This document provides an overview of metaprogramming in Ruby. It discusses writing programs that write programs, also known as metaprogramming, which is commonly used in Ruby through methods like attr_accessor. The document discusses why metaprogramming is useful and some common Ruby techniques for metaprogramming like class_eval, instance_eval, and method_missing. It also covers topics like scoping, method dispatch, defining methods, and intercepting method calls through method_missing.














![Why?
def age
@age || 'not set'
end
def gender
@gender || 'not set'
end
def name
@name || 'not set'
end
[:age, :gender, :name].each do |attr|
define_method(attr) do
instance_variable_get(:"@#{attr}") || 'not set'
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-15-320.jpg)















































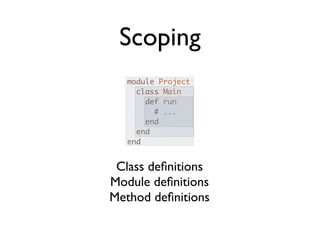

















![Interception!
method_missing(method, *args, &blk)
class MethodMissing
def method_missing(m, *args, &blk)
puts "method_missing #{m} #{args.inspect} #{blk.inspect}"
super
end
end
mm = MethodMissing.new
mm.i_dont_know_this(1, 2, 3)
# method_missing i_dont_know_this [1, 2, 3] nil
# NoMethodError: undefined method `i_dont_know_this' for #<MethodMissing>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-85-320.jpg)
![Interception!
Example: Timing
module MethodsWithTiming
def method_missing(m, *args, &blk)
if timed_method = m.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1] and respond_to?(timed_method)
respond = nil
measurement = Benchmark.measure {
respond = send(timed_method, *args, &blk)
}
puts "Method #{m} took #{measurement}"
respond
else
super
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-86-320.jpg)
![Interception!
Example: Timing
module MethodsWithTiming
def method_missing(m, *args, &blk)
if timed_method = m.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1] and respond_to?(timed_method)
respond = nil
measurement = Benchmark.measure {
respond = send(timed_method, *args, &blk)
}
puts "Method #{m} took #{measurement}"
respond
else
super
end
end
end
sc = SlowClass.new
class SlowClass
sc.slow
include MethodsWithTiming
def slow
sleep 1
sc.slow_with_timing
end
# Method slow_with_timing took 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ( 1.000088)
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-87-320.jpg)


![Interception!
Example: Simple DSL
class NameCollector
attr_reader :names
def initialize
@names = []
end
def method_missing(method, *args, &blk)
args.empty? ? @names.push(method.to_s.capitalize) : super
end
end
nc = NameCollector.new
nc.josh
nc.bob
nc.jane
nc.names.join(' ') # => Josh Bob Jane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-90-320.jpg)

![Interception!
Object#respond_to?(sym)
Example: Timing
module MethodsWithTiming
alias_method :original_respond_to?, :respond_to?
def method_missing(m, *args, &blk)
if timed_method = m.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1] and original_respond_to?(timed_method)
respond = nil
measurement = Benchmark.measure {
respond = send(timed_method, *args, &blk)
}
puts "Method #{m} took #{measurement}"
respond
else
super
end
end
def respond_to?(sym)
(timed_method = sym.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1]) ?
original_respond_to?(timed_method.to_sym) :
original_respond_to?(sym)
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-92-320.jpg)
![Interception!
Object#respond_to?(sym)
Example: Timing
module MethodsWithTiming
ge ts
alias_method :original_respond_to?, :respond_to?
It
def method_missing(m, *args, &blk)
r!
if timed_method = m.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1] and original_respond_to?(timed_method)
te
respond = nil
et
measurement = Benchmark.measure {
b
respond = send(timed_method, *args, &blk)
}
puts "Method #{m} took #{measurement}"
respond
else
super
end
end
def respond_to?(sym)
(timed_method = sym.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1]) ?
original_respond_to?(timed_method.to_sym) :
original_respond_to?(sym)
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-93-320.jpg)
![Interception!
Object#respond_to_missing?(sym) (1.9 only)
Example: Timing
module MethodsWithTiming
def method_missing(m, *args, &blk)
if timed_method = m.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1] and respond_to?(timed_method)
respond = nil
measurement = Benchmark.measure {
respond = send(timed_method, *args, &blk)
}
puts "Method #{m} took #{measurement}"
respond
else
super
end
end
def respond_to_missing?(sym)
(timed_method = sym.to_s[/^(.*)_with_timing$/, 1]) ?
respond_to?(timed_method.to_sym) :
super
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-94-320.jpg)








