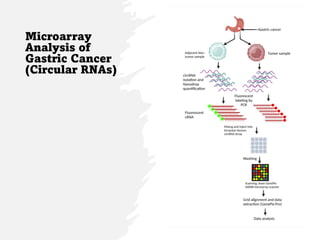
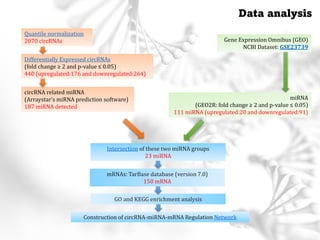
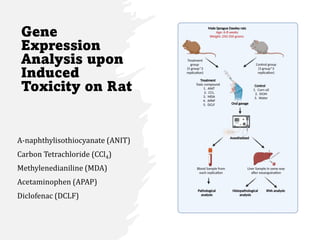
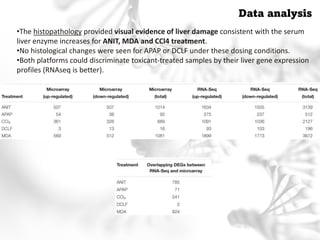
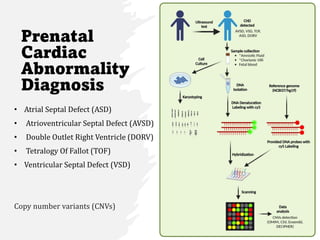
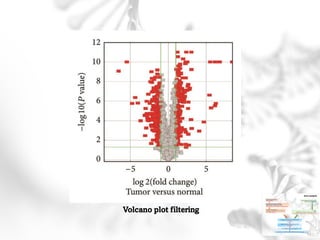
This document summarizes several case studies involving microarray analysis. It discusses a study of differentially expressed circular RNAs in gastric cancer samples that identified 440 deregulated circRNAs. It also summarizes a toxicology study that used microarrays to analyze gene expression changes in rat livers exposed to different toxins and found the arrays could distinguish treated from untreated samples. Finally, it summarizes a study using microarrays to analyze copy number variants in fetal samples with congenital heart defects that found chromosomal aberrations in 176 cases.