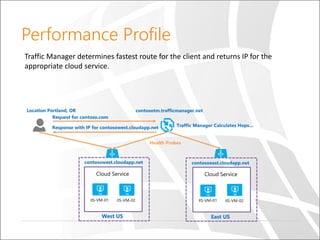
The document outlines a presentation on Azure Traffic Manager, discussing cloud basics, the importance of load balancers, and the various load balancing algorithms available. It includes technical demonstrations using PowerShell to create and manage Azure Traffic Manager profiles and endpoints. Additionally, it compares Azure's traffic management solutions with those of AWS and Google Cloud, highlighting their unique features and limitations.