![Callbacks
Module#method_added
Example: Thor!
class Tasks
def self.desc(desc)
@desc = desc
end
def self.method_added(m)
(@method_descs ||= {})[m] = @desc
@desc = nil
end
def self.method_description(m)
method_defined?(m) ?
@method_descs[m] || "This action isn't documented" :
"This action doesn't exist"
end
desc "Start server"
def start
end
def stop
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-105-320.jpg)
![Callbacks
Module#method_added
Example: Thor! Record the description
class Tasks
def self.desc(desc)
@desc = desc
When a method is added,
end record the description associated
def self.method_added(m) with that method
(@method_descs ||= {})[m] = @desc
@desc = nil
end Provide the description for a
def self.method_description(m)
method, or, if not found, some
method_defined?(m) ? default string.
@method_descs[m] || "This action isn't documented" :
"This action doesn't exist"
end
desc "Start server"
def start
end
def stop
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-106-320.jpg)
![Callbacks
Module#method_added
Example: Thor! Record the description
class Tasks
def self.desc(desc)
@desc = desc
When a method is added,
end record the description associated
def self.method_added(m) with that method
(@method_descs ||= {})[m] = @desc
@desc = nil
end Provide the description for a
def self.method_description(m)
method, or, if not found, some
method_defined?(m) ? default string.
@method_descs[m] || "This action isn't documented" :
"This action doesn't exist"
end
desc "Start server"
def start
end
Described!
def stop
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-107-320.jpg)
![Callbacks
Module#method_added
Example: Thor! Query your methods!
class Tasks puts Tasks.method_description(:start)
def self.desc(desc) # => Start server
@desc = desc puts Tasks.method_description(:stop)
end
# => This action isn't documented
def self.method_added(m) puts Tasks.method_description(:restart)
(@method_descs ||= {})[m] = @desc # => This action doesn't exist
@desc = nil
end
def self.method_description(m)
method_defined?(m) ?
@method_descs[m] || "This action isn't documented" :
"This action doesn't exist"
end
desc "Start server"
def start
end
def stop
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-108-320.jpg)











![Callbacks
Kernel#caller
def one
two
end
def two
method name
three
file name line (optional)
end
def three
p caller
end
# ["method.rb:156:in `two'", "method.rb:152:in `one'", "method.rb:163"]
https://github.com/joshbuddy/callsite](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-120-320.jpg)
![Callbacks
Module#nesting
module A
module B
module C
p Module.nesting
end
end
end
# [A::B::C, A::B, A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-121-320.jpg)



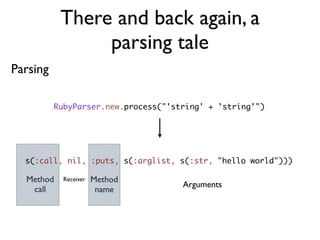
![There and back again, a
parsing tale
Parsing
require 'rubygems'
require 'ruby_parser'
RubyParser.new.process("'string'")
s(:str, "string")
[:str, "string"] # Sexp
Sexp.superclass
# Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-125-320.jpg)
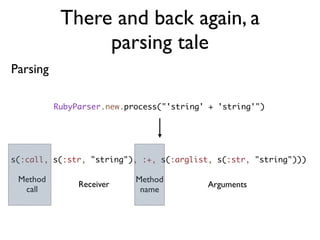
![There and back again, a
parsing tale
And, back again...
require 'rubygems'
require 'ruby2ruby'
Ruby2Ruby.new.process [:str, "hello"] # => "hello"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-128-320.jpg)
![There and back again, a
parsing tale
And, back again...
require 'rubygems'
require 'ruby2ruby'
Ruby2Ruby.new.process [:str, "hello"] # => "hello"
Ruby2Ruby.new.process [:lit, :symbol] # => :symbol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-129-320.jpg)
![There and back again, a
parsing tale
Roundtrip
require 'sexp_processor'
require 'ruby2ruby'
require 'ruby_parser'
class JarJarify < SexpProcessor
def initialize
self.strict = false
super
end
def process_str(str)
new_string = "YOUZA GONNA SAY #{str[-1]}"
str.clear
s(:str, new_string)
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-130-320.jpg)
![There and back again, a
parsing tale
Roundtrip
class JarJarify < SexpProcessor
def initialize
self.strict = false
super
end
def process_str(str)
new_string = "YOUZA GONNA SAY #{str[-1]}"
str.clear
s(:str, new_string)
end
end
ast = RubyParser.new.process('puts "hello"')
Ruby2Ruby.new.process(JarJarify.new.process(ast))
# => puts("YOUZA GONNA SAY hello")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-131-320.jpg)
![There and back again, a
parsing tale
Roundtrip
class JarJarify < SexpProcessor
def initialize
self.strict = false
Process type :str
super
end
def process_str(str)
new_string = "YOUZA GONNA SAY #{str[-1]}"
str.clear
s(:str, new_string) Consume the current sexp
end
end Return a new one
ast = RubyParser.new.process('puts "hello"')
Ruby2Ruby.new.process(JarJarify.new.process(ast))
# => puts("YOUZA GONNA SAY hello")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-110309095129-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-132-320.jpg)
